Synthesis and characterization of HA-CUR NPs
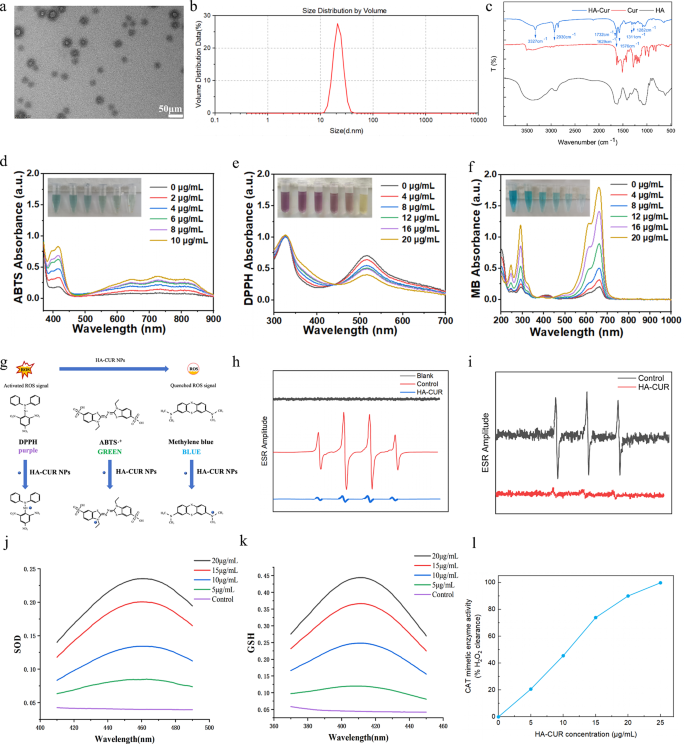
HA-CUR NPs have been synthesized through esterification between the carboxyl group of HA and the hydroxy group of CUR by way of an easy and reliable technique. Specifically, CUR was dissolved in a response system containing HA, DCC, and DMAP to type HA-CUR NPs. After 24 h of stirring, the ensuing combination turned darkish, suggesting the efficient mixture of HA and CUR. The combination was subsequently dialyzed and centrifuged to acquire HA-CUR NPs with superior aqueous dispersion. The micromorphology of the HA-CUR NPs was noticed through TEM. As proven in Fig. 1a, HA-CUR NPs have been usually within the type of uniformly distributed ultrafine particles with a measurement of twenty-two.4 ± 8.7 nm. The typical hydrodynamic dimension of the HA-CUR NPs was subsequently measured through DLS and was similar to the outcome decided through TEM (Fig. 1b). We subsequently decided the construction of the HA-CUR NPs by measuring their 1H NMR spectra. As proven in Determine S1, the peaks of HA-CUR at 1.5–2.0 ppm and 6.5–7.0 ppm have been attributed to the acetyl peak of HA (- NHCOCH3) and the fragrant proton of CUR, respectively. Moreover, the infrared intensities of the HA, CUR, and HA-CUR NPs have been analyzed through FTIR to confirm that the HA-CUR NPs have been efficiently synthesized. As proven in Fig. 1c, in contrast with the infrared spectra of HA and CUR, the obvious absorption peak at 3327 cm-1 was the absorption band of the -OH group within the curcumin construction; the apparent absorption peak at 2930 cm-1 was the absorption band of the double C = O group in curcumin; the brand new absorption peak at 1576 cm-1 was attributed to the vibration of the C = C inside the benzene ring of curcumin; and the brand new absorption peak at 1732 cm-1 was the absorption band of the newly fashioned C = O double bond within the ester. Furthermore, the HA-CUR NPs have been dissolved in three solvents: water, ethanol and 0.9% NaCl. The UV‒vis absorbance spectra indicated that there was no marked change at 0 and seven days (Determine S2). These outcomes have been in keeping with the findings of Manju S, indicating the profitable synthesis of HA-CUR NPs.
Characterization, ROS scavenging capacity, and enzyme-mimicking actions of HA-CUR NPs. (a) Transmission electron microscopy pictures of HA-CUR NPs. (b) Dynamic mild scattering information of HA-CUR NPs. (c) FTIR spectra of the HA, CUR, and HA-CUR NP samples. (d) UV‒Vis absorbance displaying the ABTS radical scavenging capacity of HA-CUR NPs. (e) UV‒Vis absorbance displaying the DPPH radical scavenging capacity of HA-CUR NPs. (f) UV‒Vis absorbance picture illustrating the power of HA-CUR NPs to scavenge ·OH to guard MB. (g) Illustration of the ROS scavenging course of. (h) ESR spectra of DMPO indicating ·OH seize with or with out HA-CUR NPs. (i) ESR spectra of TEMPO indicating single oxygen seize with or with out HA-CUR NPs. (j) SOD-like exercise of HA-CUR NPs. (WST-8 equipment assay) (n = 3 for every group). (ok) GSH-like exercise of HA-CUR NPs. (n = 3 for every group). (l) CAT-like exercise of HA-CUR NPs (n = 3 for every group)
Radical scavenging and antioxidant capability of HA-CUR NPs
CUR has sturdy antioxidant properties, however its low aqueous solubility enormously limits its widespread utility. Right here, we explored the free radical scavenging capacity and antioxidant capability of HA-CUR NPs. First, the ABTS and DPPH radical assays, that are two radical fashions extensively used for quantifying the antioxidant capability of organic samples, have been adopted to check the novel scavenging capacity [18, 19]. The capability of HA-CUR NPs to scavenge ABTS and DPPH radicals was evaluated by measuring the absorbances at 734 and 517 nm, respectively. Because the focus of HA-CUR NPs elevated, the colour progressively decreased, and decreased absorbance values have been noticed (Fig. 1d and e), suggesting the sturdy ABTS and DPPH radical scavenging talents of the HA-CUR NPs. Moreover, the OH radical (·OH) is a physiologically associated radical and is concerned in numerous sorts of mobile and histopathological injury. The power of HA-CUR NPs to scavenge ·OH was assessed through the methylene blue (MB) assay. Our findings revealed that with the safety of HA-CUR NPs, MB remained blue or light barely, indicating that HA-CUR NPs had a powerful scavenging capacity towards ·OH (Fig. 1f). The precise mechanisms of those three assays are schematically introduced in Fig. 1g. As well as, 5,5-dimethyl-1-pyrroline N-oxide (DMPO) and a couple of,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidine-1-oxyl (TEMPO) have been employed to entice •OH and single oxygen, respectively. The authors evaluated the capability of HA-CUR NPs to scavenge free radicals produced by the Fenton response by way of electron spin resonance (ESR) spectroscopy. A decreased ESR amplitude was noticed after remedy with the HA-CUR NPs, suggesting the environment friendly scavenging capacity of the HA-CUR NPs for ·OH and single oxygen (Fig. 1h and that i). In abstract, these findings point out that HA-CUR NPs could also be efficient ROS scavengers due to their sturdy antioxidant properties.
Mimetic actions of three antioxidant enzymes within the HA-CUR NPs
The results of HA-CUR NPs on SOD, GSH, and CAT exercise have been additional explored. SOD, an antioxidant enzyme that decomposes superoxide radicals into hydrogen peroxide and oxygen, has been demonstrated to exert outstanding therapeutic results in uveitis [20]. Moreover, GSH is a extensively current tripeptide thiol and one other vital intracellular and extracellular antioxidant that performs many vital roles in mobile sign transduction processes [21]. H2O2 might be eradicated from the physique by decomposition into H2O and O2 by CAT, an iron porphyrin-binding enzyme that performs a significant protecting position in organisms. As proven in Fig. 1j, ok, and l, the HA-CUR NPs demonstrated SOD, GSH, and CAT mimetic results in a dose-dependent method, suggesting that the HA-CUR NPs have wonderful antioxidant results.
Mobile uptake habits of HA-CUR NPs and in vitro cytotoxicity of HA-CUR NPs
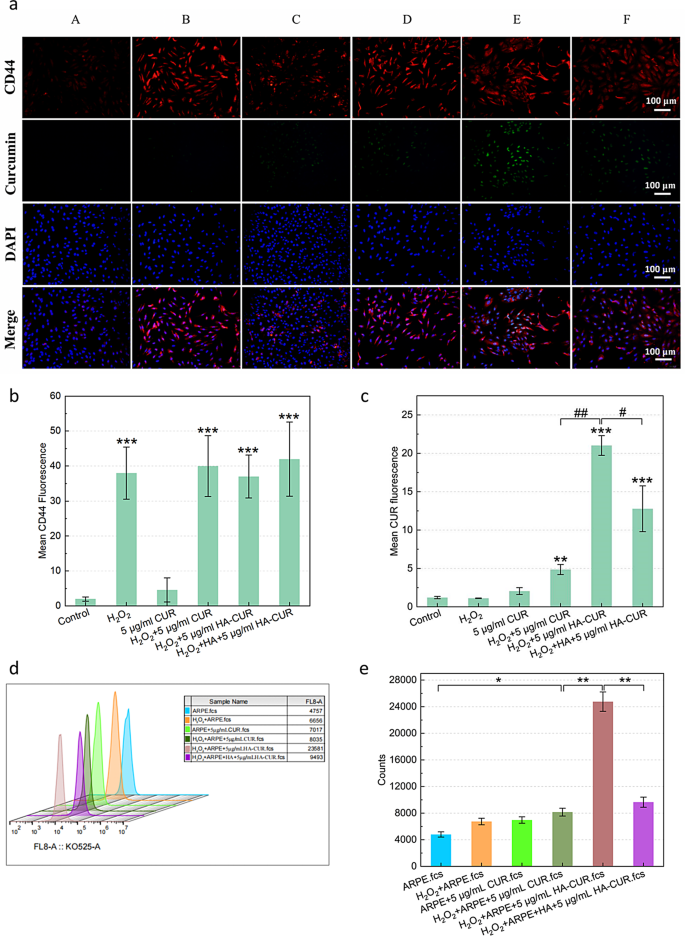
The pathogenesis and development of uveitis are intently related to the impairment of ocular immune privilege, which can be brought on by destruction of the integrity of the RPE [22]. Flourescence microscopy was employed to judge the power of HA-CUR NPs to focus on ARPE-19 cells by figuring out their internalization of HA-CUR NPs and free CUR pretreatment with or with out H2O2. CUR is represented by the inexperienced fluorescence sign, whereas the CD44 receptor is represented by the crimson sign. ARPE-19 cells that weren’t handled with H2O2 assimilated minimal quantities of free CUR, as demonstrated in Fig. 2a, and the quantitative evaluation outcomes are proven in Fig. 2b and c. The mobile uptake habits of HA-CUR NPs was extra simply noticed in ARPE cells pretreated with H2O2 than in these pretreated with free CUR. The next observations have been made to determine whether or not the elevated mobile absorption of HA-CUR NPs by ARPE-19 cells pretreated with H2O2 was a results of their capacity to focus on the CD44 receptor. Initially, pretreatment of ARPE-19 cells with H2O2 led to better expression of the CD44 receptor than that in untreated ARPE-19 cells. These findings point out that the expression of the CD44 receptor could also be promoted by extreme oxidative stress. ARPE-19 cells have been then handled with HA or HA-CUR NPs following H2O2 pretreatment. The absorption of HA-CUR NPs by cells clearly decreased, probably because of the aggressive binding of HA to the CD44 receptor, which inhibited NP-CD44 receptor binding. The outcomes have been additional verified by way of stream cytometry (Fig. 2d). MTT assays revealed that the exercise of ARPE-19 cells was lowered by incubation with greater concentrations of HA-CUR NPs (Determine S3a-b). The relative survival price of the cells and the proportion of these with a traditional morphology decreased (Determine S3c). In abstract, these information point out that the CD44 receptor concentrating on of HA-CUR NPs might promote the mobile uptake of HA-CUR NPs on account of CD44 receptor overexpression in ARPE-19 cells brought on by extreme oxidative stress.
(a) Fluorescence pictures displaying CD44 and CUR expression in numerous teams. A: Management; B: 500 µmol/L H2O2-treated APRE-19 cells for 40 min; C: 5 µg/mL CUR-treated APRE-19 cells for 12 h; D: 500 µmol/L H2O2-treated APRE-19 cells for 40 min + 5 µg/mL CUR-treated APRE-19 cells for 12 h; E: 500 µmol/L H2O2-treated APRE-19 cells for 40 min + 5 µg/mL HA-CUR NP-treated APRE-19 cells for 12 h; F: 500 µmol/L H2O2-treated APRE-19 cells for 40 min + 5 µg/mL HA-treated APRE-19 cells for 4 h + 5 µg/mL HA-CUR NP-treated APRE-19 cells for 12 h. (b) Quantification of the fluorescence depth of CD44 in numerous teams. (c) Quantification of the fluorescence depth of CUR in numerous teams. (d, e) Movement cytometry evaluation of the fluorescence depth of CUR in numerous teams. Notice: */#, P < 0.05; **/##, P < 0.01; ***/###, P < 0.001
HA-CUR NPs attenuated oxidative stress and inflammatory responses in ARPE-19 cells
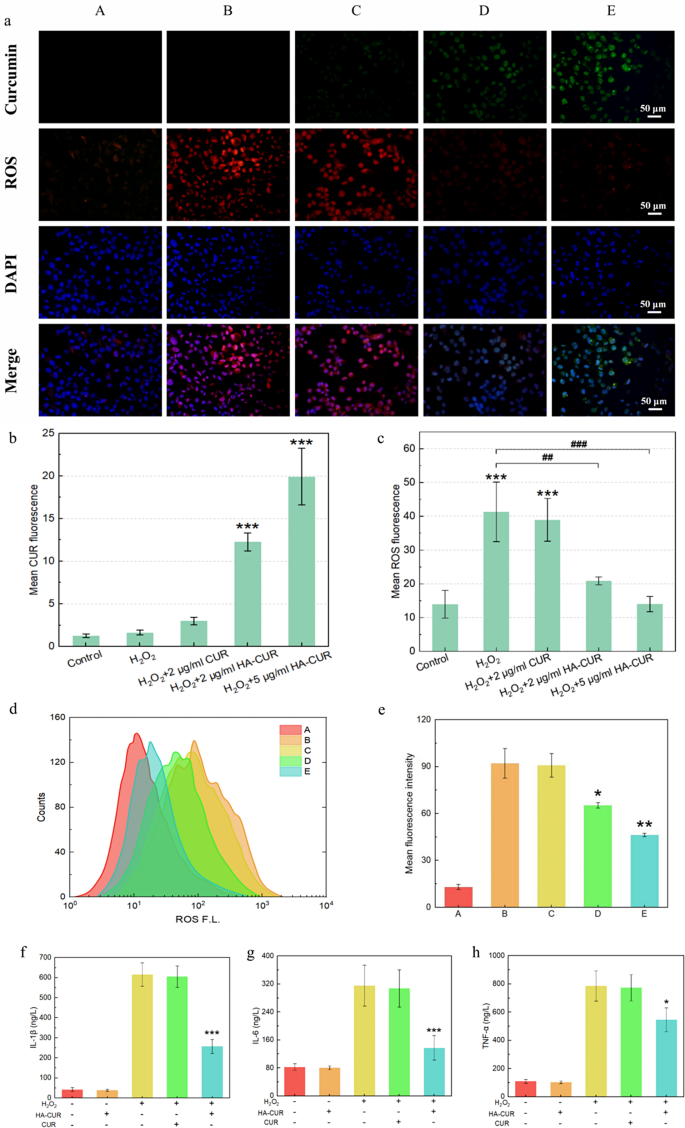
Inspired by their wonderful mobile uptake, HA-CUR NPs have been evaluated for his or her capacity to safeguard ARPE-19 cells from oxidative stress brought on by H2O2. DCFH-DA staining was performed to visualise intracellular ROS after totally different interventions. The inexperienced fluorescence sign signifies CUR, and the crimson fluorescence sign represents ROS. In contrast with people who weren’t handled with H2O2, ARPE-19 cells that have been pretreated with H2O2 introduced a crimson fluorescence sign, which steered that the intracellular ROS ranges have been elevated, as demonstrated by Fig. 3a and the outcomes of the quantitative evaluation proven in Fig. 3b and c. When the cells have been cocultured with free CUR, vital intracellular ROS and intensely low mobile uptake of CUR have been detected. Nevertheless, the crimson fluorescence sign decreased considerably, and the inexperienced fluorescence sign elevated when H2O2-pretreated ARPE-19 cells have been cocultured with HA-CUR NPs, suggesting that HA-CUR NPs may cause a dose-dependent discount in ROS.
(a) Fluorescence pictures of ARPE-19 cells stained with DFCH-DA and 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) after totally different remedies. A: Management; B: 500 µmol/L H2O2-treated APRE-19 cells for 40 min; C: 500 µmol/L H2O2-treated APRE-19 cells for 40 min + 2 µg/L CUR-treated APRE-19 cells for 12 h; D: 500 µmol/L H2O2-treated APRE-19 cells for 40 min + 2 µg/mL HA-CUR NP-treated APRE-19 cells for 12 h; E: 500 µmol/L H2O2-treated APRE-19 cells for 40 min + 5 µg/mL HA-CUR NP-treated APRE-19 cells for 12 h. (b) Quantification of the fluorescence depth of CUR in numerous teams. (c) Quantification of the fluorescence depth of ROS in numerous teams. (d) Movement cytometry quantification of ARPE-19 cells stained with DFCH-DA after totally different remedies. (e) Imply fluorescence depth calculated from the stream cytometry information in d; (f) expression stage of IL-1β in numerous teams; (g) expression stage of IL-6 in numerous teams; (h) expression stage of TNF-α in numerous teams. Notice: */#, P < 0.05; **/##, P < 0.01; ***/###, P < 0.001
These findings have been additional verified through stream cytometry (Fig. 3d and e). Moreover, H2O2-pretreated ARPE-19 cells exhibited markedly elevated manufacturing of inflammatory cytokines, together with IL-1β, IL-6 and TNF-α, which have been downregulated by HA-CUR NPs however not by CUR (Fig. 3f, g and h). These outcomes collectively point out that HA-CUR NPs might mitigate ARPE-19 cell oxidative stress and the inflammatory response.
HA-CUR NPs attenuated pathological development, relieved microvascular injury, and controlled fundus blood stream in vivo
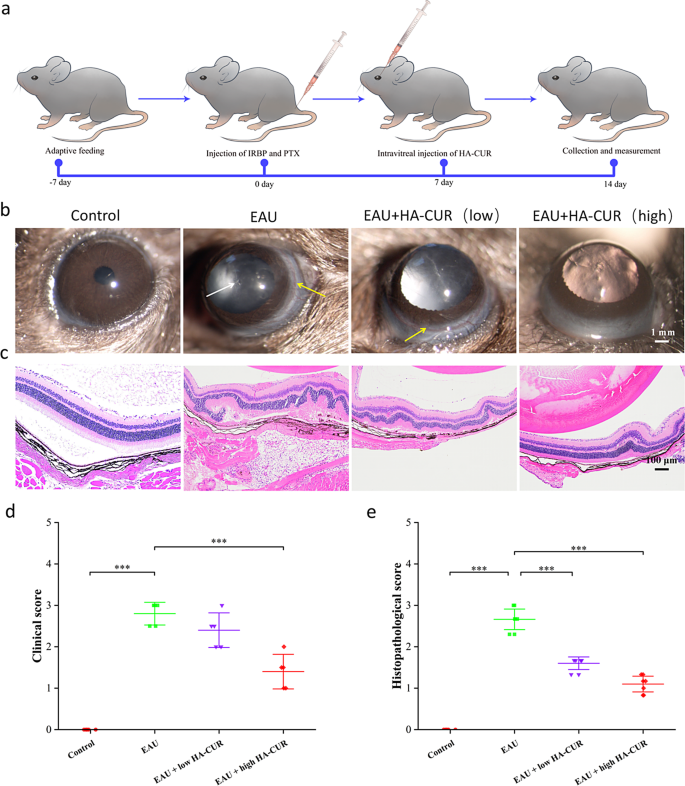
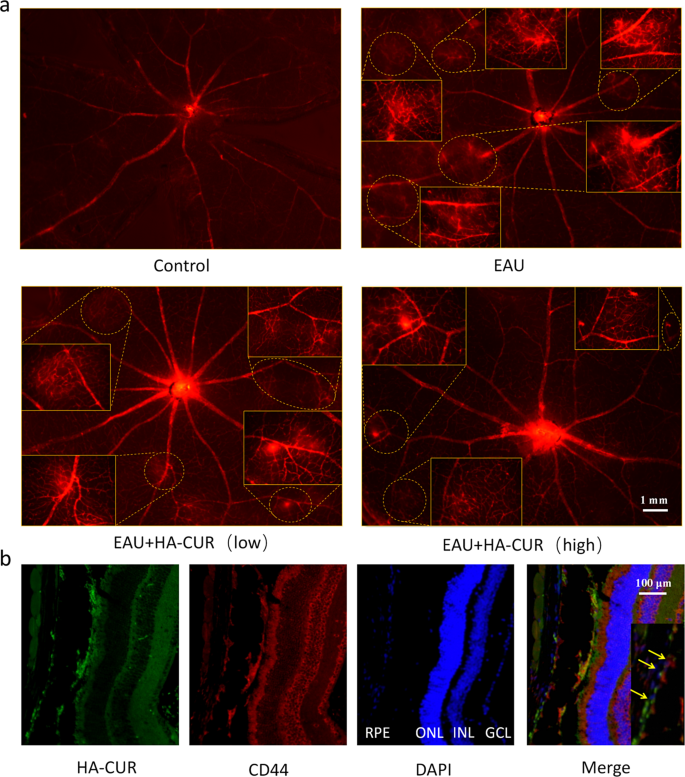
EAU mice’s scientific signs and retinal tissue pathological adjustments have been graded by severity based on earlier requirements [23, 24]. On the premise of the superb mobile uptake habits and skill of HA-CUR NPs to guard towards oxidative stress injury in vitro, we researched the therapeutic efficacy of HA-CUR NPs in vivo (Fig. 4a). In contrast with regular management rats, EAU mice introduced vital irritation within the anterior chamber and extreme ciliary and conjunctival hyperemia, whereas EAU mice handled with an intravitreal injection of excessive HA-CUR NPs introduced relieved signs (Fig. 4b). H&E staining revealed typical histopathological indicators within the EAU mannequin, together with considerably elevated retinal folds and elevated inflammatory cells, which have been markedly attenuated within the EAU mannequin mice handled with the intravitreal injection of excessive concentrations of HA-CUR NPs (Fig. 4c). Medical and histopathological scores have been additionally assessed (Fig. 4d and e). The results of HA-CUR NPs on the regulation of retinal vascularity and blood stream in vivo have been additionally totally investigated. Evans blue serves as a diazo dye that shortly and irreversibly binds to plasma ALB and due to this fact can be utilized as a extremely environment friendly retinal angiographic agent. As proven within the retinal vascular community pictures obtained from Evans blue staining in Fig. 5a, large vascular leakage websites have been noticed within the retinas of the EAU mice, and this leakage was markedly alleviated within the EAU mice handled with the intravitreal injection of excessive concentrations of HA-CUR NPs (Determine S4). Conversely, signs weren’t considerably ameliorated in EAU mannequin mice following the intravitreal injection of low concentrations of HA-CUR NPs. Moreover, immunohistochemistry was carried out to judge the concentrating on of RPE cells by HA-CUR NPs. As proven in Fig. 5b, HA-CUR NPs may very well be noticed within the cytoplasm of RPE cells. The outcomes revealed the colocalization of HA-CUR NPs and CD44-positive RPE cells.
(a) Illustration of the experimental process used to determine the experimental autoimmune uveitis (EAU) mannequin. (b) Medical manifestations of retinas within the totally different teams have been noticed through a slit lamp. The white arrows point out anterior chamber irritation; the yellow arrows point out conjunctival and ciliary congestion. (c) HE-stained histopathological pictures of retinas from the totally different teams. (d) Medical rating based mostly on the leads to (b). (e) Histopathological rating based mostly on the leads to (C). Notice: *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001
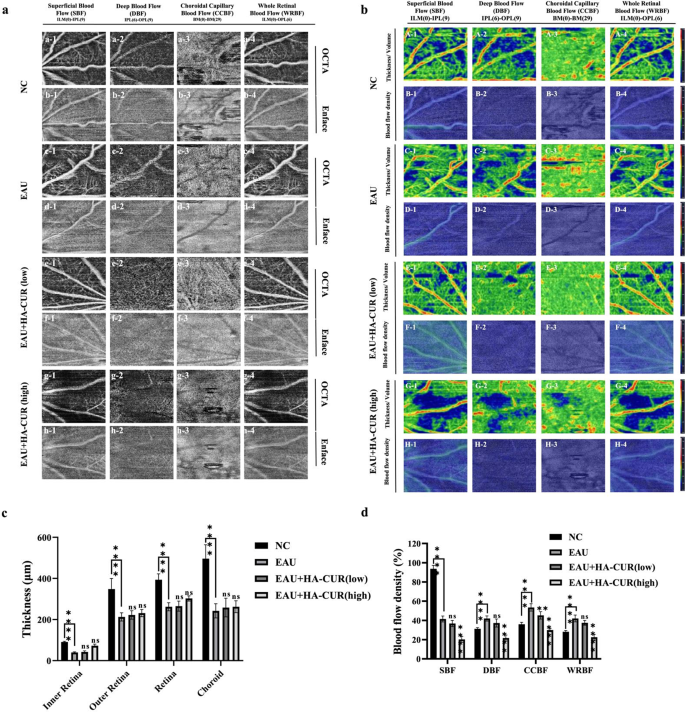
OCTA, a noninvasive fundus vascular imaging expertise that’s modern, has been extensively employed to diagnose fundus issues, together with diabetic retinopathy and uveitis. Not like conventional strategies, OCTA doesn’t require the intravenous utility of dye, stopping fluorescein leakage [25]. We employed OCTA imaging to quantify the thickness and density of blood stream in every fundus layer in distinct teams of mice. Determine 6a reveals the superficial blood stream (SBF), deep blood stream (DBF), choroidal capillary blood stream (CCBF), and entire retinal blood stream (WRBF) of the fundus of the assorted teams. In distinction to NC mice, EAU mice introduced typical retinal vascular morphological anomalies. Conversely, the retinal vascular networks of EAU mannequin mice have been regular following intravitreal injections of each high and low concentrations of HA-CUR NPs. Determine 6b reveals the OCTA fundus blood stream and thickness/quantity maps. In contrast with NC mice, EAU mice introduced extra impaired blood stream alerts and uneven vessel morphology throughout the entire retinal vascular community, indicating vital vascular dysfunction within the fundus of the EAU mice. In distinction, these irregular signs have been alleviated in EAU mannequin mice by intravitreal injections of each high and low concentrations of HA-CUR NPs. The quantitative evaluation of the SBF, DBF, CCBF, and WRBF layers of the fundus, as illustrated in Fig. 6c and d, revealed a marked lower in thickness within the EAU group in contrast with the NC group. Each the EAU mice handled with the intravitreal injection of low- and high-HA-CUR NPs subsequently exhibited outstanding enhancements to comparatively regular ranges. These outcomes point out that HA-CUR NP remedy markedly attenuated pathological development, relieved microvascular leakage, and controlled fundus blood stream; due to this fact, HA-CUR NPs function efficient brokers for retinal safety in EAU.
Optical coherence tomography angiography (OCTA) imaging, blood stream, and thickness of a number of layers of OCTA within the fundus. (a) Superficial blood stream (SBF) (a1-h1), deep blood stream (DBF) (a2-h2), choroidal capillary blood stream (CCBF) (a3-h3), and entire retinal blood stream (WRBF) (a4-h4) of the OCTA panorama in numerous teams. (b) OCTA fundus thickness/quantity (A, C, E, G) and blood stream (B, D, F, H) maps in numerous teams. (c) Quantification of the thickness of the SBF, DBF, CCBF, and WRBF retinal layers in numerous teams. (d) Quantification of blood stream within the SBF, DBF, CCBF, and WRBF retinal layers in numerous teams. Asterisks point out a big distinction. Notice: *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; ****, P < 0.0001
HA-CUR NPs mitigated oxidative stress and lowered inflammatory responses
HA-CUR NPs have been proven to mitigate oxidative stress in vitro; thus, we investigated whether or not HA-CUR NPs exert related results in vivo. MDA is normally thought to be a marker for lipid peroxidation and oxidative stress [26], whereas SOD is a metalloenzyme that safeguards the organism towards oxidative stress [27]. The redox state of uveitis is usually recommended to be imbalanced, as evidenced by the considerably greater intraocular MDA and lowered intraocular SOD in EAU animals than in regular controls (Fig. 7a-j). Fortuitously, the administration of HA-CUR NPs dose-dependently decreased excessive MDA ranges and elevated low SOD ranges in EAU mice, whereas remedy with free CUR had a minimal impact on these indicators. Moreover, provided that IL-17, IFN-γ and TNF-α are attribute inflammatory cytokines that take part within the pathogenesis and improvement of uveitis [28], we additional examined the expression of those three cytokines within the totally different teams. In contrast with NC mice, EAU mice introduced markedly better expression ranges of intraocular IL-17, IFN-γ and TNF-α, which have been decreased in a dose-dependent method by remedy with HA-CUR NPs moderately than free CUR. Moreover, we quantified the expression of the CD44 receptor in response to the extreme oxidative stress that was induced in vitro (Fig. 7ok, l). The CD44 receptor expression of the EAU mice exceeded that of the traditional controls, suggesting a probably extra intense focused interplay between HA and the receptor. The mix of CUR and HA might improve CUR bioavailability by concentrating on HA to the CD44 receptor, decreasing oxidative stress and inflammatory responses, provided that HA-CUR NPs are extra efficacious than free CUR is. Contemplating that HA-CUR NPs are considerably extra efficacious than free CUR is, one affordable conclusion might be drawn that the mix of CUR and HA may markedly improve the bioavailability of CUR, which can be mediated by the precise concentrating on of HA to the CD44 receptor, thereby effectively attenuating extreme inflammatory responses and oxidative stress.
Quantification of the serum MDA (a), SOD (b), TNF-α (c), IFN-γ (d), and IL-17 (e) ranges and the intraocular MDA (f), SOD (g), TNF-α (h), IFN-γ (i), and IL-17 (j) ranges in numerous teams. (ok, l) Expression of the CD44 receptor in management and EAU rats. Notice: */#, P < 0.05; **/##, P < 0.01; ***/###, P < 0.001
HA-CUR NPs exerted anti-inflammatory results by activating the Keap1/Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway
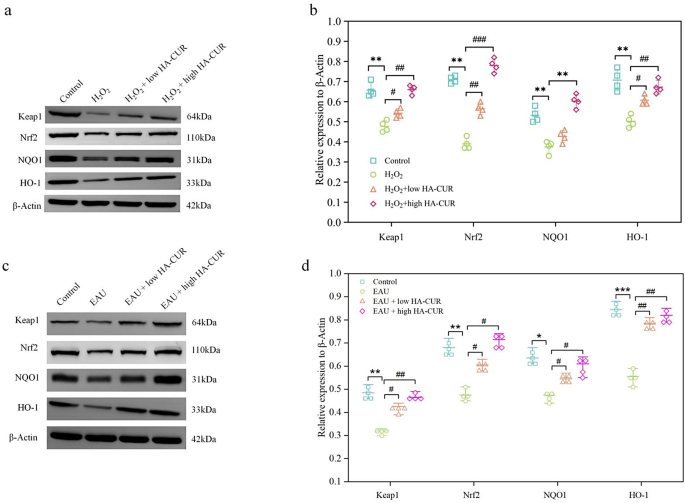
By figuring out the potential mechanism behind the distinguished oxidative stress safety of HA-CUR NPs, we could possibly higher perceive the therapeutic advantages of HA-CUR NPs and optimize their scientific utility. To additional discover the molecular mechanism of HA-CUR NPs, we performed transcriptome sequencing evaluation on ARPE-19 cells handled with totally different interventions. The Molecular Signatures Database C2 database was used to carry out GSEA on the DEGs, and the highest 20 outcomes are illustrated in Fig. 8a. Nearly all of genes whose expression was considerably upregulated by HA-CUR NPs have been related to irritation, immunology, and oxidative stress, together with REACTOME_KEAP1_NFE2L2_PATHWAY, a traditional pathway that’s concerned within the antioxidative stress response and safeguards cells from oxidative injury. Extra enrichment evaluation confirmed the activation of the Keap1/Nrf2 signaling pathway (Fig. 8b and c). A gene expression heatmap of the Keap1/Nrf2 signaling pathway revealed that a number of genes within the Keap1/Nrf2 signaling pathway, together with GSTM5, GSTO2, MGST1, KEAP1, HMOX1, and NFE2L2, have been upregulated by the HA-CUR NPs (Fig. 8d and e), which promoted the expression of anti-inflammatory and antioxidant-related proteins to withstand oxidative stress injury. As well as, the highest 5 potential signaling pathways and the highest 6 DEGs revealed by transcriptome sequencing evaluation are proven in Fig. 8f. As some of the important antioxidant axes in physiological and pathological processes, the activation of Nrf2 signaling may contribute to a collection of antioxidant responses, thereby defending cells towards oxidative stress injury [29, 30]. Particularly, Nrf2 is a transcription factor that promotes the transcription and expression of varied main antioxidative enzymes, together with heme oxygenase-1 (OH-1) and NAD(P)H quinone oxidoreductase 1 (NQO1), by binding to antioxidation stress response websites [30, 31]. In quite a few cell traces, together with RPE cells, pure merchandise have been proven to change the Keap1/Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway [32]. Notably, Nrf2 was discovered to be intently associated to the event of uveitis, serving as a possible intervention goal within the modulation of redox hemostasis [33]. Western blotting was used to find out whether or not HA-induced CUR NPs can safeguard ARPE-19 cells and EAU mannequin mice from oxidative stress-induced injury by activating the Keap1/Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway. The protein expression ranges of Keap1, Nrf2, HO-1, and NQO1 in ARPE-19 cells pretreated with hydrogen peroxide have been considerably decrease than these within the management group. Nevertheless, the H2O2-induced results on the Keap1/Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway have been reversed by HA-CUR NPs in a dose-dependent method, as illustrated in Fig. 9a and b. Moreover, in distinction to these within the management group, the protein expression ranges of Keap1, Nrf2, HO-1, and NQO1 within the EAU group have been considerably decrease. Then again, HACUR NPs have been nonetheless able to reversing the adjustments in protein expression ranges in a dose-dependent method (Fig. 9c and d). These findings point out that Keap1/Nrf2/HO-1 induces the protecting affect of the HA CUR NPs. These outcomes recommend that the Keap1/Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway contributes considerably to the anti-inflammatory impact of the HA CUR NPs. Curcumin is a pure activator of Nrf2 [34]. Mechanistic research have proven that curcumin induces conformational adjustments in Keap1 and the ubiquitination of Nrf2 by binding to Keap1Cys151 [35]. Nevertheless, the results of curcumin on the protein expression of Nrf2 in cells subjected to oxidative stress usually are not fully constant. Liu et al. confirmed that pretreatment with curcumin didn’t improve the expression of complete Nrf2 in cells subjected to oxidative stress stimulation [36]. These findings are inconsistent with our findings. Nevertheless, some research have proven that curcumin can improve the protein expression of Nrf2 in cells subjected to numerous oxidative stresses [35, 37]. The focus of curcumin used and the length of its motion could also be key components influencing the extent of Nrf2 expression.
(a) The highest 20 outcomes of GSEA enrichment evaluation of the DEGs through the Molecular Signatures Database C2 database. (b, c) Operating enrichment rating of the Keap1/Nrf2 signaling pathway. (d, e) Gene expression heatmap of the Keap1/Nrf2 signaling pathway regulated by HA-CUR NPs. (f) Protein ranges of Keap1, Nrf2, HO-1, and NQO1 in ARPE-19 cells after totally different remedies. h, i) Protein ranges of Keap1, Nrf2, HO‐1, and NQO1 in rats in numerous teams
Evaluation of biocompatibility in vivo
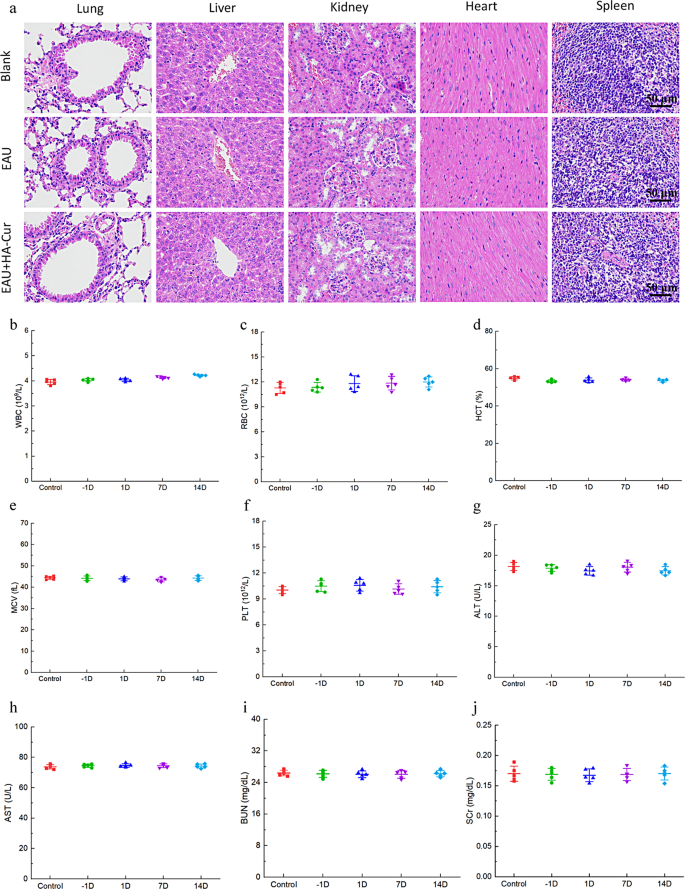
The biocompatibility of HA-CUR NPs in vivo was assessed by way of H&E staining of vital organs, together with the center, liver, spleen, lung, and kidney. As proven in Fig. 10a-j, no outstanding lesions, hemorrhage, or necrosis have been detected in these main organs. No substantial adjustments in liver or renal operate have been noticed in any of the mice within the current examine, as decided by ALT, AST, BUN, and SCR within the serum. The WBC, RBC, PLT, MCV, and HCT have been additionally measured and demonstrated no vital adjustments. No apparent lesions have been discovered within the retinal tissue after the HA-CUR NPs have been injected into the attention. (Determine S5a). We additional examined three inflammatory cytokines to judge the toxicity of HA-CUR NPs to intraocular tissues. As proven in Determine S5b, the expression ranges of IL-17, IFN-γ and TNF-α within the eyes of the mice injected with HA-CUR NPs didn’t considerably differ from these within the management group. Due to this fact, the HA-CUR NPs synthesized within the current examine have the potential to function protected and efficacious brokers for stopping the development of EAU.
In vivo biocompatibility of HA-CUR NPs. (a) Photographs of H&E-stained coronary heart, liver, spleen, lung, and kidney tissues from the totally different teams. (b–f) Quantification of white blood cells (WBCs), crimson blood cells (RBCs), platelets (PLTs), imply corpuscular quantity (MCV), and hematocrit (HCT) within the totally different teams. (g–j) Serum alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), blood urea nitrogen (BUN), and serum creatinine (SCR) ranges within the totally different teams