Synthesis and characterization of E-Au NPs
For synthesis of E-Au NPs, EGCG first self-assembled below alkaline circumstances, adopted by speedy EGCG-Au coordination with HAuCl4, finishing the synthesis course of virtually instantaneously (Fig. 1A). Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) pictures revealed that the E-Au NPs had been uniform and spherical, with a mean dimension of 5.38 ± 0.86 nm (Fig. 1B and Fig. S2). Dynamic gentle scattering (DLS) evaluation confirmed constant dimension distribution of E-Au NPs in DI water, phosphate buffer resolution (PBS), and Luria-Bertani (LB), indicating E-Au NPs had its good dispersibility. The particle sizes of E-Au NPs in numerous options had been round 40 nm, extra important than the scale noticed through TEM, probably because of the robust adhesion of NPs to the hydration floor (Fig. S3). Fourier remodel infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR) revealed a blue-shift of the -OH absorption peak from 3432 cm-1 to 3420 cm-1 and a red-shift of the carbonyl (C = O) absorption peak from 1625 cm-1 to 1628 cm-1 in E-Au NPs comparability with EGCG (Fig. 1C). These adjustments recommend that carboxyl and hydroxyl teams possible performed a job within the synthesis and stabilization of E-Au NPs. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) confirmed E-Au NPs contained attribute peaks of O 1s, C 1s and Au 4f (Fig. S4). Exactly, within the Au 4f spectrum, peaks at 83.4 eV and 87.1 eV corresponded to the 2 states 4f7/2 and 4f5/2 of Au, indicating that the Au component in E-Au NPs contained each Au3+ and Au0 (Fig. 1D). This statement confirmed the formation of an Au-O bond between Au3+ and EGCG, which served as a essential facet within the synthesis of E-Au NPs. The UV-vis spectra of E-Au NPs displayed a attribute MPN ligand-to-metal charge-transfer band at roughly 530 nm, indicating a prevalent bis-state metal-phenolic coordination (Fig. 1E). The profitable synthesis of E-Au NPs was additional verified by way of X-ray Diffraction (XRD), revealing 4 extra broad peaks at 38.3°, 44.4°, 64.7°, and 77.6°, akin to the (111), (200), (220), and (311) planes of the Au lattice (JCPDS Card NO. 04–0784) (Fig. 1F).
Synthesis and characterization of E-Au nanoparticles. (A) Schematic illustration of artificial technique of E-Au NPs. (B) TEM picture of E-Au NPs, scale bar = 2 nm. (C) FT-IR spectra of EGCG and E-Au NPs. (D) Excessive-resolution XPS spectra of E-Au NPs. (E) UV–vis absorption spectra of EGCG and E-Au NPs. (F) XRD patterns of E-Au NPs. Thermal pictures (G) and corresponding temperature variation (H) of E-Au NPs with numerous concentrations (0–200 µg/mL) below 808 nm laser irradiation (1.0 W/cm2) for five min. (I) 5 cycles of heating/cooling photothermal curves of the E-Au NPs.
The photothermal properties of E-Au NPs was then investigated by regularly monitoring temperature fluctuations uncovered to 808 nm NIR laser irradiation. As proven in Fig. 1G, the temperature change of E-Au NPs below 808 nm infrared laser irradiation for five min was recorded utilizing an infrared digital camera. It was famous that E-Au NPs exhibited a concentration-dependent temperature enhance when subjected to NIR irradiation at 1.0 W/cm2. The temperature distinction (ΔT) of E-Au NPs was exactly quantified as 36.0 °C, whereas it solely barely elevated 3.3 °C for water (Fig. 1H). Moreover, the temperature change offered a power-density-dependent photothermal efficiency (Fig. S5). A comparability was additionally made between the temperature enhance of E-Au NPs and EGCG-Ag NPs irradiated for five min at 1.0 W/cm2 laser. The ΔT of EGCG-Ag NPs was measured at solely 5.0 °C, whereas E-Au NPs exhibited a temperature enhance of 25.1 °C. Moreover, E-Au NPs displayed secure and repeatable heating capability over 5 cycles of NIR irradiation on/off, indicating their potential for long-term photothermal purposes (Fig. 1I).
In vitro antibacterial and antibiofilm exercise of E-Au NPs
S. aureus, E. coli, and MRSA had been chosen to evaluate the antibacterial exercise of E-Au NPs. First, the bacterial progress curves had been monitored utilizing the optical density at 600 nm (OD600) at numerous concentrations of E-Au NPs. All these three bacterial strains, together with each Gram-positive and Gram-negative micro organism, had been inhibited in a dose-dependent method whereas E-Au NPs administration couldn’t fully inhibit bacterial replica (Fig. 2A-C, Fig. S6). The antibacterial exercise of E-Au NPs below NIR irradiation was evaluated by colony-forming models (CFUs) on LB-agar plates. The antibacterial results for S. aureus and E. coli had been considerably enhanced below NIR irradiation with the rise of E-Au NPs focus or laser irradiation time (Figs. S7–S10). After therapy with 200 µg/mL E-Au NPs plus laser irradiation (808 nm, 1.0 W/cm2, 2.5 min), each Gram-positive and Gram-negative micro organism had been virtually eradicated and the survival charges had been solely 0.06% for S. aureus, 3.38% for MRSA, and 0.02% for E. coli, respectively (Fig. 2D-G, Fig. S8–S10). Notably, the E-Au NPs below NIR irradiation antibacterial technique exhibited glorious antibacterial means to MRSA, which was multidrug-resistant and extremely pathogenic. These outcomes urged that E-Au NPs offered antibacterial efficacy to each Gram-positive and Gram-negative micro organism which may very well be additional synergetic strengthened by laser irradiation. Apart from, EGCG and Au3+ additionally exhibited sure antibacterial exercise which couldn’t fully eradicate the MRSA (Fig. S11).
In vitro antibacterial and antibiofilm actions of E-Au NPs. Development curves of S. aureus (A), E. coli (B) and MRSA (C) upon incubation with E-Au NPs at completely different concentrations. The images (D) and survival charge (E) of MRSA handled with E-Au NPs plus laser at diversified time (1.0 W/cm2, 200 µg/mL). The images (F) and survival charges (G) of MRSA handled with E-Au NPs (at diversified concentrations of 0, 25, 50, 100, 150 and 200 µg/mL, 1.0 W/cm2, 2.5 min). 3D confocal pictures (H) and thickness (I) of MRSA biofilms stained by SYTO 9 after completely different therapies, scale bar = 50 μm. (J) Pictures of MRSA biofilms stained by crystal violet after completely different therapies. (Knowledge are offered because the imply ± s. d., *p < 0.05, *** p < 0.001)
Biofilm performs a vital position by offering a protecting defend for micro organism throughout infections, so the anti-biofilm impact is crucial to the sensible utility of antibacterial brokers [38]. The effectiveness of E-Au NPs in opposition to MRSA biofilm was first verified utilizing morphological confocal pictures. In Fig. 2H and I, the management and NIR laser alone teams exhibited intact and dense biofilms with robust inexperienced fluorescence alerts, whereas E-Au NPs partially hindered biofilm formation, leading to a fragmented construction. In E-Au NPs plus laser group, the antibiofilm impact was additional enhanced, and the micro organism might barely kind a gentle biofilm with solely sporadic microcolonies existed. Apart from, the thickness of MRSA biofilm was 3.539 ± 1.415 μm with E-Au NPs therapy and the thickness considerably decreased after therapy with E-Au NPs plus laser (1.068 ± 0.771 μm) in contrast with the management group (8.325 ± 0.928 μm) and laser alone group (8.128 ± 1.364 μm). Contemplating that biofilm biomass is a vital consider biofilm formation, its discount was evident within the E-Au NPs plus laser group, as confirmed by crystal violet staining, aligning with the findings from the morphological confocal pictures (Fig. 2J, Fig. S12). Furthermore, the efficacy in opposition to matured biofilm, which was extra vital to deal with the an infection, was additional investigated (Fig. S13). As proven in micro and macro pictures, E-Au NPs plus laser therapy exhibited notable harmful impact to mature biofilms with the sparsest biofilms and the destruction charge was greater than 90%, indicating the wonderful antibiofilm means of E-Au NPs at each biofilm formation levels.
Potential antibacterial mechanism of E-Au NPs
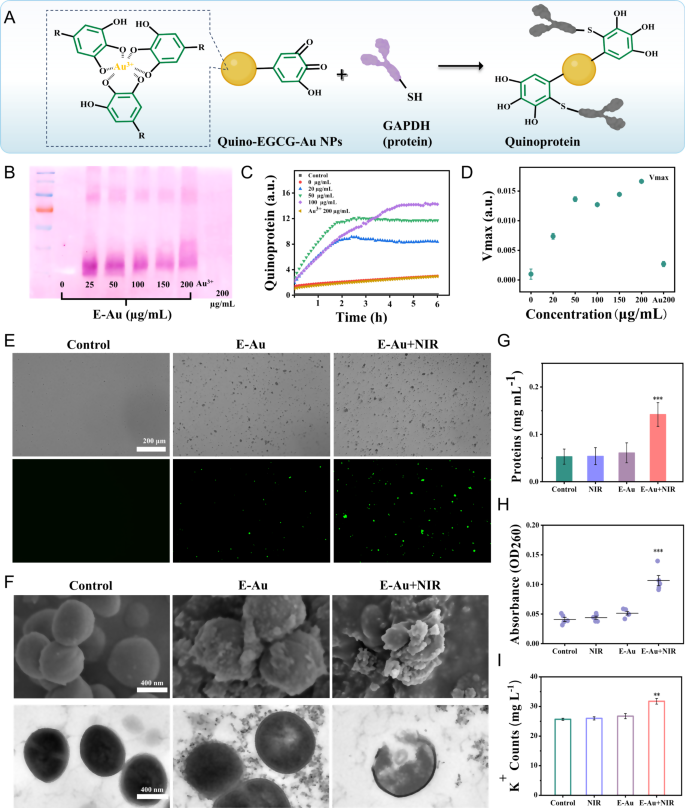
Based mostly on its glorious antibacterial properties, the doable mechanisms of the E-Au NPs had been investigated. The phenolic teams EGCG in E-Au NPs had been liable to bear oxidation to kind electron-deficient semiquinones within the presence of Au3+. These extremely reactive semiquinones might then bind with sulfhydryl residues of proteins, ensuing within the formation of quinoproteins (quinone–protein conjugates) (Fig. 3A). Though these quinoproteins have been reported to take part in a number of physiological processes, equivalent to apoptosis, their potential antibacterial results had not been additional investigated. To confirm and quantify the quantity of quinoproteins, a redox–biking staining assay was employed. This assay concerned that quinoproteins convert colorless nitroblue tetrazolium into insoluble purple formazan within the presence of glycine. Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) was used as a marked protein to chosen to detect the manufacturing of quinoprotein. Following incubation of E-Au NPs with GAPDH, the purple bands on the sodium dodecyl-sulfate polyacrylamide in agarose gel electrophoresis revealed concentration-dependent formation of quinoproteins (Fig. 3B). Subsequently, the manufacturing of quinoproteins in micro organism was additional evaluated by MRSA with E-Au NPs at various concentrations and recording the optical density at 530 nm. The outcomes confirmed a rise in quinoprotein ranges with increased concentrations and longer incubation time, with minimal quinoprotein manufacturing within the management and Au3+ alone group. This highlighted the essential position of phenolic ligands within the formation of quinoproteins (Fig. 3C, D).
Elucidation of the antibacterial modes of E-Au NPs in vitro. (A) Schematic illustration of the formation of quinoproteins owing to the polyphenols in E-Au NPs. (B) Qualitative evaluation of quinoprotein formation after therapy with E-Au NPs at completely different concentrations. (C) Quantitative evaluation of quinoprotein formation in MRSA throughout therapy with E-Au NPs. (D) Most charge of quinone protein manufacturing at completely different concentrations. (E) Brilliant-field and DCFH-DA staining pictures of ROS after completely different therapies, scale bar = 200 μm. (F) SEM and TEM pictures of MRSA with completely different therapies, scale bar = 400 nm. Leakage of protein (G), nucleic acids (H) and Ok+ (I) from MRSA with completely different therapies. (Knowledge are offered because the imply ± s. d., ** < 0.01, ***p < 0.001)
As well as, the NIR laser-induced phototherapy, together with each photodynamic and photothermal results, effectively boosted the antibacterial efficacy. As depicted in Fig. 3E and Fig. S14, there was no ROS fluorescence sign within the management group and only some alerts within the E-Au group. Nonetheless, the ROS fluorescence sign was considerably enhanced with the NIR laser because of the photodynamic impact. Elevated ROS ranges in cells can disrupt mobile physiological processes, assault key macromolecules, and harm the mobile construction of bacterial cells. Morphological examination of MRSA handled with E-Au NPs and laser irradiation was additional carried out by scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and TEM. As proven in Fig. 3F, SEM displayed intact micro organism with clean surfaces within the management group, whereas MRSA appeared shrunken and irregular after E-Au NPs therapy, and cells had been fragmented with disrupted cell constructions after therapy with E-Au NPs plus laser irradiation. Equally, TEM pictures revealed barely nonuniform MRSA cytoplasm after E-Au NPs therapy, with additional disruption and leakage of cytoplasm upon therapy with E-Au NPs plus laser irradiation. The unfinished cell wall indicated intracellular part leakage, equivalent to proteins, DNA, and Ok+, which was corroborated by way of numerous methods (e.g., bicinchoninic acid protein assay; Fig. 3G-I).
Subsequent, the antibacterial mechanisms had been additional explored by way of RNA sequencing. A lot of 1433 differentially expressed genes (DEGs) together with 763 upregulated genes and 642 down-regulated genes in contrast with the management had been analyzed by the volcano plot analyses (Fig. 4A). As proven in Fig. 4B, partially considerably modified genes of DEGs had been listed within the heatmap. Accent gene regulator (Agr) performs an vital position in intercellular signaling quorum sensing which was decreased after E-Au NPs plus laser irradiation therapy. The down-regulation of virulence issue (Spa, Hla) and antibacterial resistance-related gene (ermC) indicated the attenuation of pathogenicity and invasiveness. Apart from, the expression of genes associated to upkeep (icaA, icaD) and adhesion (Clfa, Clfb) hinted at interference with biofilm formation. In distinction to regulate group, oxidative stress-related genes had been upregulated, resulting in ROS manufacturing. Additional evaluation of RNA sequencing by way of gene ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathways evaluation, revealed enrichment in mobile processes, catalytic actions, and membrane-related pathways (Fig. 4C-F). As for KEGG evaluation, DEGs had been enriched in pathways of metabolic pathway, membrane transport, and cell progress and loss of life pathways, specializing in biosynthesis metabolites enrichment evaluation.
Gene transcriptome assay. (A) Volcano plot analyses of DEGs handled with E-Au NPs plus laser. Down-regulated genes are in blue. Up-regulated genes are in pink. Grey dots characterize genes are lower than 2-fold differential expression. (B) Heatmap of a number of differentially expressed genes related to quorum sensing, virulence, antibacterial resistance, biofilm, adhesion and oxidative stress. GO evaluation (C), GO enrichment (D), KEGG pathways evaluation (E) and KEGG enrichment (F) of DEGs between the management group and E-Au group
To sum up, the outcomes revealed that the potential antibacterial mechanism of E-Au NPs concerned quinoproteins manufacturing, ROS era from photothermal remedy, mobile construction disruption, and regulation of genes related to biofilm formation, pathogenicity, invasiveness, and quorum sensing.
In vivo therapy impact of MRSA-infected pores and skin wounds
The photothermal impact and in vivo therapeutic efficiency of E-Au NPs primarily based therapy had been initially evaluated utilizing the MRSA biofilm contaminated pores and skin wounds murine mannequin (Fig. 5A). After the institution of the MRSA biofilm contaminated pores and skin wounds mannequin, mice had been administered with E-Au NPs or management brokers on Day 1 and three, with PBS serving because the management group for wound therapeutic. With NIR irradiation, infrared thermographic pictures confirmed that the temperature of contaminated pores and skin wounds was improved each in EGCG and E-Au teams whereas the development was extra important in E-Au group indicating the potential means of PTT remedy (Fig. 5B). As proven in Fig. 5C, D, wounds with out MRSA an infection, outlined because the Un-inf group, healed naturally, and its wound space recovered to 22.91% in comparison with 37.92% for the PBS group on day 8. Wounds handled with EGCG confirmed slight enchancment at 30.77% however this impact was not enhanced by NIR laser irradiation. Conversely, the wound space recovered to twenty-eight.98% following E-Au NPs therapy and achieved one of the best therapeutic impact at 17.21% after laser irradiation, surpassing even the therapeutic charge of the Un-inf group.
In vivo therapeutic impact of E-Au NPs for MRSA-infected pores and skin wounds mannequin. (A) Schematic illustration of the therapy of E-Au NPs with laser in MRSA-infected pores and skin wounds mannequin. (B) Infrared thermographic pictures disposed of with NIR laser on mice dorsal cutaneous wounds. (C) Pictures of wound in MRSA-infected mice after completely different therapy for 7 days. The Un-inf group represents uninfected pores and skin wounds. (D) Quantification evaluation of contaminated wound space. Analysis of bacterial colonies inside contaminated pores and skin after completely different therapies (E) and relative micro organism counts (F). (G) Analysis of contaminated pores and skin wound tissue by hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining. Pink circles point out the formation of blood vessels, scale bar = 1 mm/250 µm. (H) Immunohistochemical staining evaluation of IL-6 within the pores and skin. (Knowledge are offered because the imply ± s. d., *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001)
On day 8, contaminated wound tissues had been collected for LB-agar plate CFU counting to quantify MRSA ranges. The EGCG and EGCG plus laser teams confirmed quite a few MRSA colonies in comparison with E-Au NPs group. Quite the opposite, mice handled with E-Au NPs had considerably decrease MRSA, particularly with NIR laser irradiation, confirming the in vivo antibacterial potential of E-Au NPs (Fig. 5E, F). Histopathological evaluation was carried out to judge the epithelial hole and anti inflammatory therapy impact of E-Au NPs on the MRSA-infected pores and skin wound tissues. H&E staining pictures revealed that the epithelial hole was shortened and wound therapeutic was promoted after therapy with E-Au NPs and NIR laser irradiation (Fig. 5G, Fig. S15 and Fig. S16). Apart from, immunohistochemistry (IHC) was carried out to evaluate the quantity of proinflammatory, equivalent to cytokines interleukin-6 (IL-6). As proven in Fig. 5H and Fig. S17, IL-6 was extremely expressed in PBS, EGCG, and EGCG plus NIR teams whereas notably decreased after the therapy of E-Au NPs, indicating the numerous inhibition of the inflammatory response of an infection.
In vivo therapy impact of MRSA-infected keratitis
The in vivo therapy impact efficiency of E-Au NPs was additional evaluated within the MRSA-infected keratitis mannequin (Fig. 6A). After 48 h incubation of MRSA suspension on the eyes, the everyday signs of bacterial keratitis, equivalent to cornea edema, conjunctival congestion, opacification, and periocular purulent exudation appeared, indicating the profitable institution of the MRSA-infected keratitis mannequin. Mice had been handled with E-Au NPs twice on day 2 and day 4, with PBS and cefazolin sodium (CS) used as controls for keratitis therapeutic. In the course of the 16 day-long experiments, the murine cornea of the management and CS group regularly deteriorated and confirmed extreme MRSA biofilm an infection and irritation signs in addition to plentiful corneal neovascularization, with the scientific grading scale 14.33 ± 1.16 for the management group and 13.67 ± 0.58 for the CS group on day 16 (Fig. 6B, C). When mice handled with E-Au NPs, the cornea inflammatory signs deteriorated with edema and neovascularization within the first 8 days whereas had been regularly relieved within the later 8 days (scientific grading scale: 7.67 ± 1.00). Upon laser irradiation, the signs of keratitis additional decreased and achieved one of the best therapeutic impact. The cornea turned clear with no neovascularization, and an infection of the cornea and surrounding tissue was successfully managed (scientific grading scale: 2.67 ± 0.58). Apart from, the corneal epithelium defect was evaluated by way of sodium fluorescein staining. In management and CS teams, the epithelium defect of the cornea was stained for a big space whereas the world was smaller after E-Au therapy. There was no fluorescein staining within the E-Au plus laser group, indicating superior corneal restoration and floor regularity. Keratitis may scale back tear secretion, which was assessed utilizing the phenol pink thread assay. Certainly, tear secretion within the management group was impaired, with a wetting size of the phenol pink of lower than 2 mm. After therapy with E-Au NPs plus laser, tear secretion virtually absolutely recovered to norma, with a wetting size of approximate 5.53 mm (Fig. 6D).
In vivo therapeutic impact of E-Au NPs for MRSA-infected keratitis. (A) Schematic illustration of the therapy of E-Au NPs with laser in MRSA-infected keratitis mannequin. (B) Slit lamp pictures of various therapies on day 0, 4, 8, 12, 16 and sodium fluorescein staining of corneas. (C) The scientific grading scale of various therapies. (D) Quantification evaluation of phenol pink thread check. H&E staining of the cornea (E) and quantification evaluation of the corneal thickness (F). The elements framed with the black dotted line had been enlarged, scale bar = 100 μm/20 µm. Immunohistochemical staining evaluation of IL-6 within the cornea (G) and quantification evaluation (H), scale bar = 100 μm. (I) H&E staining of the retina, scale bar = 100 μm. (J) Measurement of IOP. (Ok) Cytotoxicity of HCEC incubated with E-Au NPs for twenty-four h with or with out laser irradiation. (Knowledge are offered because the imply ± s. d., *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001)
Histopathological evaluation was carried out to evaluate the impression of E-Au NPs therapy on MRSA-infected cornea tissues by way of antibacterial and anti inflammatory results. As proven in Fig. 6E, F, extreme irritation with inflammatory cell infiltration and corneal edema with irregular epithelium and stromal matrix had been noticed in management and CS teams by way of H&E staining. Nonetheless, following therapy with E-Au NPs plus laser, a big lower in inflammatory cells and disappearance of edema had been famous, together with restoration of regular corneal construction. Moreover, the expression of proinflammatory cytokines IL-6 was notably increased within the management and CS teams in comparison with the therapy group, indicating efficient inhibition of the inflammatory response throughout the late stage of an infection (Fig. 6G, H).
On the premise of the wonderful therapeutic impact of MRSA biofilm-infected pores and skin wounds and keratitis, the native and systemic biosafety of E-Au NPs was evaluated for the potential scientific translation. Sodium fluorescein staining revealed no important corneal epithelial defect after E-Au NPs administration in comparison with the management group (Fig. S18). As depicted in Fig. 6I, pathological evaluation of retinal biosafety confirmed no obvious structural adjustments post-treatment. Intraocular stress (IOP) returned to regular ranges after therapy, indicating no disruption to aqueous humor circulation (Fig. 6J). Alternatively, cell viability of HCEC was 81.57% and 87.58% after E-Au NPs therapy even on the focus of 400 µg/mL with or with out laser irradiation (Fig. 6Ok). No important systemic or metabolic negative effects had been noticed after E-Au NPs therapy, as indicated by routine blood examinations and blood biochemical ranges remaining inside regular ranges (Fig. S19). Moreover, H&E staining of main organs confirmed no histological abnormalities or indicators of toxicity (Fig. S20). These findings collectively recommend that E-Au NPs therapy is efficient for MRSA biofilm-infected keratitis with excessive biocompatibility, marking it promising for potential scientific purposes.