Identification of scientific isolates and biofilm formation
Biofilm formation is a microbial survival technique, and these surface-associated microbial cells facilitate the adherence of microorganisms to residing and inanimate surfaces. Within the human host, biofilms can function a reservoir for spreading new infections and growing bacterial resistance to antibiotics. Among the many E. coli isolates collected on this examine, 28.6%, 32.9%, 24.3%, and 14.3% had robust, average, weak, and no biofilm formers, respectively. These knowledge had been in settlement with these of one other examine of biofilm formation by uropathogenic E. coli, which confirmed 23.6% extremely constructive, 26.3% reasonably constructive, and 50% weakly constructive biofilm formation within the 100 examined strains [42]. The virulence of those uropathogenic E. coli fimbrial adhesins was reported to be triggered by Ag43, which may be the foremost contributing issue to long-term persistence after the institution of an preliminary an infection, and the Ag43a gene was accountable for a powerful aggregation phenotype that promoted important biofilm progress [43].
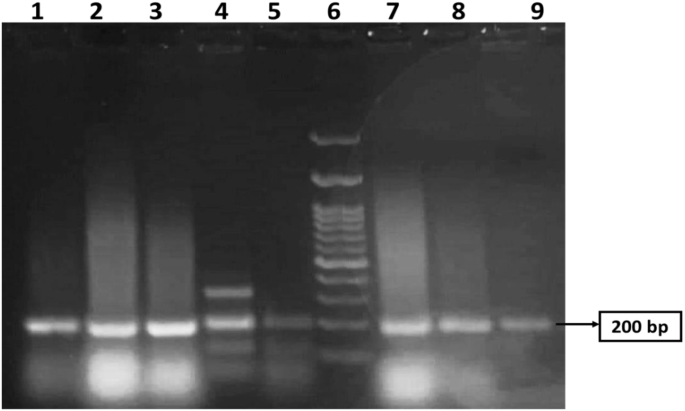
Determine 1 exhibits the 200 bp PCR-amplified csgA gene in E. coli, which was visualized through gel electrophoresis evaluation. The samples had been loaded in lanes 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 7, 8, and 9, whereas lane 6 was loaded with a 200 bp DNA ladder. All of the isolates had been constructive for the csgA gene. A picture-editing software (www.irfanview.web) was used to reinforce the illustration of the picture (unique picture, supplementary file).
PCR amplification of csgA gene with a measurement 200 bp in MDR E.coli revealed by agarose gel evaluation. Lane 6 was loaded with a 200 bp DNA ladder. Samples had been loaded in lanes 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 7, 8, and 9. All lanes are constructive for the csgA gene. The unique picture is offered in Supplementary Fig. 1
GC‒MS evaluation of rosemary oil
Phytochemical constituents recognized in dried leaf extracts of Rosmarinus officinalis L. by GC‒MS evaluation confirmed that top concentrations within the extracted rosemary oil had been 3,5-dimethoxybenzoic acid (96.56%), eucalyptol (25.68%), and bicyclo[3.3.0]oct-2-en-6-one, 3-methyl (17.84%) (Desk 2). This discovering means that rosemary oil comprises a big quantity of oxygenated compounds and phenylpropanoids, that are recognized for his or her potential therapeutic properties. Oxygenated compounds and phenylpropanoids have been reported to exhibit numerous organic actions, akin to antioxidant, antimicrobial, and anti inflammatory results [44]. GC-MS chromatogram of rosemary oil is accessible in supplementary file.
Transmission electron microscopy (TEM)
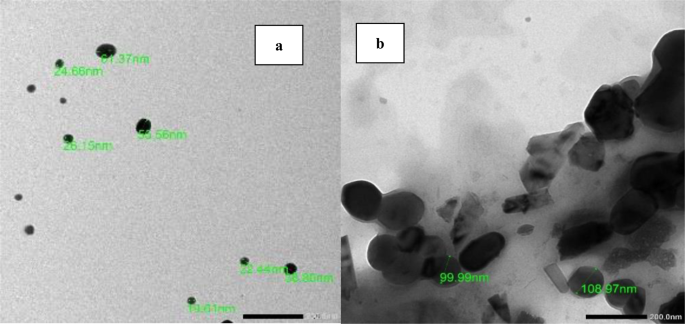
Determine 2 exhibits TEM pictures of freshly ready (a) 0.5% CS nanophytosomes and (b) NSLC nanophytosomes. The CS nanophytosomes had a well-defined spherical form with a median measurement of roughly 26 nm and had been evenly distributed with none agglomeration. In distinction, the NSLC nanophytosomes had been bigger and fewer uniform in form. The particle measurement and form outcomes of the nanoparticles are per the findings of our earlier work [45].
Particle measurement (PS), zeta potential (ZP), polydispersity index (PDI), and entrapment effectivity (EE%)
Desk 3 exhibits that the NSLC nanophytosomes had a considerably better PS (176.70 ± 12.30 nm) than did the 0.5% CS and 1% CS nanophytosomes, which had PSs of twenty-two.54 ± 2.92 nm and 34.59 ± 4.00 nm, respectively (one-way ANOVA, p < 0.001). This distinction could also be because of the composition of NSLC nanophytosomes, which features a combination of stable and liquid lipids. In distinction, the CS nanophytosomes are primarily composed of CS. The PS considerably elevated when the CS focus was elevated from 0.5 to 1% (t-test, p < 0.001).
The floor cost of nanoparticles in colloids can be utilized to foretell their long-term stability. The NSLC nanophytosomes exhibited a detrimental ZP of -32.71 ± 2.07 mV, whereas the 0.5% CS nanophytosomes had a constructive ZP of 11.5 ± 0.05 mV because of the unbranched cationic nature of the CS. The stronger floor prices of NSLC nanophytosomes counsel that they might be extra secure, because the nanoparticles can repel one another extra successfully. In distinction, the weaker floor prices across the CS nanophytosomes is probably not enough to forestall aggregation over time, suggesting the need of lyophilization for long-term storage stability.
In contrast with 0.5% CS nanophytosomes, the NSLC nanophytosomes had considerably decrease PDI values (0.45 ± 0.01 and 0.57 ± 0.14, respectively) (one-way ANOVA, p < 0.001). Because of this the NSLC nanophytosomes had been extra monodisperse than the CS nanophytosomes had been. Furthermore, growing the CS focus resulted in a extra heterogeneous combination, as indicated by a big improve within the PDI (t-test, p < 0.05). As well as, each the NSLC and CS nanophytosomes exhibited excessive entrapment efficiencies of 93.47 ± 0.90% and 93.12 ± 1.05%, respectively. Nonetheless, because of the potential advantages of smaller particle sizes in growing drug loading, 0.5% CS nanophytosomes had been chosen for additional investigation.
Lyophilization of nanoparticles
Freeze-drying is a way that converts colloidal dispersions into dry powders with enhanced long-term storage stability. The method entails freezing the nanoformulation, decreasing the stress, and eradicating water by sublimation and desorption beneath vacuum. Nonetheless, freeze-drying course of poses the problem of sustaining the unique formulation construction, as ice nucleation throughout the course of can alter the formulation morphology, trigger bodily collapse, and induce colloidal instability and nanoparticle aggregation [46]. To beat these issues, a cryoprotectant, akin to mannitol, can be utilized to immobilize nanoparticles in an amorphous matrix by changing water molecules and stopping pattern collapse on account of osmotic stress and stress. The lyophilization course of has yielded comfortable, unfastened flake look, free-flowing CS nanophytosomes powder with quick resuspension time. The decreased moisture content material by means of lyophilization enhances stability and ensures an extended shelf life by stopping microbial progress and chemical degradation. Upon reconstitution, the lyophilized powder rapidly disperses, forming a homogenous resolution, which is essential for environment friendly drug supply and affected person compliance.
Minimal inhibitory focus (MIC) and biofilm inhibition
Desk 4 presents the outcomes of MIC testing of CS and NSLC nanophytosomes towards E. coli in comparison with these of rosemary oil. The information confirmed that each kinds of nanophytosomes had considerably decrease MICs towards E. coli than rosemary oil alone, with a discount charge of 45.8% for NSLC nanophytosomes and 87.5% for 0.5% CS nanophytosomes. Additional Mann‒Whitney checks confirmed that the MIC was important decrease for CS phytosomes than for NSLC phytosomes (p < 0.01), which can be attributed to the synergistic impact of CS and rosemary oil when mixed in nanophytosomes. Consequently, CS nanophytosomes had been chosen for biofilm inhibition testing.
The outer membrane of E. coli has a singular construction that acts as a selective barrier, combining a extremely hydrophobic lipid bilayer and pore-forming proteins with particular measurement exclusion properties. Due to this fact, nanopartilces can enter the outer membrane by means of both a lipid-mediated route or normal diffusion porins for hydrophilic entry [47]. The small particles of CS nanophytosomes are in a position to make the most of the porin-mediated permeability pathway to achieve entry to the cells of E. coli and work together with the water-soluble proteins and nucleic acids inside the bacterial cell, leading to a considerably decreased MIC towards E. coli. In distinction, bigger particles of NSLC nanophytosomes need to diffuse throughout the lipid bilayer of the outer membrane, a tougher and rate-limiting course of that contributes to the noticed variation within the antimicrobial efficacy between the 2 kinds of nanophytosomes.
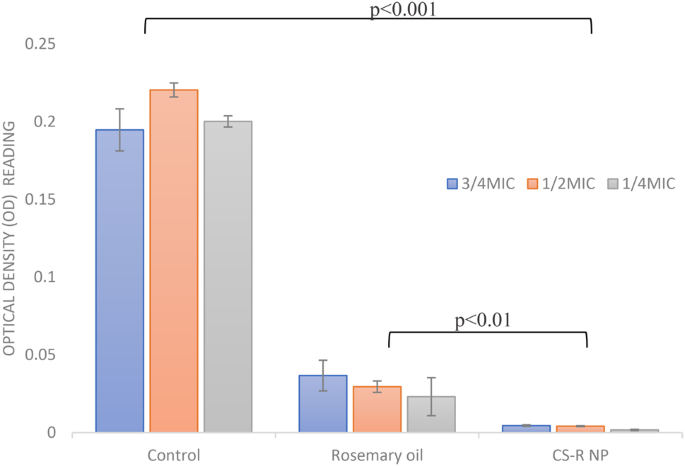
To judge the efficacy of sub-MICs of rosemary oil and 0.5% CS phytosomes at ¾ MIC, ½ MIC, and ¼ MIC in inhibiting the formation of robust biofilms produced by E. coli, a crystal violet staining assay was used. In contrast with the management, the CS nanophytosomes considerably inhibited biofilm formation in any respect concentrations (one-way ANOVA, p < 0.001), as proven in Fig. 3. In contrast with these of rosemary oil, the biofilm formation of the CS nanophytosomes additionally considerably decreased in any respect concentrations (p < 0.01). The numerous variations noticed between ¼ MIC and ½ MIC, in addition to between ¼ MIC and ¾ MIC (p < 0.001), of the CS nanophytosomes urged that decrease sub-MIC concentrations of CS phytosomes could also be more practical at inhibiting biofilms produced by MDR E. coli. Nonetheless, no important distinction was discovered between the ½ MIC and ¾ MIC (p > 0.05), indicating that growing the focus of CS nanophytosomes past a sure level could not present any extra advantages when it comes to biofilm inhibition. Total, these outcomes counsel that using sub-MIC concentrations of CS nanophytosomes may very well be a promising technique for stopping the formation of robust biofilms by MDR E. coli. Moreover, the addition of chitosan into nanophytosomes enhances its means to penetrate the biofilm matrix extra successfully by means of electrostatic interactions between positively charged chitosan molecules and negatively charged biofilm constituents which include extracellular polysaccharides, proteins, and DNA [48]. Alternatively, rosemary oil comprises bioactive metabolites with antimicrobial properties that would work together with bacterial cell membranes, disrupt genetic materials and nutrient transport resulting in compromised bacterial cell performance and structural integrity [49]. Due to this fact, incorporating rosemary oil into nanoformulation could increase synergistic antimicrobial efficacy.
Fourier rework infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopy
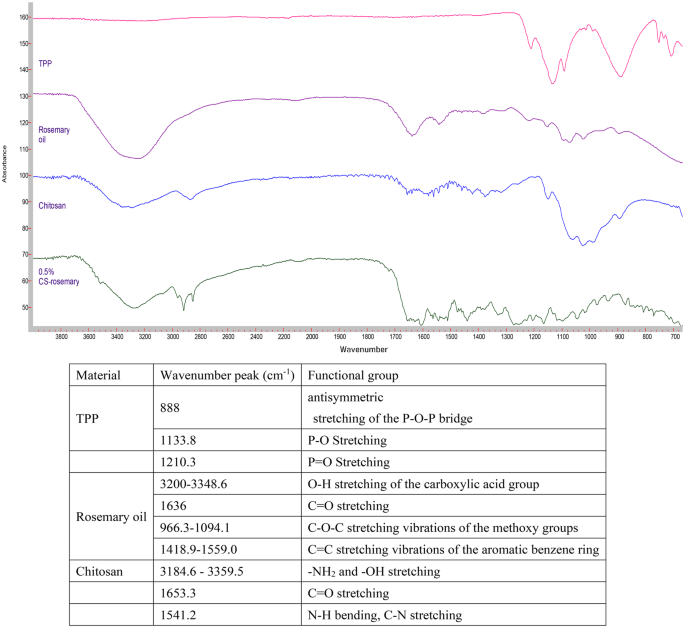
The FTIR spectra of TPP, rosemary oil, CS, and 0.5% CS nanophytosomes are offered in Fig. 4. The phosphate teams within the TPP molecule exhibit peaks at 888 cm− 1, 1133.8 cm− 1, 707.3 cm− 1, 752.4 cm− 1, and 1210.3 cm− 1 on account of their totally different vibrational modes [50]. The FTIR spectrum of the extracted rosemary oil confirmed the attribute absorption peaks of three,5-Dimethoxybenzoic acid which was the foremost element of the extracted rosemary oil. It’s an fragrant carboxylic acid with two methoxy (OCH3) substituents on the 3 and 5 positions of the benzene ring [51]. A broad absorption band noticed at round 3200–3348.6 cm− 1 equivalent to the O-H stretching vibration of the carboxylic acid group. A powerful absorption peak at 1636 cm− 1 equivalent to carbonyl double bond (C = O) stretching. Many absorption peaks appeared round 966.3–1094.1 cm− 1 had been associated to the C-O-C stretching vibrations of the methoxy teams. There have been additionally a number of absorption bands in between 1418.9 and 1559.0 cm− 1 equivalent to the C = C stretching vibrations of the fragrant benzene ring. Our FTIR examine outcome was much like the printed literature on rosemary oil [52]. FTIR absorption peaks in rosemary oil is accessible within the supplementary recordsdata.
Alternatively, the spectrum of pure chitosan exhibited the attribute broadband with peaks round 3184.6–3359.5 cm− 1 on account of amino (-NH2) and hydroxyl (-OH) stretching. A weak band with a peak at 1653.3 cm− 1 corresponds to the C = O stretching vibration and a powerful band at 1541.2 cm− 1 signifies the presence of an amide bond with the N-H bending vibration and C-N stretching vibration of the amide teams [53]. Evaluating the FTIR spectrum of the pure chitosan and CS-nanophytosomes, we recognized barely modifications within the absorption bands, their positions, intensities, and shapes which may present insights into the character and extent of the ionic interactions occurring within the CS-nanophytosomes. These modifications had been demonstrated by the shifts in a number of attribute absorption bands within the FTIR spectrum. The form of the absorption bands of CS-nanophytosomes had been changing into broader and extra advanced in comparison with the pure chitosan because of the presence of a number of overlapping vibrations. As well as, a brand new absorption band appeared at 1517.7 cm− 1 indicated the formation of ionic interactions between the amino group of chitosan and the carboxylate group of rosemary oil, equivalent to the uneven stretching of the carboxylate group.
In vitro drug launch
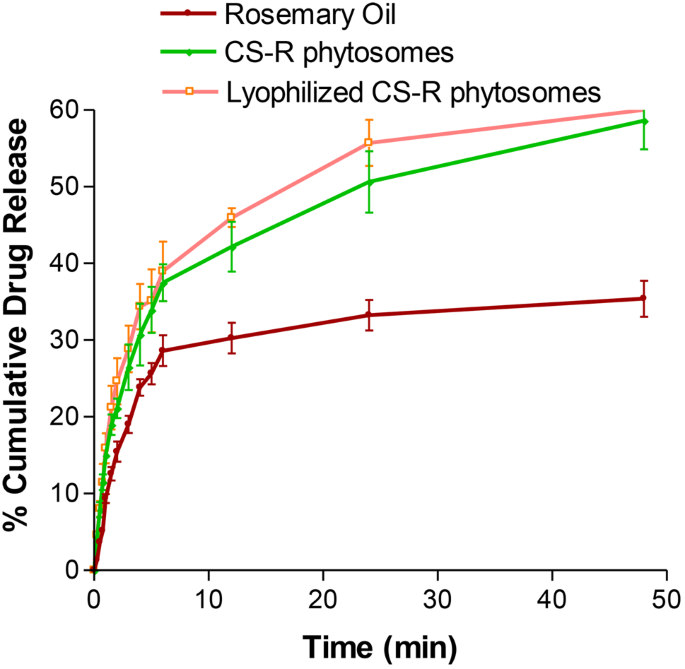
The discharge of rosemary oil, CS nanophytosomes, and lyophilized CS nanophytosomes over a 48-h interval is proven in Fig. 5. Pure rosemary oil had a considerably decrease proportion of 35.4 ± 2.36% launch over 48 h, whereas the CS nanophytosomes and lyophilized CS nanophytosomes had markedly better percentages of 58.6 ± 3.69% and 56.9 ± 5.01%, respectively (p < 0.001). This may be attributed to the hydrophilic nature of the nanophytosomes as a result of the oil is trapped within the chitosan nanoparticles; due to this fact, a rise within the launch of rosemary oil from the nanophytosomes happens when they’re involved with water. Moreover, there was no statistically important distinction between the drug launch of the unlyophilized and reconstituted lyophilized CS nanophytosomes (t-test, p > 0.05). These outcomes counsel that the freeze-drying course of didn’t adversely have an effect on drug launch or induce any important modifications within the nanophytosomes.
Value noting that the drug launch profiles of all of the examined samples confirmed an preliminary speedy launch inside the first 6 h, adopted by a extra sustained launch. This preliminary burst launch of the drug might promptly improve the specified plasma focus in a short while, which is essential for successfully combating infections. Furthermore, the next sustained launch after 6 h would possibly present extra advantages by sustaining the dose for an extended time, thereby decreasing the potential for unwanted side effects. These findings additionally spotlight the potential of CS nanophytosomes as a promising drug supply system.
The drug launch kinetics of the CS nanophytosomes had been analyzed utilizing 5 mathematical fashions: zero order, first order, Higuchi, Korsmeyer–Peppas, and Hixson–Crowell [54]. The mannequin with the very best correlation coefficient (R2) was thought of the best-fitting mannequin. The outcome confirmed that the general drug launch of the CS nanophytosomes over 48 h was greatest fitted by the first-order kinetic mannequin, with an R2 of 0. 0.9807, indicating that the speed of drug launch is instantly proportional to the quantity of drug remaining within the formulation. Nonetheless, the drug launch exhibited two patterns, with an preliminary quick launch adopted by a later regular launch. Due to this fact, the kinetic fashions had been reapplied to those two patterns individually. For each the preliminary speedy launch inside 6 h and the next sluggish launch after as much as 48 h, the Higuchi mannequin was the very best match, with R2 values of 0.9915 and 0.9938, respectively. This counsel that drug launch from CS nanophytosomes is strongly influenced by diffusion by means of the chitosan hydrogel matrix within the nanoformulation.
Bodily stability examine
The results of lyophilization on the soundness of the CS nanophytosomes had been evaluated by measuring the PS, ZP, and PDI for 3 months at room temperature (Desk 5). The information confirmed that there was no important distinction within the PS, ZP, or PDI between unlyophilized and lyophilized CS nanophytosomes (p > 0.05). Nonetheless, upon storage, each samples exhibited important modifications within the PS and ZP (p < 0.001). The PS elevated from 22.54 ± 2.92 nm to 339.33 ± 23.16 nm for unlyophilized CS nanophytosomes and from 45.66 ± 3.26 nm to 352 ± 30.25 nm for lyophilized CS-R nanophytosomes in three months. Though there have been no seen bodily modifications in any of the samples saved for 3 months, it’s anticipated that reorganization of inter/intramolecular hydrogen bonding and extra intermolecular entanglement of the CS particles may need occurred throughout long-term storage, resulting in particle agglomeration. Moreover, the residual moisture within the freeze-dried samples might additionally have an effect on the PS of the CS nanophytosomes. The ZP of the lyophilized CS nanophytosomes was decreased from a contemporary pattern of 12.36 ± 0.14 to six.03 ± 0.05 mV after three months. The presence of extra impartial floor prices across the CS nanophytosomes throughout storage may not have the ability to forestall aggregation because of the absence of an interparticle repulsive drive. Moreover, a narrowing of the PDI was noticed in each unlyophilized and lyophilized CS nanophytosomes after three months, which may be attributed to the presence of extra unified bigger nanoparticles.
Basically, nanoparticles have a excessive surface-to-volume ratio, which makes them susceptible to aggregation over time. Because the nanoparticles mixture, the general floor area-to-volume ratio modifications, ensuing within the discount of zeta potential. Throughout storage, ions or different molecules within the formulation could also be adsorbed onto the floor of CS nanophytosomes, resulting in a change within the zeta potential. The alter in PS and ZP throughout storage could also be additionally on account of different components akin to temperature variations, publicity to gentle, humidity and water content material within the formulation, impacting the efficacy of rosemary nanophytosomes. To keep up a constant zeta potential, a number of methods can be utilized sooner or later research, akin to incorporating stabilizing brokers within the formulation, use of floor coating approach, and acceptable management the storage circumstances, akin to temperature, pH, gentle and ionic power of the storage medium to optimize the storage stability.
In vivo UTI examine
Urine evaluation of WBCs
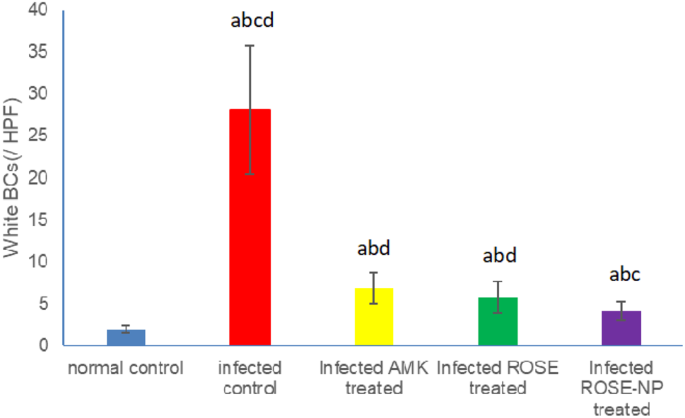
The untreated rats contaminated with UTI (Group II) exhibited a big improve in WBC rely (28.33 ± 4.12/HPF) in comparison with wholesome rats (2.08 ± 0.81/HPF) (P < 0.001). Upon remedy, contaminated rats receiving both amikacin (Group III) or pure rosemary oil (Group IV) demonstrated substantial reductions in urine WBC rely (6.83 ± 1.29/HPF and 5.83±/HPF, respectively). Curiously, no statistical distinction was noticed between the WBC counts in these two remedy teams (p > 0.05), suggesting that rosemary oil has the same impact in decreasing WBC rely as amikacin. Notably, probably the most important discount in WBCs occurred in Group V (4.17 ± 0.91/HPF), the place rats had been handled with CS nanophytosomes, in comparison with Group II (P < 0.001). The WBC rely was considerably decreased by CS nanophytosomes compared to both Group III or Group IV (p < 0.05). This discovering highlights the improved antibacterial impact of rosemary when delivered through CS nanophytosomes (Fig. 6). CS nanophytosomes successfully interacted with cell membranes, disrupting their construction and performance, resulting in leakage of mobile parts [55].
Impact of remedy with amikacin (AMK), rosemary oil (ROSE) and CS- Nanophytosomes on WBC’s rely within the urine on contaminated rats (n = 6). a: important distinction in comparison with regular management. b: important distinction in comparison with contaminated management. c: important distinction in comparison with contaminated AMK handled group. d: important distinction in comparison with contaminated ROSE handled group (p < 0.001)
Biochemical evaluation
We investigated the influence of various remedies on key biochemical markers related to UTI. Desk 6 presents a complete overview of the urea, creatinine, CRP, MDA, TAC, and IL-10 ranges throughout the 5 teams. In comparison with Group I, Group II rats exhibited elevated serum ranges of each urea and creatinine, indicating compromised kidney perform because of the an infection. All remedy cohorts (Teams III-V) confirmed a big discount in creatinine ranges in comparison with Group II (p < 0.001). Nonetheless, amikacin (Group III), a constructive management antibiotic, didn’t considerably enhance urea ranges in comparison with Group II (p > 0.05). Amikacin is thought to have nephrotoxic results, because it stays unmetabolized within the physique, resulting in its accumulation within the proximal tubule upon excretion in urine, the place it generates free radicals inflicting renal injury [56]. Conversely, rosemary oil, notably when delivered through CS nanophytosomes (Group V), normalized the serum concentrations of each urea and creatinine, underscoring its important nephroprotective attributes. This remark aligns with the findings reported by Abdel-Azeem AS et al. [57], suggesting that rosemary oil could modulate intracellular pathways related to DNA restore to ameliorate glomerular perform and mitigate renal damage. Moreover, rosemary oil has demonstrated the power to activate the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway, thereby upregulating the expression of assorted protecting genes and bolstering the efficacy of the endogenous mobile antioxidant protection system [58]. Furthermore, the administration of CS nanophytosomes additional enhanced the restoration of kidney perform to baseline ranges subsequent to UTI.
Reactive oxygen species (ROS) play a significant position in numerous organic processes, together with apoptosis, immunity, and protection mechanisms towards pathogens. Nonetheless, elevated ROS ranges can result in mobile injury and oxidative stress (OS). Antioxidants sourced from endogenous or exogenous origins can act as protecting shields and mitigate the detrimental impacts of OS [59]. Furthermore, there exists a connection between oxidative stress (OS) and irritation. These two processes are intently linked, typically influencing one another. The connection between OS and irritation entails a constructive suggestions loop: irritation generates ROS, which, in flip, exacerbate irritation. Basically, OS could be evaluated by testing MDA ranges, the first marker of lipid peroxidation attributable to ROS, and TAC ranges which displays the physique’s means to counteract ROS [60].
An infection led to a rise in serum MDA and a lower in TAC ranges had been noticed in Group II rats, indicating OS. In opposite, all remedy teams (Teams III-V) exhibited a big lower in MDA ranges and a rise in TAC ranges in comparison with Group II (p < 0.001), with Group V displaying probably the most pronounced enchancment, the place TAC ranges approached virtually regular ranges in comparison with Group I (p > 0.05). Amikacin and rosemary oil successfully alleviated OS by means of their antibacterial and anti inflammatory properties. Rosemary oil, particularly, demonstrated a stronger antioxidant impact than Amikacin, additional enhanced when delivered through CS nanophytosomes. Rosemary oil comprises lively phytochemicals akin to flavonoids, polyphenols, and diterpenes, with robust antioxidant properties. These phytochemicals exhibite antioxidant capabilities by electron donation to reactive radicals, thereby decreasing their reactivity, enhancing stability, and minimizing interactions with important biomolecules akin to DNA, lipoproteins, and polyunsaturated fatty acids [61].
Moreover, the elevation of CRP and IL-10 ranges are used to evaluate the development of irritation. UTI typically ends in irritation as a response to bacterial invasion, resulting in irritation. When micro organism infiltrate the physique, macrophages launch cytokines like IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α. These cytokines provoke a collection of inflammatory cascade by means of autocrine and paracrine mechanisms. Though this response goals to remove the an infection, it could possibly additionally end in substantial hurt to the host tissue [62].
CRP is an acute-phase inflammatory protein that turns into elevated throughout numerous inflammatory circumstances, together with cardiovascular illnesses, rheumatoid arthritis, and infections [63]. Alternatively, IL-10 is an anti-inflammatory cytokine which performs an important position in regulating irritation throughout UTIs. On this examine, untreated UTI rats (Group II) confirmed a big improve in CRP ranges and a lower in IL-10 ranges in comparison with these in regular management rats (Group I) (p < 0.001). In distinction, all remedy teams (Teams III-V) demonstrated a big lower in CRP ranges and a rise in IL-10 ranges, with Group V handled with CS nanophytosomes exhibiting probably the most outstanding enchancment in comparison with the untreated rats in Group II (p < 0.001).
The antibacterial impact of each amikacin and rosemary oil results in alleviation of irritation, nonetheless, rosemary oil has extra anti-inflammatory mechanisms which have been documented [64]. It exerts anti-inflammatory exercise by means of the discount of the transcription issue NK-κB, hindering the pro-inflammatory mediators, akin to TNF-α, IL-1β, synthesis and inhibiting synthesis of COX-2 enzyme, resulting in lower of arachidonic acid-metabolites downstream manufacturing [65]. The flexibility of rosemary oil to neutralize the reactive species generated throughout irritation by its anti-oxidant properties may additionally mitigate injury attributable to irritation [66]. Moreover, the anti-inflammatory impact was enhanced when rosemary oil was delivered through nanophytosomes on account of improved bioavailability.
Histopathological examination
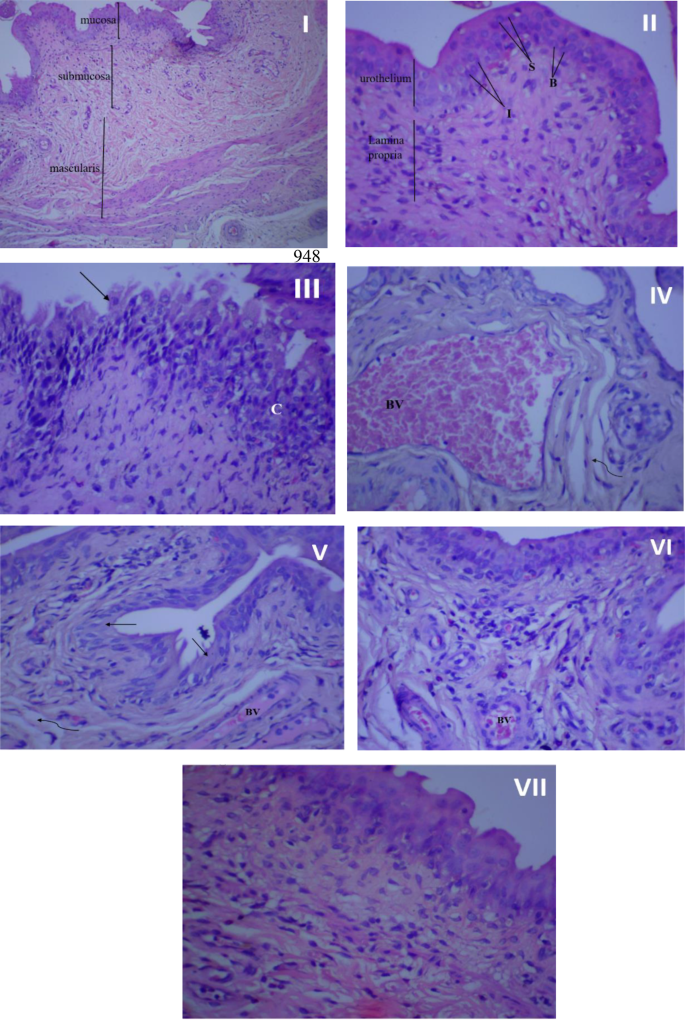
Determine 7 illustrates the histopathological findings of the rat urothelial mucosa. The bladder tissue of rats within the management teams (I, II) appeared regular, devoid of hyperplasia or inflammatory cells. Nonetheless, following an infection, the bladder tissues suffered important injury, characterised by necrosis, urothelium desquamation, inflammatory cell infiltration, fibrosis, and congested blood vessels (III, IV). Remedy with amikacin (V), rosemary oil (VI), or CS-R nanophytosomes (VII) mitigated these pathological modifications. Amongst these remedies, the CS-R nanophytosome-treated rats exhibited probably the most outstanding enchancment, displaying a considerably enhanced and well-defined urinary bladder structure.
Histopathological examination of rat’s urothelial mucosa. (I) Regular bladder tissue (no an infection and no remedy), x100 magnification. (II) Regular bladder tissue, x 400 magnification. (III) Bladder urothelium within the contaminated management group with persistent irritation (C) in lamina propria, and urothelium desquamation (↑), x 400 magnification. (IV) Bladder urothelium within the contaminated management group displaying dilated, congested blood vessel (BV), and gentle fibrosis (wavy arrow). (V) Urinary bladder of rat handled with amikacin displaying average irritation in lamina propria, desquamation of urothelium (↑), gentle fibrosis (wavy arrow) and congested blood vessels (BV), x 400 magnification. (VI) urinary bladder of rosemary oil handled rat displaying many inflammatory cells beneath to urothelium, small congested blood vessel (BV) and Intact urothelium, x 400 magnification. (VII) urinary bladder of CS nanophytosomes handled rat displaying important enchancment with well-defined urinary bladder structure and a few inflammatory cells in lamina propria, x 400 magnification
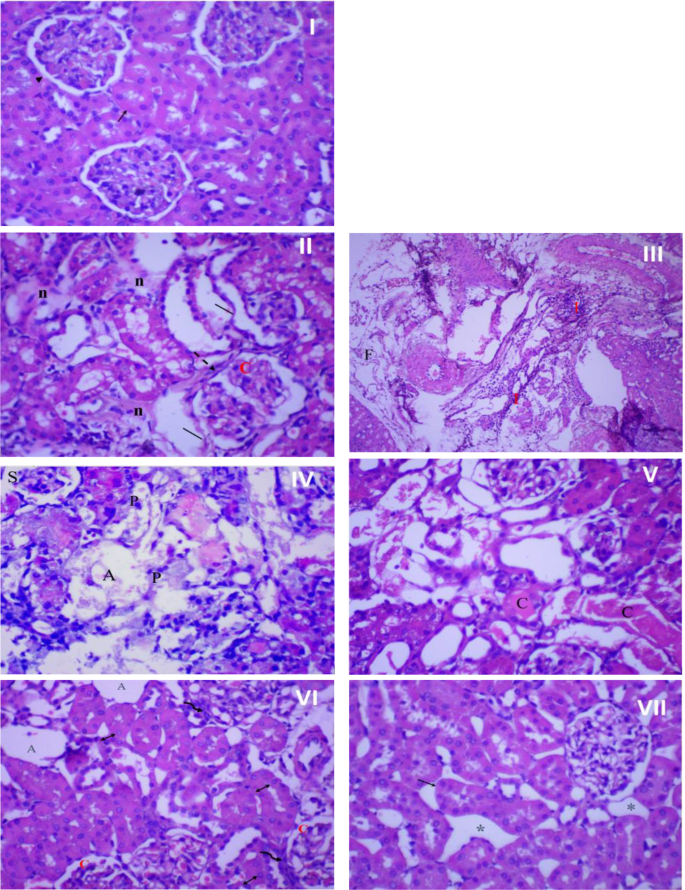
Determine 8 presents the histopathological examination outcomes of rat kidney tissue. Within the management group (I), the kidney tissue confirmed a traditional construction with a wholesome epithelial lining. Nonetheless, an infection resulted in important kidney tissue injury characterised by necrosis, architectural loss, and infiltration of inflammatory cells (II), accompanied by fibrosis and congested blood vessels (III). Curiously, the influence of amikacin remedy on kidney tissue differed from its impact on bladder tissue. Within the kidneys, the renal tubules had been broken, shrank, and atrophied, with pyknotic nuclei in most cells (IV, V). Nonetheless, remedy with rosemary oil (VI) or CS nanophytosomes (VII) alleviated these pathological modifications. Probably the most substantial enchancment was noticed in rats handled with CS nanophytosomes (VII). These rats exhibited a dramatic enchancment with well-defined renal tubules displaying gentle dilatation and spacing between them. The improved structure of each the kidney and bladder, noticed in CS nanophytosomes, helps their antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, and nephroprotective results, as demonstrated in our examine.
Histopathological examination of rat’s kidney. (I) Regular kidney tissue (no an infection and no remedy) displaying regular kidney structure of proximal tubules (↑) with regular epithelial lining, and glomerulus (►), x 400 magnification. (II) Kidney within the contaminated management group displaying extreme injury with lack of kidney structure, gentle necrosis (n), congested glomerulus (C) with thick glomerulus wall (sprint arrow), and enlarged, disorganized, desquamated (│) renal tubules, x 400 magnification. (III) Kidney within the contaminated management group displaying extreme irritation (I) and fibrosis (F), x 100 magnification. (IV) Kidney of rat handled with amikacin displaying injury and disorganization of kidney tubules, shrank (S), and atrophied (A) glomeruli. Most cells displaying pyknotic (P) nuclei, x 400 magnification. (V) kidney of rat handled with amikacin displaying extreme and widespread necrosis of tubular epithelial cells. Most cells lose its structure with solid (C) formation, x 400 magnification. (VI) kidney of rosemary oil handled rat displaying atrophied (A) and congested (C) glomeruli surrounded by inflammatory cells (wavy arrow) and tubular dilatation with vesiculated nuclei (↕), x 400 magnification. (VII) kidney of CS nanophytosomes handled rat displaying dramatic enchancment, well-defined renal tubules with gentle dilatation (↑) and spacing (*) between tubules, x 400 magnification