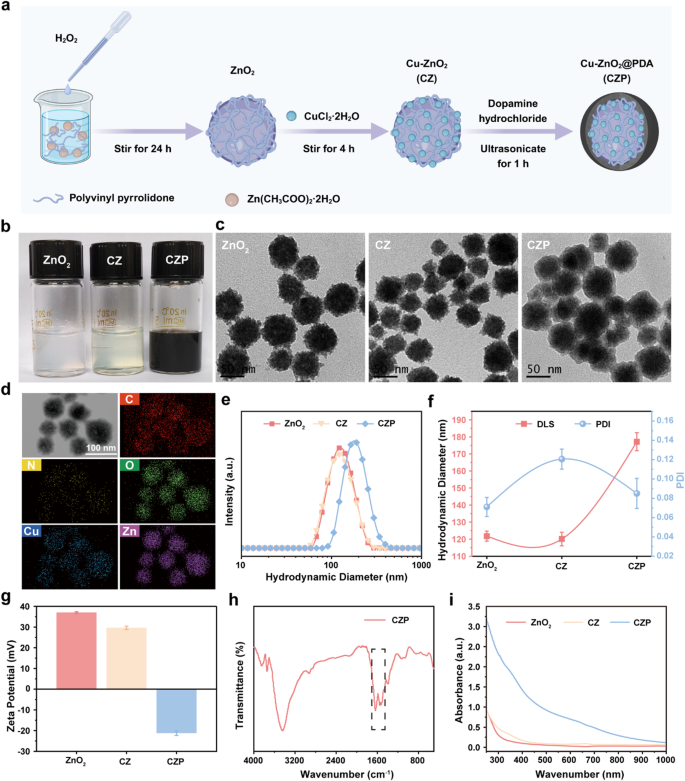
Synthesis and characterization of CZP NPs
The detailed preparation strategy of the Cu-ZnO2@PDA nanoplatform (CZP NPs) is summarized in Fig. 2a. Initially, the Zinc acetate dihydrate (Zn (CH3COO)2·2H2O), polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP), and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) have been blended and stirred at room temperature for twenty-four h to acquire the ZnO2 nanoparticles. The presence of PVP may complicated zinc ions and assemble them into uniformly spherical nanoparticles. Then, the obtained opalescent answer was stirred with cupric chloride dihydrate (CuCl2·2H2O) for 4 h, forming Cu-ZnO2 (CZ) nanoparticles. Including copper ions altered the answer’s colour to a smooth inexperienced. In the end, via the in situ self-polymerization of dopamine, the nanoparticles have been coated with polydopamine (PDA), and a brownish-black answer was obtained (Fig. 2b). Transmission electron microscope (TEM) photos revealed {that a} pronounced core-shell construction was constructed after the PDA coating on the floor of Cu-ZnO2 (Fig. 2c). In the meantime, the vitality dispersive X-ray (EDS) mapping illustrated that the nanoparticles consisted of carbon (C), nitrogen (N), oxygen (O), copper (Cu), and zinc (Zn) parts, validating the profitable synthesis of CZP NPs (Fig. 2d). To additional confirm the composition of CZP NPs particularly the valence state of parts, we performed X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) evaluation with a complete spectrum confirmed the simultaneous presence of Cu, Zn, C, N, and O parts in CZP NPs (Fig. S1a). Particularly, Determine S1b shows two distinct peaks at 1045.1 and 1022.0 eV, equivalent to the Zn 2p1/2 and Zn 2p3/2 orbitals of Zn2+, respectively. Moreover, Determine S1c signifies that copper ions exist in each Cu2+ (934.7 eV) and Cu+ (932.9 eV) valence states, with a ratio of 1.24. Dynamic mild scattering (DLS) measurement disclosed that the hydrodynamic diameter of CZP NPs is roughly 177.2 nm, notably exceeding that of ZnO2 (∼121.8 nm) and CZ (~ 120.1 nm), accompanied by the polydispersity index (PDI) have been measured to be 0.07, 0.12, 0.09, respectively (Fig. 2e and f). Moreover, the zeta potential of ZnO2 and CZ nanoparticles confirmed a constructive cost of 37.0 ± 0.42 mV and 29.7 ± 0.78 mV, respectively, and finally regulated at -21.2 ± 1.13 mV after PDA adhesion (Fig. 2g). The outcomes of Fourier remodel infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR) confirmed an absorption band at roughly 1510 cm− 1 equivalent to the shear vibration of N − H (Fig. 2h), confirming the profitable coating of PDA. Notably, inside the spectral vary of 250 to 1000 nm, the CZP NPs exhibited markedly increased absorption values than these of ZnO2 and CZ, suggesting their promising photothermal properties (Fig. 2i).
Synthesis and characterization of CZP NPs. (a) Schematic illustration of the synthesis of CZP NPs. (b) {Photograph} and (c) TEM micrograph of ZnO2, CZ, and CZP NPs. (d) The EDS mapping of C, N, O, Cu, and Zn of ready CZP NPs. (e, f) The hydrodynamic diameter, polydispersity index, and (g) zeta potentials of ZnO2, CZ, and CZP NPs. (h) FT-IR spectrum of CZP NPs. (i) UV-Vis spectra of ZnO2, CZ, and CZP NPs
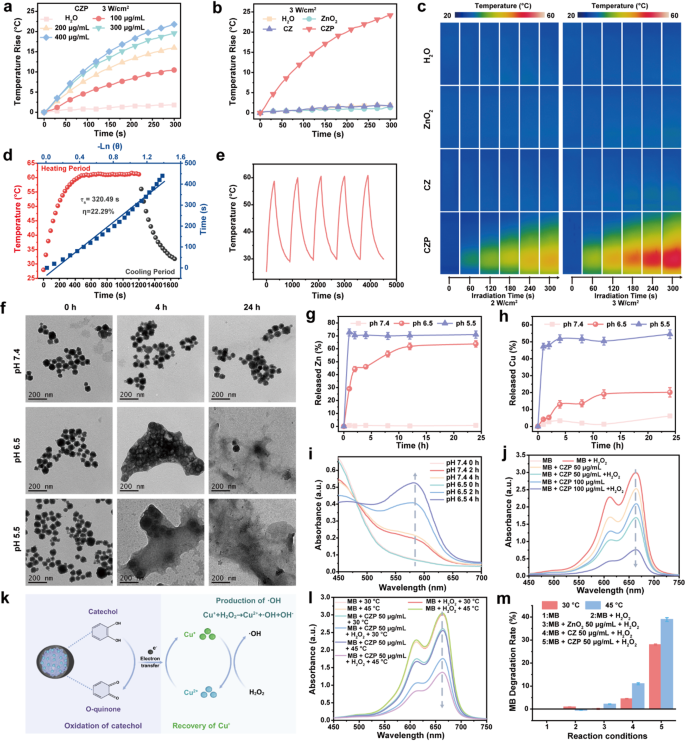
Photothermal efficiency analysis
Determine 2i exhibits that CZP NPs possess a broad absorbance throughout the wavelength vary of 250–1000 nm. Notably, at an equal focus, the absorbance of CZP NPs at 808 nm is 9.5 occasions that of ZnO2 and 4.3 occasions that of CZ, highlighting their wonderful photothermal therapeutic potential. Subsequently, we subsequent evaluated the photothermal efficiency of CZP NPs. Following a 5-minute publicity to an 808 nm laser irradiation, CZP NPs confirmed a pronounced temperature elevation correlated with rising irradiation energy density and focus. The CZP NPs on the focus of 500 µg/mL exhibited a major temperature enhance (ΔT) of 24.63 °C (3 W/cm2), markedly surpassing the H2O, ZnO2, and CZ teams, which have been just one.90 °C, 1.33 °C, and 1.84 °C, respectively (Fig. 3a, b and Fig. S2). This temperature rise is enough to induce necrosis and apoptosis in tumor cells. The modifications proven within the thermal photos have been additionally in step with the above outcomes (Fig. 3c). Subsequently, the photothermal conversion effectivity (𝜂) of CZP NPs was additional assessed. After 20 min of 808 nm NIR irradiation at 3 W/cm², the temperature of CZP NPs at 500 µg/mL reached 61.14℃, whereas the temperature of H2O merely reached 30.78℃. The η worth of CZP NPs was then calculated to be 22.29% (Fig. 3d and Fig. S3), which isn’t considerably completely different from the revealed results of PDA nanoparticles [46]. The photothermal efficiency exhibited by CZP NPs totally demonstrates that the Cu-ZnO2 core doesn’t significantly impair the photothermal efficiency of PDA. Furthermore, after 5 consecutive heating-cooling cycles, there have been no vital modifications within the real-time temperature change curve and UV-Vis spectra of the CZP answer earlier than and after laser irradiation, demonstrating its wonderful photothermal stability (Fig. 3e and Fig. S4). Consequently, the CZP NPs we have now developed exhibit wonderful photothermal capabilities and might be utilized to subsequent tumor photothermal remedy.
pH-triggered Zn-Cu ions/H2O2 launch and ROS technology
In line with our speculation, CZP NPs can selectively decompose and launch zinc, copper ions, and H2O2 inside the acidic TME. To evaluate the pH-responsive conduct of CZP NPs, TEM was utilized to watch their morphological modifications after present process completely different pH situations (pH = 7.4, 6.5, and 5.5). As anticipated, the CZP NPs have been virtually wholly decomposed inside 24 h at pH 5.5 whereas remaining secure at pH 7.4 (Fig. 3f). Subsequently, an inductively coupled plasma-atomic emission spectrometer (ICP-AES) was utilized to research the pH-dependent launch of zinc and copper ions. The outcomes confirmed that the discharge of zinc and copper ions in a pH 7.4 buffer answer was conspicuously sluggish, with merely 0.7% and 6.2%, respectively, over a 24-hour incubation (Fig. 3g and h). In stark distinction, the discharge charges at pH 5.5 elevated to 71% and 54.5%, respectively. Moreover, to research the impression of PDA coating on the degradation of CZP NPs, a comparative evaluation between CZ and CZP was performed. Regardless of a slight discount within the launch price noticed after the PDA coating, CZP NPs may quickly decompose and launch a considerable quantity of metallic ions inside 24 h for tumor remedy (Fig. S5). As well as, we additionally analyzed the discharge of H2O2 from CZP NPs by utilizing a hydrogen peroxide assay equipment. The detection reagent can acknowledge H2O2 and react to kind a purple compound, exhibiting a most absorption peak of round 560 nm. Co-incubation of CZP NPs with the detection reagent at pH 6.5 considerably enhanced the absorbance of the answer at 560–580 nm (Fig. 3i), demonstrating CZP’s capability to launch H2O2 underneath acidic situations.
Theoretically, the Cu+ and H2O2 within the TME may induce the technology of ·OH and Cu2+through the Fenton-like catalytic response [47,48,49], thereby selling oxidative stress inside tumor cells. Methylene blue (MB) was chosen because the indicator to evaluate the capability of ·OH technology, which is a dye probe that ·OH may cause MB to fade. As proven in Fig. 3j, upon co-incubation of CZP NPs with H2O2 and MB, the colour of the answer progressively lightened from mild blue because the CZP focus elevated. Concurrently, the absorption peak of MB within the vary of 600–700 nm regularly decreased. Nonetheless, MB co-incubated with H2O2 alone confirmed no vital colour or absorption spectra modifications. Moreover, we in contrast the ·OH technology capabilities amongst completely different nanoparticles. Within the presence of H2O2, MB was degraded by 100µg/mL CZP NPs, with a degradation price of 44.2%, roughly 4.25 occasions increased than that of the CZ group (Fig. S6a-c). Nonetheless, the proportion of copper ions in CZ, as beforehand decided by ICP evaluation, was roughly 11.58%, surpassing the 8.93% present in CZP NPs (Fig. S7). The superior Fenton-like response efficiency of CZP NPs could also be attributed to the presence of PDA. The plentiful catechol in PDA can act as a redox mediator [50], facilitating the switch of electrons to Cu2+ and selling the regeneration of Cu+. This course of helps preserve excessive catalytic exercise within the Fenton-like response and constantly generates ·OH (Fig. 3okay). Lastly, we examined the affect of temperature on the catalytic effectivity of CZP NPs. These nanoparticles exhibited enhanced catalytic exercise at 45 °C, reaching an MB degradation price of 38.9% at a focus of fifty µg/mL, which was significantly increased than the 27.9% noticed at 30 °C (Fig. 3l, m and Fig. S6d, e). Subsequently, the experimental outcomes confirmed that CZP NPs can spontaneously launch zinc and copper ions, H2O2, and generate ·OH within the acidic TME.
Photothermal, pH-responsive degradation, and ROS technology capabilities of CZP NPs. (a) Focus-dependent temperature-time curves of CZP options. (b) Temperature-time curves and (c) thermal photos (500 µg/mL) of H2O, ZnO2, CZ, and CZP options underneath NIR irradiation. (d) Photothermal conversion effectivity and (e) recycling-heating curves of CZP answer underneath NIR irradiation (3.0 W cm2). (f) TEM photos of CZP NPs following incubation at numerous pH ranges. (g) The discharge of zinc and (h) copper ions from CZP NPs at completely different pH situations. (i) UV–Vis spectra of the CZP NPs incubated with a Hydrogen Peroxide Assay Equipment at pH 7.4 or 6.5 situations. (j) UV–Vis spectra of MB after incubated with completely different concentrations of CZP NPs. (okay) The mechanism of the electron switch of CZP NPs for selling the Fenton-like response. (l) UV–Vis spectra of MB and (m) MB degradation charges throughout numerous teams
In vitro mobile uptake and cytotoxicity
Pushed by the numerous photothermal and Fenton-like catalytic actions of CZP NPs, we hypothesize that these nanoparticles can effectively kill tumor cells in vitro. To watch the mobile uptake conduct of CZP NPs, FITC labeled CZP to acquire FITC-CZP. Concurrently, we labeled the cell membrane and nucleus to visualise the intracellular localization and distribution of CZP. The confocal laser scanning microscope (CLSM) outcomes revealed that distinct inexperienced fluorescence was noticed following a 4-hour co-incubation of FITC-CZP with 4T1 cells (Fig. 4a). The fluorescence was predominantly colocalized with the cytoplasm, indicating profitable internalization of CZP into the cells. The circulate cytometry was utilized for additional evaluation. As proven in Fig. 4b-e, a gradual enhance within the fluorescence depth in 4T1 cells was detected with rising CZP focus and extended incubation time. After 8 h of incubation with 40 µg/mL FITC-CZP, the imply fluorescence depth (MFI) in 4T1 cells was roughly 1.7-fold that of the 4-hour incubation and about 3.0-fold that of the 1-hour incubation. These findings exhibit that CZP NPs may quickly be taken up by 4T1 cells.
The cytotoxicity of assorted therapies was assessed utilizing the Cell Counting Equipment-8. As proven in Fig. 4f, CZP NPs exhibited an evident dose and time-dependent cytotoxicity towards 4T1 cells, with cell-killing charges reaching roughly 91.7% and 98.1% at a focus of solely 40 µg/mL after 12 and 24 h of incubation, respectively. We additional analyzed the variations in cytotoxicity among the many ZnO2, CZ, and CZP NPs. After 4 h of co-incubation with 4T1 cells, ZnO2 and CZ displayed restricted cytotoxicity, even at a excessive focus of 100 µg/mL, with cell-killing charges of merely 34.7% and 43.8%, respectively. In distinction, CZP NPs achieved a cell-killing price of round 56.0% (Fig. 4g). Furthermore, when uncovered to an 808 nm laser at an influence density of two W/cm2 for five min, the killing price of CZP NPs additional elevated to a powerful 93.8% (Fig. 4h). Subsequently, we investigated the apoptosis and necrosis charges in 4T1 cells following numerous therapies utilizing the Annexin V-FITC Apoptosis Detection Equipment. Stream cytometry evaluation revealed that the apoptotic and necrotic price of 4T1 cells handled with CZP + NIR was 47.7%, which was 8.4, 7.7, and 1.7 occasions increased than that of Management, Management + NIR, and CZP remedy teams, respectively (Fig. 4i and Fig. S8). These outcomes verify that the mix technique of CZP + NIR may elicit passable synergistic antineoplastic results in vitro.
In vitro cuproptosis induced by CZP NPs
The substantial accumulation of copper ions inside tumor cells induces intracellular oxidative stress by producing poisonous ·OH and promotes the aggregation of lipoylated proteins and the lack of Fe-S cluster proteins, which ends up in the disruption of the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle in mitochondrial metabolism and induces cuproptosis [51]. Earlier experiments have confirmed that CZP NPs can launch many copper ions in an acidic atmosphere. Subsequently, we additional investigated the impression of launched copper ions on tumor cells. Firstly, the Reactive Oxygen Species Assay Equipment (DCFH-DA) was utilized to judge the intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) ranges. Pictures obtained from the inverted fluorescence microscope distinctly highlighted variations in fluorescence depth throughout numerous remedy teams (Fig. 4j). 4T1 cells handled with CZP NPs exhibited probably the most sturdy inexperienced fluorescence, suggesting the best manufacturing of ROS. Stream cytometry outcomes confirmed that the MFI of CZP-treated cells was 18.2, 7.2, and 4.6 occasions better than that of the Management, ZnO2, and CZ teams, respectively (Fig. 4okay and l). As a result of extreme ROS technology can induce mitochondrial injury and subsequent launch of mtDNA [52], we performed a Bio-TEM to investigate the modifications in mitochondria construction in 4T1 cells following CZP remedy. The pictures revealed that CZP remedy induced vital mitochondrial injury in 4T1 cells in comparison with the management group, characterised by mitochondrial swelling, shortened cristae, and the formation of vacuoles (Fig. 4m).
Moreover, we examined the expression ranges of Fe-S cluster proteins in 4T1 cells utilizing Western blot evaluation. As depicted in Fig. 4n, tumor cells handled with ZnO2 confirmed no vital change within the expression of Fe-S cluster proteins in comparison with the Management group, which is in step with our expectations. Notably, CZP and CZP + NIR therapies considerably downregulated the expression of Fe-S cluster proteins, together with FDX1, LIAS, ACO-2, and SDHB. These findings verify the bimetallic nanoplatform efficiently induced the 4T1 cells’ cuproptosis. Collectively, CZP NPs have the potential to raise intracellular ROS ranges, trigger mitochondrial injury, and induce cuproptosis.
In vitro mobile uptake and antitumor impact of CZP NPs. (a) Consultant confocal microscopy photos of 4T1 cells following a 4-hour incubation with FITC-CZP NPs. The cell nuclei have been stained with DAPI (blue) and the cell membranes with Dil (pink). (b-e) Stream cytometric profiles and corresponding quantification of 4T1 cells incubated with FITC-CZP NPs over numerous concentrations and time factors (n = 3). (f-h) The cell viability of 4T1 cells after numerous therapies (n = 3). (i) Stream cytometric evaluation of apoptosis and necrosis in 4T1 cells. (j-l) Fluorescent imaging and circulate cytometric evaluation of intracellular ROS ranges of 4T1 cells. (m) Bio-TEM photos of untreated 4T1 cells or handled with CZP + NIR. (n) Western blot evaluation of FDX1, LIAS, ACO-2, and SDHB from 4T1 cells following numerous therapies
mtDNA launch and cGAS-STING pathway stimulation
To determine whether or not mitochondrial injury induced by CZP NPs may set off the discharge of mtDNA, we employed Quantitative real-time PCR (qPCR) assays to measure the discharge of mtDNA into the cytoplasm. As proven in Fig. 5a, therapies with ZnO2, CZ, and CZP NPs induced the discharge of mtDNA in 4T1 cells, with the CZP + NIR remedy ensuing within the highest ranges of detected mitochondrial DNA. Particularly, mtDNA ranges have been 3.49-fold increased than the Management, 3.19-fold increased than the Management + NIR, 2.10-fold increased than the ZnO2, 1.52-fold increased than the CZ, and 1.37-fold increased than the CZP alone. Earlier analysis has indicated that mtDNA launched from broken mitochondria can even mediate the activation of the cGAS-STING signaling pathway [37, 38]. Moreover, zinc ions are essential in modulating cGAS exercise inside cells. They promote cGAS activation by facilitating its section separation, activating STING protein, and initiating downstream signaling pathways. To confirm the activation of the cGAS-STING signaling pathway after mtDNA launch induced by numerous therapies, we analyzed the expression ranges of cGAS and associated genes through qPCR. The findings indicated that therapies with laser irradiation alone, ZnO2, and CZ had restricted results on cGAS expression, roughly 0.96, 1.57, and a couple of.28 occasions that of the management group, respectively. In distinction, combining CZP with NIR irradiation yielded probably the most vital upregulation of cGAS expression, roughly 7.84 occasions increased than the management. (Fig. 5b). This disparity could also be attributed to the differential of mtDNA launch.
Additional evaluation revealed that the CZP + NIR remedy additionally considerably enhanced the expression of cGAS goal genes, together with IFNB1, CXCL10, IGS56, and ISG15 (Fig. 5c-f), confirming the efficient activation of the cGAS-STING pathway. Notably, the expression ranges of IFNB1 and CXCL10 in 4T1 cells after CZP + NIR remedy have been considerably elevated, reaching 47.17-fold and 34.57-fold that of the management group, respectively. Furthermore, Western blot evaluation of STING and TBK1 protein phosphorylation ranges demonstrated that the CZP + NIR remedy elevated the phosphorylation of STING and TBK1 in comparison with different teams. The ratio of phosphorylated STING to whole STING was roughly 1.77-fold that of the management group, whereas the ratio of phosphorylated TBK1 to whole TBK1 was 2.25-fold (Fig. 5g-i). These findings verify that the cytosolic launch of mtDNA triggered by CZP + NIR remedy, together with zinc ions, can successfully activate the cGAS-STING signaling pathway.
Provided that the activation of the cGAS-STING pathway can improve the maturation and activation of antigen-presenting cells (APCs) by selling the secretion of cytokines comparable to sort I interferons and CXCL10, we assessed the impression of CZP NPs on DCs maturation in vitro. Initially, we remoted bone marrow-derived dendritic cells (BMDCs) from BALB/c mice and co-cultured them with the supernatant of 4T1 cells that had undergone numerous therapies for twenty-four h. We then evaluated DCs maturation utilizing circulate cytometry. As proven in Fig. 5j and S9, in comparison with the Management group, the Management + NIR remedy didn’t considerably alter the share of mature DCs (CD11c+CD80+CD86+), whereas the CZP + NIR remedy considerably elevated the common degree from roughly 52.1 to 63.9%, aligning our expectations.
Notably, the activation of STING not solely stimulates the secretion of sort I interferons by activating the TBK1/IRF3 axis but in addition triggers NF-κB activation, which is intimately linked to PD-L1 expression on tumor cells [40,41,42]. And the extent of PD-L1 expression in TNBC has been confirmed to be intently associated to the efficacy of ICIs [43]. Accordingly, we additional examined the expression of PD-L1 on tumor cells after publicity to numerous therapies. Stream cytometry outcomes indicated that the common PD-L1 expression on 4T1 cells handled with CZP NPs was considerably increased than that of the Management group, roughly 2.3 occasions better (Fig. 5okay and l). This discovering was additional confirmed by qPCR evaluation (Fig. S10). These outcomes counsel that the CZP NPs can upregulate PD-L1 expression in tumor cells, implying that combining CZP NPs with αPD-L1 could possibly be a promising method for most cancers remedy.
CZP NPs promote the activation of the cGAS-STING signaling pathway. (a) The detection of mitochondrial DNA copy quantity in 4T1 cells after indicated therapies (n = 4). (b) The expression of cGAS and cGAS goal genes together with (c)IFNB1, (d)CXLC10, (e)ISG56, and (f)ISG15 in 4T1 cells with the indicated remedy (n = 3–5). (g-i) Western blot evaluation of p-STING, p-TBK1, STING, and TBK1 protein ranges in 4T1 cells after numerous remedy. β-actin was used because the management (n = 3). (j) Consultant circulate cytometry photos of mature DCs after completely different therapies. (okay) Consultant circulate cytometry photos and (l) corresponding quantification information of PD-L1 expression on 4T1 cells following completely different therapies (n = 3)
Transcription evaluation of CZP + NIR handled 4T1 cells
We investigated the transcriptomic modifications in 4T1 cells handled with CZP NPs mixed with NIR laser irradiation via RNA sequencing. Principal element evaluation revealed a definite separation between the CZP + NIR and Management teams (Fig. 6a). Remarkably, 7548 genes exhibited vital differential expression (p < 0.05) following CZP + NIR remedy in comparison with the Management, with 4770 genes upregulated and 2778 genes downregulated (Fig. 6b). Subsequent evaluation confirmed substantial downregulation of gene expression associated to Fe-S cluster proteins (e.g., LIAS), mitochondrial proteins (FDXR, OMA1), TCA cycle and respiratory electron transport (e.g., DBT, OGDH), and DNA restore (e.g., RAD51, MRNIP) in 4T1 cells following CZP + NIR remedy (Fig. 6c). Conversely, the expression of genes related to the interferon signaling pathway (e.g., cGAS, IFITT, ISG15, CXCL10) and CD274 (PD-L1) was markedly upregulated within the CZP + NIR group, in step with prior experimental observations. Gene ontology (GO) enrichment evaluation highlighted the involvement of organic processes within the CZP + NIR group, comparable to ‘Mobile response to emphasize’, ‘Regulation of immune system course of’, ‘Response to oxidative stress’, ‘Unfavorable regulation of development’, and ‘Mobile response to copper ion’ (Fig. 6d and Fig. S11). Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) enrichment evaluation additional demonstrated a major correlation between a number of pathways and the therapeutic results mediated by CZP + NIR remedy, together with the TNF signaling pathway, FoxO signaling pathway, Toll-like receptor signaling pathway, IL-17 signaling pathway, and Cytokine-cytokine receptor interplay (Fig. 6e and Fig. S12). These findings counsel that CZP + NIR remedy induces cytotoxicity in tumor cells through cuproptosis and oxidative stress whereas enhancing antitumor immune responses by regulating immune-related signaling pathways. Moreover, enrichment of the NF-κB signaling pathway within the CZP + NIR remedy group was additionally noticed (Fig. 6e), which is intently associated to the expression of PD-L1 in tumor cells. Furthermore, Gene set enrichment evaluation (GSEA) confirmed the sturdy upregulation of pathways concerned within the mobile response to oxidative stress, response to warmth, and cytokines and inflammatory response following CZP + NIR remedy (Fig. 6f-h), aligning with the above-mentioned discovering.
RNA sequencing evaluation of 4T1 cells in management and CZP + NIR remedy teams. (a) Principal element evaluation, (b) volcano plot, and (c) warmth map of differentially expressed genes in CZP + NIR group in comparison with Management. (d) GO, (e) KEGG, and (f-h) GSEA enrichment evaluation of differentially expressed genes within the CZP + NIR group
In vivo biosafety and biodistribution analysis
Guaranteeing biosafety and biocompatibility is essential for the protected software of prescription drugs in vivo. Subsequently, we initially assessed the biosafety of CZP NPs. Wholesome ICR mice have been administered CZP NPs at escalating doses (10, 20, 30, 40, and 50 mg/kg) through tail vein injection, with saline as a management. The mice have been monitored for modifications in physique weight and conduct each different day. After 28 days, every group’s blood and main organs have been harvested for additional evaluation. The outcomes confirmed no discernible behavioral abnormalities of mice have been noticed, and physique weights steadily elevated over time with out vital variations between completely different doses of CZP-treated teams and the saline (Fig. S13), which suggests the CZP NPs exhibit low systemic toxicity even on the most examined dose of fifty mg/kg. The organ coefficients and macroscopic examinations of the principle organs (coronary heart, liver, spleen, lung, and kidney) additionally confirmed that CZP remedy didn’t trigger atrophy of the key organs at completely different doses (Figs. S14 and S15). Subsequently, we scrutinized the physiological and biochemical parameters of the blood in mice in every group. The degrees of whole protein (TP), blood urea nitrogen (BUN), creatinine (CREA), and routine blood parameters in CZP-treated mice weren’t considerably completely different from the saline (Figs. S16 and S17). Nonetheless, it needs to be identified that CZP remedy reasonably lowered the degrees of alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), uric acid (UA), and creatine kinase (CK) within the serum. Even at a excessive focus of fifty mg/kg, the serum AST and ALT ranges in mice remained low, at solely 74.8% and 61% of the management group’s ranges, respectively. This means that CZP NPs have low toxicity to regular tissues and don’t trigger liver cell injury, suggesting their potential for in vivo functions. Lastly, histological examination of the key organs utilizing hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining revealed no vital morphological or pathological alterations in mice handled with CZP NPs relative to the saline-treated group (Fig. S18). Collectively, these outcomes exhibit the excellent biosafety of CZP NPs in vivo.
Subsequent, we constructed an orthotopic breast most cancers mannequin based mostly on 4T1 cells to research the biodistribution of CZP NPs in vivo. Indocyanine inexperienced (ICG)-labeled CZP NPs (CZP-ICG) have been injected through tail vein, and the next fluorescence depth within the mice was monitored at numerous time intervals utilizing an In Vivo Imaging System (IVIS). The outcomes confirmed {that a} robust fluorescence sign was nonetheless current on the tumor web site even 24 h after the injection (Fig. S19), indicating the buildup of CZP-ICG inside the tumor. Furthermore, mice have been sacrificed 4- and 24-hours post-injection, and main organs and tumor tissues have been harvested for ex vivo bioimaging. The outcomes confirmed that the whole fluorescence depth in tumors 24 h after administration was roughly 1.4 × 108 p/s, rating third amongst all tissues, following the liver and spleen (Fig. S20). This means that CZP NPs can quickly goal and accumulate on the tumor web site, which is extremely helpful for its software. Moreover, it’s noteworthy that CZP can attain the kidneys via the bloodstream, and the fluorescence indicators in all organs at 24 h are decrease than these at 4 h. This means that CZP could also be excreted via the kidneys, thereby lowering its accumulation in regular tissues. Moreover, histological sections of main organs after HE staining confirmed no vital CZP NPs deposition 28 days after i.t. injection (Fig. S18), indicating that our synthesized CZP has good biocompatibility and is metabolizable.
In vivo antitumor impact of CZP NPs
The therapeutic impact of CZP NPs was additional evaluated in vivo. Initially, a main orthotopic breast tumor mannequin was established by injecting 4T1 cells into the left fourth mammary fats pad of BALB/c mice. As soon as tumors reached 60–100 mm3, mice have been randomly divided into six teams: (1) Management, (2) Management + NIR, (3) ZnO2, (4) CZ, (5) CZP, and (6) CZP + NIR and acquired correspond remedy (Fig. 7a). Every group of mice acquired a complete of 4 i.t. drug injections, and the NIR group was subjected to a single near-infrared laser irradiation on Day 0. As proven in Fig. 7b and c, the thermal imaging and the corresponding temperature-time curves revealed that the common temperature on the tumor web site within the CZP + NIR handled mice reached 53.0 °C. In stark distinction, the temperature enhance within the NIR group was fairly restricted, solely reaching 38℃. That is attributed to the nice tissue penetration of 808 nm near-infrared mild, which is minimally absorbed by regular tissues. By administering CZP through i.t. injection, we achieved focused photothermal remedy within the tumor tissue, minimizing thermal injury to surrounding regular tissues. On the primary day after PTT, mice have been injected with 4T1 cells subcutaneously on the contralateral dorsal area to ascertain a distant tumor mannequin and hold them rising naturally. Tumor dimension and physique weight have been recorded each different day from day 0. The outcomes confirmed that no statistically vital physique weight modifications have been noticed all through therapies (Fig. 7d), suggesting minimal unwanted side effects of CZP NPs. Moreover, mice handled with CZP + NIR exhibited the simplest tumor development inhibition on day 12, with a median main tumor quantity of 111.2 mm3, which was 22.0% of the Management group (506.2 mm3), 20.3% of the Management + NIR group (548.5 mm3), and 48.6% of the CZP group (228.6 mm3), whereas the ZnO2 (394.9 mm3) and CZ (297.1 mm3) teams confirmed restricted tumor inhibitory results (Fig. 7e and Fig. S21). The tumor weights (Fig. 7f) and corresponding pictures (Fig. 7g, left) additional substantiated these findings. Lastly, we analyzed the formation price of distant tumors in every group. As proven in Fig. 7g (proper), mice handled with CZP + NIR confirmed efficient resistance to distant tumor formation, confirming that CZP + NIR remedy can induce a sustained antitumor immune response, successfully inhibiting the expansion of metastatic tumors at distant websites.
CZP reprogrammed the tumor immune microenvironment in vivo
As beforehand mentioned, CZP NPs can successfully activate the cGAS-STING pathway via PTT mixed with cuproptosis, resulting in the discharge of sort I interferons that promote the maturation of DCs inside tumor-draining lymph nodes (TDLNs). Thus, we utilized circulate cytometry to investigate the maturation of DCs in TDLNs of mice throughout numerous remedy teams. The outcomes revealed that the proportion of mature DCs (CD11c+CD80+CD86+) in TDLNs from mice handled with CZP + NIR was roughly 37.6% (Fig. 7h and that i), which is 1.3 occasions increased than that noticed in Management (29.4%) and Management + NIR teams (30.0%), suggesting that the mixed CZP + NIR remedy can considerably improve DCs maturation. Provided that mature DCs are pivotal in presenting antigens to T cells, thereby initiating tumor-specific adaptive immune responses, we evaluated the infiltration of T cells inside tumors. Notably, mice handled with CZP + NIR exhibited the best infiltration of CD3+CD8+ cytotoxic T cells (61.4%), which is 1.9 occasions and 1.6 occasions better than that of the Management (32.6%) and Management + NIR teams (39.2%), respectively (Fig. 7j and okay). Moreover, we noticed a major discount within the ratio of immunosuppressive regulatory T cells (Tregs, CD4+CD25+Foxp3+) within the CZP + NIR group relative to different remedy teams (Fig. 7l and m). The CZP + NIR remedy additionally markedly restricted the presence of immunosuppressive M2-like tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs, CD11b+F4/80+CD206+) (Fig. 7n and o). Immunofluorescence staining outcomes additional substantiated these findings, displaying a pronounced enhance in CD8+ T cell infiltration inside tumor tissues following CZP + NIR remedy (Fig. 7p and Fig. S22). Furthermore, the results of TUNEL staining confirmed that the inexperienced fluorescence depth (indicating DNA injury) in tumor tissues of mice handled with CZP + NIR was probably the most intense. H&E staining additionally indicated probably the most extreme tumor necrosis within the CZP + NIR handled group in comparison with others, demonstrating its potent antitumor impact (Fig. 7p). In abstract, these findings exhibit that the CZP + NIR remedy can successfully induce systemic antitumor immune responses by activating the cGAS-STING pathway, enhancing the recruitment of cytotoxic T lymphocytes and reprogramming the immunosuppressive TME.
CZP mediated remedy on 4T1 tumor. (a) Schematic illustration of the experimental schedule for 4T1 tumor-bearing mice. (b) Temperature-time curves and (c) thermal photos of tumor-bearing mice underneath NIR irradiation (1 W/cm2, n = 5). (d) Physique weight modifications of mice over 12 days. (e) Tumor development curves, (f) tumor weights and (g) corresponding pictures of main and distant tumors (n = 5). Consultant circulate cytometry plots and corresponding quantifications of (h, i) mature DCs in TDLNs, (j, okay) CD3+ CD8+ T cells, (l, m) Tregs, and (n, o) M2 phenotype tumor-associated macrophages in tumors from mice following numerous therapies (n = 4). (p) Immunofluorescence staining of CD8+ and CD4+ T cells, TUNEL, and H&E staining of tumor tissues from mice given numerous therapies
Evaluation of lung metastasis inhibition
To completely assess the power of CZP + NIR remedy to suppress distant metastasis induced by a systemic antitumor immune response, we established a mouse mannequin of whole-body metastasis. Initially, the institution of the 4T1 orthotopic breast most cancers mannequin and the remedy protocol adopted the strategies detailed beforehand, with the only modification of injecting 4T1-luc cells intravenously on day 1 to simulate malignant tumor invasion and hematogenous unfold (Fig. S23). Tumor cells coming into the bloodstream can infiltrate numerous organs, with a specific propensity for the lungs. On day 12, D-luciferin potassium salt was administered intraperitoneally to every group of mice, adopted by the evaluation of fluorescence depth utilizing the IVIS to judge tumor metastasis. The outcomes indicated intensive tumor metastasis in each the Management and Management + NIR teams, with fluorescence intensities within the lungs of 1.28 × 107 p/s and 1.39 × 107 p/s, respectively (Fig. S24). Whereas therapies with numerous nanoparticles have reasonably diminished distant metastasis, the CZP and CZP + NIR therapies have been probably the most potent, considerably reducing lung fluorescence intensities to six.55 × 105 p/s and seven.24 × 105 p/s, respectively. Furthermore, H&E staining confirmed that CZP + NIR remedy resulted within the fewest lung metastatic nodules amongst all teams (Fig. S25), signifying a potent suppression of lung metastasis.
CZP mixed with αPD-L1 synergistically enhanced antitumor efficacy
Having confirmed that CZP + NIR remedy robustly stimulates antitumor immunity, we evaluated the antineoplastic results of CZP + NIR together with αPD-L1 in vivo (Fig. 8a). Our preliminary findings have established that CZP NPs can considerably upregulate PD-L1 expression in tumors, pointing to a possible synergistic enhancement when mixed with αPD-L1. As depicted in Fig. 8b, no vital modifications in physique weight have been noticed throughout the remedy. The mice handled with CZP + NIR + αPD-L1 confirmed probably the most pronounced tumor development inhibition, with a median tumor quantity of 75.2 mm3 on day 12 (Fig. 8c and Fig. S26). In distinction, the Management, αPD-L1, and CZP + NIR teams recorded common volumes of 630.5 mm3, 490.0 mm3, and 220.9 mm3, respectively. Moreover, the CZP + NIR + αPD-L1 remedy resulted in a markedly lowered common tumor weight of 0.11 g, which was considerably decrease in comparison with the Management (0.80 g), αPD-L1 (0.71 g), and CZP + NIR (0.29 g) teams (Fig. 8d). These outcomes counsel that our combinatorial CZP + NIR + αPD-L1 technique is simpler at inhibiting tumor development than monotherapy.
For additional evaluation, TDLNs and tumor tissues from the mice throughout all remedy teams have been harvested for a complete evaluation of the TME. Particularly, within the CZP + NIR + αPD-L1 group, the proportion of mature DCs in TDLNs considerably rose to twenty.7% (Fig. 8e and f), 1.95 occasions increased than the Management group (10.6%). Per this, an identical enhance in mature DCs was additionally noticed inside the tumor tissues (Fig. 8g and h). Furthermore, The CZP + NIR + αPD-L1 remedy resulted in a major enhance within the tumoral infiltration of CD3+ T cells, CD3+CD4+ T cells, and CD3+ CD8+ T cells, with respective percentages elevated to 17.4%, 19.7%, and 33.6%, all notably increased than these noticed in different teams (Fig. 8i-m). Concurrently, this mixed remedy additionally elevated the proportion of pro-inflammatory M1-like TAMs (CD11b+F4/80+CD86+) whereas lowering the proportion of anti-inflammatory M2-like TAMs (CD11b+F4/80+CD206+) (Fig. 8n, o and Fig. S27), which resulted in a dramatic enhance within the M1/M2 ratio, rising sharply from 33.9% within the Management group to 162.7% (Fig. 8p). In conclusion, the mixed CZP + NIR + αPD-L1 remedy successfully remodels the immunosuppressive TME, triggering a potent antitumor immune response.
Immune activation and antitumor impact of CZP NPs mixed with αPD-L1 in vivo. (a) Schematic illustration of the experimental schedule for 4T1 tumor-bearing mice. (b) Physique weights, (c) Tumor development curves, and (d) tumor weights of 4T1 tumor-bearing mice after numerous remedy (n = 5). Consultant circulate cytometry plots and corresponding quantifications of (e, f) mature DCs in TDLNs (n = 4), (g, h) mature DCs in tumors, (i, j) CD3+ T cells, (k-m) CD3+CD4+, CD3+CD8+ T cells and (n, o) M2 phenotype tumor-associated macrophages in tumors from mice following numerous therapies (n = 5). (p) Evaluation of the M1/M2 ratio variations