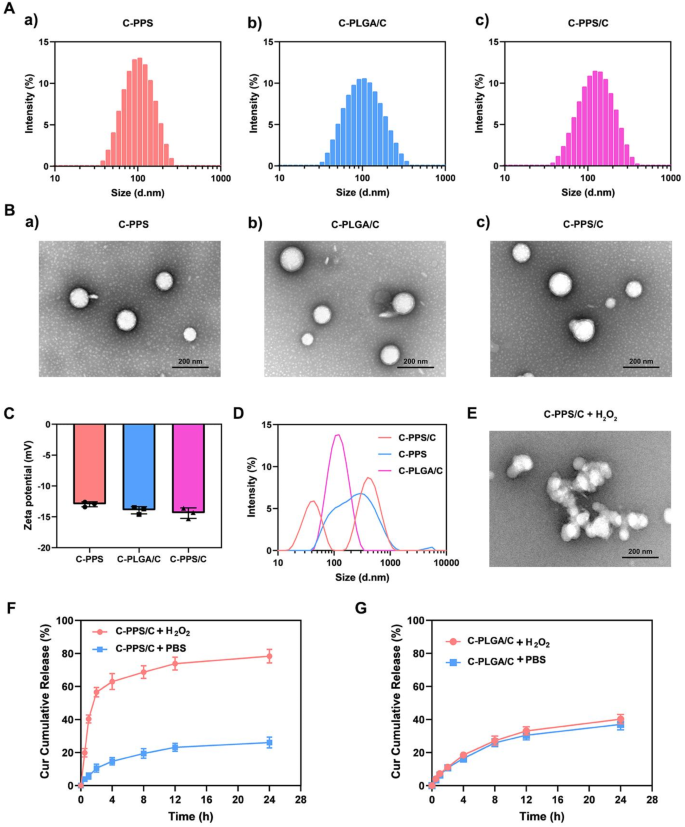
Preparation and characterization of C-PPS/C
The purpose of this examine was to develop nanoparticles with the flexibility to scavenge ROS and ship Cur. First, hydrophobic PPS120 was synthesized utilizing reversible addition-fragmentation chain switch polymerization. Below the motion of ROS, the hydrophobic polysulfide items in PPS are transformed into hydrophilic polysulfoxide items [19]. In the course of the degradation of PPS, ROS within the microenvironment had been consumed. Thus, PPS120 serves because the hydrophobic core of the nanoparticles, exhibiting ROS-responsive traits and the flexibility to scavenge ROS. The construction of the synthesized PPS120 was confirmed by 1H NMR (Fig. S1). Nanoparticles concentrating on the injured space post-TBI (C-PPS) had been fashioned by single-step nanoprecipitation self-assembly utilizing PPS120, DSPE-PEG2000, DSPE-PEG2000-CAQK, and lecithin. These nanoparticles had been designed for the supply of Cur (C-PPS/C). Moreover, nanoparticles with a poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA) hydrophobic core loaded with Cur (C-PLGA/C) had been ready as a management group for subsequent experiments. The typical diameter of C-PPS was 99.6 ± 2.57 nm, that of C-PLGA/C was 108.1 ± 4.06 nm, and that of C-PPS/C was 115.17 ± 3.06 nm (Fig. 2A). Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) photographs revealed that the C-PPS, C-PLGA/C, and C-PPS/C nanoparticles had been spherical, exhibited good monodispersity, and had been comparatively uniform (Fig. 2B). The zeta potentials of C-PPS, C-PLGA/C and C-PPS/C nanoparticles had been − 12.96 ± 0.4 mV, -13.93 ± 0.59 mV and − 14.4 ± 0.85 mV, respectively (Fig. 2C).
Preparation and characterization of nanoparticles. (A) Measurement distribution of (a) C-PPS, (b) C-PLGA/C and (c) C-PPS/C nanoparticles. (B) TEM picture of (a) C-PPS, (b) C-PLGA/C and (c) C-PPS/C nanoparticles. Scale bar, 200 nm. (C) Zeta potentials of C-PPS, C-PLGA/C and C-PPS/C nanoparticles. (D) Measurement distribution of nanoparticles in H2O2. (E) TEM picture of C-PPS/C nanoparticles in H2O2. (F) The drug launch effectivity of Cur from C-PPS/C nanoparticles in numerous environments (PBS and H2O2) in vitro. n = 3. (G) The drug launch effectivity of Cur from C-PLGA/C nanoparticles in numerous environments (PBS and H2O2) in vitro. n = 3. Knowledge are offered because the means ± SD
The important thing facet of synthesized nanoparticles is to evaluate their responsiveness to ROS. We performed a number of experiments to confirm their responsiveness to ROS and their capability to launch Cur. We added H2O2 to options of C-PPS, C-PLGA/C, and C-PPS/C nanoparticles and measured their particle sizes. We noticed that the particle sizes of the C-PPS and C-PPS/C teams elevated, displaying bimodal peaks, whereas these of the C-PLGA/C group remained steady because of the incapacity of PLGA to answer H2O2 (Fig. 2D). Transmission electron microscopy observations of C-PPS/C nanoparticles within the presence of H2O2 revealed that the spherical nanostructures had modified, with the nanoparticles decomposing. These findings point out that nanoparticles ready with PPS because the hydrophobic core can reply to ROS, resulting in their degradation. As proven in Fig. 2F and G, we used excessive efficiency liquid chromatography (HPLC) to detect the Cur launch functionality of C-PPS/C and C-PLGA/C nanoparticles within the presence and absence of H2O2. Because of the responsiveness of PPS to H2O2, C-PPS/C nanoparticles can launch Cur extra quickly within the presence of H2O2 however exhibit a decrease drug launch effectivity within the absence of H2O2. Nevertheless, C-PLGA/C nanoparticles, which lack ROS responsiveness due to the presence of PLGA, constantly exhibit a decrease drug launch effectivity beneath each situations.
C-PPS/C nanoparticles have antioxidant results in vitro
We additional validated the flexibility of C-PPS/C nanoparticles to scavenge ROS and inhibit oxidative stress by cell-level experiments. Two neural cell traces, human astrocyte 1800 (HA1800) and a microglial cell line (BV2), had been used to evaluate the antioxidant capability of the nanoparticles following H2O2-induced harm (0.25 mM, 0.5 mM). Ranges of ROS had been analyzed utilizing fluorescent probes (Fig. 3A and B) and stream cytometry (Fig. 3C and D). The C-PPS group exhibited notable antioxidant capability because of the polysulfide items in PPS reacting with H2O2, remodeling into hydrophilic polysulfoxide items and instantly consuming H2O2, thereby decreasing oxidative stress at its supply (C-PPS vs. C-PPS/C; Fig. 3Ab 0.5 mM, p = 0.0252, 95percentCI: 1.358 to 18.98; Fig. 3Ab 0.25 mM, p = 0.0465, 95% CI: 0.127 to fifteen.94; Fig. Bb 0.5 mM, p = 0.0011, 95% CI: 8.246 to 25.29; Fig. Bb 0.25 mM, p = 0.0106, 95% CI: 3.766 to 24.97; Fig. 3Cb 0.5 mM, p = 0.0005, 95% CI: 439 to 1160; Fig. 3Cb 0.25 mM, p < 0.0001, 95% CI: 639.6 to 1277; Fig. Db 0.5 mM, p < 0.0001, 95% CI: 1261 to 2142; Fig. 3Db 0.25 mM, p < 0.0068, 95% CI: 210 to 1118). The C-PLGA/C group additionally offered some antioxidant results attributable to the presence of Cur, which might cut back ROS ranges to a sure extent (C-PLGA/C vs. C-PPS/C; Fig. 3Ab 0.5 mM, p = 0.0033, 95% CI: 5.691 to 23.31; Fig. 3Ab 0.25 mM, p = 0.0077, 95% CI: 3.427 to 19.24; Fig. Bb 0.5 mM, p < 0.0001, 95% CI: 17.98 to 35.02; Fig. Bb 0.25 mM, p = 0.0004, 95% CI: 13.67 to 34.87; Fig. 3Cb 0.5 mM, p < 0.0001, 95% CI: 790.4 to 1511; Fig. 3Cb 0.25 mM, p < 0.0001, 95% CI: 690.6 to 1328; Fig. 3Db 0.5 mM, p < 0.0001, 95% CI: 1780 to 2661; Fig. 3Db 0.25 mM, p = 0.0002, 95% CI: 684.7 to 1593). Importantly, the C-PPS/C nanoparticles demonstrated one of the best antioxidant capability; this occurred as a result of C-PPS/C nanoparticles not solely instantly eat H2O2 by PPS but in addition launch encapsulated Cur inside PPS, enhancing antioxidant capability and additional decreasing oxidative stress ranges in cells post-H2O2 harm. Nevertheless, in scientific eventualities, the oxidative stress course of following TBI is extra extreme and sophisticated. Subsequently, single-cell degree assays are inadequate. Consequently, subsequent experiments will additional confirm the antioxidant capability on the animal degree.
C-PPS/C nanoparticles have antioxidant results in vitro. (A) a) ROS manufacturing in HA1800 with 0.5 mM and 0.25 mM H2O2. Scale bar = 100 μm. b) Quantitative imply fluorescence depth in every group. n = 3. (B) (a) ROS manufacturing in BV2 with 0.5 mM and 0.25 mM H2O2. Scale bar = 100 μm. (b) Quantitative imply fluorescence depth in every group. n = 3. (C) (a) ROS manufacturing in HA1800 with 0.5 mM and 0.25 mM H2O2 are indicated with stream cytometry. (b) Quantitative imply fluorescence depth in every group. n = 3. (D) (a) ROS manufacturing in BV2 with 0.5 mM and 0.25 mM H2O2 are indicated with stream cytometry. (b) Quantitative imply fluorescence depth in every group. n = 3. Knowledge are offered because the means ± SD. **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 and ****p < 0.0001
Focused supply of C-PPS/C nanoparticles to the TBI website
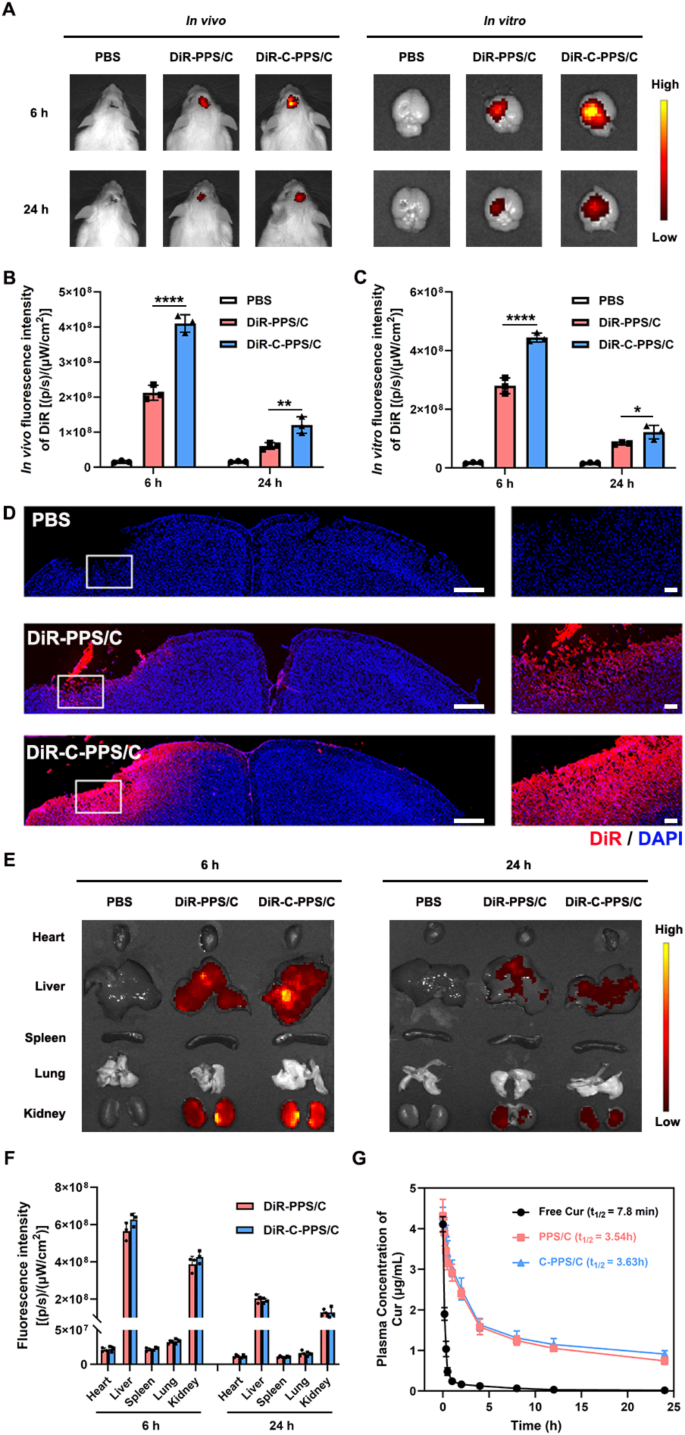
To successfully exert the neuroprotective results of Cur, it’s essential to attain excessive concentrations of Cur on the website after TBI. Nevertheless, the BBB acts as a selective barrier, stopping Cur from coming into mind tissue from the blood. In line with earlier research, CAQK is a tetrapeptide that may goal chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans on the harm website following TBI, delivering medicine to the mind harm website [20, 21]. Subsequently, C-PPS nanoparticles had been ready as drug carriers. These nanoparticles can successfully cross the BBB and, as a result of floor modification with CAQK, goal the harm are after TBI. This concentrating on permits for the enrichment of the drug on the trauma website, thereby enhancing its therapeutic impact. Subsequently, to judge the concentrating on impact, we intravenously injected 1,1’-dioctadecyl-3,3,3’,3-tetramethylin-dotricarbocyanine iodide (DiR)-conjugated nanoparticles had been launched into mice through the tail vein after TBI. We constructed two varieties of nanoparticles: PPS/C nanoparticles with out CAQK modification (DiRi-PPS/C) and C-PPS/C nanoparticles with CAQK modification (DiR-C-PPS/C). Six and 24 h post-injection, observations had been made utilizing an small animal in vivo imaging system. As proven in Fig. 4A-C, at each 6 and 24 h post-injection, the DiR fluorescence depth within the brains of the mice handled with DiR-C-PPS/C nanoparticles was higher than that within the brains of the mice handled with DiR-PPS/C nanoparticles (DiR-PPS/C vs. DiR-C-PPS/C; Fig. 4B 6 h, p < 0.0001, 95% CI: -245154450 to -150178883; Fig. 4B 24h, p = 0.006, 95% CI: -96430994 to -22902339; Fig. 4C 6 h, p < 0.0001, 95% CI: -209747298 to -119586035; Fig. 4C 24h, p = 0.0327, 95% CI: -72664878 to -3935122). To additional confirm whether or not the nanoparticles can accumulate within the harm area, we remoted mind tissue from mice 24 h after drug injection and carried out histological evaluation. We noticed that the CAQK-modified nanoparticles gathered higher within the injured space (Fig. 4D). These outcomes point out that the CAQK-modified nanoparticles can successfully cross the BBB and goal the mind harm space.
Pharmacokinetics, concentrating on and metabolic profile of C-PPS/C nanoparticles. (A) The DiR fluorescence photographs of TBI mice after injection of PBS, DiR-PPS/C and DiR-C-PPS/C nanoparticles to watch their concentrating on harm area capability. Quantitative evaluation of fluorescence depth in vivo (B) and in vitro (C). (D) Mind distribution of PBS, DiR-PPS/C and DiR-C-PPS/C nanoparticles. scale bar = 100 μm. (E) The DiR fluorescence photographs of main organs after i.v. injection of PBS, DiR-PPS/C and DiR-C-PPS/C. (F) Quantification of DiR accumulation in main organs. n = 3. (G) In vivo pharmacokinetics of Free Cur, PPS/C and C-PPS/C in mice. Knowledge are offered because the means ± SD. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ****p < 0.0001
Evaluation of the distribution of nanoparticles within the coronary heart, liver, spleen, lungs, and kidneys revealed that the nanoparticles had been metabolized primarily by the liver and kidneys. Because of the concentrating on impact of CAQK, DiR-C-PPS/C nanoparticles gathered extra within the mind tissue, leading to a decrease distribution within the liver and kidneys than DiR-PPS/C nanoparticles (Fig. 4E and F). Evaluation of drug concentrations in serum revealed that free Cur was cleared extra quickly, whereas its formulation into nanoparticles elevated the drug’s half-life, thereby extending its length of motion. Furthermore, CAQK modification didn’t alter the half-life of the nanoparticles (Fig. 4G).
C-PPS/C nanoparticles have good biocompatibility
Biocompatibility is a vital issue influencing the scientific utility of a fabric. As proven in Fig. S2A, on the seventh day post-injury, biocompatibility was evaluated by histopathological examination of organs (coronary heart, liver, spleen, lung, and kidney) and blood exams of tissues from every group of mice. No vital pathological adjustments had been noticed in any group. The degrees of aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), creatinine (CREA), and blood urea nitrogen (BUN) in every group had been inside regular ranges (Fig. 2SB-E). These outcomes point out that the nanoparticles have good biocompatibility.
C-PPS/C nanoparticles cut back mind edema and defend the BBB after TBI in vivo
Disruption of the BBB and the ensuing mind edema are two interrelated pathological processes that considerably affect the development of TBI. When the BBB is broken, plasma constituents akin to water and proteins can infiltrate mind tissue, resulting in fluid accumulation and subsequent mind edema. This edema will increase intracranial stress, which in flip exacerbates BBB injury [7, 22, 23]. Elevated intracranial stress compresses and deforms endothelial cells, additional impairing the integrity of the BBB and making a vicious cycle [24]. Defending and restoring the integrity of the BBB can successfully cut back the transmission of fluid from the vasculature into mind tissue, thereby assuaging mind edema [25]. Consequently, safeguarding the BBB is a crucial technique within the remedy of cerebral edema [26]. Subsequently, defending the BBB and breaking the “BBB disruption-brain edema” cycle represent essential methods within the remedy of mind edema. On this examine, we performed a number of experiments to show whether or not C-PPS/C nanoparticles can enhance cerebral edema following traumatic mind harm by defending the BBB. The diagram and schedule are proven in Fig. 5A. As proven in Fig. 5B and Fig. S3, the extent of mind edema within the injured mind tissue of mice after TBI was noticed utilizing the T2 sequence of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Mice handled with C-PPS and C-PLGA/C nanoparticles exhibited various levels of enchancment in mind edema, with the C-PPS/C group exhibiting the least edema (C-PPS vs. C-PPS/C, p = 0.0169, 95% CI: 0.4923 to six.776; C-PLGA/C vs. C-PPS/C, p = 0.0438, 95% CI: 0.06226 to six.346). The identical development was noticed within the water content material experiment (Fig. 5C) (C-PPS vs. C-PPS/C, p = 0.0047, 95% CI: 0.6455 to three.720; C-PLGA/C vs. C-PPS/C, p = 0.0105, 95% CI: 0.4245 to three.499). We evaluated the integrity of the BBB in every group of mice utilizing the Evans blue assay (Fig. 5D). Notably, C-PPS/C nanoparticles exhibited one of the best therapeutic impact, with much less BBB injury and correspondingly milder mind edema (Management vs. C-PPS/C, p < 0.0001, 95% CI: 9.609 to 13.06; Free Cur vs. C-PPS/C, p < 0.0001, 95% CI: 8.228 to 11.68; C-PPS vs. C-PPS/C, p < 0.0001, 95% CI: 4.278 to 7.729; C-PLGA/C vs. C-PPS/C, p < 0.0001, 95% CI: 3.403 to six.854). This phenomenon signifies that C-PPS/C nanoparticles mix the antioxidant properties of PPS with the neuroinflammatory inhibition of Cur. By bettering oxygenation and the inflammatory microenvironment after TBI, this mixture breaks the “BBB disruption-brain edema” vicious cycle, protects the BBB, and alleviates mind edema.
C-PPS/C nanoparticles cut back mind edema and defend BBB after TBI. (A) Schematic diagram of TBI mannequin experiments. (B) Consultant T2-weighted photographs of every group. (C) Water content material in mind tissue of every group. (D) (a) Quantification of Evans Blue leakage of every group. (b) Consultant Evans Blue leakage photographs of every group. n = 5. C-PPS/C nanoparticles have antioxdant results in vivo. (E) Fluorescence depth of DHE fold change of every group. n = 5. (F) SOD, (G) GSH-px and (H) MDA of every group. n = 5. C-PPS/C nanoparticles have neuroprotective results in vivo. (I) Consultant photographs of TUNEL staining on the seventh day after TBI. Scale bar = 50 μm. (J) Sagittal H&E mind staining. (Ok) Nissl mind staining. Scale bar = 50 μm. Knowledge are offered because the means ± SD. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 and ****p < 0.0001
C-PPS/C nanoparticles have antioxidant results in vivo
Primarily based on the antioxidant capability demonstrated by C-PPS/C nanoparticles in vitro, we performed a sequence of in vivo experiments to additional confirm its capability to inhibit extreme oxidative stress following TBI. As proven in Fig. 5E, on the third day post-TBI, we utilized dihydroethidium (DHE) staining to detect superoxide ranges within the mouse mind. We discovered that the superoxide ranges within the C-PPS, C-PLGA/C, and C-PPS/C teams decreased to various levels, with the C-PPS/C group exhibiting a big discount in DHE ranges (Management vs. C-PPS/C, p < 0.0001, 95% CI: 13.88 to 21.69; Free Cur vs. C-PPS/C, p < 0.0001, 95% CI: 8.037 to fifteen.85; C-PPS vs. C-PPS/C, p = 0.0034, 95% CI: 1.463 to 9.273; C-PLGA/C vs. C-PPS/C, p = 0.0001, 95% CI: 3.075 to 10.89). We additional assessed the endogenous antioxidant ranges and had been pleasantly stunned that, along with the inherent ROS scavenging functionality, additionally they enhanced the mind’s personal antioxidant capability. The degrees of superoxide dismutase (SOD), glutathione peroxidase (GSH-px), and malondialdehyde (MDA) function indicators of antioxidant exercise within the mind: SOD eliminates the initiators of free radical reactions, GSH-px interrupts the lipid peroxidation chain response, and MDA, as the top product of oxidative stress, displays the extent of injury attributable to ROS in mind (Fig. 5F-H). Cur and PPS not solely instantly react with and get rid of ROS but in addition improve the endogenous antioxidant capability of mind tissue; this led to elevated ranges of SOD and GSH-px and decreased ranges of MDA within the C-PPS and C-PLGA/C teams. The C-PPS/C group, combining the benefits of each PPS and Cur, demonstrated much more higher antioxidant capability (Fig. 5F Management vs. C-PPS/C, p < 0.0001, 95% CI: -135.0 to -79.86; Free Cur vs. C-PPS/C, p < 0.0001, 95% CI: -93.97 to -38.83; C-PPS vs. C-PPS/C, p = 0.0034, 95% CI: -65.45 to -10.31; C-PLGA/C vs. C-PPS/C, p = 0.0007, 95% CI: -70.95 to -15.81; Fig. 5G Management vs. C-PPS/C, p < 0.0001, 95% CI: -14.19 to -8.162; Free Cur vs. C-PPS/C, p < 0.0001, 95% CI: -10.90 to -4.878; C-PPS vs. C-PPS/C, p = 0.0017, 95% CI: -7.418 to -1.394; C-PLGA/C vs. C-PPS/C, p = 0.0007, 95% CI: -7.780 to -1.756; Fig. 5H Management vs. C-PPS/C, p < 0.0001, 95% CI: 13.21 to 21.33; Free Cur vs. C-PPS/C, p < 0.0001, 95% CI: 6.615 to 14.74; C-PPS vs. C-PPS/C, p = 0.0005, 95% CI: 2.503 to 10.63; C-PLGA/C vs. C-PPS/C, p = 0.0011, 95% CI: 2.103 to 10.23).
C-PPS/C nanoparticles have neuroprotective results in vivo
Essentially the most direct affect of TBI on the mind is neuronal cell demise, which might result in extreme penalties. To evaluate the neuroprotective impact of C-PPS/C nanoparticles, we examined neuronal cells in mind tissue sections. As proven in Fig. 5I, Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUTP nick finish labeling (TUNEL) staining revealed a excessive degree of neuronal apoptosis within the injured mind tissue of the Management group. Whereas the Free Cur group confirmed some enchancment in decreasing apoptosis, the dearth of concentrating on resulted in much less efficient remedy in contrast with that within the C-PLGA /C group. The C-PPS group exhibited decreased apoptosis because of the scavenging of ROS post-TBI, which decreased lipid peroxidation, protein oxidation, and DNA injury. C-PPS/C nanoparticles, combining the benefits of each PPS and Cur and concentrating on broken mind tissue, demonstrated the bottom TUNEL ranges in injured tissue afterTBI.
We noticed mind tissue and neuronal injury in every group of mice through hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) and Nissl staining. Hematoxylin and eosin staining photographs revealed that the mind tissue defects within the mice handled with nanomedicine had been much less extreme than these within the Management group, with the C-PPS/C group exhibiting the least quantity of tissue injury (Fig. 5J). Nissl staining supplied a direct indication of neuronal injury. Within the Sham group, quite a few regular Nissl our bodies had been noticed, whereas within the Management group, Nissl our bodies had been considerably decreased, with injured neurons exhibiting shrunken cell our bodies, condensed or displaced nuclei, and irregular cell outlines. Put up-treatment, an elevated variety of regular Nissl our bodies had been noticed within the broken areas, indicating a higher presence of wholesome neurons. The quantity and construction of Nissl our bodies within the C-PPS/C group had been much like these within the Sham group, suggesting that C-PPS/C successfully protects neurons and mitigates the severity of the pathological adjustments (Fig. 5Ok).
C-PPS/C nanoparticles have anti-neuroinflammatory results in vivo
The neuroinflammatory response following TBI performs a crucial position in mind tissue injury. Neuroinflammation is the repose of the central nervous system to harm or pathological situations, and includes varied cell sorts [11]. Microglia, the first immune cells of the central nervous system, play an essential position in neuroinflammation [27, 28]. Following TBI, microglia are quickly activated and migrate to the harm website, the place they launch a wide range of inflammatory mediators akin to cytokines (e.g., interleukin-6 (IL-6), interleukin-1β (IL-1β)), tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α)), and chemokines (e.g., C-X-C ligand-1 (CXCL-1)). These mediators are essential within the native inflammatory response, influencing neurons and different glial cells [29]. Microglia will be activated into completely different states after TBI [30]. M2-type microglia are important for the decision of irritation and tissue restore, aiding within the restoration of neural operate and defending neurons. By modulating the polarization state of microglia and selling their shift in direction of the M2 phenotype, the discharge of inflammatory mediators will be decreased, neuronal injury will be minimized, and neuroregeneration will be facilitated [31, 32]. Utilizing stream cytometry to detect M2-type microglia in mind tissue post-TBI, we discovered that PPS and Cur elevated the variety of M2-type microglia in TBI mice (Fig. 6A and Fig. S4) (Management vs. C-PPS/C, p < 0.0001, 95% CI: -18.13 to -11.00; Free Cur vs.C-PPS/C, p < 0.0001, 95% CI: -13.53 to -6.405; C-PPS vs. C-PPS/C, p = 0.0006, 95% CI: -9.962 to -2.838; C-PLGA/C vs. C-PPS/C, p = 0.0096, 95% CI: -8.162 to -1.038). Moreover, by measuring cytokines and chemokines, we noticed that neuroinflammation in TBI mice handled with nanomedicine was correspondingly inhibited (Fig. 6B-E) (Fig. 6B Management vs. C-PPS/C, p < 0.0001, 95% CI: 37.74 to 51.03; Free Cur vs. C-PPS/C, p < 0.0001, 95% CI: 33.90 to 47.19; C-PPS vs. C-PPS/C, p < 0.0001, 95% CI: 15.72 to 29.00; C-PLGA/C vs. C-PPS/C, p = 0.0028, 95% CI: 2.643 to fifteen.93; Fig. 6C Management vs. C-PPS/C, p < 0.0001, 95% CI: 49.40 to 63.08; Free Cur vs. C-PPS/C, p < 0.0001, 95% CI: 46.24 to 59.92; C-PPS vs. C-PPS/C, p < 0.0001, 95% CI: 17.26 to 30.95; C-PLGA/C vs. C-PPS/C, p < 0.0001, 95% CI: 14.12 to 27.81; Fig. 6D Management vs. C-PPS/C, p < 0.0001, 95% CI: 59.37 to 74.42; Free Cur vs. C-PPS/C, p < 0.0001, 95% CI: 47.69 to 62.74; C-PPS vs. C-PPS/C, p < 0.0001, 95% CI: 13.51 to twenty-eight.57; C-PLGA/C vs. C-PPS/C, p = 0.0001, 95% CI: 6.186 to 21.24; Fig. 6E Management vs. C-PPS/C, p < 0.0001, 95% CI: 54.74 to 74.95; Free Cur vs.C-PPS/C, p < 0.0001, 95% CI: 44.34 to 64.55; C-PPS vs. C-PPS/C, p < 0.0001, 95% CI: 28.38 to 48.60; C-PLGA/C vs. C-PPS/C, p = 0.0001, 95% CI: 8.337 to twenty-eight.55). The C-PPS/C group offered the best ranges of M2-type microglia and the bottom ranges of inflammatory cytokines and chemokines. That is attributed to the C-PPS/C nanoparticles combining the direct antioxidant results of PPS with the superb anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties of Cur. C-PPS/C nanoparticles modulate the post-TBI oxygen and inflammatory microenvironment, thereby offering superior neuroprotection.
C-PPS/C nanoparticles have neuroprotective and anti inflammatory results in vivo. (A) Detection of macrophage kind in mind tissue of every group. n = 3. (B) IL-6, (C), IL-1β, (D) TNF-α, and (E) CXCL-1 ranges of every group. n = 5. (F) Consultant photographs of GFAP and Iba-1 staining of the injured facet of the cerebral cortex (CTX) of every group. Scale bar = 50 μm. (G) Consultant photographs of GFAP and Iba-1 staining of the hippocampal space of every group. Scale bar = 50 μm. Knowledge are offered because the means ± SD. **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 and ****p < 0.0001
Within the neuroinflammatory response, glial fibrillary acid protein (GFAP) and ionized calcium-binding adapter molecule 1(Iba-1) are two essential markers used to establish the activation states of astrocyte and microglia, respectively [33, 34]. By concurrently detecting GFAP and Iba-1, it’s doable to comprehensively assess the activation states of microglia and astrocytes, offering perception into the neuroinflammatory response within the central nervous system following TBI. We assessed the expression of GFAP and Iba-1 within the mind tissue of mice following TBI utilizing immunohistochemistry (Fig. 6F). By inspecting the expression of GFAP and Iba-1 within the cortical harm websites, we noticed that the degrees had been decreased to various levels within the C-PPS and C-PLGA/Cur teams, indicating that the nanomedicine delivered to the mind harm website exerted anti-inflammatory results. The C-PPS/C group offered the bottom expression ranges of GFAP and Iba-1, demonstrating the simplest therapeutic end result.
The hippocampus performs a crucial position in varied cognitive capabilities and emotional regulation; it’s a central hub for episodic and spatial reminiscence. Moreover, the hippocampus is concerned in emotion processing and regulation, significantly in relation to emphasize responses and emotional reminiscence. Following trauma, the inflammatory response within the hippocampus intensifies, and degenerative adjustments on this area are carefully related to the prognosis of TBI. As proven in Fig. 6G, we noticed the expression ranges of GFAP and Iba-1 within the Cornu Ammonis 1 (CA1), Cornu Ammonis 3 (CA3), and Dentate Gyrus (DG) areas of the hippocampus throughout completely different teams. We discovered an analogous development to that noticed within the injured cortex.
RNA-sequencing evaluation of irritation adjustments following C-PPS/C remedy
To additional discover the mechanism by which C-PPS/C nanoparticles exert their results on TBI, we performed transcriptomic evaluation on mind tissues earlier than and after remedy. A heatmap of differentially expressed genes (DEGs) revealed vital variations between the 2 teams (Fig. 7A). Utilizing|log fold change| > 1 and p-value < 0.05 because the screening thresholds, a complete of 658 differentially expressed genes had been detected within the mind tissue of mice handled with C-PPS/C nanoparticles in comparison with the Management group. The highest 10 DEGs within the mind tissues of mice handled with C-PPS/C nanoparticles in contrast with these within the Management group had been all carefully associated to irritation (Fig. 7B). Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) and Gene Ontology (GO) enrichment analyses of the DEGs revealed enrichment in inflammation-related pathways akin to “KEGG: NF-κB signaling pathway” and “GO: Leukocyte migration” (Fig. 7C-D). These findings recommend that the mechanism by which C-PPS/C nanoparticles exert their results on TBI is carefully related to the suppression of irritation.
RNA-sequencing evaluation of irritation adjustments following C-PPS/C remedy. n = 6. (A) C-PPS/C, and Management teams’ gene heatmaps. (B) Evaluation of variations in expression of genes between the C-PPS/C group and the Management group. (C) Enrichment evaluation of KEGG pathway within the C-PPS/C group versus the Management group. (D) GO evaluation within the C-PPS/C group and the Management group. C-PPS/C nanoparticles exert their results by modulating the NF-κB signaling pathway. (E) Western blotting of NF-κB and P-IκBα in injured tissue. (F) Quantification of (a) NF-κB and (b) P-IκBα of every group. n = 3. Knowledge are offered because the means ± SD. ***p < 0.001 and ****p < 0.0001
C-PPS/C nanoparticles exert their results by modulating the NF-κB signaling pathway
RNA sequencing evaluation revealed vital adjustments within the NF-κB signaling pathway in mind tissue from TBI mice handled with C-PPS/C. Following TBI, the NF-κB pathway performs a crucial position in secondary mind harm. As a key transcription issue, NF-κB is activated post-injury, regulating the expression of quite a few genes associated to immune and inflammatory responses [35]. Its activation is usually accompanied by oxidative stress and the discharge of inflammatory components, which exacerbate neuroinflammation and contribute to secondary mind injury [36]. Phospho-IκBα (P-IκBα) is a pivotal molecule in NF-κB pathway regulation. Below resting situations, NF-κB binds with IκBα and stays sequestered within the cytoplasm, stopping gene activation. Upon stimulation (akin to by irritation or oxidative stress), IκBα is phosphorylated by IκB kinase, producing P-IκBα. P-IκBα is then ubiquitinated and degraded, releasing NF-κB to translocate to the nucleus, the place it prompts varied pro-inflammatory and immune-related genes. As proven in Fig. 7E and F, C-PPS/C nanoparticles inhibited the extreme activation of NF-κB and P-IκBα following TBI, thus suppressing neuroinflammation and offering a protecting impact (Fig. 7E Management vs. C-PPS/C, p < 0.0001, 95% CI: 0.4088 to 0.9385; Free Cur vs. C-PPS/C, p = 0.0003, 95% CI: 0.2572 to 0.7869; C-PPS vs. C-PPS/C, p = 0.0409, 95% CI: 0.009477 to 0.5392; C-PLGA/C vs. C-PPS/C, p = 0.0231, 95% CI: 0.03619 to 0.5659; Fig. 7F Management vs. C-PPS/C, p < 0.0001, 95% CI: 0.6179 to 1.042; Free Cur vs. C-PPS/C, p < 0.0001, 95% CI: 0.3040 to 0.7284; C-PPS vs. C-PPS/C, p = 0.0429, 95% CI: 0.005776 to 0.4301; C-PLGA/C vs. C-PPS/C, p = 0.0141, 95% CI: 0.04752 to 0.4719).
C-PPS/C nanoparticles enhance emotion and neurological operate after TBI
Bettering the lack of neurological operate attributable to TBI is of serious scientific significance. TBI not solely leads to the lack of neurological operate but in addition profoundly impacts emotional and psychological well being. In our examine, we assessed the motor, emotional, studying, and reminiscence talents of mice following TBI. The diagram and schedule are proven in Fig. 8A.
C-PPS/C nanoparticles enhance emotion and neurological operate after TBI. (A) mNSS, open subject take a look at, and Morris water maze evaluation schedule. n = 5. (B) Consultant photographs of the open subject take a look at outcomes of every group on Day 14 after TBI. (C) Frequency in heart on Day 14 after TBI. (D) Time spent in heart on Day 14 after TBI. (E) mNSSs had been calculated on Day 3, 7, and 14 after TBI. (F) Consultant photographs of the Morris water maze of every group in the course of the studying and reminiscence durations. (G) Swimming distance to the platform in the course of the studying interval, (H) looking out time for the platform in the course of the studying interval, (I) frequency of being on the platform space, (J) time in platform, (Ok) goal quadrant distance and (L) goal quadrant time in the course of the reminiscence interval. Knowledge are offered because the means ± SDs, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 and ****p < 0.0001
Nervousness is a typical emotional situation in TBI, the place hippocampal injury and neuroinflammation disrupt the mind’s microenvironment, impairing the regulation of emotional and stress responses and growing the danger of tension. Within the open subject take a look at, we noticed that mice exhibited vital anxiousness after TBI, with decreased exercise and reluctance to discover extra areas of the sector. The mice handled with C-PPS/C nanoparticles demonstrated essentially the most vital discount in anxiousness, with conduct extra carefully resembling that of the Sham group (Fig. 8B-D) (Fig. 8C Management vs. C-PPS/C, p < 0.0001, 95% CI: -78.82 to -48.38; Free Cur vs. C-PPS/C, p < 0.0001, 95% CI: -51.82 to -21.38; C-PPS vs. C-PPS/C, p = 0.0036, 95% CI: -36.02 to -5.581; C-PLGA/C vs. C-PPS/C, p = 0.0059, 95% CI: -35.02 to -4.581; Fig. 8D Management vs. C-PPS/C, p < 0.0001, 95% CI: -35.32 to -17.74; Free Cur vs. C-PPS/C, p < 0.0001, 95% CI: -25.46 to -7.881; C-PPS vs. C-PPS/C, p = 0.0213, 95% CI: -18.67 to -1.091; C-PLGA/C vs. C-PPS/C, p = 0.0609, 95% CI: -17.32 to 0.2630). To additional assess the affect of nanoparticles on long-term emotional and neurological capabilities, we performed an open subject take a look at on day 28 post-injury in mice from completely different remedy teams (Fig. S5). Over time, anxiousness ranges improved in all teams, with the TBI mice handled with C-PPS/C nanoparticles exhibiting extra vital restoration. These findings recommend that C-PPS/C nanoparticles can, to some extent, alleviate mid- and long-term anxiousness and neurological deficits in TBI mice.
The modified neurological severity rating (mNSS) is a generally used system for evaluating neurological impairment in mice after TBI, the place greater scores point out extra extreme useful injury [37]. We assessed the scores at 3, 7, and 14 days post-TBI in every group and located that the mice within the C-PPS/C group exhibited vital enchancment in neurological operate (Fig. 8E).
The Morris water maze is a extensively used behavioral take a look at to judge spatial studying and reminiscence in mice [38, 39]. On the twenty first day post-injury, mice had been positioned in a big pool and inspired to discover a clearly seen platform. Over the next 7 days (Days 21–27), the mice underwent trials in the identical pool. Lastly, on Day 28, the platform was eliminated, and the paths of the mice had been assessed (reminiscence section). By recording the variations within the capability of the mice to find the platform in the course of the studying and reminiscence phases, we assessed the spatial studying and reminiscence capabilities of every group (Fig. 8F). As proven in Fig. 8G and H, in the course of the studying section, the C-PPS, C-PLGA/C, and C-PPS/C teams of mice spent much less time and coated shorter distances to seek out the platform than the Management and Free Cur teams. Within the reminiscence section, the C-PPS/C group exhibited vital enhancements in varied metrics, together with frequency and time spent within the platform space, distance traveled within the goal quadrant, and time spent within the goal quadrant (Fig. 8I-L) (Fig. 8I Management vs. C-PPS/C, p < 0.0001, 95% CI: -6.604 to -2.596; Free Cur vs. C-PPS/C, p = 0.0028, 95% CI: -4.804 to -0.7962; C-PPS vs. C-PPS/C, p = 0.0506, 95% CI: -4.004 to 0.0038; C-PLGA/C vs. C-PPS/C, p = 0.6413, 95% CI: -3.004 to 1.004; Fig. 8J Management vs. C-PPS/C, p < 0.0001, 95% CI: -35.51 to -14.89; Free Cur vs. C-PPS/C, p = 0.0059, 95% CI: -23.71 to -3.089; C-PPS vs. C-PPS/C, p = 0.2925, 95% CI: -17.51 to three.111; C-PLGA/C vs. C-PPS/C, p = 0.3509, 95% CI: -17.11 to three.511; Fig. 8Ok Management vs. C-PPS/C, p < 0.0001, 95% CI: -29.16 to -15.75; Free Cur vs. C-PPS/C, p < 0.0001, 95% CI: -22.57 to -9.161; C-PPS vs. C-PPS/C, p = 0.0028, 95% CI: -16.08 to -2.667; C-PLGA/C vs. C-PPS/C, p = 0.0008, 95% CI: -17.24 to -3.827; Fig. 8L Management vs. C-PPS/C, p < 0.0001, 95% CI: -35.76 to -14.96; Free Cur vs. C-PPS/C, p < 0.0001, 95% CI: -30.01 to -9.214; C-PPS vs. C-PPS/C, p = 0.0147, 95% CI: -22.63 to -1.828; C-PLGA/C vs. C-PPS/C, p = 0.1446, 95% CI: -19.03 to 1.766).