Introducing KitikiPlot, a Python library designed for visualizing sequential and time-series categorical “Sliding Window” patterns. This revolutionary device is designed to empower information practitioners throughout numerous fields, together with genomics, air high quality monitoring, and climate forecasting to uncover insights with enhanced readability and precision. Designed with simplicity and flexibility, it integrates seamlessly with Python’s information ecosystem whereas providing visually interesting outputs for sample recognition. Let’s discover its potential, and rework the best way of analyzing categorical sequences.
Studying Aims
- Perceive the KitikiPlot sliding window visualization method for sequential and time-series categorical information.
- Discover its parameters to tailor visualizations for particular datasets and functions.
- Apply KitikiPlot throughout numerous domains, together with genomics, climate evaluation, and air high quality monitoring.
- Develop proficiency in visualizing advanced information patterns utilizing Python and Matplotlib.
- Acknowledge the importance of visible readability in categorical information evaluation to boost decision-making processes.
This text was printed as part of the Knowledge Science Blogathon.
KitikiPlot: Simplify Complicated Knowledge Visualization
KitikiPlot is a robust visualization device designed to simplify advanced information evaluation, particularly for functions like sliding window graphs and dynamic information illustration. It gives flexibility, vibrant visualizations, and seamless integration with Python, making it splendid for domains equivalent to genomics, air high quality monitoring, and climate forecasting. With its customizable options, KitikiPlot transforms uncooked information into impactful visuals effortlessly.
- KitikiPlot is a Python library for visualizing sequential and time-series categorical “Sliding Window” information.
- The time period ‘kitiki‘(కిటికీ) means ‘window‘ in Telugu.
Key Options
- Sliding Window: The visible illustration consists of a number of rectangular bars, every similar to information from a selected sliding window.
- Body: Every bar is split into a number of rectangular cells referred to as “Frames.” These frames are organized side-by-side, every representing a price from the sequential categorical information.
- Customization Choices: Customers can customise home windows extensively, together with choices for colour maps, hatching patterns, and alignments.
- Versatile Labeling: The library permits customers to regulate labels, titles, ticks, and legends in accordance with their preferences.
Getting Began: Your First Steps with KitikiPlot
Dive into the world of KitikiPlot with this quick-start information. From set up to your first visualization, we’ll stroll you thru each step to make your information shine.
Set up KitikiPlot utilizing pip
pip set up kitikiplotImport “kitikiplot”
import pandas as pd
from kitikiplot import KitikiPlotLoad the dataframe
Thought-about the information body ‘weatherHistory.csv’ from https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/muthuj7/weather-dataset.
df= pd.read_csv( PATH_TO_CSV_FILE )
print("Form: ", df.form)
df= df.iloc[45:65, :]
print("Form: ", df.form)
df.head(3)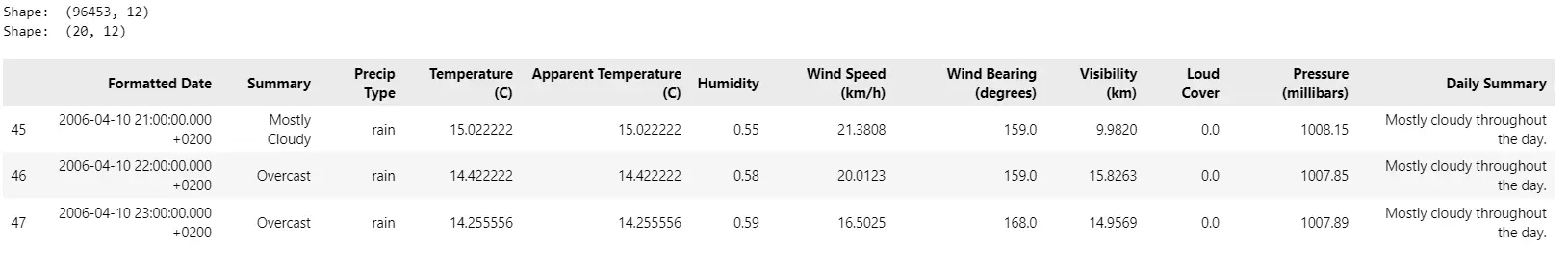
ktk= KitikiPlot( information= df["Summary"].values.tolist() )
ktk.plot( ) 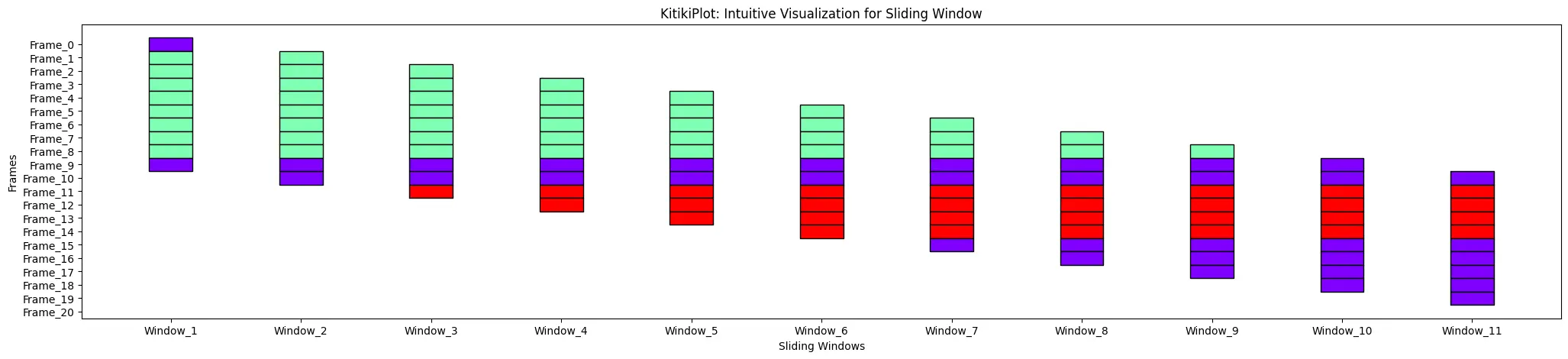
Understanding KitikiPlot Parameters
To completely leverage the facility of KitikiPlot, it’s important to know the varied parameters that management how your information is visualized. These parameters mean you can customise elements equivalent to window measurement, step intervals, and different settings, guaranteeing your visualizations are tailor-made to your particular wants. On this part, we’ll break down key parameters like stride and window_length that can assist you fine-tune your plots for optimum outcomes.
stride : int (elective)
- The variety of components to maneuver the window after every iteration when changing an inventory to a DataFrame.
- Default is 1.
index= 0
ktk= KitikiPlot( information= df["Summary"].values.tolist(), stride= 2 )
ktk.plot( cell_width= 2, transpose= True )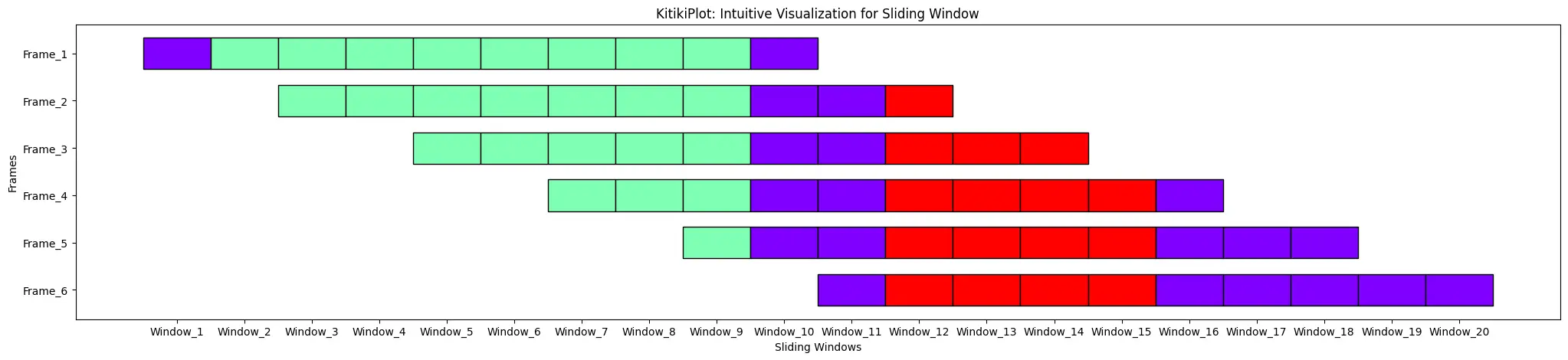
window_length : int (elective)
- The size of every window when changing an inventory to a DataFrame.
- Default is 10.
index= 0
ktk= KitikiPlot( information= df["Summary"].values.tolist(), window_length= 5 )
ktk.plot( transpose= True,
xtick_prefix= "Body",
ytick_prefix= "Window",
cell_width= 2 ) 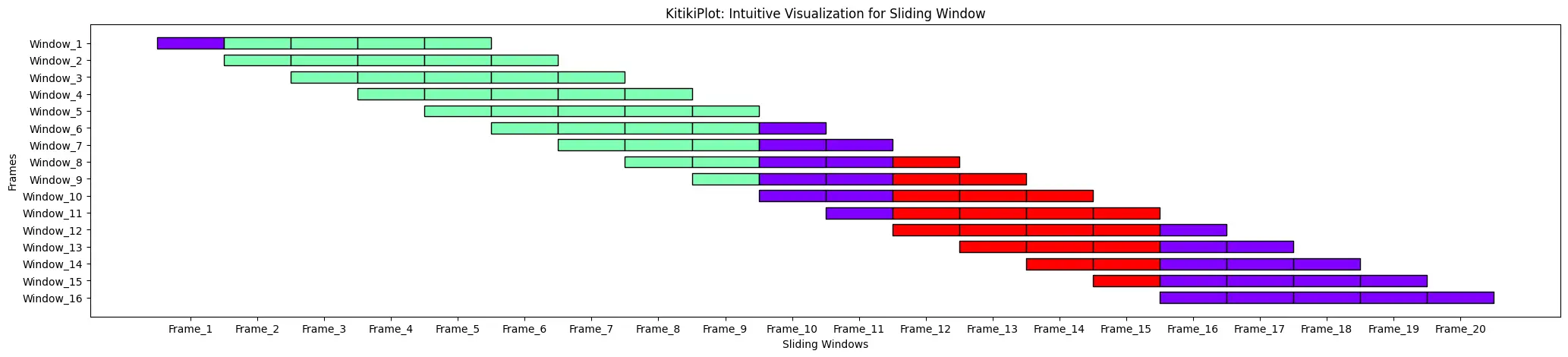
figsize : tuple (elective)
- The scale of the determine (width, top).
- Default is (25, 5).
ktk= KitikiPlot( information= df["Summary"].values.tolist() )
ktk.plot( figsize= (20, 8) )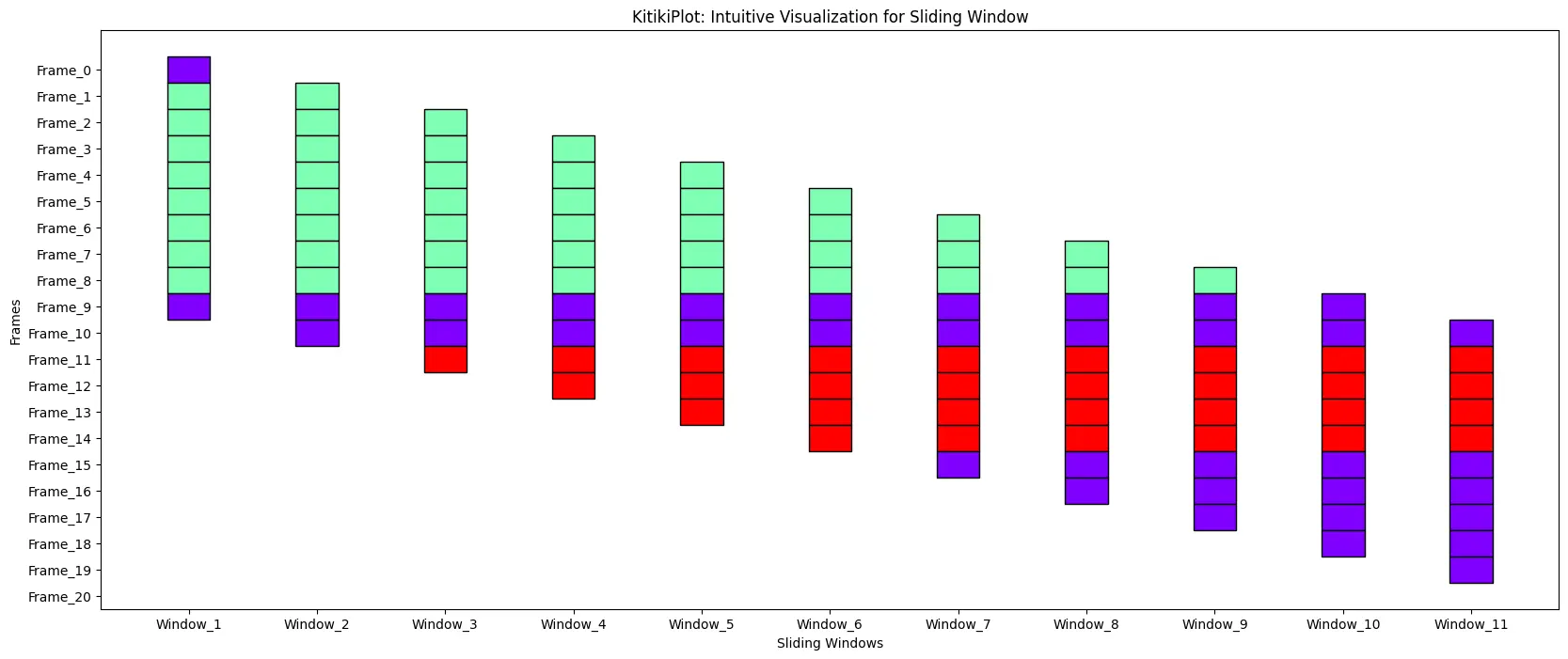
cell_width : float
- The width of every cell within the grid.
- Default is 0.5.
ktk= KitikiPlot( information= df["Summary"].values.tolist() )
ktk.plot( cell_width= 2 )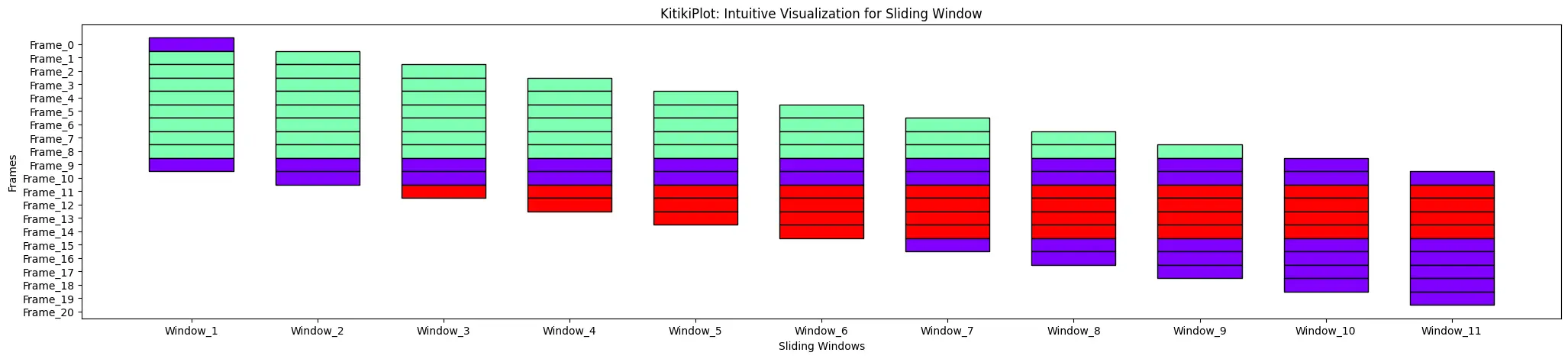
cell_height : float
- The peak of every cell within the grid.
- Default is 2.0.
ktk= KitikiPlot( information= df["Summary"].values.tolist() )
ktk.plot( cell_height= 3 )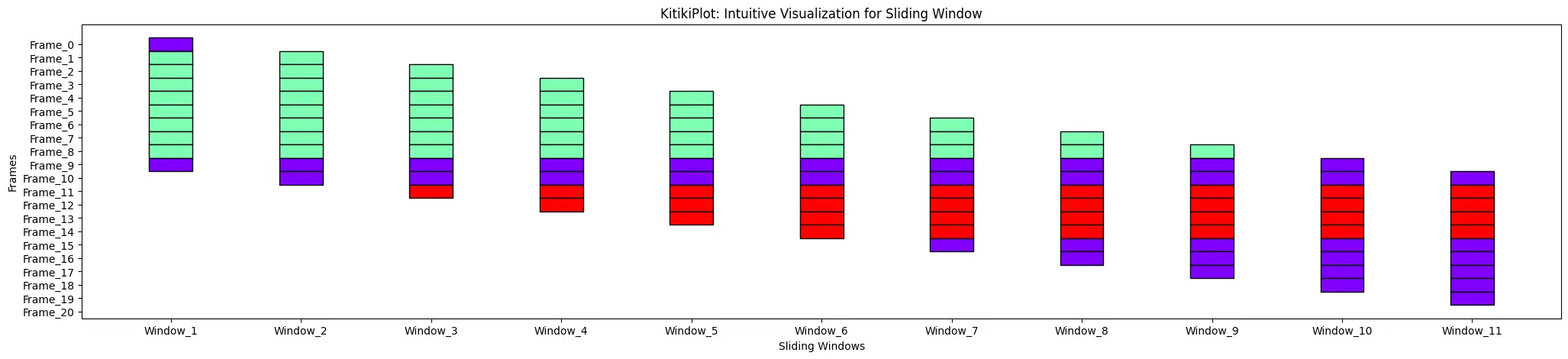
transpose : bool (elective)
- A flag indicating whether or not to transpose the KitikiPlot.
- Default is False.
ktk= KitikiPlot( information= df["Summary"].values.tolist() )
ktk.plot( transpose= False )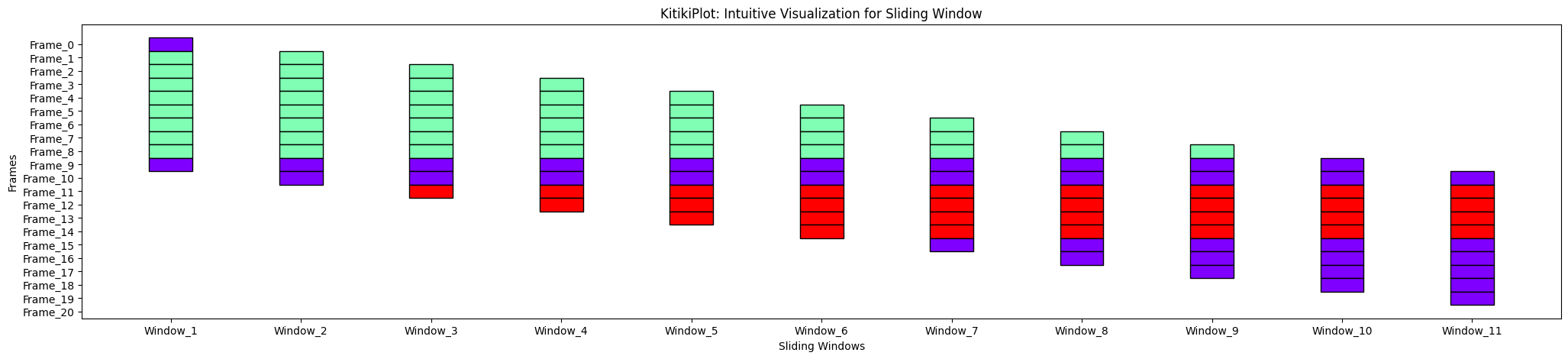
ktk= KitikiPlot( information= df["Summary"].values.tolist() )
ktk.plot(
cell_width= 2,
transpose= True,
xtick_prefix= "Body",
ytick_prefix= "Window",
xlabel= "Frames",
ylabel= "Sliding_Windows" )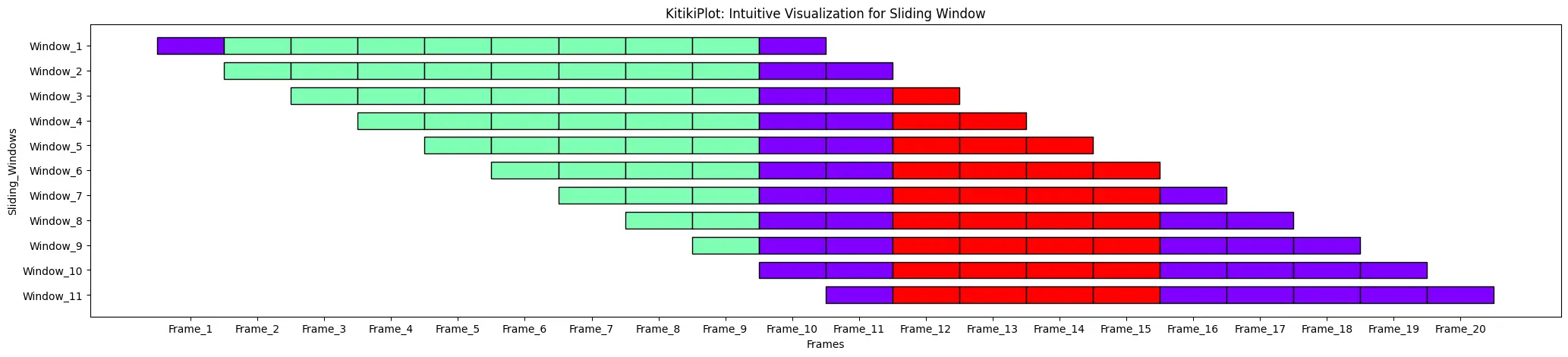
window_gap : float
- The hole between cells within the grid.
- Default is 1.0.
ktk= KitikiPlot( information= df["Summary"].values.tolist() )
ktk.plot( window_gap= 3 )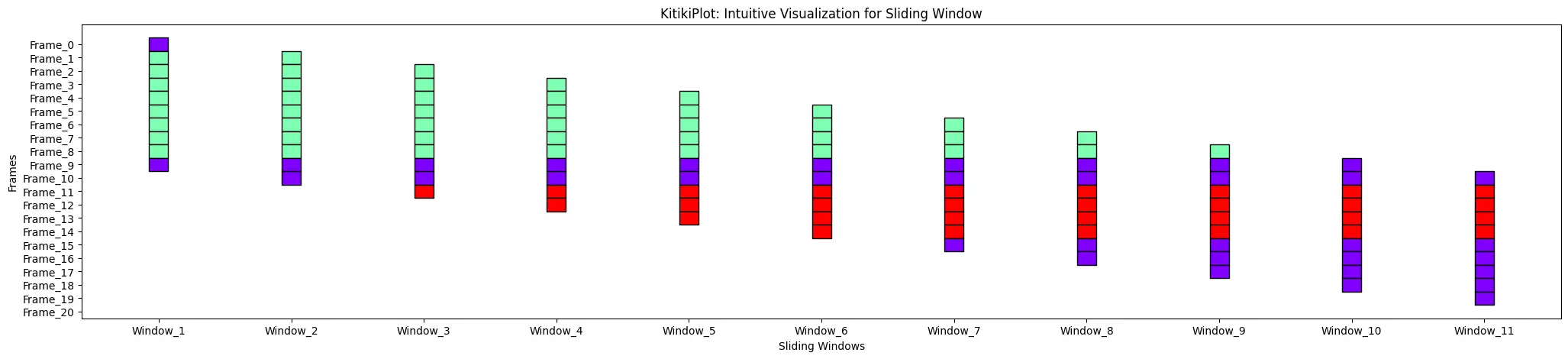
window_range : str or tuple (elective)
- The vary of home windows to show.
- Use “all” to point out all home windows or specify a tuple (start_index, end_index).
- Default is “all”.
ktk= KitikiPlot( information= df["Summary"].values.tolist() )
ktk.plot( window_range= "all" )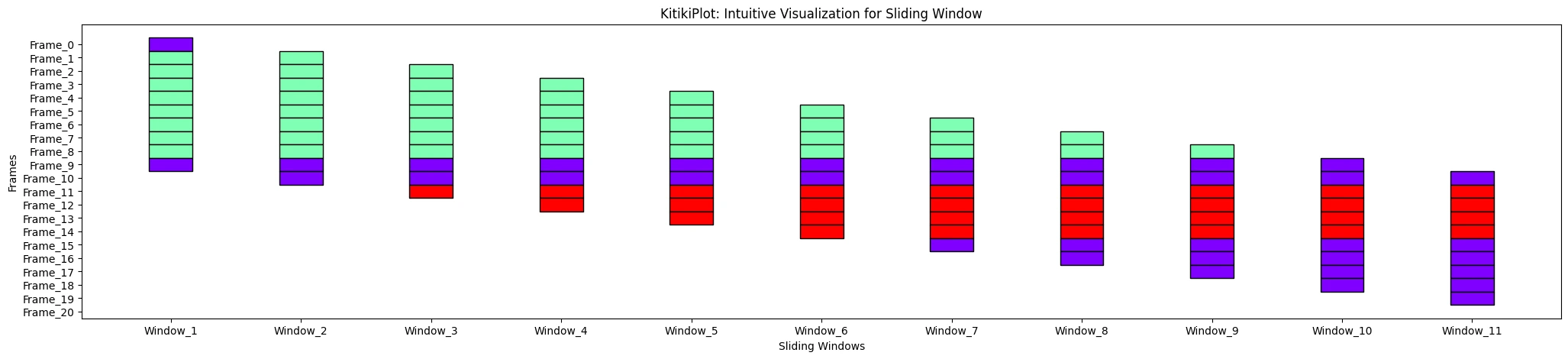
ktk= KitikiPlot( information= df["Summary"].values.tolist() )
ktk.plot( window_range= (3,8) )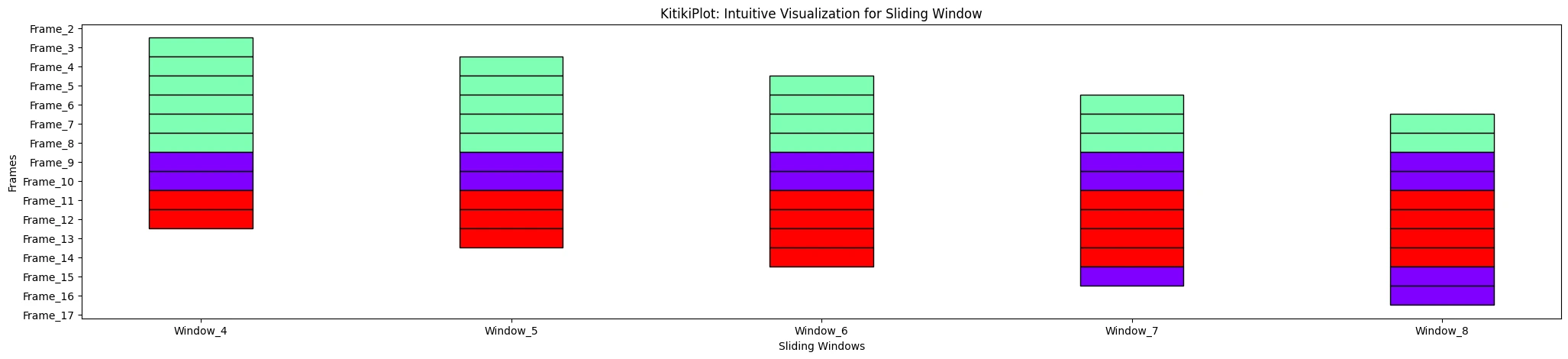
align : bool
- A flag indicating whether or not to shift consecutive bars vertically (if transpose= False), andhorizontally(if transpose= True) by stride worth.
- Default is True.
ktk= KitikiPlot( information= df["Summary"].values.tolist() )
ktk.plot( align= True )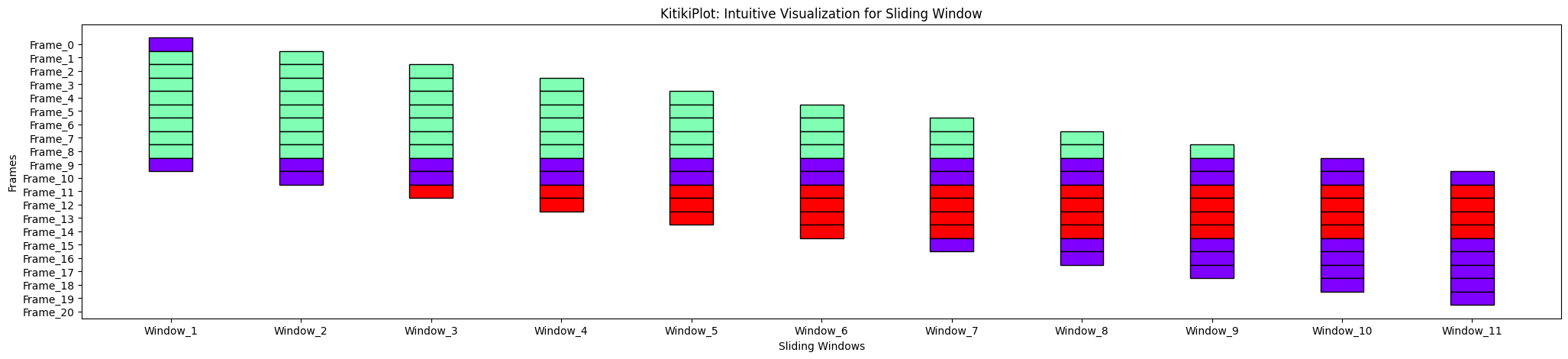
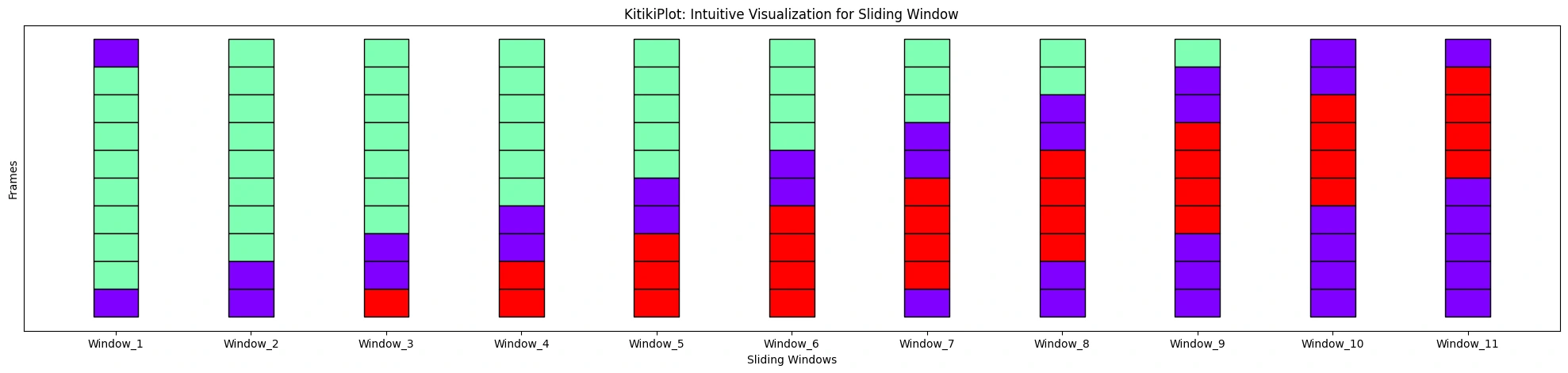
ktk.plot(
align= False,
display_yticks= False # Show no yticks
)
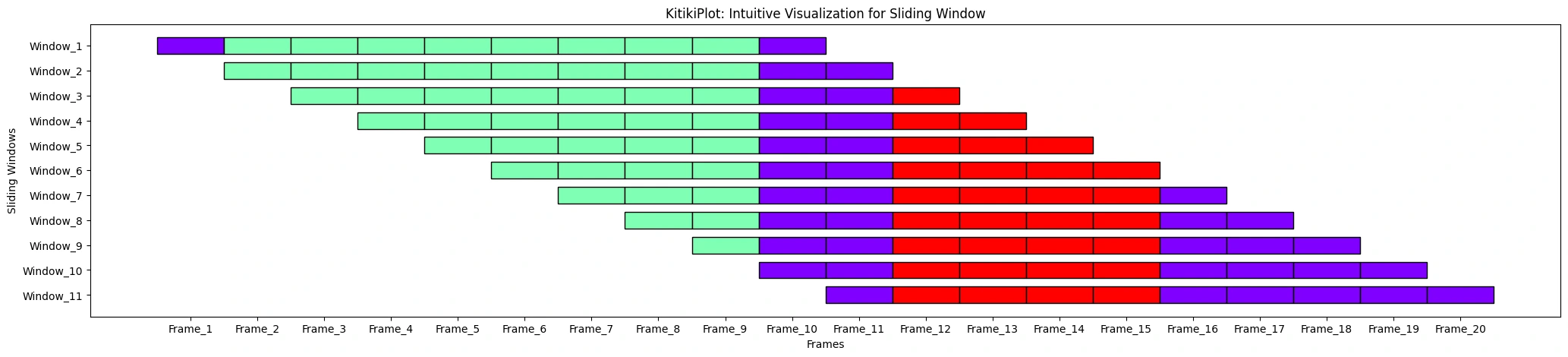
ktk.plot(
cell_width= 2,
align= True,
transpose= True,
xlabel= "Frames",
ylabel= "Sliding Home windows",
xtick_prefix= "Body",
ytick_prefix= "Window"
)
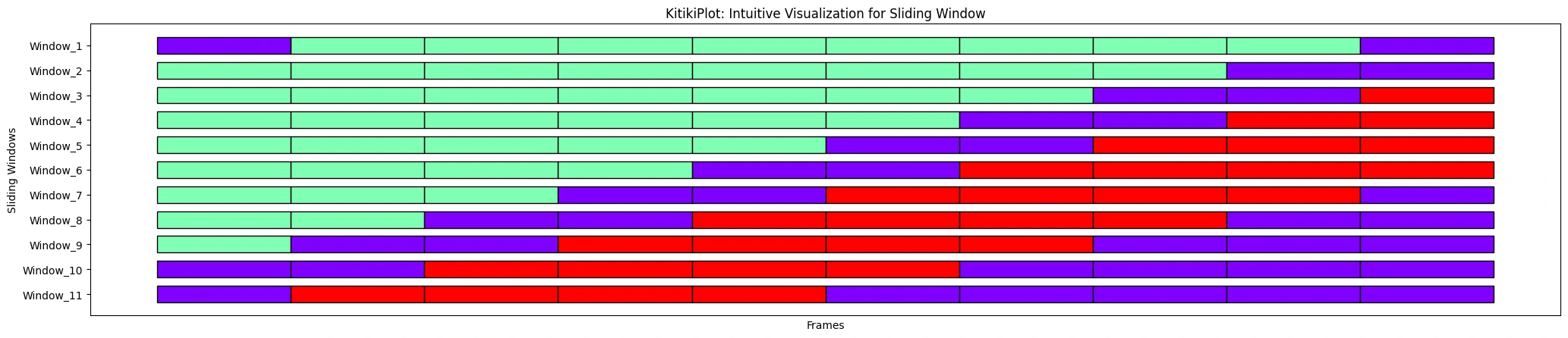
ktk.plot(
cell_width= 2,
align= False,
transpose= True,
xlabel= "Frames",
ylabel= "Sliding Home windows",
ytick_prefix= "Window",
display_xticks= False
)
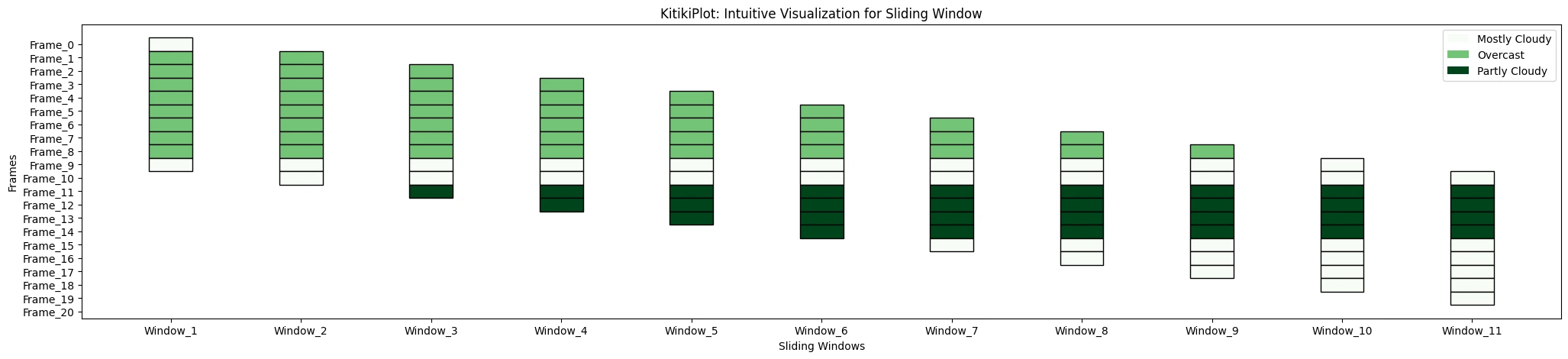
cmap : str or dict
- If a string, it must be a colormap identify to generate colours.
- If a dictionary, it ought to map distinctive values to particular colours.
- Default is ‘rainbow’.
ktk= KitikiPlot( information= df["Summary"].values.tolist() )
ktk.plot(
cmap= "Greens",
display_legend= True
)
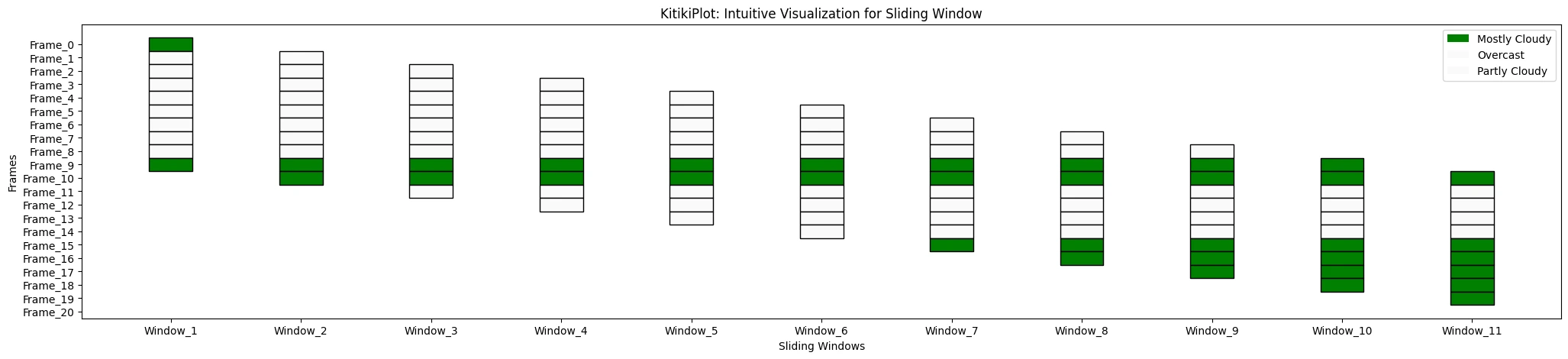
ktk.plot(
cmap= {"Largely Cloudy": "Inexperienced"},
display_legend= True
)
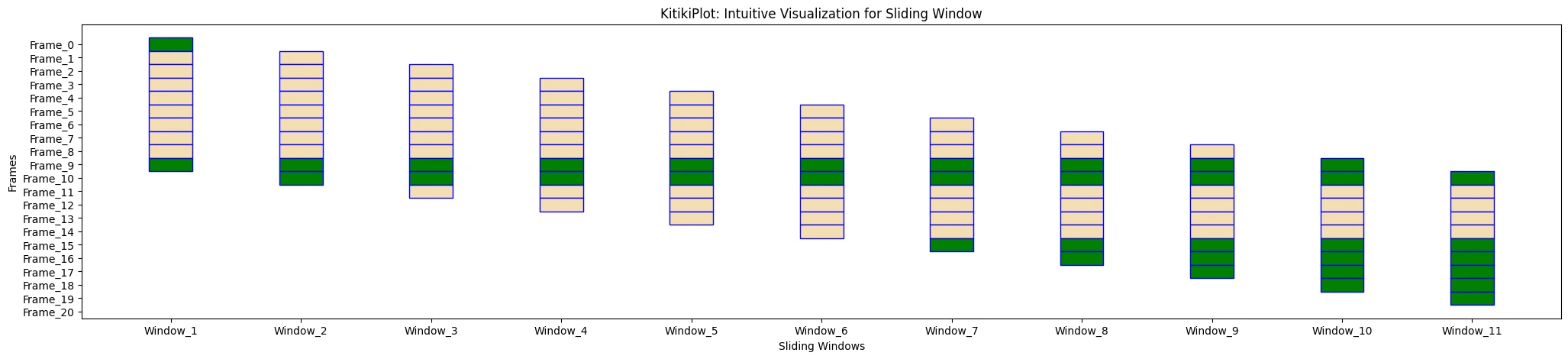
edge_color : str
- The colour to make use of for the sides of the rectangle.
- Default is ‘#000000’.
ktk.plot(
cmap= {"Largely Cloudy": "Inexperienced"},
fallback_color= "wheat",
edge_color= "blue",
)
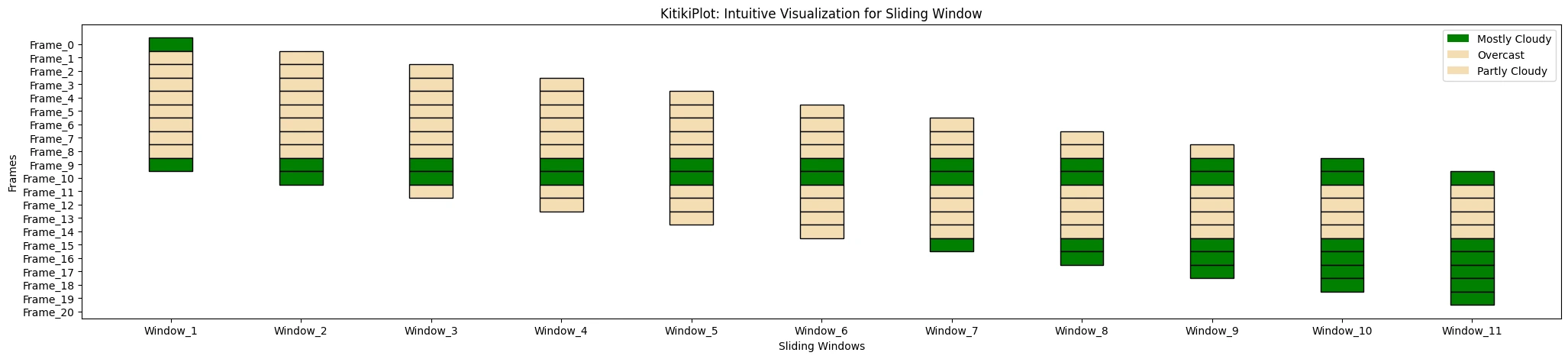
fallback_color : str
- The colour to make use of as fallback if no particular colour is assigned.
- Default is ‘#FAFAFA’.
ktk.plot(
cmap= {"Largely Cloudy": "Inexperienced"},
fallback_color= "wheat",
display_legend= True
)
hmap : dict
- A dictionary mapping distinctive values to their corresponding hatch patterns.
- Default is ‘{}’.
ktk= KitikiPlot( information= df["Summary"].values.tolist() )
ktk.plot(
cmap= {"Largely Cloudy": "gray"},
fallback_color= "white",
hmap= *,
display_hatch= True
)
fallback_hatch : str
- The hatch sample to make use of as fallback if no particular hatch is assigned.
- Default is ‘” “‘ (string with single house).
ktk= KitikiPlot( information= df["Summary"].values.tolist() )
ktk.plot(
cmap= {"Largely Cloudy": "gray"},
fallback_color= "white",
hmap= *,
fallback_hatch= "",
display_hatch= True
)
display_hatch : bool
- A flag indicating whether or not to show hatch patterns on cells.
- Default is False.
ktk= KitikiPlot( information= df["Summary"].values.tolist() )
ktk.plot(
cmap= {"Largely Cloudy": "#ffffff"},
fallback_color= "white",
display_hatch= True
)
xlabel : str (elective)
- Label for the x-axis.
- Default is “Sliding Home windows”.
ktk= KitikiPlot( information= df["Summary"].values.tolist() )
ktk.plot( xlabel= "Statement Window" )
ylabel : str (elective)
- Label for the y-axis.
- Default is “Frames”.
ktk= KitikiPlot( information= df["Summary"].values.tolist() )
ktk.plot( ylabel= "Body ID" )
display_xticks : bool (elective)
- A flag indicating whether or not to show xticks.
- Default is True.
ktk= KitikiPlot( information= df["Summary"].values.tolist() )
ktk.plot( display_xticks= False )
display_yticks : bool (elective)
- A flag indicating whether or not to show yticks
- Default is True
ktk= KitikiPlot( information= df["Summary"].values.tolist() )
ktk.plot( display_yticks= False )
xtick_prefix : str (elective)
- Prefix for x-axis tick labels.
- Default is “Window”.
ktk= KitikiPlot( information= df["Summary"].values.tolist() )
ktk.plot( xtick_prefix= "Statement" )
ytick_prefix : str (elective)
- Prefix for y-axis tick labels.
- Default is “Body”.
ktk= KitikiPlot( information= df["Summary"].values.tolist() )
ktk.plot( ytick_prefix= "Time" )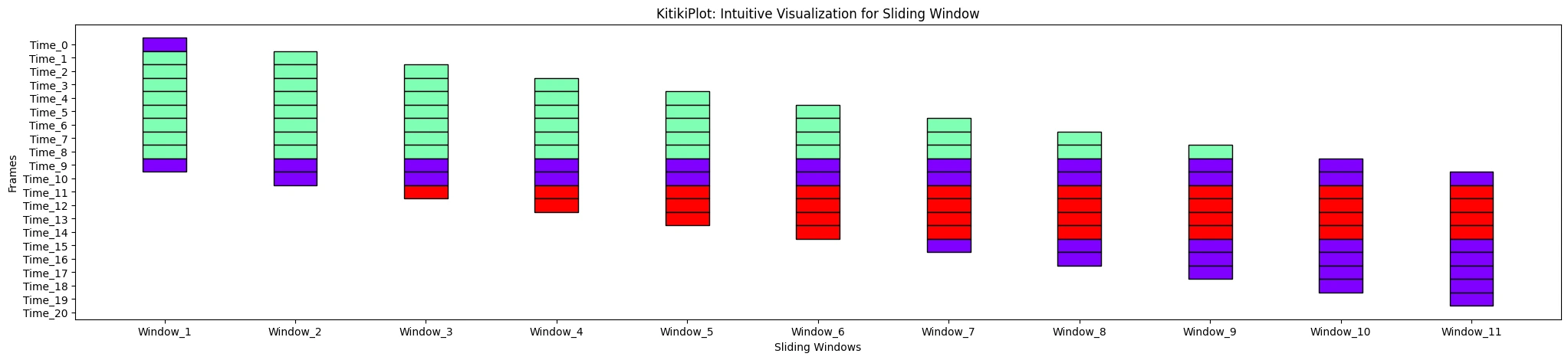
xticks_values : checklist (elective)
- Listing containing the values for xticks
- Default is []
ktk= KitikiPlot( information= df["Summary"].values.tolist() )
xtick_values= ['Start', "T1", "T2", "T3", "T4", "T5", "T6", "T7", "T8", "T9", "End"]
ktk.plot( xticks_values= xtick_values )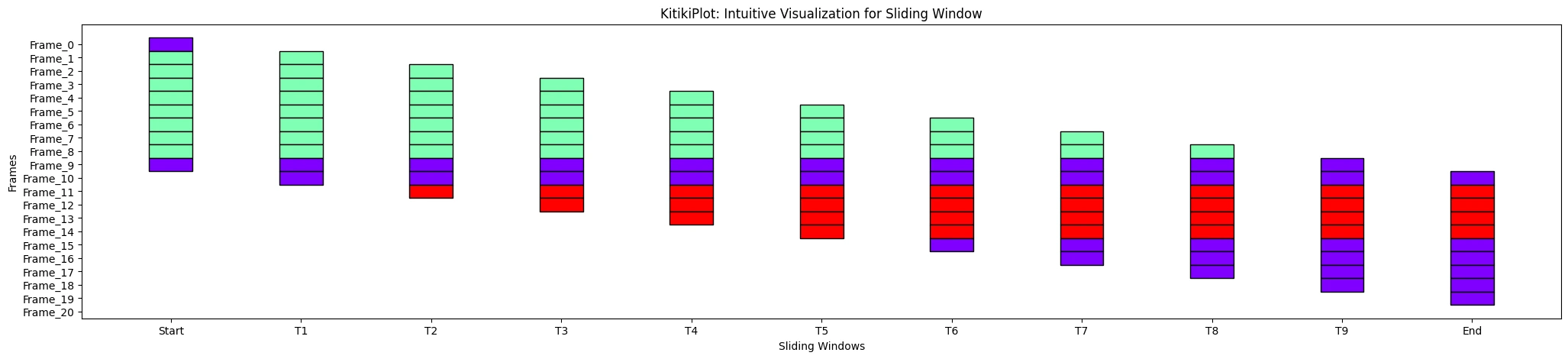
yticks_values : checklist (elective)
- Listing containing the values for yticks
- Default is []
ktk= KitikiPlot( information= df["Summary"].values.tolist() )
yticks_values= [(str(i.hour)+" "+i.strftime("%p").lower()) for i in pd.to_datetime(df["Formatted Date"])]
ktk.plot( yticks_values= yticks_values )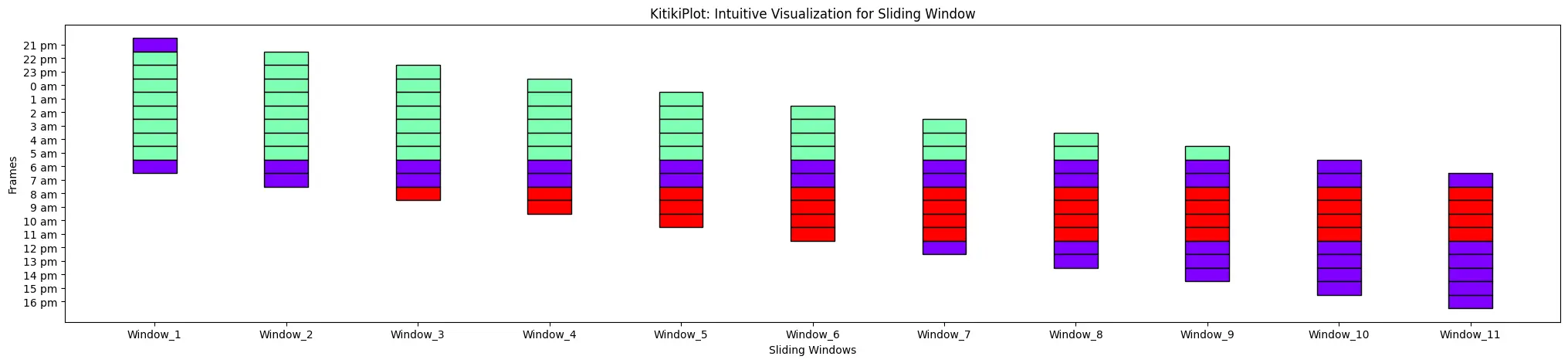
xticks_rotation : int (elective)
- Rotation angle for x-axis tick labels.
- Default is 0.
ktk= KitikiPlot( information= df["Summary"].values.tolist() )
ktk.plot( xticks_rotation= 45 )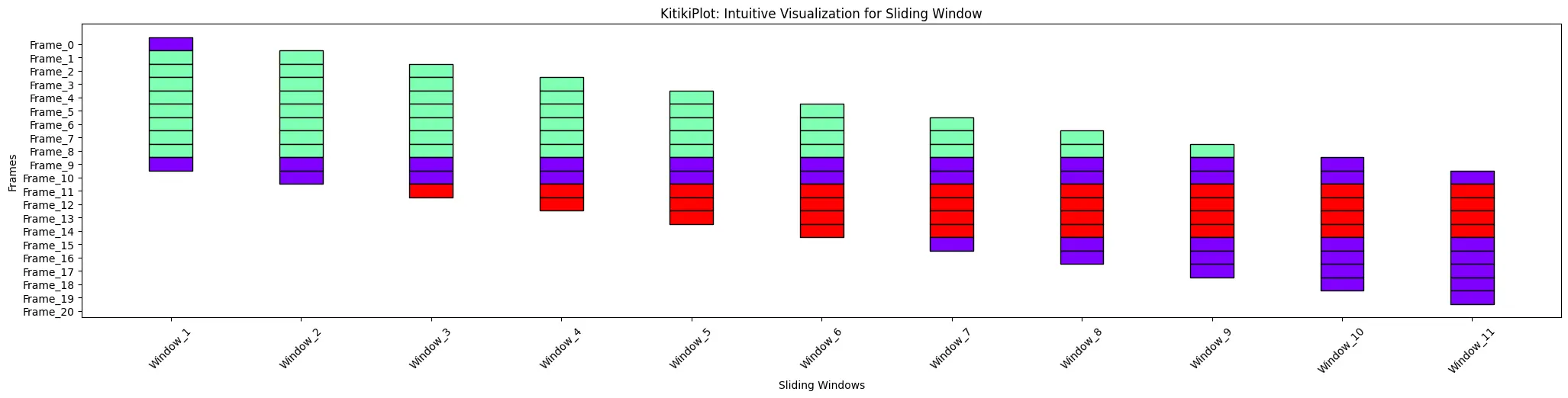
yticks_rotation : int (elective)
- Rotation angle for y-axis tick labels.
- Default is 0.
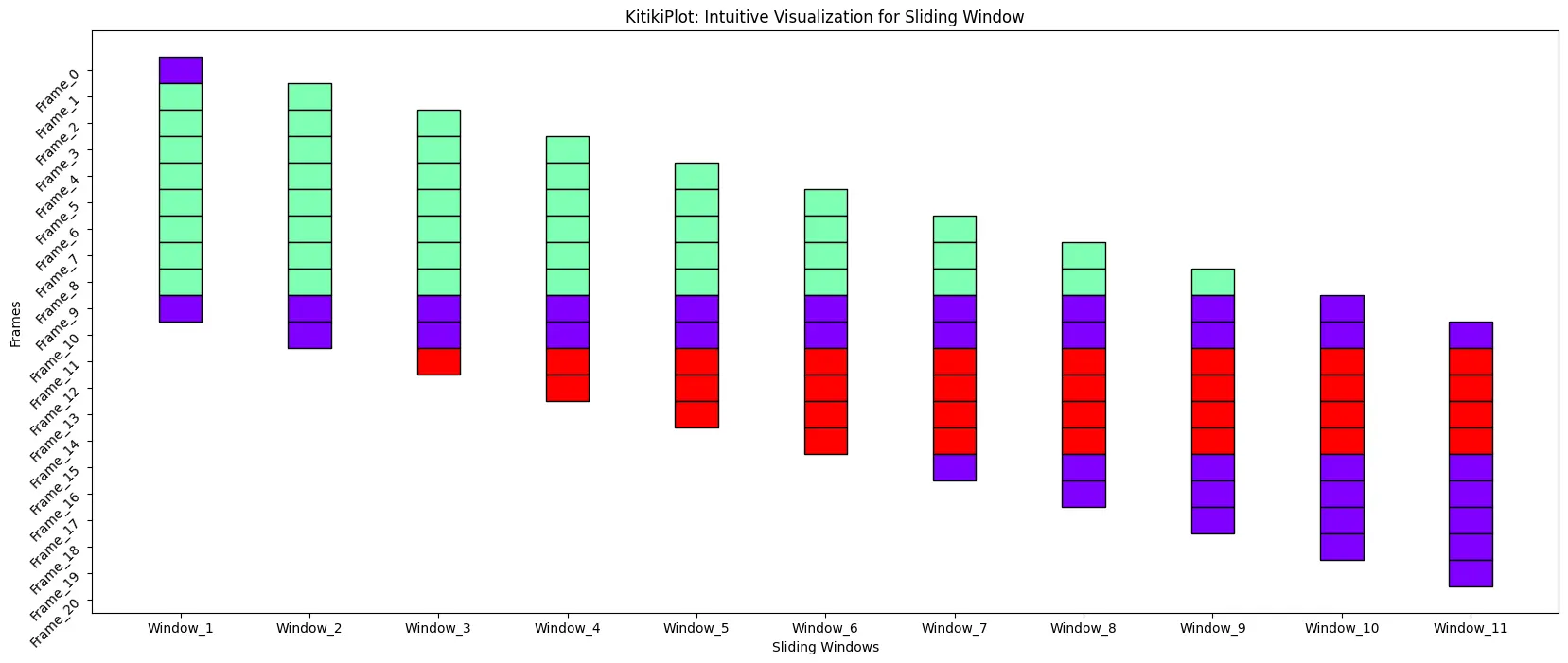
ktk= KitikiPlot( information= df["Summary"].values.tolist() )
ktk.plot( figsize= (20, 8), # Enhance top of the plot for good visualization (right here)
yticks_rotation= 45
)
title : str (elective)
- The title of the plot.
- Default is “KitikiPlot: Intuitive Visualization for Sliding Window”.
ktk= KitikiPlot( information= df["Summary"].values.tolist() )
ktk.plot( title= "KitikiPlot for Climate Dataset")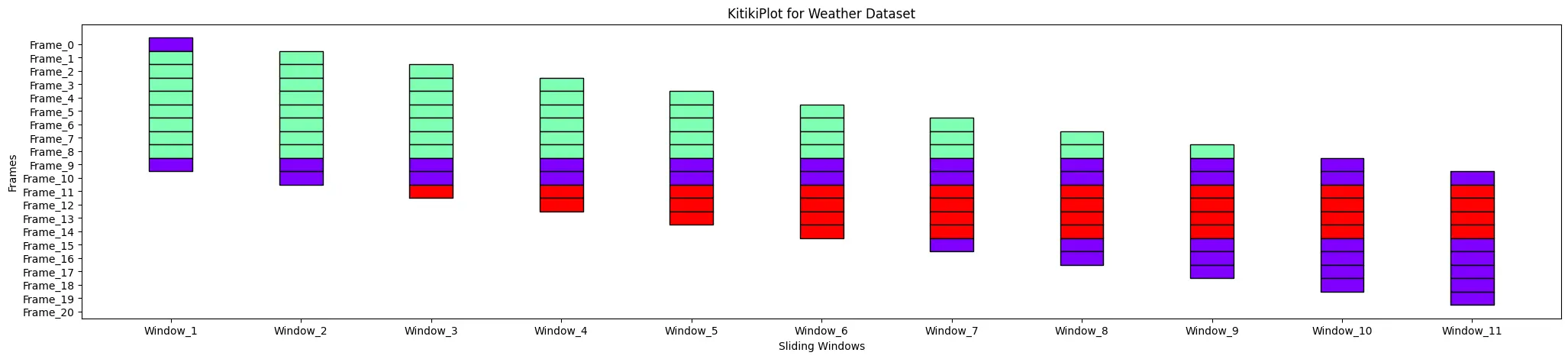
display_grid : bool (elective)
- A flag indicating whether or not to show grid on the plot.
- Default is False.
ktk= KitikiPlot( information= df["Summary"].values.tolist()[:15] )
ktk.plot( display_grid= True )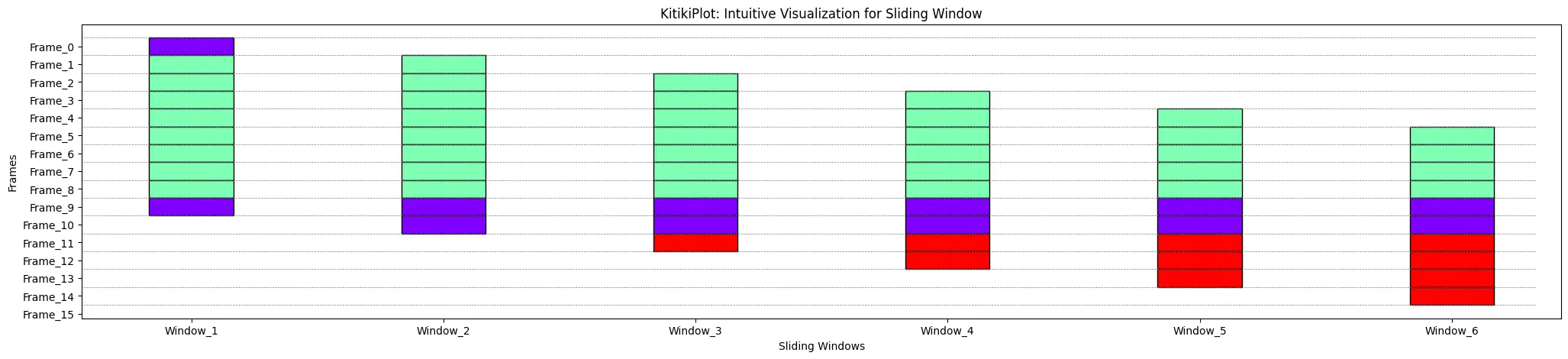
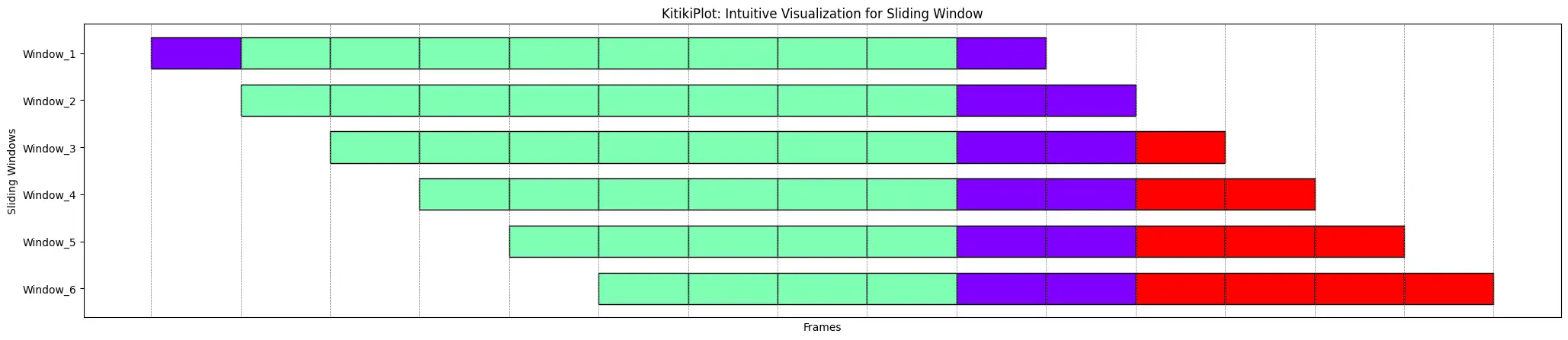
ktk= KitikiPlot( information= df["Summary"].values.tolist()[:15] )
ktk.plot(
cell_width= 2,
transpose= True,
xlabel= "Frames",
ylabel= "Sliding Home windows",
ytick_prefix= "Window",
display_xticks= False,
display_grid= True
)
display_legend : bool (elective)
- A flag indicating whether or not to show a legend on the plot.
- Default is False.
ktk= KitikiPlot( information= df["Summary"].values.tolist() )
ktk.plot( display_legend= True )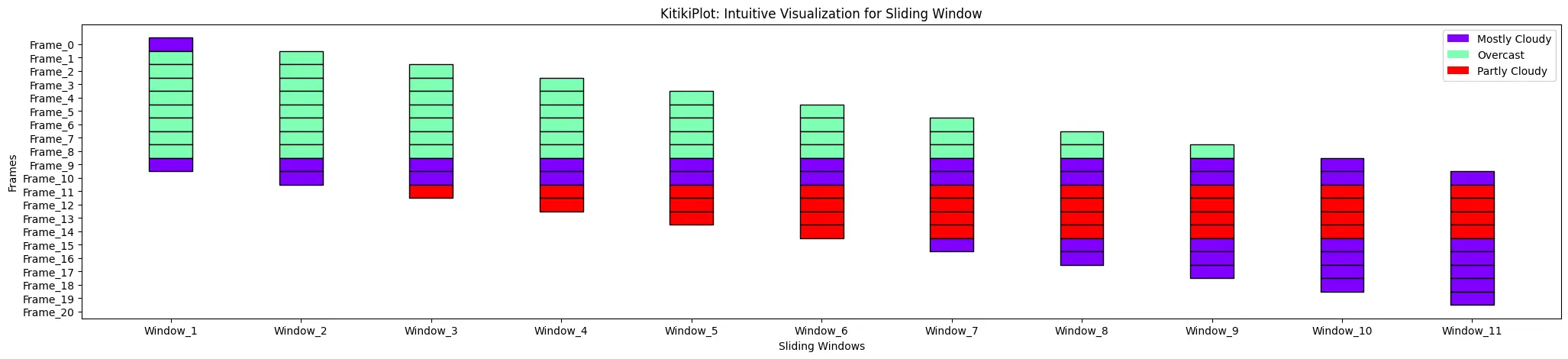
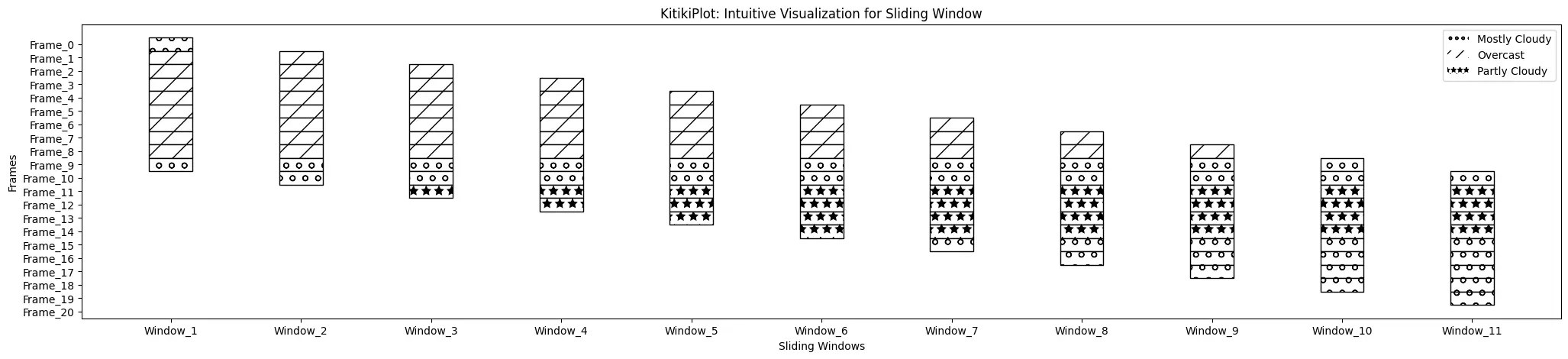
legend_hatch : bool (elective)
- A flag indicating whether or not to incorporate hatch patterns within the legend.
- Default is False.
ktk= KitikiPlot( information= df["Summary"].values.tolist() )
ktk.plot(
cmap= {"Largely Cloudy": "#ffffff"},
fallback_color= "white",
display_hatch= True,
display_legend= True,
legend_hatch= True
)
legend_kwargs : dict (elective)
- Extra key phrase arguments handed to customise the legend.
- Default is {}.
Place legend exterior of the Plot
ktk= KitikiPlot( information= df["Summary"].values.tolist()[:15] )
ktk.plot(
figsize= (15, 5),
display_legend= True,
legend_kwargs= {"bbox_to_anchor": (1, 1.0), "loc":"higher left"} )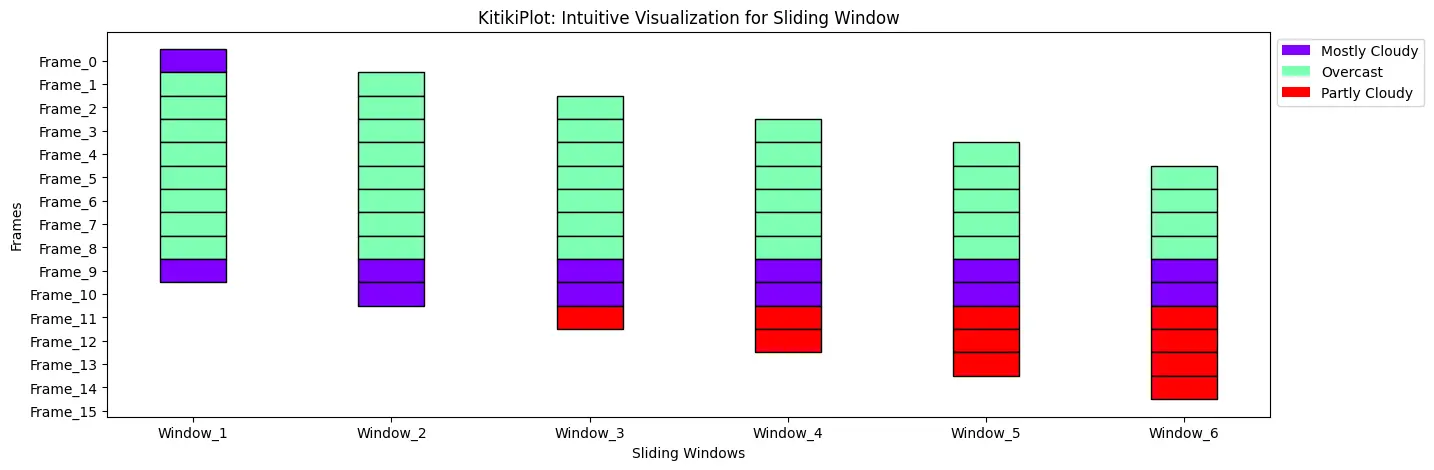
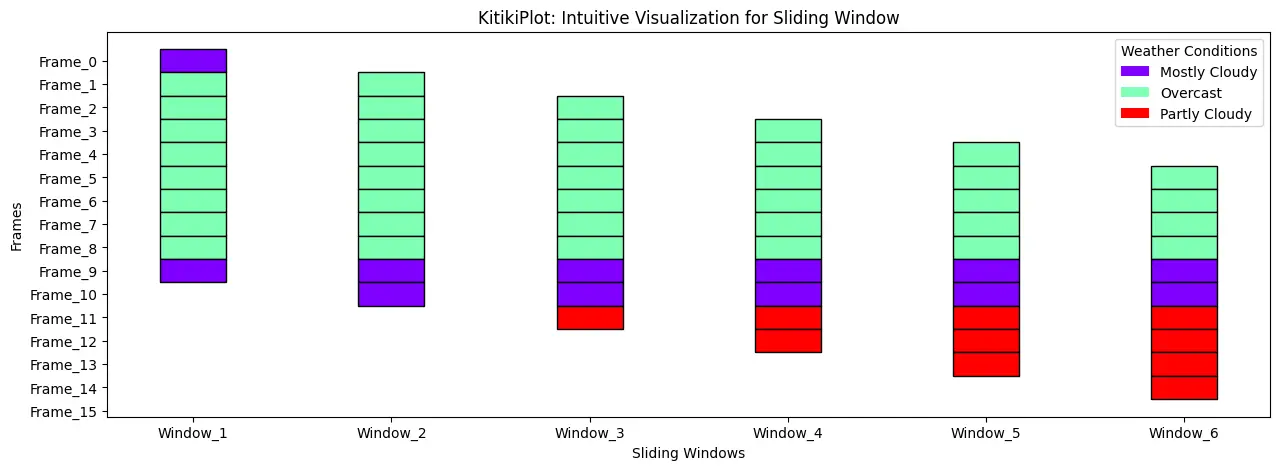
Set title for the legend————————————
ktk= KitikiPlot( information= df["Summary"].values.tolist()[:15] )
ktk.plot(
figsize= (15, 5),
display_legend= True,
legend_kwargs= {"title": "Climate Situations"}
)
Change edgecolor of the legend
ktk= KitikiPlot( information= df["Summary"].values.tolist()[:15] )
ktk.plot(
figsize= (15, 5),
display_legend= True,
legend_kwargs= {"edgecolor": "lime"}
)
kitiki_cell_kwargs : dict (elective)
- Extra key phrase arguments handed to customise particular person cells.
- Default is {}.
Set the road fashion
ktk= KitikiPlot( information= df["Summary"].values.tolist()[:15] )
ktk.plot(
figsize= (15, 5),
kitiki_cell_kwargs= {"linestyle": "--"} )
Alter the road width
ktk= KitikiPlot( information= df["Summary"].values.tolist()[:15] )
ktk.plot(
figsize= (15, 5),
kitiki_cell_kwargs= {"linewidth": 3} )
Alter the alpha
ktk= KitikiPlot( information= df["Summary"].values.tolist()[:15] )
ktk.plot(
figsize= (15, 5),
kitiki_cell_kwargs= {"alpha": 0.4} )
Actual-World Functions of KitikiPlot
KitikiPlot excels in various fields the place information visualization is essential to understanding advanced patterns and tendencies. From genomics and environmental monitoring to finance and predictive modeling, KitikiPlot empowers customers to rework uncooked information into clear, actionable insights. Whether or not you’re analyzing giant datasets, monitoring air high quality over time, or visualizing tendencies in inventory costs, KitikiPlot gives the flexibleness and customization wanted to satisfy the distinctive calls for of assorted industries.
Genomics
- KitikiPlot permits clear visualization of gene sequences, serving to researchers determine patterns and motifs.
- It facilitates the evaluation of structural variations in genomes, important for understanding genetic problems.
- By offering visible representations, it aids in deciphering advanced genomic information, supporting developments in customized drugs.
Dataset URL: https://archive.ics.uci.edu/dataset/69/molecular+biology+splice+junction+gene+sequences
# Import obligatory libraries
from kitikiplot import KitikiPlot
import pandas as pd
# Load the dataset
df= pd.read_csv( "datasets/molecular+biology+splice+junction+gene+sequences/splice.information", header= None )
# Rename the columns
df.columns= ["Label", "Instance_Name", "Nucleotide_Sequence"]
# Choose 3 gene sequences randomly
df= df.pattern(3, random_state= 1)
# Take away the white areas from the "Nucleotide_Sequence"
df["Nucleotide_Sequence"]= df["Nucleotide_Sequence"].str.strip()
df
index= 0
ktk= KitikiPlot( information= [i for i in df.iloc[index, 2]], stride= 1, window_length= len(df.iloc[index, 2]) )
ktk.plot(
figsize= (20, 0.5),
cell_width= 2,
cmap= {'A': '#007FFF', 'T': "#fffc00", "G": "#00ff00", "C": "#960018"},
transpose= True,
xlabel= "Nucleotides",
ylabel= "Sequence",
display_yticks= False,
xtick_prefix= "Nucleotide",
xticks_rotation= 90,
title= "Genome Visualization: "+df.iloc[index, 1].strip()+", Label : "+df.iloc[index,0].strip(),
display_legend= True,
legend_kwargs= {"bbox_to_anchor": (1.01, 1), "loc":'higher left', "borderaxespad": 0.})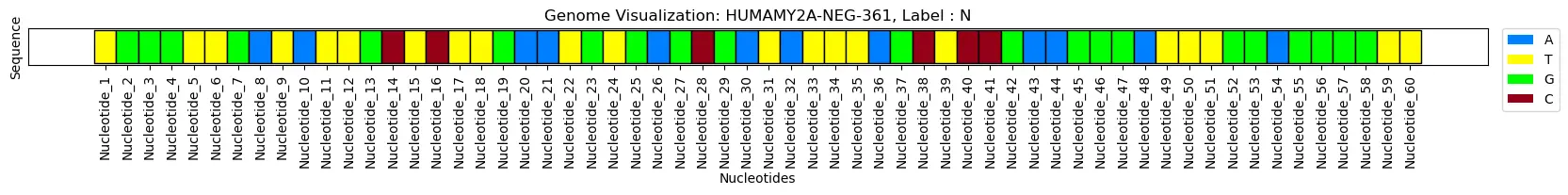
Climate Forecasting
- The library can successfully signify temporal climate information, equivalent to temperature and humidity, over sequential time home windows to determine tendencies.
- This visualization aids in detecting patterns and fluctuations in climate situations, enhancing the accuracy of forecasts.
- Moreover, it helps the evaluation of historic information, permitting for higher predictions and knowledgeable decision-making concerning weather-related actions.
Dataset URL: https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/muthuj7/weather-dataset
# Import obligatory libraries
from kitikiplot import KitikiPlot
import pandas as pd
# Learn csv
df= pd.read_csv( "datasets/weatherHistory/weatherHistory.csv")
print("Form: ", df.form)
# Choose a subset of information for visualization
df= df.iloc[45:65, :]
print("Form: ", df.form)
df.head(3)
index= 0
weather_data= ['Mostly Cloudy', 'Overcast', 'Overcast', 'Overcast', 'Overcast', 'Overcast','Overcast', 'Overcast',
'Overcast', 'Mostly Cloudy', 'Mostly Cloudy', 'Partly Cloudy', 'Partly Cloudy', 'Partly Cloudy',
'Partly Cloudy', 'Mostly Cloudy', 'Mostly Cloudy', 'Mostly Cloudy', 'Mostly Cloudy', 'Mostly Cloudy']
time_period= ['21 pm', '22 pm', '23 pm', '0 am', '1 am', '2 am', '3 am', '4 am', '5 am', '6 am', '7 am', '8 am',
'9 am', '10 am', '11 am', '12 pm', '13 pm', '14 pm', '15 pm', '16 pm']
ktk= KitikiPlot( information= weather_data, stride= 1, window_length= 10 )
ktk.plot(
figsize= (20, 5),
cell_width= 2,
transpose= False,
xlabel= "Window",
ylabel= "Time",
yticks_values= time_period,
xticks_rotation= 90,
cmap= {"Largely Cloudy": "brown", "Partly Cloudy": "#a9cbe0","Overcast": "#fdbf6f"},
legend_kwargs= {"bbox_to_anchor": (1.01, 1), "loc":'higher left', "borderaxespad": 0.},
display_legend= True,
title= "Climate Sample on 10-04-2006")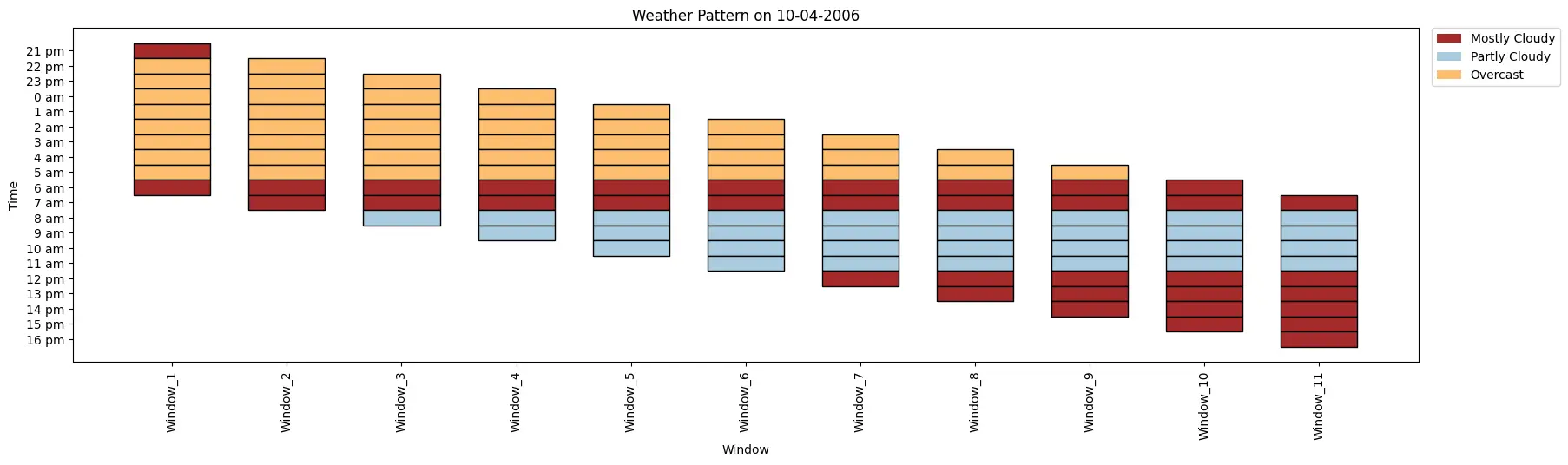
Air High quality Monitoring
- Customers can analyze pollutant ranges over time with KitikiPlot to detect variations and correlations in environmental information.
- This functionality permits for the identification of tendencies in air high quality, facilitating a deeper understanding of how completely different pollution work together and fluctuate on account of numerous components.
- Moreover, it helps the exploration of temporal relationships between air high quality indices and particular pollution, enhancing the effectiveness of air high quality monitoring efforts.
Dataset URL: https://archive.ics.uci.edu/dataset/360/air+high quality
from kitikiplot import KitikiPlot
import pandas as pd
# Learn excel
df= pd.read_excel( "datasets/air+high quality/AirQualityUCI.xlsx" )
# Extract information from sooner or later (2004-11-01)
df= df[ df['Date']== "2004-11-01" ]
print("Form : ", df.form)
df.head( 3 )
# Convert float to int
df["CO(GT)"]= df["CO(GT)"].astype(int)
CO_values= [3, 3, 3, 3, -200, 2, 1, 1, 1, 1, 2, 3, 4, 4, 3, 3, 3, 2]
time_period= ['0 am', '1 am', '2 am', '3 am', '4 am', '5 am', '6 am', '7 am', '8 am', '9 am', '10 am',
'11 am', '12 pm', '13 pm', '14 pm', '15 pm', '16 pm', '17 pm']
ktk= KitikiPlot( information= CO_values )
ktk.plot(
figsize= (20, 5),
cell_width= 2,
cmap= {-200: "cornflowerblue", 1: "#ffeaea", 2: "#feb9b9", 3: "#ff7070", 4: "#b00"},
transpose= True,
xlabel= "Time",
ylabel= "Sliding Home windows of CO(GT) values (in mg/m^3)",
display_xticks= True,
xticks_values= time_period,
ytick_prefix= "Window",
xticks_rotation= 90,
display_legend= True,
title= "CO(GT) Development in Air",
legend_kwargs= {"bbox_to_anchor": (1.01, 1), "loc":'higher left', "borderaxespad": 0.})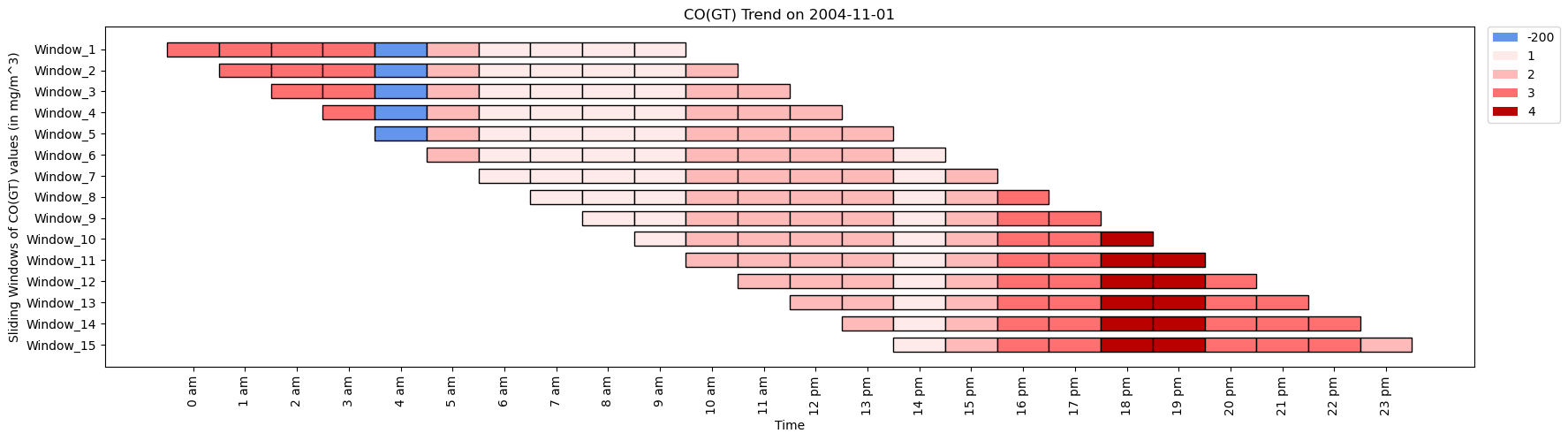
Conclusion
KitikiPlot simplifies the visualization of sequential and time-series categorical sliding window information, making advanced patterns extra interpretable. Its versatility spans numerous functions, together with genomics, climate evaluation, and air high quality monitoring, highlighting its broad utility in each analysis and trade. With a deal with readability and value, KitikiPlot enhances the extraction of actionable insights from categorical information. As an open-source library, it empowers information scientists and researchers to successfully deal with various challenges.
Key Takeaways
- KitikiPlot is a flexible Python library designed for exact and user-friendly sliding window information visualizations.
- Its customizable parameters enable customers to create significant and interpretable visualizations tailor-made to their datasets.
- The library helps a variety of real-world functions throughout numerous analysis and trade domains.
- As an open-source device, KitikiPlot ensures accessibility for information science practitioners and researchers alike.
- Clear and insightful visualizations facilitate the identification of tendencies in sequential categorical information.
Sources
Quotation
@software program{ KitikiPlot_2024
writer = {Boddu Sri Pavan and Boddu Swathi Sree},
title = {{KitikiPlot: A Python library to visualise categorical sliding window information}},
yr = {2024},
model = {0.1.2},
url = {url{https://github.com/BodduSriPavan-111/kitikiplot},
doi = {10.5281/zenodo.14293030}
howpublished = {url{https://github.com/BodduSriPavan-111/kitikiplot}}
}Continuously Requested Questions
A. KitikiPlot focuses on visualizing sequential and time-series categorical information utilizing a sliding window method.
A. Whereas primarily meant for categorical information, KitikiPlot might be tailored for different information varieties by inventive preprocessing strategies, equivalent to discretization, and so forth,.
A. Sure, KitikiPlot integrates seamlessly with standard libraries like Pandas and Matplotlib for efficient preprocessing and enhanced visualization.
The media proven on this article is just not owned by Analytics Vidhya and is used on the Creator’s discretion.

