After a earlier model of this information put face-to-face chips from Qualcomm, MediaTek, Apple, Samsung, and Huawei/HiSilicon, a bunch of issues modified within the smartphone part area, notably the arrival of Google, the dying and rebirth of flagship chips from Huawei as a consequence of US sanctions, and Samsung getting back from a hiatus from the flagship area. First, let’s check out an general specs comparability of right this moment’s contestants.
Snapdragon vs. Dimensity vs. Exynos vs. Tensor vs. Apple: Specs In contrast
| Late 2024 ~ Early 2025 | Late 2023 ~ Early 2024 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Product |
MediaTek Dimensity 9400 |
Apple A18 Professional |
Google Tensor G4 |
Qualcomm Snapdragon 8 Gen 3 |
Samsung Exynos 2400 |
HiSilicon Kirin 9000S |
MediaTek Dimensity 9300 rgb(236, 148, 48) |
Google Tensor G3 |
Apple A17 Professional |
| Prime core | 1x Cortex-X925 @ 3.62 GHz | 2x Apple Everest @ 4.05 GHz | 1x Cortex-X4 @ 3.1 GHz | 1x Cortex-X4 @ 3.3 GHz | 1x Cortex-X4 @ 3.2 GHz | 1x Taishan V120 @ 2.62 GHz | 1x Cortex-X4 @ 3.25 GHz | 1x Cortex-X3 @ 2.91 GHz | 2x Apple Everest @ 3.78 GHz |
| Efficiency core | 3x Cortex-X4 @ 3.3 GHz | 3x Cortex-A720 @ 2.6 GHz | 3x Cortex A720 @ 3.15 GHz 2x Cortex A720 @ 2.96 GHz |
2x Cortex A720 @ 2.9 GHz 3x Cortex A720 @ 2.6 GHz |
3x Taishan V120 @ 2.15 GHz | 3x Cortex-X4 @ 2.85 GHz | 4x Cortex-A715 @ 2.37 GHz | ||
| Effectivity core | 4x Cortex-A720 @ ? | 4x Apple Sawtooth @ 2.42 GHz | 4x Cortex-A520 @ 1.92 GHz | 2x Cortex-A520 @ 2.3 GHz | 4x Cortex-A520 @ 1.95 GHz | 4x Cortex-A510 @ 1.53 GHz | 4x Cortex-A720 @ 2.0 GHz | 4x Cortex-A510 @ 1.7 GHz | 4x Apple Sawtooth @ 2.11 GHz |
| RAM | LPDDR5x-10667 4x 16-bit @ 5333 MHz (85.4 GB/s) |
LPDDR5x-7500 4x 16-bit @ 3750 MHz (60 GB/s) |
LPDDR5x 4x 16-bit |
LPDDR5x-9600 4x 16-bit @ 4800 MHz (76.8 GB/s) |
LPDDR5x-8533 4x 16-bit @ 4266 MHz (68.2 GB/s) |
LPDDR5x-8533 4x 16-bit @ 4266 MHz (68.2 GB/s) |
LPDDR5T-9600 4x 16-bit @ 4800 MHz (76.8 GB/s) |
LPDDR5x-8533 4x 16-bit @ 4266 MHz (68.2 GB/s) |
LPDDR5x-6400 4x 16-bit @ 3200 MHz (51.2 GB/s) |
| GPU | 12x ARM Immortalis-G925 | 6x Apple GPU (2227 GFLOPS) |
7x ARM Mali-G715 | Adreno 750 (2774 GFLOPS) |
AMD RDNA3 (3406 GFLOPS) |
HiSilicon Maleoon 910 (1536 GFLOPS) |
12x ARM Immortalis-G720 (3993.6 GFLOPS) |
7x ARM Mali-G715 | 6x Apple GPU (2147 GFLOPS) |
| 5G modem | MediaTek (7/3.5 Gbps) |
Exterior Snapdragon X71 (10/3.5 Gbps) |
Exterior Exynos 5400c | Snapdragon X75 (10/3.6 Gbps) |
Exterior Exynos 5153 (12/3.67 Gbps) |
Balong 5000 | MediaTek (7/3.5 Gbps) |
Exterior Exynos 5300i | Exterior Snapdragon X71 (10/3.5 Gbps) |
| Wi-fi connectivity | Wi-Fi 7 Bluetooth 5.4 |
Exterior Wi-Fi 7 Bluetooth 5.3 |
Wi-Fi 7 Bluetooth 5.3 |
Wi-Fi 7 Bluetooth 5.4 |
Wi-Fi 6E Bluetooth 5.3 |
Wi-Fi 6 Bluetooth 5.2 |
Wi-Fi 7 Bluetooth 5.4 |
Wi-Fi 7 Bluetooth 5.3 |
Exterior Wi-Fi 6E Bluetooth 5.3 |
| Course of node | TSMC N3E | TSMC N3E | Samsung 4LPP+ | TSMC N4P | Samsung 4LPP+ | SMIC N+2 (“7nm”) | TSMC N4P | Samsung 4LPP | TSMC N3B |
SoC components
Cellular system-on-chip (SoC) design has been fairly steady prior to now few years, with most chip producers following the same multi-core design with many specialised blocks devoted to offloading processing duties from the central processing unit (CPU):
- Graphics Processing Unit (GPU): Answerable for accelerating visible calculations, particularly 3D rendering.
- Picture Sign Processor (ISP): Course of information captured from the digital camera sensors.
- Digital Sign Processor (DSP): Course of information obtained from different sensors, typically employed for media and/or communication processing.
- Neural Processing Unit (NPU) (aka AI Accelerator): Specialised in synthetic intelligence and machine studying duties.
- Modem: Answerable for including help for mobile networks (e.g. 4G/LTE, 5G Sub-6 GHz, 5G mmWave…).
CPU cores are generally break up between effectivity cores and efficiency cores, with the primary consuming significantly much less vitality however not significantly quick. Heavier duties are offloaded when essential to the efficiency cores, with Android chips adopting a 3rd tier of even sooner CPUs denominated as “Prime cores”.
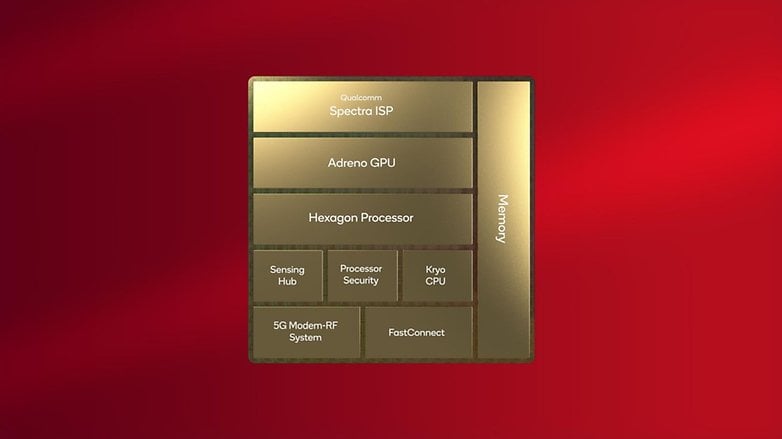
For nearly 10 years, all smartphones from conventional manufacturers have used the identical CPU structure: ARM. Nonetheless, not all ARM CPUs are equal. Apple, for instance, designs its personal CPU cores which can be appropriate with the ARM instruction set, whereas the Android suppliers undertake reference CPU cores from ARM, often called the Cortex cores.
With the success of Apple’s in-house designs, each Qualcomm and Samsung are anticipated to as soon as once more supply customized ARM designs, one thing that mirrors the early days of Android SoCs with Qualcomm Krait and Samsung Mongoose cores. As of 2024, ARM’s reference cores for cell processors are break up between Cortex-X, Cortex A7xx, and Cortex-A5xx cores for prime, efficiency, and effectivity cores, respectively.
Prior to now three years, Android flagship SoCs had one predominant differentiating issue when in comparison with mid-range chips: The prime cores. Qualcomm’s launch of the Snapdragon 7+ Gen 2, nonetheless, made that distinction out of date, however that chip nonetheless contains a barely much less succesful GPU, ISP, and modem in comparison with the corporate’s flagship choices.
Manufacturing course of
One other area wherein Apple has the higher hand is the fabrication course of it makes use of, extra particularly, the preferential therapy it has with the world’s most superior chip producer, Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Firm (TSMC). Because of its sheer scale, with chips for smartphones, tablets, and now even PCs, Apple has dibs on utilizing the latest course of nodes from the Taiwanese firm.
Newer processes often translate into extra transistor density—the flexibility to pack extra cores, cache, and different buildings, or just match extra chips into the identical space—, greater processing frequencies, and/or much less energy consumption.
Apple had the primary shopper processors made on TSMC’s 7-nm—technically introduced after a Huawei Kirin chip, however reaching shops first—, 5-nm, and 3-nm, the latter used for the present A17 processor used on the iPhone 15 Professional fashions. The identical privilege additionally applies to mid-cycle refreshes of these generations, such because the extra environment friendly N3E course of used on the A18 chips for the iPhone 16 household, adopted quickly after by the Dimensity 9400 chip.
This new MediaTek flagship confirmed how far the partnership with its countrymen at TSMC developed, as MediaTek’s chips have been historically one course of node behind Apple’s. Prior to now, the corporate was identified for not having energy-efficient processors, however that was influenced through the use of outdated fabrication processes from each TSMC and UMC, additionally from Taiwan. The Dimensity chips, then again, are fabbed utilizing trendy processes, making them aggressive in vitality consumption.
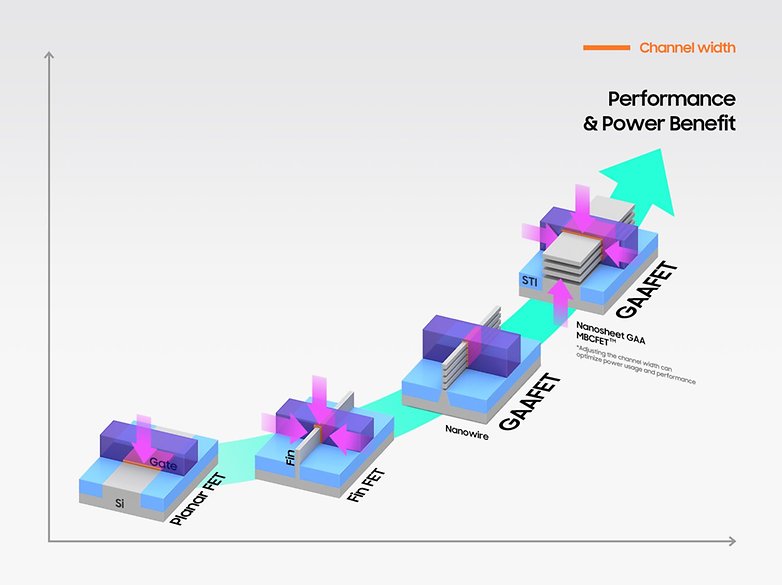
Qualcomm, for its half, often maintains a foundry-agnostic technique, with manufacturing booked in keeping with availability. The Snapdragon 888/888+ and eight Gen 1, for instance, have been made by Samsung Foundry, however their successor, the Snapdragon 8+ Gen 1 makes use of TSMC’s N4 course of, leading to much less energy consumption and warmth dissipation.
Samsung’s in-house chips (from its LSI division) are clearly made by Samsung Foundry, which for the previous few years has not been aggressive with TSMC’s nodes from the identical “nm” era. The South Koreans are optimistic, nonetheless, that its 3 nm-class course of will supply a 45% enchancment in energy utilization, which might be a welcome evolution in cellphones.
As for Google, because the Tensor cell chips are based mostly on Samsung LSI’s merchandise, its processors are additionally fabbed by Samsung Foundry, with rumors suggesting a future change to TSMC, time will inform. Tensor chips often distinguish themselves from Exynos SoCs by using completely different CPU and GPU clusters, and most significantly, Google’s in-house Tensor NPU.
Huawei, for its half, is soldiering on within the SoC area, getting a lot of headlines for its “7nm” chip, made by Chinese language foundry SMIC. Nonetheless, the identical US sanctions that stopped them from contracting TSMC to make chips additionally block Huawei’s subsidiary HiSilicon from licensing trendy ARM CPU and GPU cores. Our exams with a Kirin 9000WL-powered system revealed a efficiency stage on par with mid-range chips just like the Snapdragon 7 collection or the Exynos 1480.
GPU developments
Prior to now two years, cell processors joined the pattern in PC GPUs to undertake ray tracing (RT) and different rendering options present in trendy GeForce and Radeon graphics playing cards. Regardless of not anticipating to see desktop-level graphics anytime quickly in cell gadgets, there have been a few fascinating developments that got here with that pattern.
The primary one was AMD becoming a member of the cell SoC area with its Radeon GPUs on the Samsung Exynos 2200, utilizing the identical RDNA2 structure—though with far fewer cores—on the most recent PlayStation and Xbox consoles. Samsung’s retreat from the flagship cell SoC area, nonetheless, meant that it did not have a follow-up till two years later, with the Exynos 2400 chip used on the Galaxy S24 fashions packing an RDNA3 GPU.
Qualcomm’s Adreno GPUs comply with their very own path, with only a few publicly obtainable particulars in terms of specs. Current generations help ray tracing, alongside different superior options, making them additionally appropriate to be used in different Snapdragon chips designed for Home windows laptops.
MediaTek principally makes use of ARM’s reference GPUs in its Dimensity vary, with the newer Dimensity 9300/9400 powered by 12 cores of the RT-capable ARM Immortalis GPU. Prior to now, the Helio SoC household featured significantly fewer ARM Mali GPU cores than its Exynos and Kirin rivals, resulting in decrease efficiency, one thing that the flagship Dimensity fashions are altering due to a extra premium positioning and superior TSMC nodes.
Google would not fairly match with different SoC manufacturers within the Android area, happening a unique tempo on GPUs similar to on the CPU cores. The Tensor chips function a comparatively low seven GPU cores from ARM Mali household, so it’s incompatible with the identical options obtainable on its rivals.
Apple would not disclose a lot about its in-house GPU designs, which share a variety of historical past with old-school PowerVR video processors. iPhone GPUs are however very succesful when it comes to options, sharing their core design with the bigger Apple M chips used on Mac PCs.
AI all over the place

With synthetic intelligence (AI) and machine studying (ML) much more within the highlight than in earlier years due to Steady Diffusion and ChatGPT, the significance of AI-dedicated cores is just anticipated to extend. In that regard, flagship cell chips have been getting more and more extra highly effective in ML duties due to devoted cores akin to Apple’s Neural Engine, Qualcomm’s Hexagon, MediaTek’s NPU, and Google’s TPU.
Sadly, manufacturer-advertised numbers are usually not comparable between manufacturers, with Apple saying 16 trillion operations per second (TOPS) on its A16 Bionic chip, whereas Qualcomm’s numbers used to incorporate processing accomplished between the DSP, CPU, and GPU till the corporate stopped disclosing TOPS numbers for its Snapdragon chips.
Regardless, anticipate corporations to maintain promoting AI options on chips, throwing daring claims on efficiency enhancements, whereas working programs and apps attempt to catch up in supporting them.
Diminishing returns?
Flagship processors are certain to maintain advancing within the subsequent few years, particularly with the return of customized designs from Qualcomm and Samsung, and AI taking the highlight. Nonetheless, it stays to be seen if software program help will be capable to sustain since these developments often take a variety of time to succeed in mainstream processors.
Moreover, extra devoted cores often imply extra transistors used, one thing that isn’t at all times economically viable with out additional advances in fabrication processes. Rumors round future era chips getting dearer persist, even whether it is the kind of info that’s secretly held between chip and telephone producers.
However, previous predictions about Qualcomm turning into a monopoly on Android’s flagship SoCs have been unsuitable, with competitors coming not solely from Samsung but in addition from MediaTek and newcomer Google. It’s a far cry from the aggressive panorama from 10 years in the past, however nonetheless some competitors to look ahead to.
Article up to date in October 2024 with new fashions launched because the final replace in April.

