It’s not information that 2024 has been a tumultuous yr on many fronts. For our second Lively Adversary Report of 2024, we’re trying particularly at patterns and developments we famous throughout the first half of the yr (1H24). Although the yr itself was in some ways unremarkable on the floor for these charged with the safety of small- and medium-scale enterprises – the battle between attackers and defenders raged on, as ever – we see some outstanding exercise slightly below that floor.
Key takeaways
- Abuse of built-in Microsoft providers (LOLbins) is up — means up
- RDP abuse continues rampant, with a twist
- The ransomware scene: Banyans vs poplars
The place the information comes from
The info for this report is drawn from instances dealt with within the first half of 2024 by a) our external-facing IR group and b) the response group that handles vital instances occurring amongst our Managed Detection and Response (MDR) prospects. The place acceptable, we evaluate findings from the 190 instances chosen for this report with information amassed from earlier Sophos X-Ops casework, stretching again to the launch of our Incident Response (IR) service in 2020.
For this report, 80 % of the dataset was derived from organizations with fewer than 1000 workers. That is decrease than the 88 % in our final report; the distinction is primarily (however not solely) because of the addition of MDR’s instances to the combination. Slightly below half (48%) of organizations requiring our help have 250 workers or fewer.
And what do these organizations do? As has been the case in our Lively Adversary Studies since we started issuing them in 2021, the manufacturing sector was the most probably to request Sophos X-Ops response providers, although the proportion of consumers hailing from Manufacturing is down sharply, from 25 % in 2023 to 14 % within the first half of 2024. Development (10%), Schooling (8%), Info Expertise (8%), and Healthcare (7%) spherical out the highest 5. In whole, 29 completely different trade sectors are represented on this dataset. Additional notes on the information and methodology used to pick out instances for this report will be discovered within the Appendix.
The stability of the report analyzes our findings, as listed in the important thing takeaways above, and supplies updates on a collection of points raised by earlier editions of the report. Evaluation of the complete dataset for 2024 shall be undertaken within the subsequent version of the report, slated for early 2025.
Born to run (natively): LOLbin use on a speedy rise
LOLbins – abused-but-legitimate binaries already current on the machine or generally downloaded from reliable sources related to the OS – have all the time been a part of the Lively Adversary panorama. We distinction these to the findings we name “artifacts,” that are third-party packages introduced onto the system illegitimately by attackers (e.g., mimikatz, Cobalt Strike, AnyDesk). LOLbins are reliable information, they’re signed, and when utilized in seemingly benign methods they’re much less seemingly to attract a system administrator’s consideration.
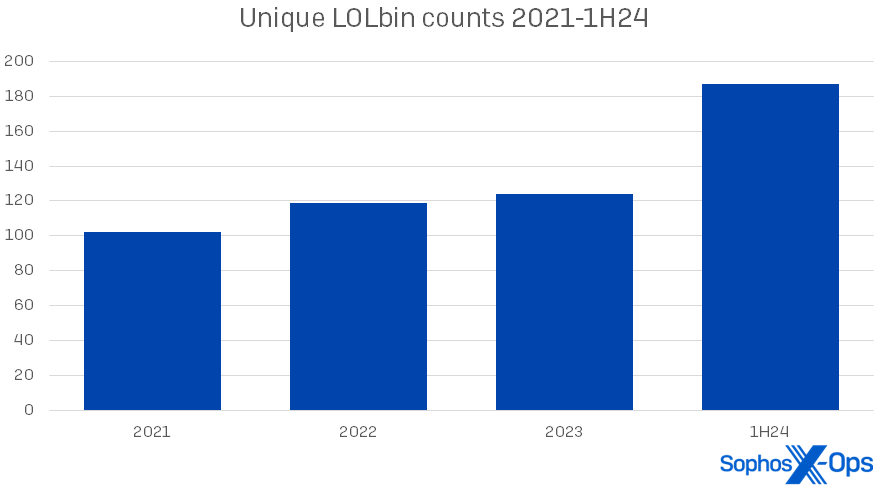
We noticed a modest enhance this yr within the use and number of artifacts, and we’ll have a look at these modifications later on this report. The rise in LOLbins, nevertheless, is arresting. (For the needs of this version of the report, we’re primarily specializing in binaries within the Microsoft Home windows working system, although we additionally see these abused in different OSes.) Within the first half of 2024, we discovered 187 distinctive Microsoft LOLbins used amongst our 190 instances – over a 3rd of them (64) showing simply as soon as in our dataset. This represents an increase of 51 % over 2023’s LOLbin numbers. The general rise in LOLbin counts since 2021 is proven in Determine 1.
Determine 1: The abrupt rise in LOLbin use in 1H24 comes after years of gradual enhance in utilization
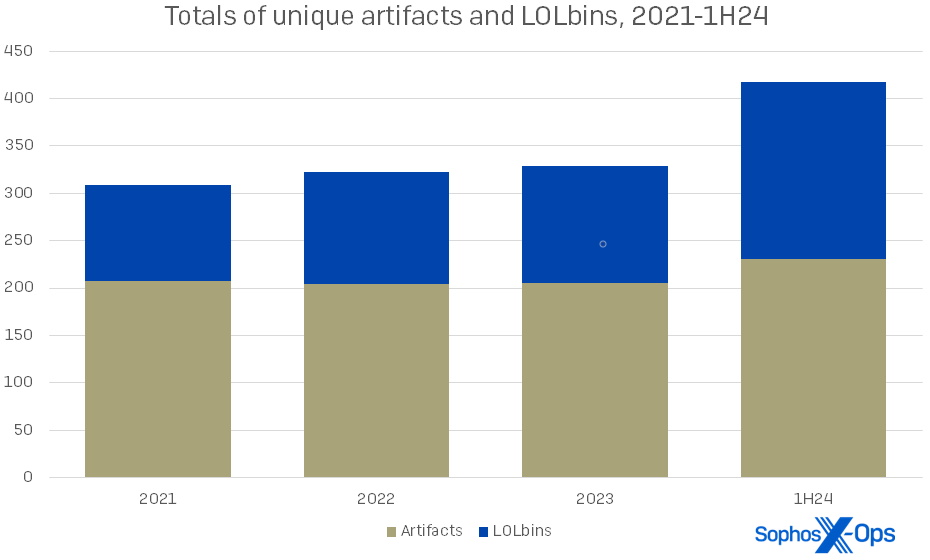
Simply three years in the past, our 2021 statistics confirmed that artifacts had been greater than twice as frequent as LOLbins in our instances. Now the ratio is nearer to five:4, as proven in Determine 2.
Determine 2: The usage of each artifacts and LOLbins is growing general, and attackers are throwing extra of each on the wall to see what sticks. In a selected incident this yr, the responding group famous 14 artifacts and 39 LOLbins in play
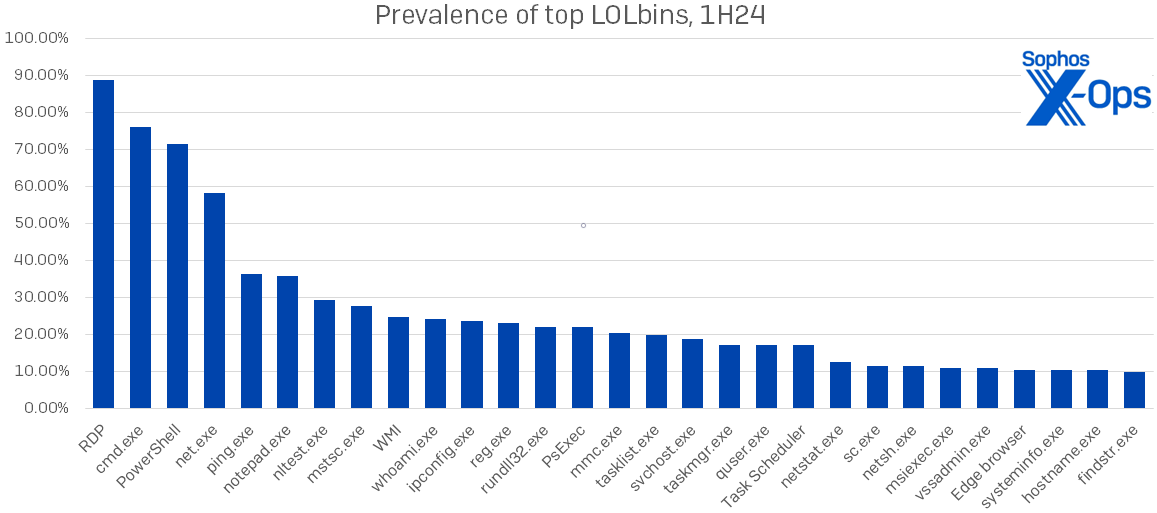
Which LOLbins are attackers utilizing? Main the pack as all the time is RDP, about which we’ll have extra to say within the subsequent part. We discovered 29 particular LOLbins in use in at the very least 10 % of instances; their names and prevalence are proven in Determine 3. This represents a considerable enhance over final yr’s distribution, the place solely 15 of the 124 distinctive LOLbins noticed appeared in over 10 % of instances.
Determine 3: Probably the most generally logged LOLbins of 1H24; all of those appeared in at the very least 10 % of instances
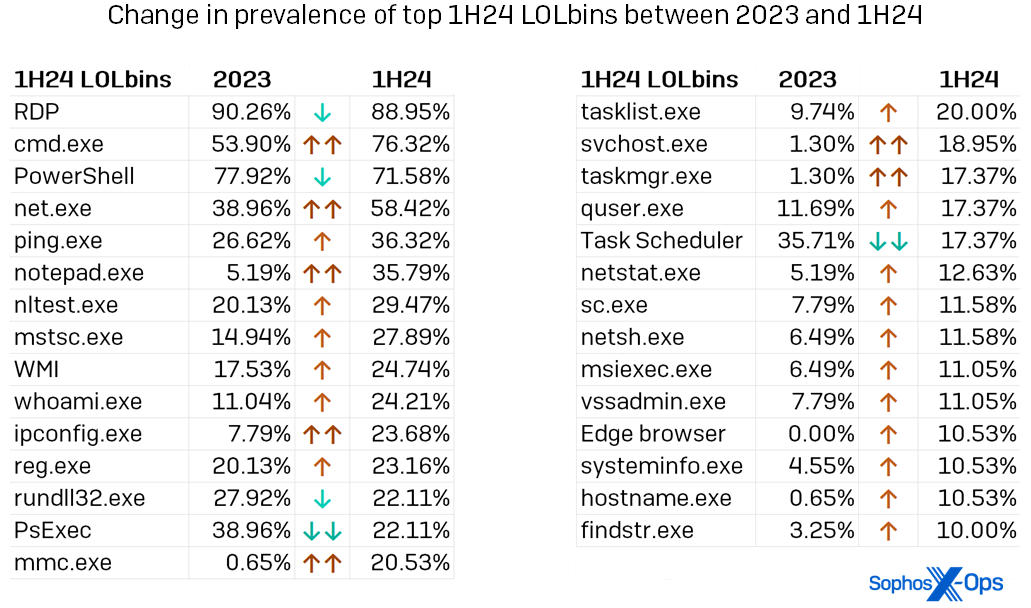
For essentially the most half the names within the determine above aren’t any shock to common readers of the Lively Adversary Report – RDP guidelines the panorama, with cmd.exe, PowerShell, and internet.exe making their ordinary sturdy exhibiting. Nevertheless, we will see elevated use of even a few of these acquainted LOLbins in Determine 4, which additionally reveals the proportion enhance in utilization for each LOLbin seen in over 10 % of 1H24 instances. Notice the prevalence of binaries used for discovery or enumeration – 16, by our rely.
Determine 4: Of the highest 29 LOLbins we noticed in use throughout 1H24, solely 5 had been noticed much less ceaselessly than they had been in 2023. (LOLbins for which utilization modified considerably – both 15 % larger or decrease than within the earlier yr’s information – are indicated above with double arrows). Please observe that within the context of this record, “Job Scheduler” contains each Job Scheduler and schtasks.exe, whereas WMI contains the now-deprecated WMIC
What’s a defender to do? First, this variation in tooling signifies that it isn’t sufficient to simply keep watch over your community for objects that don’t belong. Each LOLbin is indirectly a part of the working system, from RDP all the way down to fondue.exe, tracert.exe, and time.exe (three of the one-use-only LOLbins we noticed within the information). Greater than ever, it’s essential to grasp who’s in your community and what they need to be doing. If Alice and Bob from IT are doing issues with PowerShell, most likely okay. If Mallory from PR is doing issues with PowerShell, ask questions.
As well as, logging and well-informed community monitoring are key. At one level in our evaluation we requested ourselves whether or not the will increase we had been seeing had been maybe merely the results of incorporating the information from our MDR group. After normalizing the information we had been capable of conclude that they’re not, however we had been as soon as once more startled by the distinction having MDR-type eyes on the system makes in terms of each preliminary entry and impression. (Extra on these in a minute.)
To study extra about LOLbins, together with capabilities of particular person binaries and the place they (often) match into the MITRE ATT&CK framework, we advocate visiting the LOLBAS collaborative mission on Github.
RDP (stands for Repeating the Rattling Downside)
For a report that enjoys throwing in pop-music references, Lively Adversary appears like a damaged file: RDP, RDP, RDP. As proven within the figures above, RDP is undefeated as a supply of infosecurity woe, with slightly below 89 % of the instances we noticed in 1H24 exhibiting some indication of RDP abuse.
Trying extra intently on the instances involving RDP, there’s not a lot change in whether or not assaults used RDP internally or externally. These statistics have been steady over time, as proven in Determine 5.
Determine 5: In 2022 and 2023, there have been a number of instances wherein attackers kicked over the traces of their RDP exercise so totally that the responding group couldn’t confidently discern precisely which actions had been profitable; 1H24 was higher in that facet at the very least
Trying simply outdoors this report’s timeframe, the monotony of RDP abuse statistics was solely barely damaged in September by Microsoft’s announcement that the corporate is rolling out a multiplatform “Home windows App” (that is its identify) designed to offer distant entry to Home windows 10 and 11 machines from “work or college accounts,” with RDP entry promised later. Nevertheless, regardless of the corporate’s claims of enhanced safety together with multifactor authentication functionality, most observers had been fast to explain Home windows App as primarily a rebrand of the Distant Desktop consumer. Whether or not our subsequent Lively Adversary Report has joyful information of a drop in RDP abuse or not, solely time will inform.
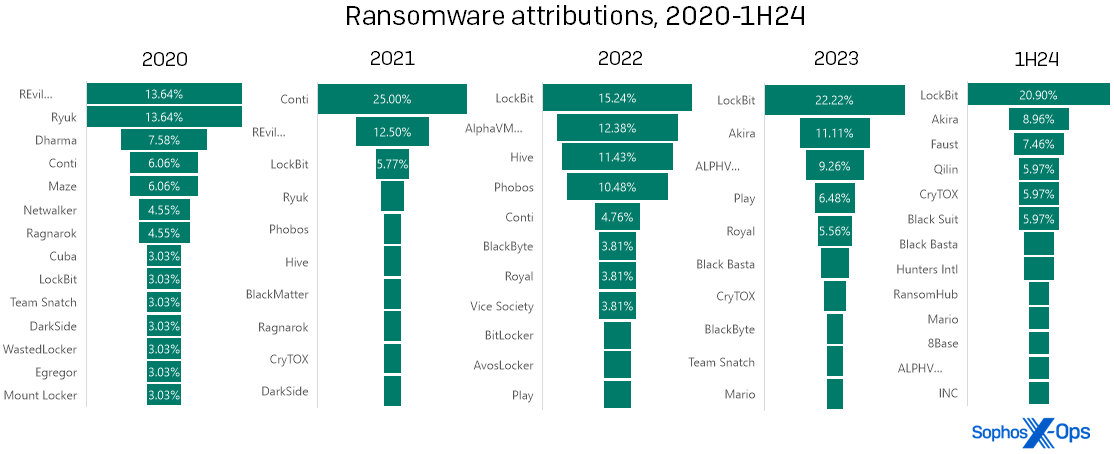
Shaking the tree: The poplars and banyans of ransomware
Turning our consideration now to ransomware, a stroll by the information on ransomware infections led to an attention-grabbing remark: With regards to attribution, the corollary between high-profile ransomware takedowns and diminished presence on our charts isn’t all the time as sturdy as one would hope.
In our expertise, some years have one dominant ransomware model that overshadows the others like the cover of a banyan tree, and different years distribute the ransomware instances comparatively evenly amongst a number of manufacturers, like a row of poplars. The distinction usually corresponds with authorized disruptions (“takedowns”) of high-profile ransomware teams. Nevertheless, the primary half of 2024 didn’t replicate this sample in our information. LockBit was the dominant ransomware of 2023, however was the topic of a law-enforcement disruption in late February 2024. Regardless of that, LockBit remained the dominant ransomware seen by the IR group within the first half of the yr.
Determine 6: Poplar, banyan, poplar, banyan… banyan?! The sample we’ve noticed in ransomware attributions over the previous a number of years appears to have damaged down in 1H24 with LockBit… possibly. (Two of the labels above are truncated for house; “REvil….” is extra totally “REvil / Sodinokibi,” whereas “ALPHV….” is “ALPHV/BlackCat”)
To be truthful, authorized motion in the end doesn’t make an enormous dent within the general ransomware scene – it disrupts the focused risk actor, however doesn’t completely cease many of the entities concerned. With each main authorized motion, the sheer variety of different manufacturers jockeying for place signifies that the hole is crammed, after which some. Discover that Conti represented a mere 6 % of infections seen in 2020… after which first Ryuk (2020) and Revil (2021) had been hit by takedowns of the gang or, in Ryuk’s case, the Trickbot distribution system on which it relied. After that Conti (seemingly descended from Ryuk) flourished for a yr (2021), however dropped to single-digit incidence ranges by the top of 2022. In LockBit’s case, the proprietor of the model tried a mid-2024 “comeback,” rebuilding its infrastructure and even restarting its weblog. (A model of LockBit’s ransomware builder was additionally famously leaked by a disgruntled affiliate in September 2022, which can have an effect on its prevalence.)
What’s subsequent? First, it’s attainable that the sample will resolve itself within the information from the second half of the yr – that’s, the “banyan” will morph right into a “poplar” as predicted. Within the month or so after the LockBit takedown, Sophos’ MDR and IR groups, respondents to our 2024 State of Ransomware survey, and different trade observers all reported a lower in LockBit infections. These bounced up once more for some time in Could; it’s commonplace to see that form of echo impact after a disruption by legislation enforcement, however ultimately the echo does fade.
Second, the identify of the subsequent ubiquitous ransomware might be someplace within the determine above, which signifies that even when system directors won’t wish to place bets on any explicit model, the wrongdoer is probably going already on defenders’ radar. These seeking to parry the following assault on their methods can begin by maintaining a tally of information regarding each identified names and up-and-comers. It’s completely affordable to have a good time that creatures like Mikhail Matveev and Ekaterina Zhdanova are dealing with jail time, however the track isn’t over.
Total, ransomware infections had been down barely within the first half of the yr. For IR, 61.54 % of instances dealt with concerned ransomware, in comparison with 70.13 % in 2023. (The slack was greater than taken up by community breaches, which almost doubled their incidence in IR instances – 34.62 % in 1H24, in comparison with 18.83 % in 2023. Shut examination of all information out there to us causes us to suspect that the drop, although actual, gained’t be as pronounced when the complete yr’s numbers are analyzed.)
In the meantime, MDR dealt with primarily community breaches in 1H24, with simply 25.36 % of their instances chalked as much as ransomware. It needs to be famous that MDR, because of the nature of the service, tends to come across and include ransomware far earlier in its an infection cycle than the IR group does – often, previous to encryption or deployment, which signifies that they by no means rise to the extent of requiring response of the kind the Lively Adversary Report covers. (Sadly, “assault detected” for the IR group typically means “the client realized that they could be beneath assault after they acquired a ransom observe and all their computer systems had been bricked.”) For the MDR group, LockBit was already flattening out in prevalence by the top of June, with 17.14 % of their ransomware attributions chalked as much as that model and each Akira and BlackSuit shut on its heels at 11.43 % apiece. (And finishing the circle, each Akira and BlackSuit are descendants of… Conti. Similar track, subsequent verse.)
Comin’ out and in of your life: Preliminary entry and impression
The third and fourteenth steps of the MITRE ATT&CK Matrix invariably appeal to reader curiosity; we’ve even written in a earlier report concerning the variations we noticed between two very comparable instances dealt with by our IR and MDR processes. For this report, we’ll focus our MITRE-related evaluation on the classes themselves, Preliminary Entry and Affect.
Preliminary Entry within the first half of 2024 seemed a lot because it did in earlier years. As one would count on from the RDP statistics, Exterior Distant Companies assault strategies dominated the class, representing 63.16 % of instances in comparison with 2023’s 64.94 %. Legitimate Accounts (59.47%, down from 61.04%) and Exploit [of] Public-facing Utility (30%, up from 16.88%) spherical out the highest three. (Since instances might exhibit many mixtures of initial-access strategies, the chances won’t ever add as much as 100.)
The scenario is extra attention-grabbing with Affect, the ultimate class within the MITRE matrix. After years of dominating the Affect class by factoring right into a minimal of two-thirds of all instances, Information Encrypted for Affect (a typical step in ransomware assaults) tumbles to second place with 31.58 %, simply above up-and-comer Information Manipulation (30%) and trailing No Affect at 38.95 %.
We now have written up to now about “No Affect” which means one thing a bit completely different in terms of ATT&CK. The newest version of ATT&CK lists fourteen strategies that it acknowledges as “Affect.” These strategies are evolving to maintain tempo with present realities of ransomware payouts and misplaced productiveness, and we’ve refined our evaluation of earlier case information to replicate these enhancements (thus retroactively trimming down the variety of instances for which the impression discovering is No). However it could be an excessive amount of to ask that the ATT&CK class embody intangibles similar to reputational loss or employees burnout. Incident responders are all too conscious that no person needs to wish their providers; although “no” impression sounds refreshing and nice, and although lots of the MDR-handled instances had been certainly triggered in time to dam would-be attackers from succeeding of their targets, “No Affect” doesn’t imply there was no impression – it signifies that no matter occurred is past ATT&CK’s vocabulary to explain.
The place are they now: Checking on earlier AAR findings
In an try to hold this version of the report comparatively brief, there are just a few subjects of earlier curiosity on which we’ll contact briefly, upfront of our full-year 2024 report.
Dwell time: Dwell-time numbers have been dropping, as we confirmed in our first 2023 report. The 1H24 numbers point out that this decline has leveled off and even barely reversed for instances dealt with by our Incident Response group. For ransomware, median dwell occasions hover at 5.5 days; factoring in all different varieties of incidents, the median lingers at 8 days. Although we don’t but have earlier years’ MDR instances out there to the report group for evaluation, a have a look at their 1H24 information reveals what a distinction monitoring makes – medians of three days for ransomware and at some point for all sorts of incidents. Because the MDR instances requiring incident response are a really small sliver of all of the exercise MDR sees day-to-day, the impact of getting watchful eyes in place is left as an train for the reader.
Time-to-AD: In our second 2023 report we seemed on the time it takes for attackers to achieve management of the goal’s Lively Listing — a degree at which one can moderately say that the goal is compromised — and the interval from when the attacker beneficial properties management of AD to when the assault is detected. That is one other statistic for which MDR’s information varies radically from that compiled by IR. The IR numbers fluctuated in 1H24 from these of years previous, with attackers taking about two hours longer to succeed in Lively Listing (15.35 hours in 2023, 17.21 hours in 1H24). An obvious lower in dwell time between AD acquisition and assault detection (29.12 hours in 1H24, down from 48.43 hours in 2023) is attention-grabbing and should benefit scrutiny within the subsequent report, if a bigger accumulation of knowledge reveals it to be an actual growth.
We’ll observe that the three variations of Lively Listing we most ceaselessly noticed compromised had been Server 2019 (43%), Server 2016 (26%), and Server 2012 (18%), collectively accounting for 87 % of compromised AD servers. All three of those variations at the moment are out of mainstream Microsoft assist, though Patch Tuesday launch data nonetheless states which updates would apply to every model. In case your methods are working on drained variations of Server, think about these numbers your wake-up name to replace. (For individuals who observe our Patch Tuesday protection, we’ve began this month to relay extra data on exactly which variations of Server are affected by every month’s patches.)
Compromised credentials: We additionally spotlighted the rise in compromised credentials as a root reason behind assaults in our second 2023 report. In 2023, 56 % of all incidents had compromised credentials as their root trigger. Within the first half of 2024, that dominance was dialed again considerably. Although compromised credentials had been nonetheless the main root trigger general for 2024, that quantity was led primarily by the IR instances, as proven in Determine 7. For MDR prospects, exploited vulnerabilities led the root-cause leaderboard, although by lower than one %.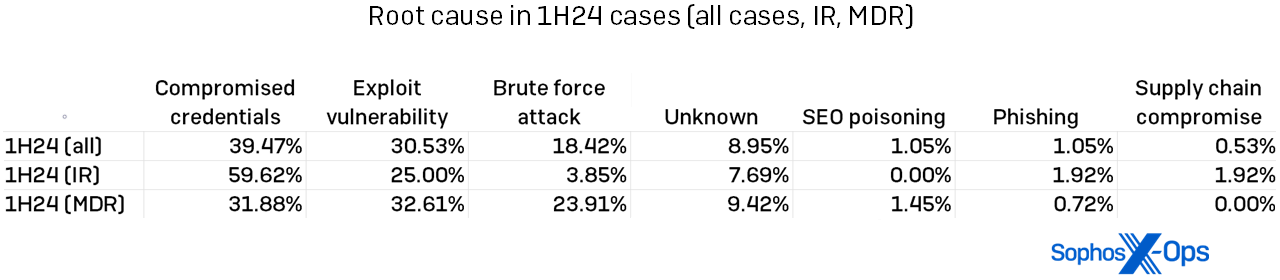
Determine 7: The foundation causes of IR-handled and MDR-handled incidents assorted, with instances extra equally distributed amongst MDR and compromised credentials “successful” in a stroll for IR
Only a track about artifacts earlier than I am going
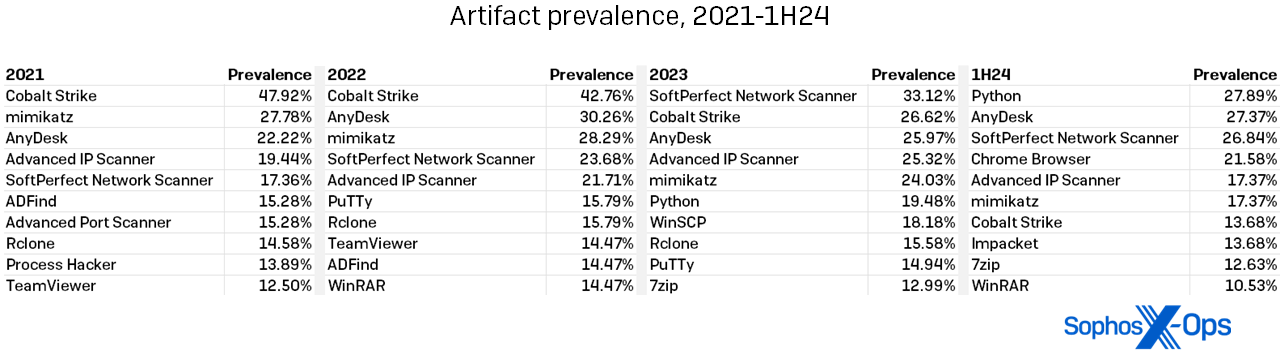
As talked about above, our information discovered not solely LOLbins however third-party artifacts on the rise within the instances we noticed within the first half of 2024. The rise in artifact utilization will not be as placing as that of the LOLbins, however just a few facets bear additional dialogue.
First, the numbers are up, although barely. We noticed 230 distinctive artifacts on focused methods within the first half of 2024, in comparison with 205 in all of 2023 – a 12 % enhance. (By the use of comparability, 2022 had 204 artifacts; 2021 had 207.)
Second, the names of essentially the most generally discovered artifacts don’t a lot range from yr to yr, as proven in Determine 8. We did observe that Cobalt Strike utilization continues the retreat it started in 2023, current in simply 13.68 % of infections within the first half. (In earlier years, Cobalt Strike was at one level current in almost half the instances, and it nonetheless sits atop the leaderboard of all-time artifact findings. Higher defender detections for Cobalt Strike are seemingly resulting in this drop.) 127 artifacts seem solely as soon as within the 1H24 information, which is lower than 2023’s 102 single-use findings.
Determine 8: The years-long pattern towards extra numerous artifact use continues, with no single artifact occurring in additional than 30 % of instances within the first half of 2024
A defender studying that over half of all artifacts are single-use instruments might maybe despair of catching the whole lot an attacker would possibly throw at them. We’d encourage that defender to take a look at the desk above and keep in mind that the supporting solid might change, however the “stars” of the Artifacts galaxy all shine on. The desk above reveals each artifact that appeared in over 10.00 % of instances over the course of 4 years. Maintaining a relentless eye out for these packages is each doable and helpful. Take into account growing and making use of a default-block coverage for functions in your methods; this requires a good quantity of labor up entrance, however saves hassle as attackers broaden their tool-usage repertoire.
Conclusion
It has been a unprecedented present to the AAR evaluation and writing group to see how the statistics modified as we integrated the big tranche of knowledge from Sophos X-Ops’ MDR group with the years-deep database from our IR colleagues. The method of interrogating the information led us to each outstanding panorama modifications – who knew that LOLbins could possibly be thrilling? – and to patterns similar to RDP abuse that stay immune to finest practices similar to vigilant monitoring.
Above all, although, we stay bemused by the variety of instances that hinged on fundamentals – not simply the three immortalized within the Sophos “haiku”
however easy sample consciousness that may have prevented prospects from ever changing into a part of a dataset similar to this. It’s our hope {that a} shut, tight snapshot of the latest Lively Adversary Report panorama aids practitioners to sharpen their give attention to the basics that may hold us all safer and safer.
Acknowledgements
The authors want to thank Chester Wisniewski, Anthony Bradshaw, and Matt Wixey for his or her contributions to the AAR course of.
Appendix: Demographics and methodology
For this report, we centered on 190 instances that could possibly be meaningfully parsed for helpful data on the state of the adversary panorama as of the primary half of 2024. Defending the confidential relationship between Sophos and our prospects is after all our first precedence, and the information herein has been vetted at a number of levels throughout this course of to make sure that no single buyer is identifiable by this information – and that no single buyer’s information skews the combination inappropriately. When unsure a couple of particular case, we excluded that buyer’s information from the dataset.
We must always make point out of a multi-year case that concerned our MDR group. That case, which concerned nation-state exercise in a number of areas, has been lined elsewhere as “Crimson Palace.” Although fascinating and in some ways a bellwether for particular assault techniques we’ve seen elsewhere since, it’s in a number of methods such an outlier to the overwhelming majority of the Lively Adversary dataset that we’ve chosen to depart its numbers out of the report.
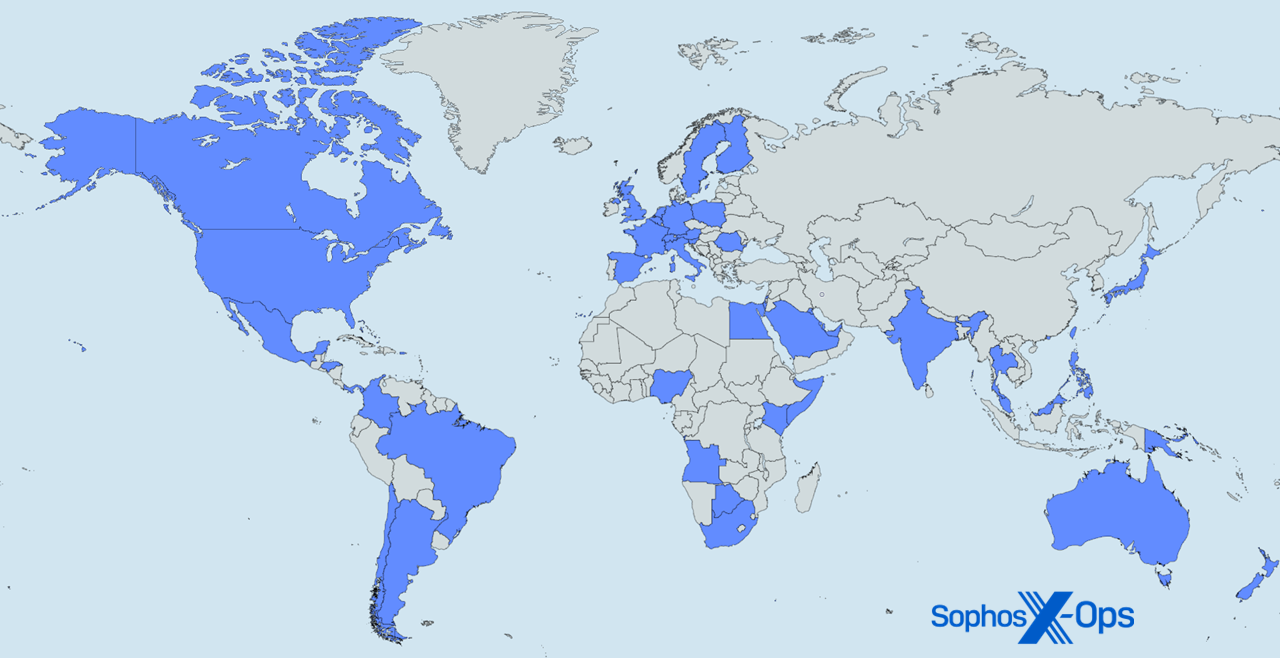
Determine A1: Right here, there, and all over the place — it’s Sophos X-Ops MDR and IR around the globe (Map technology courtesy mapchart.internet)
The next 48 nations and different areas are represented within the 1H24 information analyzed for this report:
| Angola | Honduras | Poland |
| Argentina | Hong Kong | Qatar |
| Australia | India | Romania |
| Austria | Israel | Saudi Arabia |
| Bahamas | Italy | Singapore |
| Bahrain | Japan | Slovenia |
| Belgium | Kenya | Somalia |
| Botswana | Kuwait | South Africa |
| Brazil | Malaysia | Spain |
| Canada | Mexico | Sweden |
| Chile | Netherlands | Switzerland |
| Colombia | New Zealand | Taiwan |
| Egypt | Nigeria | Thailand |
| Finland | Panama | United Arab Emirates |
| France | Papua New Guinea | United Kingdom |
| Germany | Philippines | United States of America |
Industries
The next 29 industries are represented within the 1H24 information analyzed for this report:
| Promoting | Monetary | MSP/Internet hosting |
| Agriculture | Meals | Non-profit |
| Structure | Authorities | Pharmaceutical |
| Communication | Healthcare | Actual property |
| Development | Hospitality | Retail |
| Schooling | Info Expertise | Companies |
| Electronics | Authorized | Transportation |
| Power | Logistics | Utilities |
| Engineering | Manufacturing | Wholesale |
| Leisure | Mining |
Methodology
The info on this report was captured over the course of particular person investigations undertaken by Sophos’ X-Ops Incident Response and MDR groups. For this second report of 2024, we gathered case data on all investigations undertaken by the groups within the first half of the yr and normalized it throughout 63 fields, analyzing every case to make sure that the information out there was acceptable intimately and scope for combination reporting as outlined by the main focus of the proposed report. We additional labored to normalize the information between our MDR and IR reporting processes.
When information was unclear or unavailable, the authors labored with particular person IR and MDR case results in clear up questions or confusion. Incidents that would not be clarified sufficiently for the aim of the report, or about which we concluded that inclusion risked publicity or different potential hurt to the Sophos-client relationship, had been put aside. We then dissected every remaining case’s timeline to achieve additional readability on such issues as preliminary ingress, dwell time, exfiltration, and so forth. We retained 190 instances, and people are the muse of the report.