Plenty of cybercriminal improvements are making it simpler for scammers to money in in your upcoming journey plans. This story examines a latest spear-phishing marketing campaign that ensued when a California lodge had its reserving.com credentials stolen. We’ll additionally discover an array of cybercrime providers geared toward phishers who goal inns that depend on the world’s most visited journey web site.
In line with the market share web site statista.com, reserving.com is by far the Web’s busiest journey service, with almost 550 million visits in September. KrebsOnSecurity final week heard from a reader whose shut pal acquired a focused phishing message through SMS inside minutes of creating a reservation at a California lodge through reserving.com.
The missive bore the title of the lodge and referenced particulars from their reservation, claiming that reserving.com’s anti-fraud system required extra details about the client earlier than the reservation might be finalized.
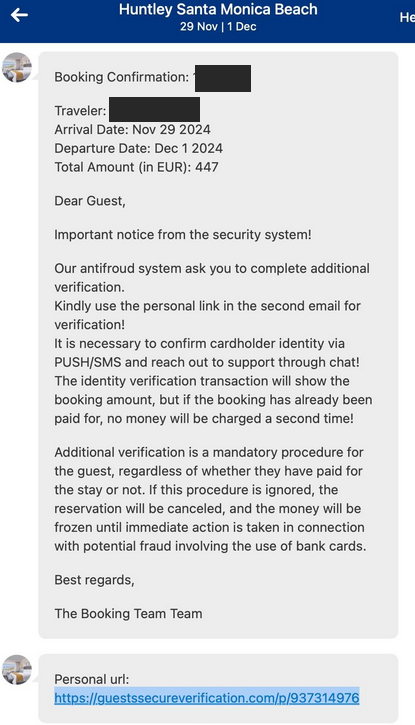
The phishing SMS our reader’s pal acquired after making a reservation at reserving.com in late October.
In an e mail to KrebsOnSecurity, reserving.com confirmed one in all its companions had suffered a safety incident that allowed unauthorized entry to buyer reserving info.
“Our safety groups are at present investigating the incident you talked about and might verify that it was certainly a phishing assault concentrating on one in all our lodging companions, which sadly is just not a brand new scenario and fairly frequent throughout industries,” reserving.com replied. “Importantly, we wish to make clear that there was no compromise of Reserving.com’s inside techniques.”
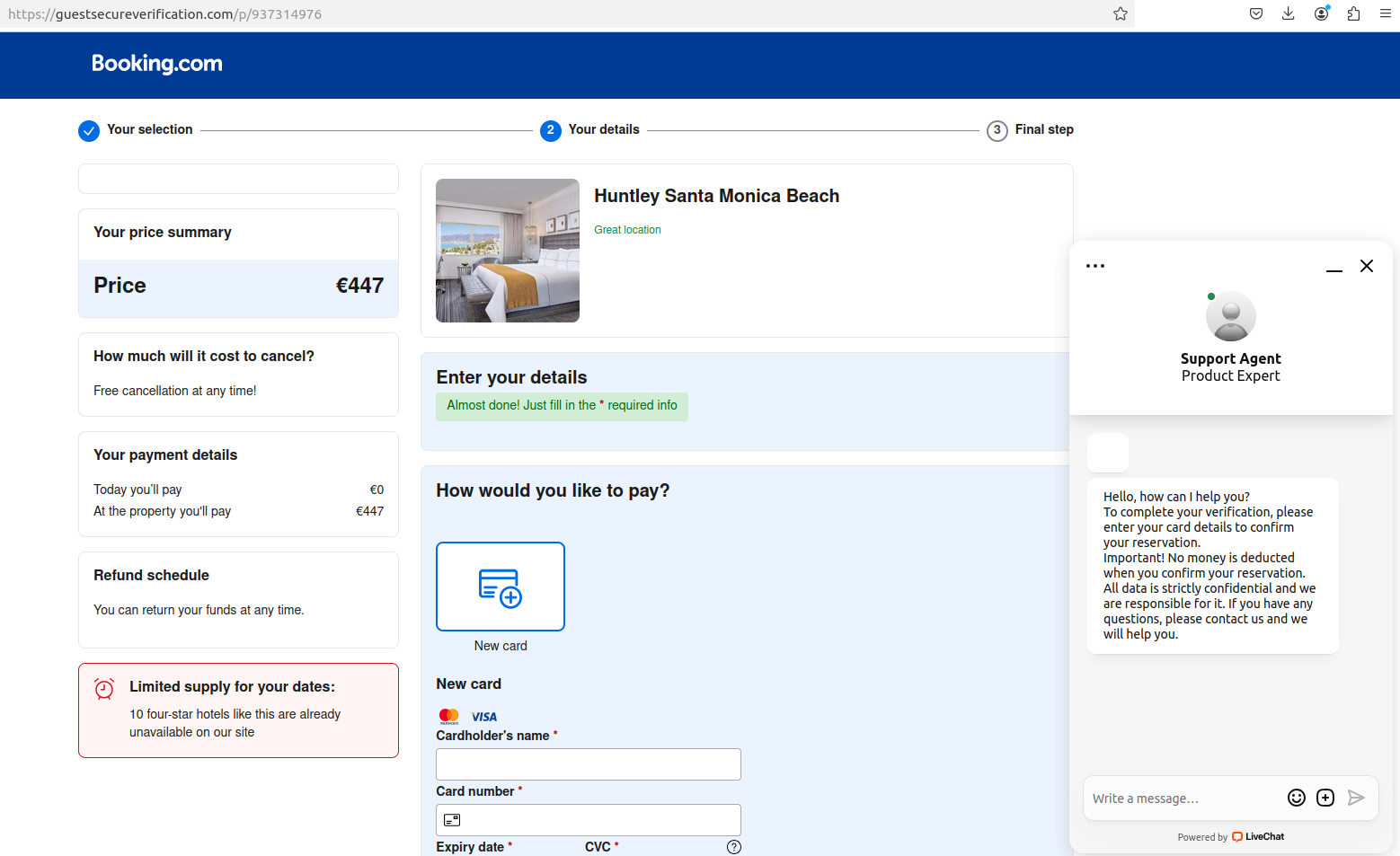
The phony reserving.com web site generated by visiting the hyperlink within the textual content message.
Reserving.com stated it now requires 2FA, which forces companions to supply a one-time passcode from a cellular authentication app (Pulse) along with a username and password.
“2FA is required and enforced, together with for companions to entry fee particulars from clients securely,” a reserving.com spokesperson wrote. “That’s why the cybercriminals follow-up with messages to attempt to get clients to make funds exterior of our platform.”
“That stated, the phishing assaults stem from companions’ machines being compromised with malware, which has enabled them to additionally acquire entry to the companions’ accounts and to ship the messages that your reader has flagged,” they continued.
It’s unclear, nonetheless, if the corporate’s 2FA requirement is enforced for all or simply newer companions. Reserving.com didn’t reply to questions on that, and its present account safety recommendation urges clients to allow 2FA.
A scan of social media networks confirmed this isn’t an unusual rip-off.
In November 2023, the safety agency SecureWorks detailed how scammers focused reserving.com hospitality companions with data-stealing malware. SecureWorks stated these assaults had been happening since not less than March 2023.
“The lodge didn’t allow multi-factor authentication (MFA) on its Reserving.com entry, so logging into the account with the stolen credentials was simple,” SecureWorks stated of the reserving.com companion it investigated.
In June 2024, reserving.com advised the BBC that phishing assaults concentrating on vacationers had elevated 900 p.c, and that thieves benefiting from new synthetic intelligence (AI) instruments had been the first driver of this development.
Reserving.com advised the BCC the corporate had began utilizing AI to battle AI-based phishing assaults. Reserving.com’s assertion stated their investments in that area “blocked 85 million fraudulent reservations over greater than 1.5 million phishing makes an attempt in 2023.”
The area title within the phony reserving.com web site despatched through SMS to our reader’s pal — guestssecureverification[.]com — was registered to the e-mail tackle ilotirabec207@gmail.com. In line with DomainTools.com, this e mail tackle was used to register greater than 700 different phishing domains up to now month alone.
Most of the 700+ domains seem to focus on hospitality firms, together with platforms like reserving.com and Airbnb. Others appear crafted to phish customers of Shopify, Steam, and quite a lot of monetary platforms. A full, defanged checklist of domains is accessible right here.
A cursory overview of latest posts throughout dozens of cybercrime boards monitored by the safety agency Intel 471 exhibits there’s a nice demand for compromised reserving.com accounts belonging to inns and different companions.
One submit final month on the Russian-language hacking discussion board BHF provided as much as $5,000 for every lodge account. This vendor claims to assist folks monetize hacked reserving.com companions, apparently through the use of the stolen credentials to arrange fraudulent listings.
A service marketed on the English-language crime neighborhood BreachForums in October courts phishers who might need assistance with sure features of their phishing campaigns concentrating on reserving.com companions. These embrace greater than two million lodge e mail addresses, and providers designed to assist phishers set up giant volumes of phished data. Prospects can work together with the service through an automatic Telegram bot.
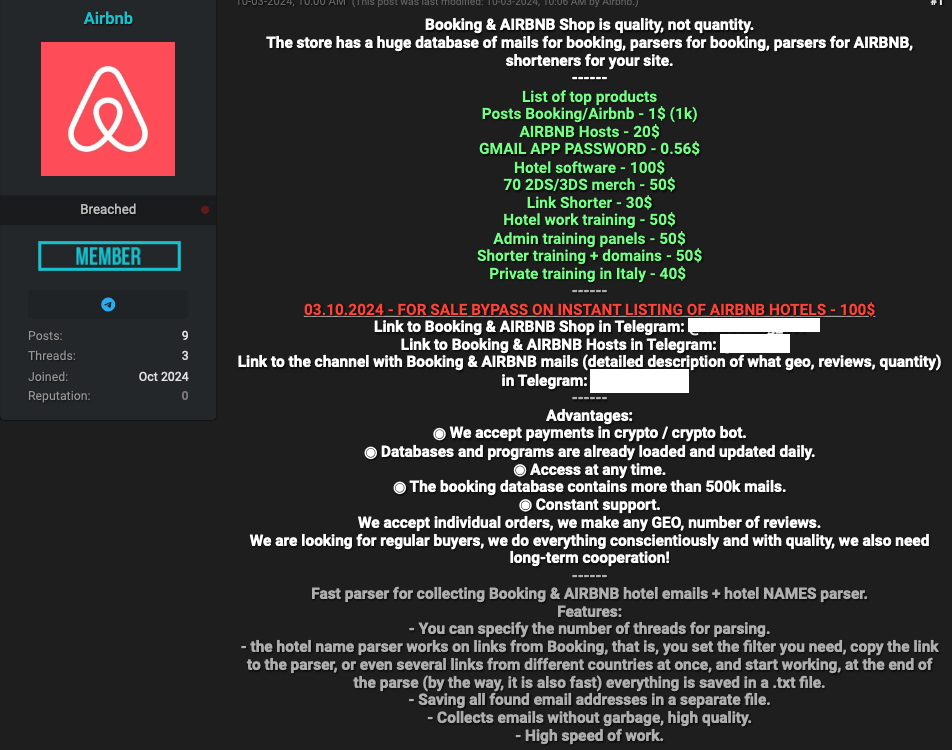
Some cybercriminals seem to have used compromised reserving.com accounts to energy their very own journey companies catering to fellow scammers, with as much as 50 p.c reductions on lodge reservations by means of reserving.com. Others are promoting ready-to-use “config” recordsdata designed to make it easy to conduct automated login makes an attempt towards reserving.com administrator accounts.
SecureWorks discovered the phishers concentrating on reserving.com companion inns used malware to steal credentials. However as we speak’s thieves can simply as simply simply go to crime bazaars on-line and buy stolen credentials to cloud providers that don’t implement 2FA for all accounts.
That’s precisely what transpired over the previous yr with many purchasers of the cloud information storage large Snowflake. In late 2023, cybercriminals discovered that whereas tons of firms had stashed huge quantities of buyer information at Snowflake, lots of these buyer accounts weren’t protected by 2FA.
Snowflake responded by making 2FA necessary for all new clients. However that change got here solely after thieves used stolen credentials to siphon information from 160 firms — together with AT&T, Lending Tree and TicketMaster.

