In an age of more and more superior robotics, one staff has effectively and actually bucked the pattern, as a substitute discovering inspiration throughout the pinhead-sized mind of a tiny flying insect with a purpose to construct a robotic that may deftly keep away from collisions with little or no effort and power expenditure.
An insect’s tiny mind is an unlikely supply of biomimicry, however researchers from the College of Groningen within the Netherlands and Bielefeld College in Germany believed it was a super system to use to how robots transfer. Fruit flies (Drosophila melanogaster) possess remarkably easy however efficient navigational abilities, utilizing little or no brainpower to swiftly journey alongside invisible straight strains, then adjusting accordingly – flying in a line angled to the left or the suitable – to keep away from obstacles.
With such a tiny mind, the fruit fly has restricted computational assets out there to it whereas in flight – a organic mannequin, the scientists believed, that may very well be tailored to make use of within the ‘mind’ of a robotic for environment friendly, low-energy and obstacle-avoiding locomotion.
“Like whenever you’re on a practice,” stated physicist Elisabetta Chicca, from the College of Groningen. “The bushes close by seem to maneuver quicker than the homes distant. Bugs use this info to deduce how distant issues are.
“What we study from that is: when you don’t have sufficient assets, you possibly can simplify the issue together with your conduct,” she added.
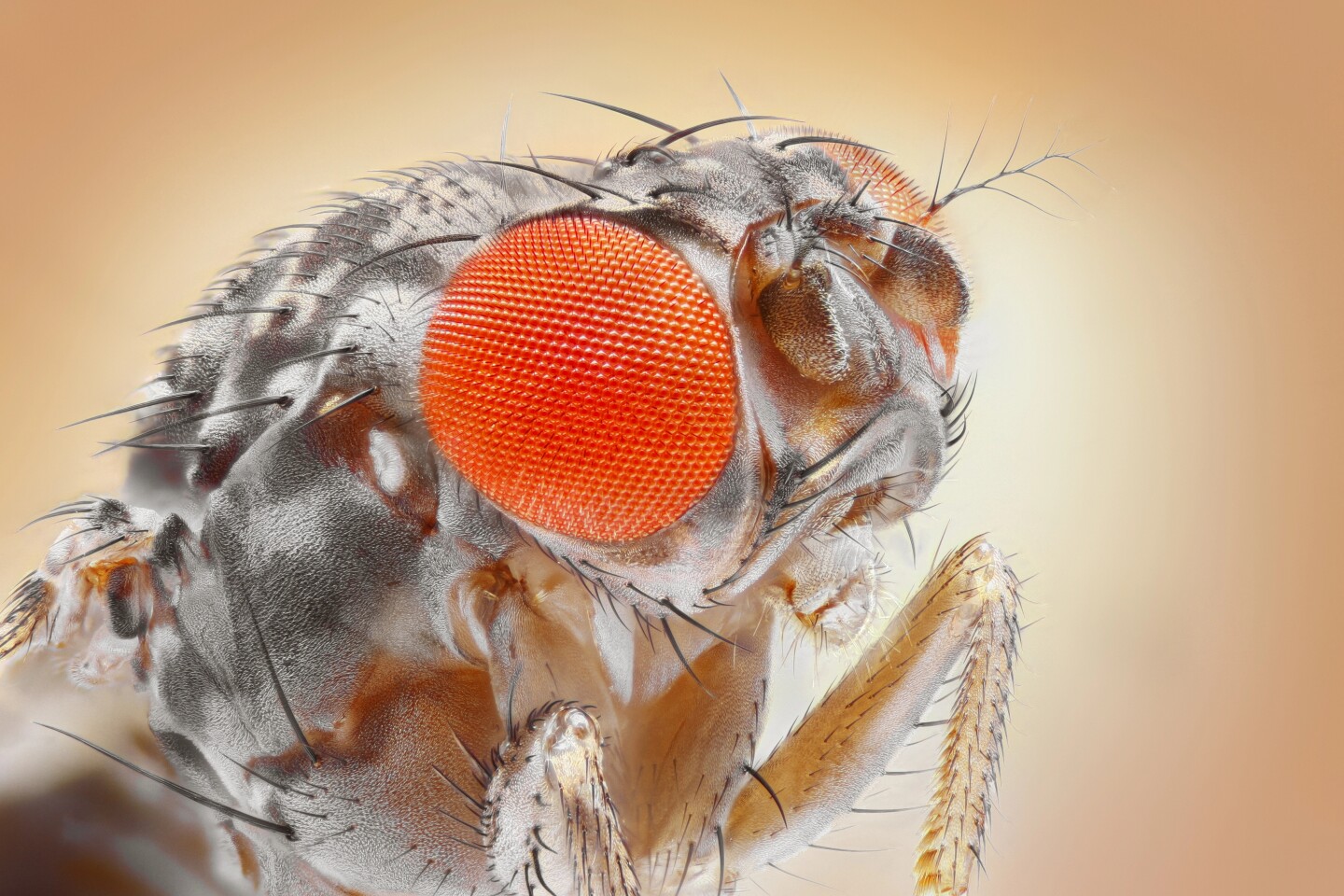

In fruit flies’ brains, the movement of surrounding objects is processed by the optical neurons T4 and T5. With the assistance of Bielefeld College neurobiologist Martin Egelhaaf, the staff algorithmically mimicked this neural exercise of their small robotic ‘mind’, giving it the flexibility to course of directional info to maneuver effectively and keep away from collisions with any obstacles in its path.
“A lot of robotics will not be involved with effectivity,” stated Chicca. “We people are inclined to study new duties as we develop up, and inside robotics, that is mirrored within the present pattern of machine studying. However bugs are in a position to fly instantly from start. An environment friendly approach of doing that’s hardwired of their brains.”
The tip result’s a compact robotic with one essential goal – to steer in direction of the realm with the least motion detected. College of Groningen’s Thorben Schoepe, who engineered the {hardware}, put the wheeled robotic by a collection of exams, and located that it could middle itself between objects, and likewise deftly modify its path to information itself round obstacles – as an insect would in flight.
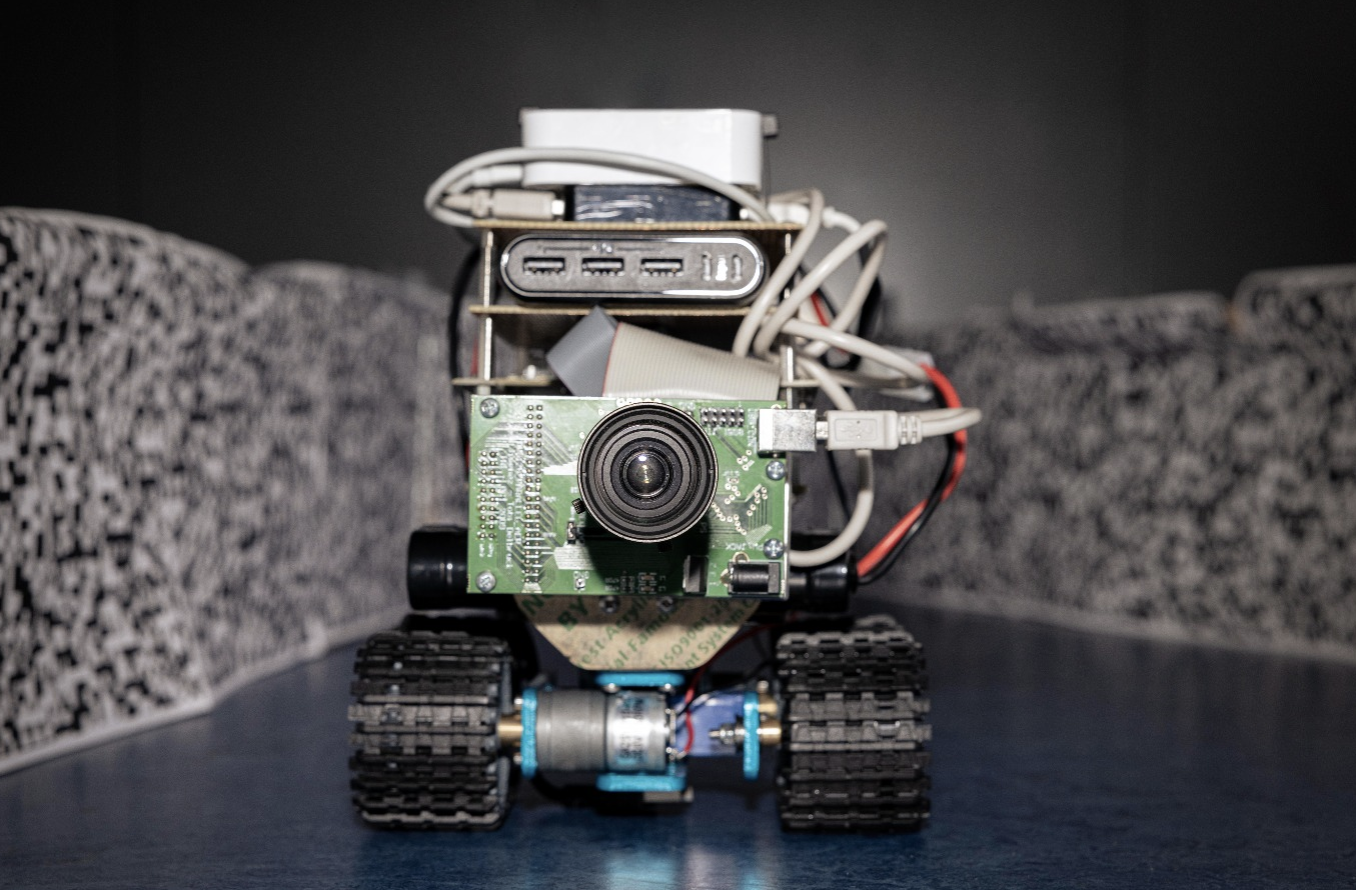
Leoni von Ristok/College of Groningen
“The mannequin is so good,” Chicca stated, “that when you set it up, it should carry out in every kind of environments. That’s the fantastic thing about this end result.”
The staff believes that is the primary research of its sort to deal with impediment avoidance, and it takes an enormous step ahead within the improvement of neuromorphic {hardware} in robotics. Sooner or later, such a machine may very well be used to navigate cluttered terrain akin to catastrophe websites, with extraordinarily low power output, and it may very well be outfitted with totally different sorts of sensors relying on use, akin to radar to detect structureless objects.
“We developed a robotic impressed by bugs,” stated Chicca. “It has outstanding capabilities to journey in dense terrain, avoiding collisions, crossing gaps and deciding on secure passages. These capabilities are completed by a neuromorphic community steering the robotic towards areas of low obvious movement. Our system leverages information about imaginative and prescient processing and impediment avoidance in bugs.”
The analysis was printed within the journal Nature Communications.
Supply: College of Groningen

