On this weblog publish I evaluate choices for real-time analytics on DynamoDB – Elasticsearch, Athena, and Spark – when it comes to ease of setup, upkeep, question functionality, latency. There may be restricted assist for SQL analytics with a few of these choices. I additionally consider which use circumstances every of them are finest fitted to.
Builders usually have a must serve quick analytical queries over information in Amazon DynamoDB. Actual-time analytics use circumstances for DynamoDB embody dashboards to allow dwell views of the enterprise and progress to extra advanced software options resembling personalization and real-time consumer suggestions. Nevertheless, as an operational database optimized for transaction processing, DynamoDB isn’t well-suited to delivering real-time analytics. At Rockset, we just lately added assist for creating collections that pull information from Amazon DynamoDB – which mainly means you’ll be able to run quick SQL on DynamoDB tables with none ETL. As a part of this effort, I spent a major period of time evaluating the strategies builders use to carry out analytics on DynamoDB information and understanding which technique is finest suited based mostly on the use case and located that Elasticsearch, Athena, and Spark every have their very own execs and cons.
DynamoDB has been some of the fashionable NoSQL databases within the cloud since its introduction in 2012. It’s central to many fashionable purposes in advert tech, gaming, IoT, and monetary companies. Versus a conventional RDBMS like PostgreSQL, DynamoDB scales horizontally, obviating the necessity for cautious capability planning, resharding, and database upkeep. Whereas NoSQL databases like DynamoDB usually have glorious scaling traits, they assist solely a restricted set of operations which might be targeted on on-line transaction processing. This makes it tough to develop analytics straight on them.
So as to assist analytical queries, builders sometimes use a mess of various programs along side DynamoDB. Within the following sections, we’ll discover just a few of those approaches and evaluate them alongside the axes of ease of setup, upkeep, question functionality, latency, and use circumstances they match properly.
If you wish to assist analytical queries with out encountering prohibitive scan prices, you’ll be able to leverage secondary indexes in DynamoDB which helps a restricted sort of queries. Nevertheless for a majority of analytic use circumstances, it’s price efficient to export the info from DynamoDB into a special system like Elasticsearch, Athena, Spark, Rockset as described under, since they mean you can question with increased constancy.
DynamoDB + Glue + S3 + Athena
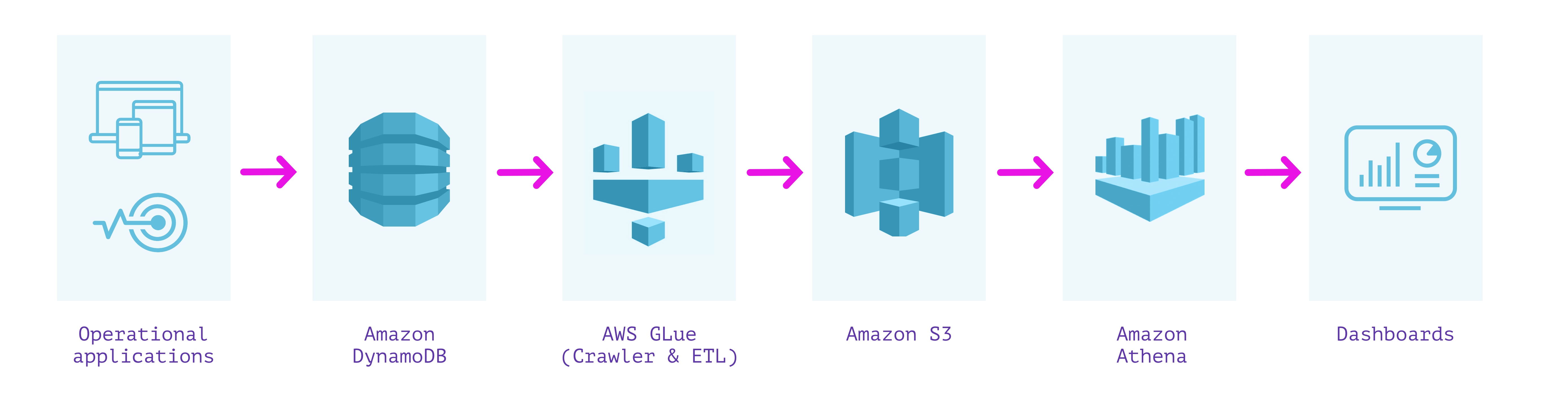
One strategy is to extract, remodel, and cargo the info from DynamoDB into Amazon S3, after which use a service like Amazon Athena to run queries over it. We will use AWS Glue to carry out the ETL course of and create an entire copy of the DynamoDB desk in S3.
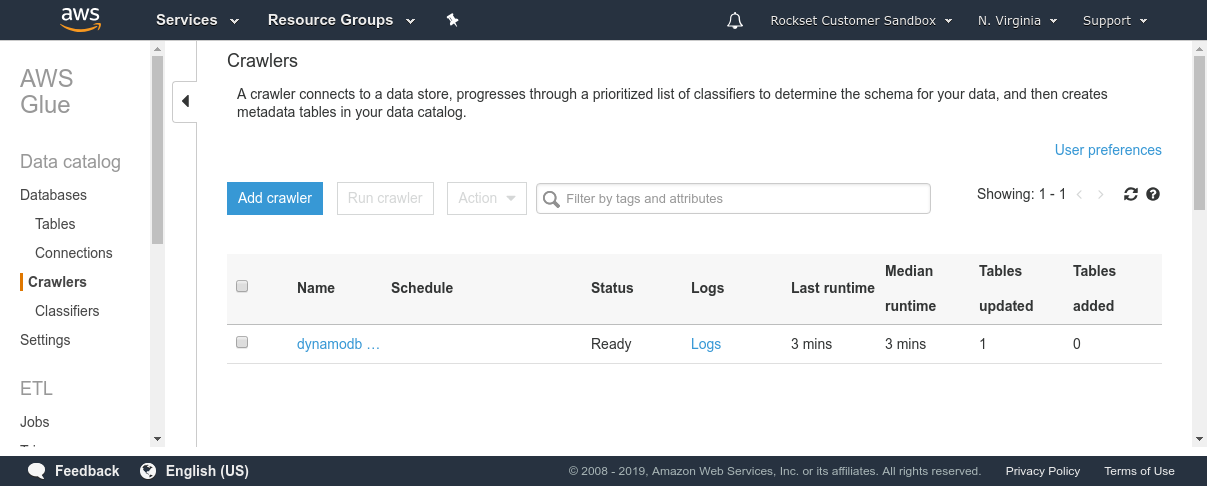
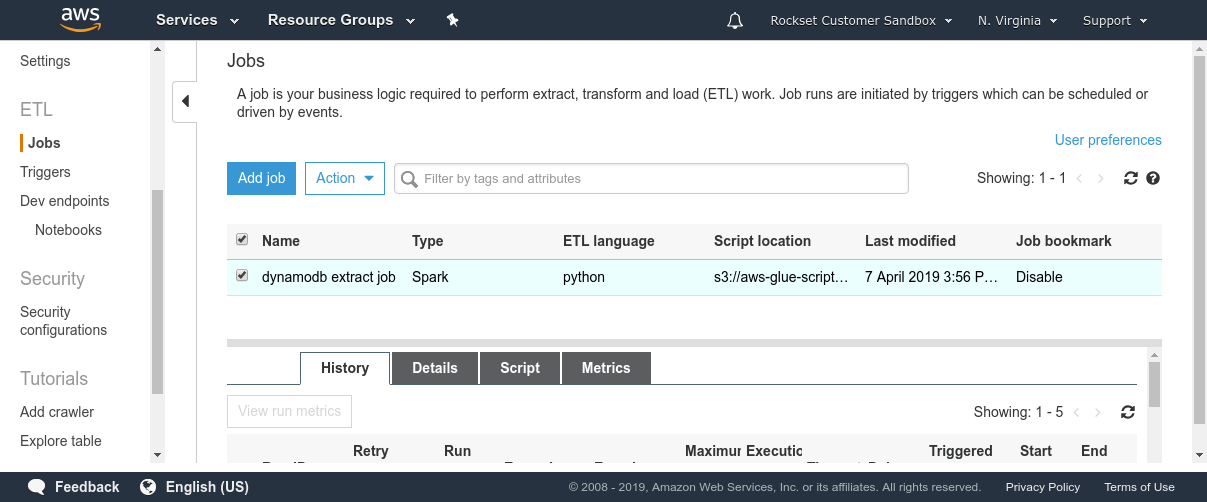
Amazon Athena expects to be offered with a schema so as to have the ability to run SQL queries on information in S3. DynamoDB, being a NoSQL retailer, imposes no fastened schema on the paperwork saved. Due to this fact, we have to extract the info and compute a schema based mostly on the info varieties noticed within the DynamoDB desk. AWS Glue is a completely managed ETL service that lets us do each. We will use two functionalities supplied by AWS Glue—Crawler and ETL jobs. Crawler is a service that connects to a datastore (resembling DynamoDB) and scans via the info to find out the schema. Individually, a Glue ETL Apache Spark job can scan and dump the contents of any DynamoDB desk into S3 in Parquet format. This ETL job can take minutes to hours to run relying on the dimensions of the DynamoDB desk and the learn bandwidth on the DynamoDB desk. As soon as each these processes have accomplished, we are able to fireplace up Amazon Athena and run queries on the info in DynamoDB.
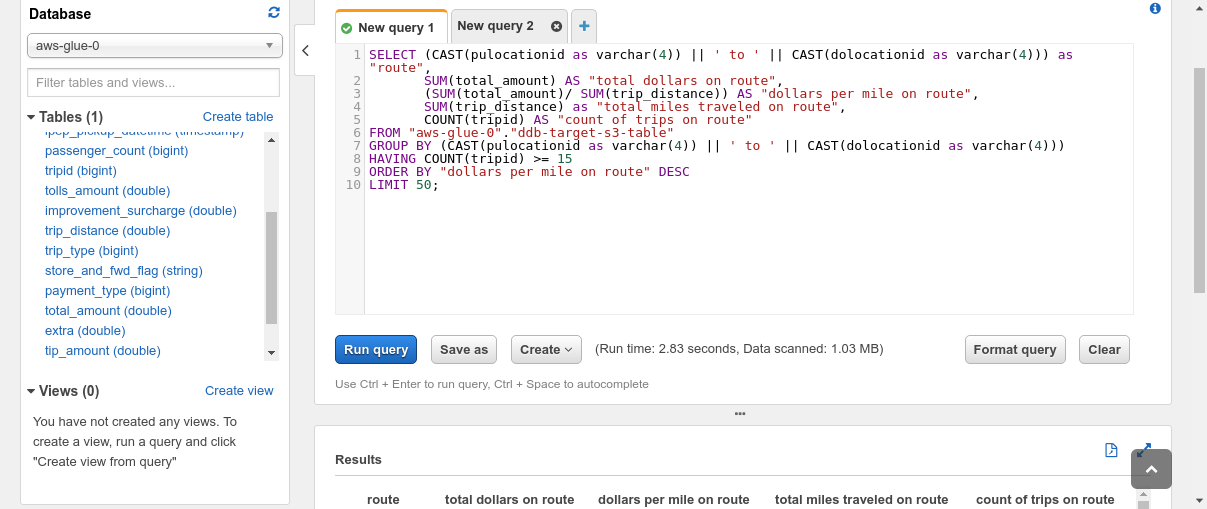
This whole course of doesn’t require provisioning any servers or capability, or managing infrastructure, which is advantageous. It may be automated pretty simply utilizing Glue Triggers to run on a schedule. Amazon Athena will be linked to a dashboard resembling Amazon QuickSight that can be utilized for exploratory evaluation and reporting. Athena relies on Apache Presto which helps querying nested fields, objects and arrays inside JSON.
A significant drawback of this technique is that the info can’t be queried in actual time or close to actual time. Dumping all of DynamoDB’s contents can take minutes to hours earlier than it’s out there for operating analytical queries. There isn’t a incremental computation that retains the 2 in sync—each load is a completely new sync. This additionally means the info that’s being operated on in Amazon Athena might be a number of hours outdated.
The ETL course of may also lose data if our DynamoDB information incorporates fields which have combined varieties throughout totally different gadgets. Discipline varieties are inferred when Glue crawls DynamoDB, and the dominant sort detected will probably be assigned as the kind of a column. Though there may be JSON assist in Athena, it requires some DDL setup and administration to show the nested fields into columns for operating queries over them successfully. There can be some effort required for upkeep of the sync between DynamoDB, Glue, and Athena when the construction of information in DynamoDB adjustments.
Benefits
- All elements are “serverless” and require no provisioning of infrastructure
- Straightforward to automate ETL pipeline
Disadvantages
- Excessive end-to-end information latency of a number of hours, which implies stale information
- Question latency varies between tens of seconds to minutes
- Schema enforcement can lose data with combined varieties
- ETL course of can require upkeep on occasion if construction of information in supply adjustments
This strategy can work properly for these dashboards and analytics that don’t require querying the most recent information, however as an alternative can use a barely older snapshot. Amazon Athena’s SQL question latencies of seconds to minutes, coupled with the big end-to-end latency of the ETL course of, makes this strategy unsuitable for constructing operational purposes or real-time dashboards over DynamoDB.
DynamoDB + Hive/Spark

An alternate strategy to unloading all the DynamoDB desk into S3 is to run queries over it straight, utilizing DynamoDB’s Hive integration. The Hive integration permits querying the info in DynamoDB straight utilizing HiveQL, a SQL-like language that may specific analytical queries. We will do that by organising an Amazon EMR cluster with Hive put in.
As soon as our cluster is ready up, we are able to log into our grasp node and specify an exterior desk in Hive pointing to the DynamoDB desk that we’re trying to question. It requires that we create this exterior desk with a specific schema definition for the info varieties. One caveat is that Hive is learn intensive, and the DynamoDB desk should be arrange with adequate learn throughput to keep away from ravenous different purposes which might be being served from it.
hive> CREATE EXTERNAL TABLE twitter(hashtags string, language string, textual content string)
> STORED BY 'org.apache.hadoop.hive.dynamodb.DynamoDBStorageHandler'
> TBLPROPERTIES (
> "dynamodb.desk.title" = "foxish-test-table",
> "dynamodb.column.mapping" = "hashtags:hashtags,language:language,textual content:textual content"
> );
WARNING: Configured write throughput of the dynamodb desk foxish-test-table is lower than the cluster map capability. ClusterMapCapacity: 10 WriteThroughput: 5
WARNING: Writes to this desk may lead to a write outage on the desk.
OK
Time taken: 2.567 seconds
hive> present tables;
OK
twitter
Time taken: 0.135 seconds, Fetched: 1 row(s)
hive> choose hashtags, language from twitter restrict 10;
OK
music km
music in
music th
music ja
music es
music en
music en
music en
music en
music ja
music en
Time taken: 0.197 seconds, Fetched: 10 row(s)
This strategy provides us extra up-to-date outcomes and operates on the DynamoDB desk straight reasonably than constructing a separate snapshot. The identical mechanism we noticed within the earlier part applies in that we have to present a schema that we compute utilizing a service like AWS Glue Crawler. As soon as the exterior desk is ready up with the proper schema, we are able to run interactive queries on the DynamoDB desk written in HiveQL. In a really comparable method, one may also join Apache Spark to a DynamoDB desk utilizing a connector for operating Spark SQL queries. The benefit of those approaches is that they’re able to working on up-to-date DynamoDB information.
A drawback of the strategy is that it could possibly take a number of seconds to minutes to compute outcomes, which makes it lower than splendid for real-time use circumstances. Incorporating new updates as they happen to the underlying information sometimes requires one other full scan. The scan operations on DynamoDB will be costly. Operating these analytical queries powered by desk scans ceaselessly may also adversely influence the manufacturing workload that’s utilizing DynamoDB. Due to this fact, it’s tough to energy operational purposes constructed straight on these queries.
So as to serve purposes, we could must retailer the outcomes from queries run utilizing Hive/Spark right into a relational database like PostgreSQL, which provides one other element to keep up, administer, and handle. This strategy additionally departs from the “serverless” paradigm that we utilized in earlier approaches because it requires managing some infrastructure, i.e. EC2 cases for EMR and presumably an set up of PostgreSQL as properly.
Benefits
- Queries over newest information in DynamoDB
- Requires no ETL/pre-processing apart from specifying a schema
Disadvantages
- Schema enforcement can lose data when fields have combined varieties
- EMR cluster requires some administration and infrastructure administration
- Queries over the most recent information includes scans and are costly
- Question latency varies between tens of seconds to minutes straight on Hive/Spark
- Safety and efficiency implications of operating analytical queries on an operational database
This strategy can work properly for some sorts of dashboards and analytics that do not need tight latency necessities and the place it isn’t price prohibitive to scan over all the DynamoDB desk for advert hoc interactive queries. Nevertheless, for real-time analytics, we want a approach to run a variety of analytical queries with out costly full desk scans or snapshots that shortly fall outdated.
DynamoDB + AWS Lambda + Elasticsearch
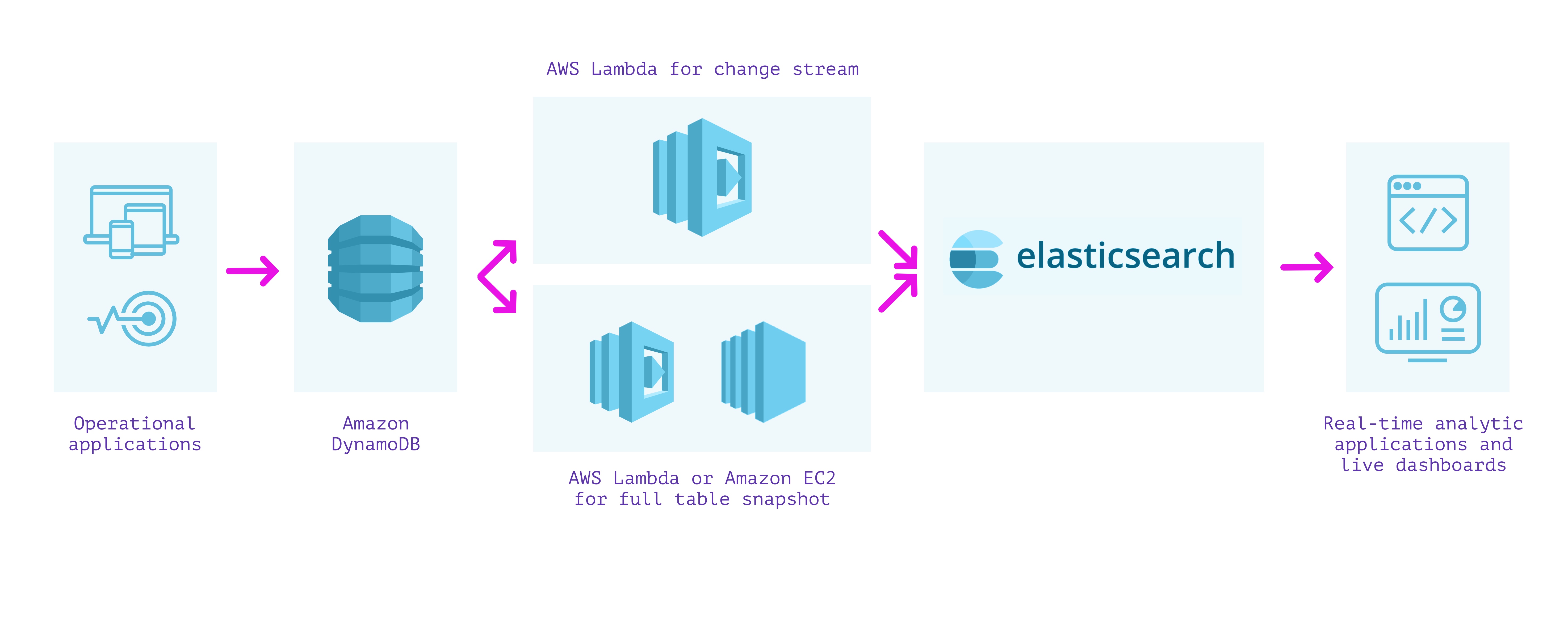
One other strategy to constructing a secondary index over our information is to make use of DynamoDB with Elasticsearch. Elasticsearch will be arrange on AWS utilizing Amazon Elasticsearch Service, which we are able to use to provision and configure nodes based on the dimensions of our indexes, replication, and different necessities. A managed cluster requires some operations to improve, safe, and maintain performant, however much less so than operating it completely by oneself on EC2 cases.
Because the strategy utilizing the Logstash Plugin for Amazon DynamoDB is unsupported and reasonably tough to arrange, we are able to as an alternative stream writes from DynamoDB into Elasticsearch utilizing DynamoDB Streams and an AWS Lambda perform. This strategy requires us to carry out two separate steps:
- We first create a lambda perform that’s invoked on the DynamoDB stream to publish every replace because it happens in DynamoDB into Elasticsearch.
- We then create a lambda perform (or EC2 occasion operating a script if it is going to take longer than the lambda execution timeout) to publish all the prevailing contents of DynamoDB into Elasticsearch.
We should write and wire up each of those lambda capabilities with the proper permissions as a way to make sure that we don’t miss any writes into our tables. When they’re arrange together with required monitoring, we are able to obtain paperwork in Elasticsearch from DynamoDB and may use Elasticsearch to run analytical queries on the info.
The benefit of this strategy is that Elasticsearch helps full-text indexing and several other kinds of analytical queries. Elasticsearch helps shoppers in numerous languages and instruments like Kibana for visualization that may assist shortly construct dashboards. When a cluster is configured accurately, question latencies will be tuned for quick analytical queries over information flowing into Elasticsearch.
Disadvantages embody that the setup and upkeep price of the answer will be excessive. As a result of lambdas fireplace after they see an replace within the DynamoDB stream, they will have have latency spikes as a result of chilly begins. The setup requires metrics and monitoring to make sure that it’s accurately processing occasions from the DynamoDB stream and in a position to write into Elasticsearch. It’s also not “serverless” in that we pay for provisioned assets versus the assets that we truly use. Even managed Elasticsearch requires coping with replication, resharding, index progress, and efficiency tuning of the underlying cases. Functionally, when it comes to analytical queries, it lacks assist for joins, that are helpful for advanced analytical queries that contain multiple index.
Benefits
- Full-text search assist
- Help for a number of kinds of analytical queries
- Can work over the most recent information in DynamoDB
Disadvantages
- Requires administration and monitoring of infrastructure for ingesting, indexing, replication, and sharding
- Requires separate system to make sure information integrity and consistency between DynamoDB and Elasticsearch
- Scaling is guide and requires provisioning extra infrastructure and operations
- No assist for joins between totally different indexes
This strategy can work properly when implementing full-text search over the info in DynamoDB and dashboards utilizing Kibana. Nevertheless, the operations required to tune and keep an Elasticsearch cluster in manufacturing, with tight necessities round latency and information integrity for real-time dashboards and purposes, will be difficult.
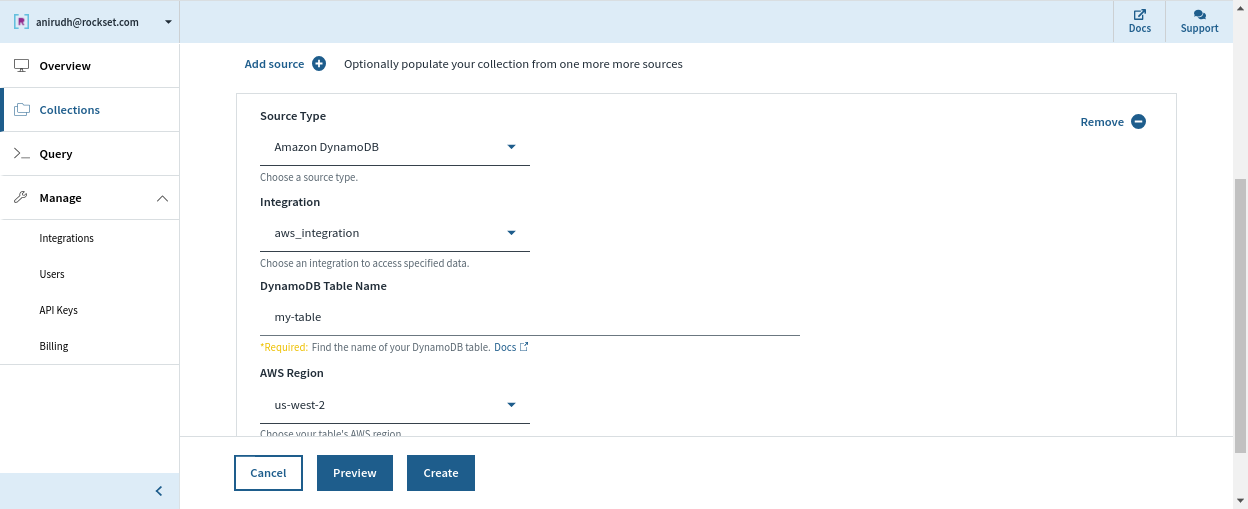
DynamoDB + Rockset
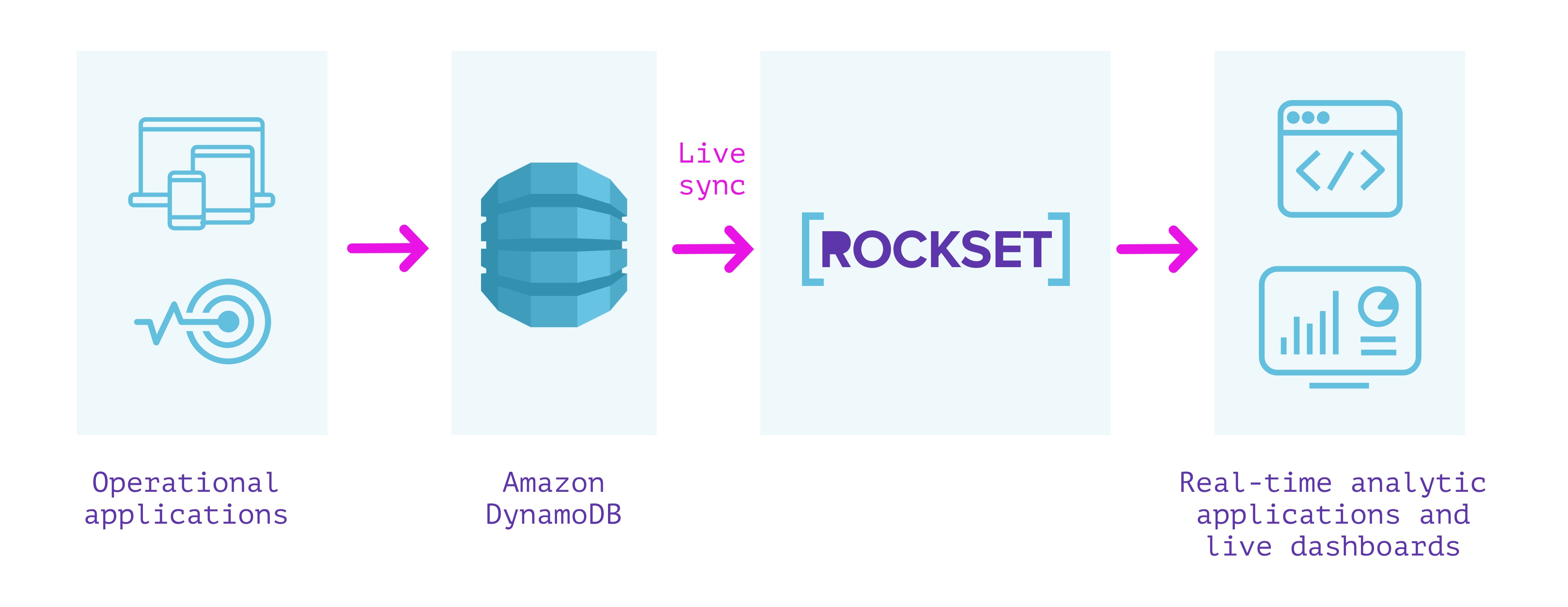
Rockset is a totally managed service for real-time indexing constructed primarily to assist real-time purposes with excessive QPS necessities.
Rockset has a dwell integration with DynamoDB that can be utilized to maintain information in sync between DynamoDB and Rockset. We will specify the DynamoDB desk we wish to sync contents from and a Rockset assortment that indexes the desk. Rockset indexes the contents of the DynamoDB desk in a full snapshot after which syncs new adjustments as they happen. The contents of the Rockset assortment are at all times in sync with the DynamoDB supply; no quite a lot of seconds aside in regular state.
Rockset manages the info integrity and consistency between the DynamoDB desk and the Rockset assortment routinely by monitoring the state of the stream and offering visibility into the streaming adjustments from DynamoDB.
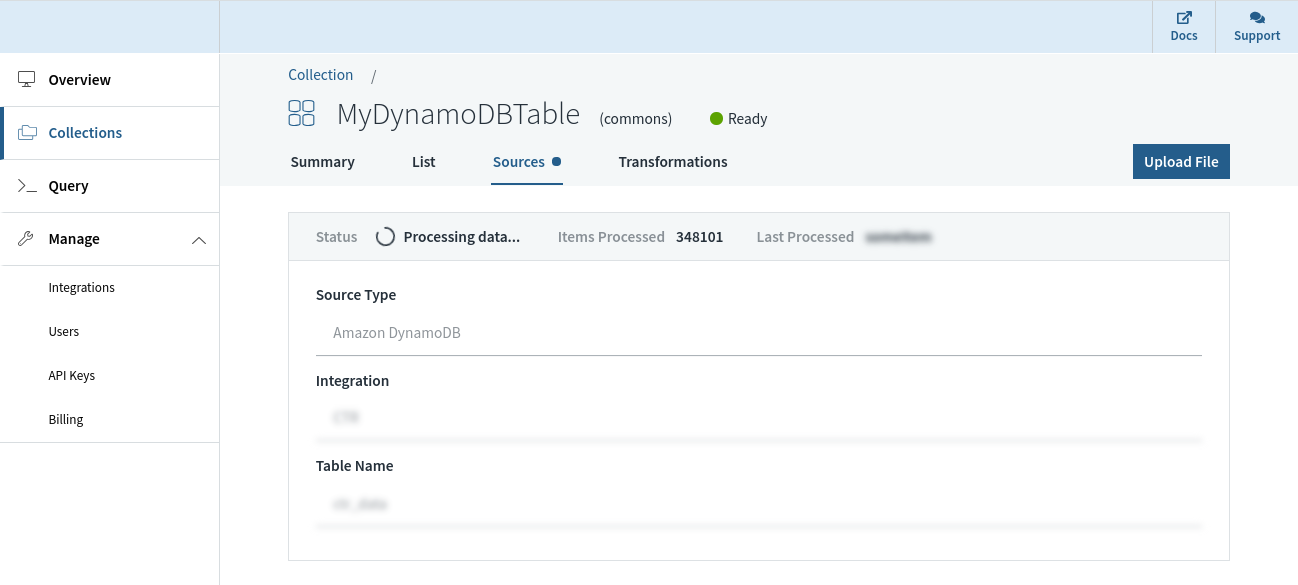
And not using a schema definition, a Rockset assortment can routinely adapt when fields are added/eliminated, or when the construction/sort of the info itself adjustments in DynamoDB. That is made doable by sturdy dynamic typing and sensible schemas that obviate the necessity for any extra ETL.
The Rockset assortment we sourced from DynamoDB helps SQL for querying and will be simply used to construct real-time dashboards utilizing integrations with Tableau, Superset, Redash, and so forth. It can be used to serve queries to purposes over a REST API or utilizing shopper libraries in a number of programming languages. The superset of ANSI SQL that Rockset helps can work natively on deeply nested JSON arrays and objects, and leverage indexes which might be routinely constructed over all fields, to get millisecond latencies on even advanced analytical queries.
As well as, Rockset takes care of safety, encryption of information, and role-based entry management for managing entry to it. We will keep away from the necessity for ETL by leveraging mappings we are able to arrange in Rockset to change the info because it arrives into a set. We will additionally optionally handle the lifecycle of the info by organising retention insurance policies to routinely purge older information. Each information ingestion and question serving are routinely managed, which lets us give attention to constructing and deploying dwell dashboards and purposes whereas eradicating the necessity for infrastructure administration and operations.
Rockset is an effective match for real-time analytics on prime of operational information shops like DynamoDB for the next causes.
Abstract
- Constructed to ship excessive QPS and serve real-time purposes
- Fully serverless. No operations or provisioning of infrastructure or database required
- Reside sync between DynamoDB and the Rockset assortment, in order that they’re by no means quite a lot of seconds aside
- Monitoring to make sure consistency between DynamoDB and Rockset
- Computerized indexes constructed over the info enabling low-latency queries
- SQL question serving that may scale to excessive QPS
- Joins with information from different sources resembling Amazon Kinesis, Apache Kafka, Amazon S3, and so forth.
- Integrations with instruments like Tableau, Redash, Superset, and SQL API over REST and utilizing shopper libraries.
- Options together with full-text search, ingest transformations, retention, encryption, and fine-grained entry management
We will use Rockset for implementing real-time analytics over the info in DynamoDB with none operational, scaling, or upkeep issues. This may considerably velocity up the event of dwell dashboards and purposes.
If you would like to construct your software on DynamoDB information utilizing Rockset, you will get began at no cost on right here. For a extra detailed instance of how one can run SQL queries on a DynamoDB desk synced into Rockset, try our weblog on operating quick SQL on DynamoDB tables.
Different DynamoDB assets:


