Characterization of the micelles
Twin-targeted and dual-response clever micelles had been ready to take advantage of the inflammatory microenvironment of RA. The fabrication course of is proven in Scheme 1. The transmission electron microscopy revealed that TK-HA-Cel@Ms had a homogeneous, spherical morphology on the nanoscale, with easy and rounded surfaces, uniform sizes, and diameters of roughly 40 nm (Fig. 1A), which corresponded properly with Nano Sequence Zen 4003 Zetasizer measurements (Fig. 1B) of 46.63 ± 1.82 nm and zeta potential of − 4.70 ± 0.36 mV (Fig. 1C).
Characterization of micelles. (A) TEM picture of TK-HA-Cel@Ms, scale bar = 50 nm; (B) Particle dimension distribution of TK-HA-Cel@Ms; (C) Zeta potential distribution of TK-HA-Cel@Ms; (D) Quantitative evaluation of particle dimension of micelles; (E) Quantitative evaluation of zeta potential of the various micelles; (F) Quantitative evaluation of PDI worth of the various micelles; (G) Quantitative evaluation of encapsulation effectivity of the various micelles; (H) Launch fee of Cel from the various formulations; (I) Hemolysis of induction of TK-HA-Cel@Ms, the place “-” and “+” represented unfavorable management and constructive management; (J–L) Adjustments in PDI (J), encapsulation effectivity (Ok), and particle dimension (L) of TK-HA-Cel@Ms had been quantitatively analyzed after 28 d of placement at 4 °C or RT. Knowledge are introduced because the imply ± SD (n = 3). a, Clean@Ms; b, Cel@Ms; c, HA-Cel@Ms; d, TK-HA-Cel@Ms; e, TK-HA-Cel@Ms + H2O2; f, TK-HA-Cel@Ms + H2O2 + HCl
Furthermore, the particle dimension, zeta potential, and PDI values of the micelles are proven in Fig. 1D-F. All of the micellar formulations had a particle dimension of lower than 50 nm, a weakly unfavorable potential, and a slim polydispersity coefficient. Furthermore, the particle dimension of TK-HA-Cel@Ms modified from 46.63 ± 1.82 nm to 40.24 ± 1.97 nm within the presence of H2O2, suggesting that it had a size-shrinkable property, which means that the TK bond is cleaved in ROS-rich setting, shedding the hydration layer of PEG5000 and restoring its focusing on results. PEG5000, as an extended linear polymer, has a diameter between 31 nm and 40 nm. And when PEG5000 was modified to the floor of the micelles, the particle dimension of the micelles solely elevated by about 10 nm, which indicated that PEG5000 fashioned a shell on the floor of the micelles, which could wrap the micelles, and this shell may not be monolayer, however had a sure thickness, which made the whole particle dimension of the micelles improve. The particle dimension of TK-HA-Cel@Ms elevated to 108.05 ± 5.50 nm within the presence of each H2O2 and HCl (pH = 5.5), indicating that the acid-sensitive materials mPEG114-PDPA10 responded to the acidic setting, which led to the disassembly of the micellar construction. The CMC of TK-HA-Cel@Ms was 0.0357 mg·mL− 1, as proven in Fig. S1. As well as, the EE of every drug-loaded micelles was larger than 90%, and TK-HA-Cel@Ms had an EE of 93.83% ± 1.00% (Fig. 1G).
The steadiness of micelles beneath oxidising situations was examined by monitoring the adjustments in particle dimension and PDI by DLS (Fig. S2). The particle dimension and PDI of TK-HA-Cel@Ms didn’t change a lot after 6 h within the absence of H2O2. Whereas, the particle dimension of TK-HA-Cel@Ms contracted by about 10 nm after which levelled off after 2 h in presence of 200 µM H2O2, and the PDI additionally elevated considerably. This indicated that beneath the motion of H2O2, the TK-sensitive bonds had been damaged, the PEG5000 layer on the micelle floor had been shed off, and the particle dimension shrunk.
The drug-release habits is a key parameter to make sure excessive drug exercise, particularly the sensitivity of medicine to inflammatory environments. Supreme nanoparticle methods can management drug launch in sure stimulatory environments, reminiscent of pH or ROS, permitting for exact drug supply [22]. Due to this fact, the drug launch from Cel was decided utilizing high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), and the drug-release profile of TK-HA-Cel@Ms in inflammatory microenvironments was simulated. Fig. 1H demonstrates the in vitro launch kinetic outcomes of TK-HA-Cel@Ms and free Cel. Free Cel was nearly fully launched inside 48 h, whereas about 35% of Cel was launched from TK-HA-Cel@Ms, which was considerably decrease than that of free Cel. This indicated that TK-HA-Cel@Ms had vital retardation as a result of the outermost layer of the micelles, PEG5000, fashioned a hydration layer, thus rising the soundness of the micelles and delaying the discharge of Cel. In distinction, TK-HA-Cel@Ms launched greater than 40% of the Cel in PBS (pH 7.4) containing 200 µM H2O2. It was in all probability because of the H2O2-induced breakage of the TK bond, which facilitated the discharge of Cel afterward. The discharge of TK-HA-Cel@Ms was considerably accelerated in PBS (pH 5.5) containing 200 µM H2O2, with greater than 60% of Cel launched for 48 h. The speedy launch of Cel was attributed to the breakage of the TK-sensitive bond within the presence of ROS. This stripped off the hydration layer of PEG5000, which in flip led to the decomposition of the micelles beneath acidic situations, thereby accelerating drug launch. These outcomes advised that it was potential to make sure the steady supply of TK-HA-Cel@Ms in circulation and set off the cascade focusing on of micelles on the website of irritation for exact drug supply, which is essential for the efficient remedy of RA.
After intravenous administration, TK-HA-Cel@Ms are uncovered to blood cells and inflammation-related cells. Due to this fact, the hemocompatibility of TK-HA-Cel@Ms must be understood. We carried out a hemolysis experiment. The group with numerous concentrations of drug-loaded micelles displayed a pale-yellow colour. In distinction, the constructive management group confirmed a shiny pink colour (Fig. 1I). This advised that the drug-loaded micelles exhibited good biocompatibility and will subsequently be administered intravenously to some extent.
The steadiness of the micelles at 4 °C and RT was evaluated by measuring the particle dimension, PDI, and EE (Fig. 1J-L). The outcomes confirmed that the EE of micelles barely decreased and the particle dimension and PDI barely elevated inside 28 days, however these variations had been throughout the permissible vary, indicating good stability of TK-HA-Cel@Ms.
Mobile uptake and distribution
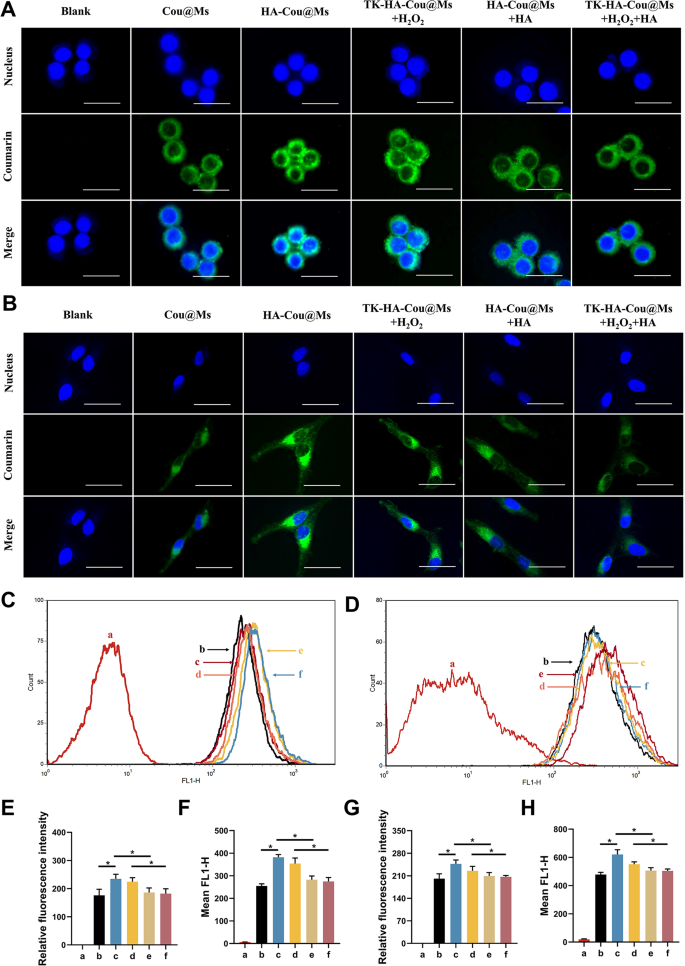
The power of the nanoparticle methods to enter cells straight determines their therapeutic effectivity. LPS-activated RAW264.7 cells and RA-FLSs had been used to evaluate the energetic focusing on and mobile uptake talents of assorted micelles. Confocal laser scanning imaging (Fig. 2A and B) and circulate cytometry (Fig. 2C and D) confirmed that the inexperienced fluorescence of activated macrophages and RA-FLSs incubated with HA-Cou@Ms was the strongest. The fluorescence depth within the TK-HA-Cou@Ms group co-incubated with H2O2 was near that within the HA-Cou@Ms group. As well as, the uptake of HA-Cou@Ms and TK-HA-Cou@Ms co-incubated with H2O2 by activated macrophages with RA-FLSs was considerably inhibited after pretreating the cells with HA first. These outcomes indicated that TK-HA-Cou@Ms prompted the cleavage of the TK-sensitive bond by ROS, the PEG5000 on the floor of the micelles was shed, and the focusing on molecule HA was uncovered. HA particularly certain to the CD44 receptors on the floor of the inflammatory cells, considerably rising the uptake and entry of the drug into the inflammatory cells via CD44-mediated endocytosis and thus displaying energetic focusing on functionality [23].
Mobile uptake after incubation with various formulations. (A) Confocal microscope photos of RAW264.7 cells handled with LPS with completely different formulations, scale bar, 25 μm; (B) Confocal microscope photos of RA-FLSs handled with completely different formulations, scale bar, 25 μm; (C) Mobile uptake of various formulations to RAW264.7 cells handled with LPS; (D) Mobile uptake of various formulations to RA-FLSs; (E) Quantitative evaluation of (A); (F) Quantitative evaluation of (C); (G) Quantitative evaluation of (B); (H) Quantitative evaluation of (D). Knowledge are introduced as imply ± SD (n = 3). a, Clean; b, Cou@Ms; c, HA-Cou@Ms; d, TK-HA-Cou@Ms + H2O2; e, HA-Cou@Ms + HA; f, TK-HA-Cou@Ms + H2O2 + HA. *P < 0.05
Cell viability and apoptosis assays
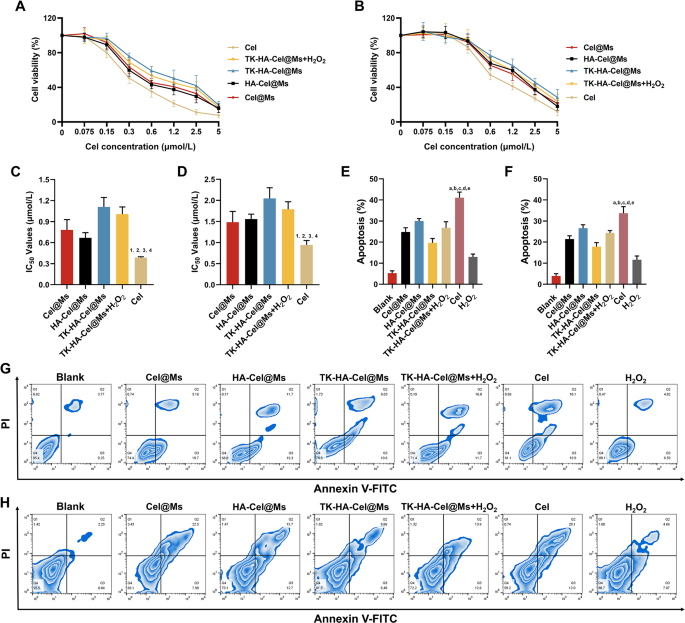
Cel has vital toxicity and unwanted side effects. Therefore, the results of free Cel and completely different Cel-loaded micelles on the viability of LPS-activated RAW264.7 cells and RA-FLSs in vitro had been examined utilizing the cell counting package 8 assay. Earlier than analyzing the cytotoxicity of various preparations, we first examined the results of various concentrations of H2O2 on RAW264.7 cells and RA-FLSs cells, as proven in Fig. S3, H2O2 confirmed a dose-dependent cytotoxicity, but it surely had little impact on cell survival beneath 200 µM, and it was additionally capable of successfully mimic the excessive ROS ranges in vivo, subsequently, we selected 200 µM of H2O2 for the next experiments. As proven in Fig. 3A and B, all teams of medicine inhibited cell viability dose-dependently, with the free Cel displaying the very best cytotoxicity and TK-HA-Cel@Ms the bottom. It was primarily as a result of the Cel answer existed as free small molecules, which may cross the cell membrane shortly and effectively to exert an impact. The added H2O2 elevated the cytotoxicity of TK-HA-Cel@Ms, doubtless as a result of the hydrated membrane fashioned by PEG5000 on the micelle floor successfully diminished mobile, thereby decreasing cytotoxicity. Thus, it diminished regular cell injury throughout in vivo biking, achieved exact supply, and improved therapeutic effectivity. Fig. 3C and D exhibits the IC50 values of various preparations on LPS activation of RAW264.7 cells and RA-FLSs, extra intuitively demonstrating the inhibitory impact of assorted formulations on cells. The power of free Cel and completely different Cel-loaded micelles to induce the apoptosis of activated RAW264.7 cells and RA-FLSs was additional detected utilizing circulate cytometry, and the apoptosis outcomes had been quantified (Fig. 3E-H). Cel-induced apoptosis occurred in roughly 40% of LPS-activated RAW264.7 cells and 30.0% of RA-FLSs in the course of the 24-h take a look at interval. The micellar formulations induced decrease apoptosis charges than Cel. TK-HA-Cel@Ms displayed the weakest apoptosis induction, with roughly 20% and 15% apoptosis within the aforementioned two cells, respectively, aligning with the cell viability outcomes.
Cell viability and apoptosis after incubation with various formulations. (A) Progress curves of various formulations of RAW264.7 cells at various concentrations of Cel; (B) Progress curves of various formulations of RA-FLSs at various concentrations of Cel; (C) Statistical evaluation of IC50 values of RAW264.7 cells; (D) Statistical evaluation of IC50 values of RA-FLSs; (E) The full percentages of apoptosis of RAW264.7 cells after administration with various formulations; (F) The full percentages of apoptosis of RAW264.7 cells after administration with various formulations; (G) The apoptosis of RAW264.7 cells after incubation with various formulations; (H) The apoptosis of RA-FLSs after incubation with various formulations. Knowledge are introduced because the imply ± SD (n = 3). 1, vs. Cel@Ms; 2, vs. HA-Cel@Ms; 3, vs. TK-HA-Cel@Ms; 4, vs. TK-HA-Cel@Ms + H2O2. P < 0.05. a, vs. Clean; b, vs. Cel@Ms; c, vs. HA-Cel@Ms; d, vs. TK-HA-Cel@Ms; e, vs. TK-HA-Cel@Ms + H2O2. P < 0.05
Macrophage polarization in vitro
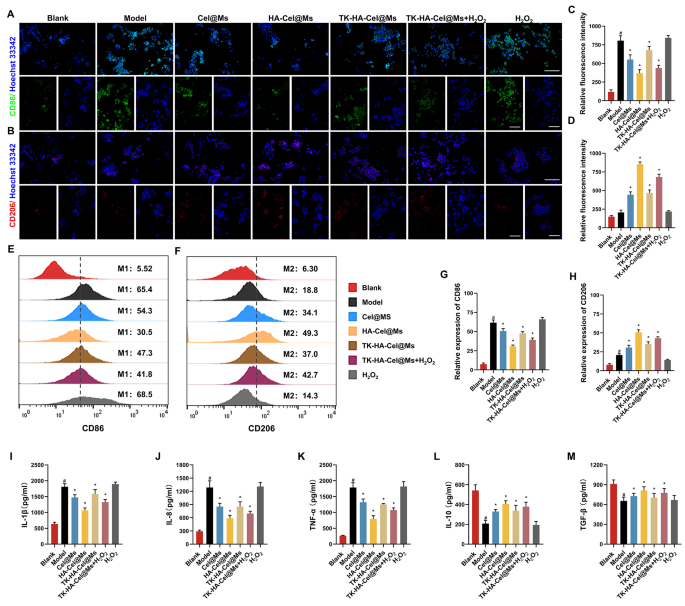
The M1/M2 transformation of macrophages is a key issue within the pathogenesis of RA. Only some macrophages are current within the knee synovium of wholesome people [24,25,26]. Nonetheless, the depth and filtration space of macrophage are considerably elevated within the knee synovium of sufferers with RA [27]. Given the power of TK-HA-Cel@Ms to focus on each activated macrophages and RA-FLSs, we predicted that TK-HA-Cel@Ms may be advantageous in reprogramming the phenotype of macrophages. Due to this fact, we first analyzed macrophage phenotypes by immunofluorescence staining of CD86 (M1 marker) and CD206 (M2 marker) and assessed whether or not TK-HA-Cel@Ms may successfully repolarize M1 macrophages to the M2 phenotype. As proven in Fig. 4A and B, many of the regular macrophages had been of M0 phenotype with insignificant CD86 and CD206 fluorescence alerts. Nonetheless, the macrophages had been considerably polarized to the M1 phenotype after LPS stimulation, thus displaying enhanced CD86 immunity. The macrophages shifted from M1 to M2 phenotype to various levels after administering completely different drug interventions, with HA-Cel@Ms having essentially the most pronounced impact and TK-HA-Cel@Ms co-incubated with H2O2 having the second simplest impact. The impact of TK-HA-Cel@Ms on the polarization of LPS-treated macrophages was additional detected and quantified utilizing circulate cytometry. It was clearly seen that the proportion of CD86 and CD206 was about 65% and 20%, respectively, after remedy with LPS. Nonetheless, a notable shift was noticed in HA-Cel@Ms-treated macrophages, with a 35% lower within the M1 phenotype marker CD86 and a 30% improve within the M2 phenotype marker CD206, indicating a major impact on the reprogrammed macrophage polarization (Fig. 4E and F). The impact of TK-HA-Cel@Ms co-incubated with H2O2 was near its impact, suggesting that TK-HA-Cel@Ms with out the PEG5000 hydration layer within the inflammatory microenvironment considerably repolarized the M1 to M2 phenotype and diminished the M1/M2 ratio to regular ranges.
Macrophage polarization and anti inflammatory exercise in vitro after incubation with various formulations. (A) Consultant fluorescence photos of CD86 staining of macrophages on completely different formulations; (B) Consultant fluorescence photos of CD206 staining of macrophages on completely different formulations; (C–D) Quantitative evaluation of fluorescence depth in (A) and (B); (E) Circulate cytometric histograms of the polarization of LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages to the M1 phenotype; (F) Circulate cytometric histograms of the polarization of LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages to the M2 phenotype; (G–H) Evaluation of relative fluorescence depth in (E) and (F); (I–M) Ranges of IL-1β, IL-8, TNF-α, IL-10 and TGF-β in cell tradition supernatant. Knowledge had been introduced as imply ± SD (n = 3). #, vs. Clean; *, vs. Mannequin. P < 0.05
Anti-inflammatory exercise in vitro
Inflammatory cytokines are main mediators of the inflammatory response in RA, reflecting the severity of the illness and enjoying an necessary function within the pathogenesis of immune-related RA [8, 28]. Professional-inflammatory cytokines, reminiscent of interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-8, and tumor necrosis issue (TNF)-α secreted by M1 macrophages, can result in elevated irritation, synoviocyte invasion, and bone destruction in RA [29]. Anti-inflammatory cytokines reminiscent of IL-10 and tumor progress issue (TGF)-β secreted by M2 macrophages are important in inhibiting irritation and decreasing the secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines [30]. The anti-inflammatory potential of assorted preparations was assessed by incubating LPS-treated RAW264.7 cells after which measuring the degrees of cytokines reminiscent of IL-1β, IL-8, TNF-α, IL-10, and TGF-β. As proven in Fig. 4I-M, the degrees of pro-inflammatory cytokines elevated considerably, whereas the degrees of anti-inflammatory cytokines decreased considerably after LPS activation. Nonetheless, remedy with completely different preparations downregulated the degrees of pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-1β, IL-8, and TNF-α) whereas upregulated the degrees of anti-inflammatory cytokines (IL-10 and TGF-β) in activated macrophages, with essentially the most pronounced therapeutic impact of HA-Cel@Ms, adopted by the second simplest impact of TK-HA-Cel@Ms co-incubated with H2O2. It advised that the therapeutic impact of TK-HA-Cel@Ms on RA beneath inflammatory situations may be attributed to the modulation of macrophage phenotypes by concurrently enhancing anti-inflammatory macrophages and decreasing pro-inflammatory macrophages.
Analysis of proliferative, migratory and invasive actions in vitro
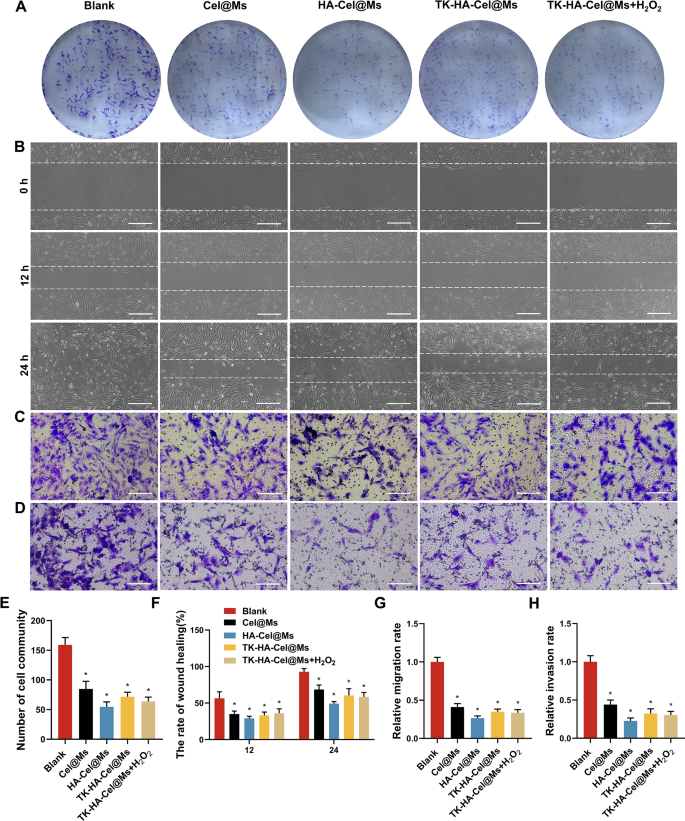
RA-FLSs current tumor-like cell progress, much like tumor cells by way of malignant proliferation, elevated expression of intracellular anti-apoptotic genes, and subsequent erosion of cartilage, in the end resulting in joint destruction, which performs an important function within the pathogenesis of the aggressive phenotype of RA [31, 32]. Due to this fact, inhibiting the irregular progress and proliferation of RA-FLSs is important for RA remedy. We carried out colony formation assays to research the results of various micelles on RA-FLSs proliferation. The clone formation was considerably inhibited within the HA-Cel@Ms-treated group in contrast with the management group. The inhibitory results on cell colony formation was considerably enhanced by TK-HA-Cel@Ms on including H2O2 to the tradition medium, which was in line with the inhibitory results of HA-Cel@Ms (Fig. 5A and E).
Analysis of proliferative, migratory and invasive actions in vitro. (A) Colony formation assays of RA-FLSs on completely different formulations; (B) Picture of wound therapeutic on RA-FLSs in 12 h and 24 h after remedy with various formulations, Scale bar = 50 μm; (C–D) The consequences of micelles on RA-FLSs migration (C) and invasion (D) had been additional decided by transwell assay, Scale bar = 50 μm; (E) Variety of cell neighborhood; (F) The speed of wound therapeutic; (G–H) Relative migration and invasion fee. Knowledge had been introduced as imply ± SD (n = 3). *, vs. Clean. P < 0.05
The proliferation of RA-FLSs and their subsequent migration and invasion of cartilage and bone can exacerbate joint destruction in RA. The outcomes of the impact of every group of micellar preparations on the wound therapeutic of RA-FLSs are proven in Fig. 5B and F. The outcomes confirmed that the width of the scratches was diminished in every group 12 and 24 h after administration in contrast with that after 0 h, and the scratches had been principally healed after 24 h within the clean group. Totally different micelles inhibited the therapeutic of scratches to a sure extent in contrast with that within the clean group, and the HA-Cel@Ms group confirmed the obvious diploma of inhibition. The consequences of micelles on the migration and invasion of RA-FLSs had been additional decided utilizing the transwell assay. Fig. 5C, D, G, and H exhibits the pictures of the cells in every group after administering micelles and passage via the transwell. A lot of cells had been seen within the clean group passing via the chamber, indicating that the RA-FLSs cells had sturdy migration and invasion talents. A major lower within the variety of cells crossing the transwell was noticed in every administration group in contrast with the clean group, which was most evident within the HA-Cel@Ms group. The impact of TK-HA-Cel@Ms co-incubated with H2O2 was near it.
Focusing on and circulation habits in vivo
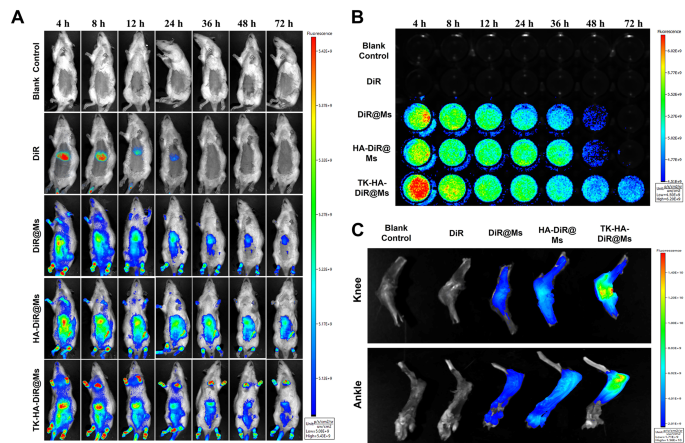
The enrichment and in vivo distribution of TK-HA-DiR@Ms of CIA mannequin rats had been noticed by real-time fluorescence imaging utilizing DiR as a substitute of Cel as a fluorescent probe. As proven in Fig. 6A, no fluorescence sign distribution was seen within the clean group. The fluorescence of free DiR was primarily gathered within the liver of rats, which might be defined by speedy metabolism and nonspecific focusing on. Nonetheless, apparent fluorescence alerts had been noticed on the binding website in every micelle group, and these alerts confirmed various levels of attenuation with time. Nonetheless, the fluorescence alerts of TK-HA-DiR@Ms remained concentrated on the binding website for an extended period and had been stronger in depth.
Focusing on and circulation habits in vivo. (A) Actual-time imaging remark of CIA rats handled with various formulations in vivo; (B) Lengthy circulation impact after intravenous administration of various formulations in CIA rats; (C) Ex vivo imaging of the knee and ankle joints harvested from CIA rats handled with completely different formulations after 72 h (n = 3)
Then, the blood samples had been collected from rats with CIA at applicable time factors to observe the fluorescence depth of the medicine within the blood and preliminarily consider the pharmacokinetic profile of TK-HA-DiR@Ms. No fluorescent alerts had been detected within the clean management and free DiR teams (Fig. 6B). In distinction, the depth of the fluorescent alerts within the blood of the rats in every micellar group steadily weakened with time. The circulation time of every agent within the blood adopted the order TK-HA-DiR@Ms > HA-DiR@Ms > DiR@Ms > DiR.
The rats had been executed 72 h later to gather the knee and ankle joints for fluorescence depth evaluation. As proven in Fig. 6C and D, the buildup of every micelle on the infected joints considerably elevated in contrast with free DiR, confirming that together with the suitable particle dimension of micelles allowed their accumulation on the lesion website utilizing the ELVIS impact [33, 34]. As well as, the buildup of TK-HA-DiR@Ms was most pronounced in infected joints. PEG5000 considerably extended the retention time of the micelles within the bloodstream, successfully avoiding phagocytosis by the liver and the reticuloendothelial system. Additionally, it hid the focusing on ligands, stopping the binding of the micelles to normal-functioning inflammatory cells, thus exerting excellent passive focusing on capacity. The extended circulation time assisted it in reaching the location of irritation. At this website, the excessive ranges of ROS cleaved the delicate bonds, exposing the HA. This publicity enhanced the energetic focusing on of the micelles, rising the drug focus within the joint tissues and additional enhancing the therapeutic effectivity.
Therapeutic efficacy in vivo
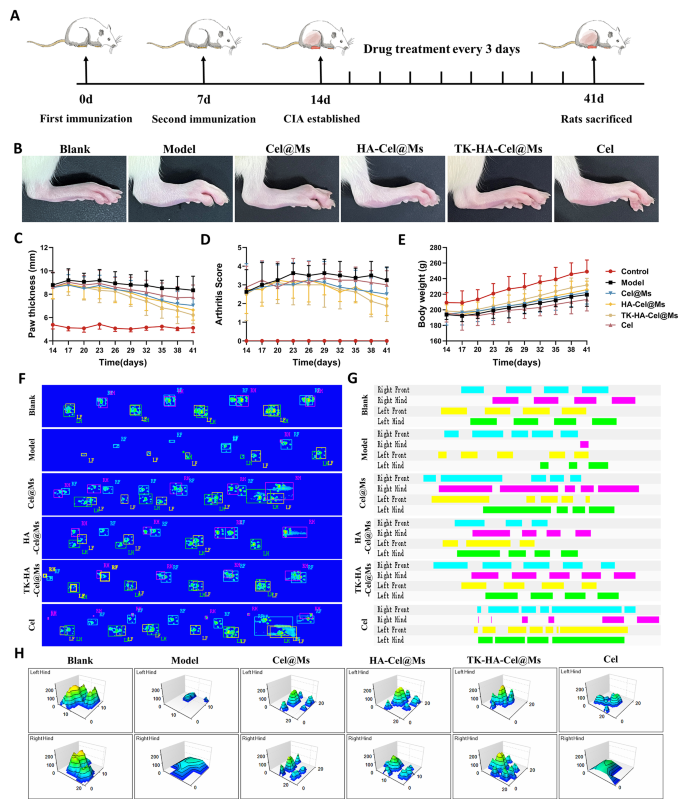
Primarily based on the aptitude of TK-HA-Cel@Ms to effectively goal irritation and slow-release medicine on demand in rats with CIA, we evaluated its mixed therapeutic results in a CIA rat mannequin, following the protocol proven in Fig. 7A. Evaluating medical indicators, we discovered that the mannequin group of rats with CIA exhibited erythema and extreme deformities in a number of joints all through the paw. In distinction, Cel@Ms, HA-Cel@Ms, and TK-HA-Cel@Ms therapies delayed the development of RA, with TK-HA-Cel@Ms displaying one of the best outcomes; no vital erythema or deformities had been noticed in handled hind paws (Fig. 7B). As well as, TK-HA-Cel@Ms considerably diminished paw thickness and arthritis index in rats with CIA (Fig. 7C and D). The standard of lifetime of rats with CIA was assessed by evaluating the adjustments in physique weight. Rats within the mannequin group confirmed gradual weight achieve from illness onset to peak, whereas rats handled with TK-HA-Cel@Ms demonstrated weight achieve much like that of wholesome rats. This indicated that TK-HA-Cel@Ms improved the standard of lifetime of the rats (Fig. 7E).
Anti-arthritic efficacy in CIA rats. (A) Schematic illustration of remedy regimens; (B) Consultant images of hindlimbs from every group; (C) Paw thickness of arthritic rats over time from every group; (D) Arthritis rating of arthritic rats over time from every group; (E) Physique weight of arthritic rats over time from every group; (F) Footprint-pressure thermographic map in CIA rats; (G) 2D imaging of rat plantar strain; (H) 3D imaging of rat plantar strain (n = 6)
We then assessed whether or not TK-HA-Cel@Ms may restore rats with CIA to a traditional strolling sample. The fluorescence photos of the rat paws touching the floor of the glass plate confirmed that static parameters, together with imply paw strain and imply paw space, had been diminished in rats with CIA in contrast with regular rats. Nonetheless, TK-HA-Cel@Ms considerably restored paw strain and paw space (Fig. 7F). Additionally, the 2D and 3D plots revealed that the rats within the TK-HA-Cel@Ms group had vital plantar pressures and longer retention instances in contrast with the rats within the mannequin group, which was near that within the clean group (Fig. 7G and H).
Additional, the serum ranges of IL-1β, IL-8, TNF-α, IL-10, and TGF-β had been measured to confirm the impact of TK-HA-Cel@Ms on the manufacturing of inflammatory cytokines, that are carefully associated to the event of RA. As proven in Fig. S4, TK-HA-Cel@Ms may considerably downregulate the degrees of pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-1β, IL-8, and TNF-α) within the serum of rats with CIA whereas up-regulating the degrees of anti-inflammatory cytokines (IL-10 and TGF-β) within the serum. It was in line with the outcomes of the in vitro experiments.
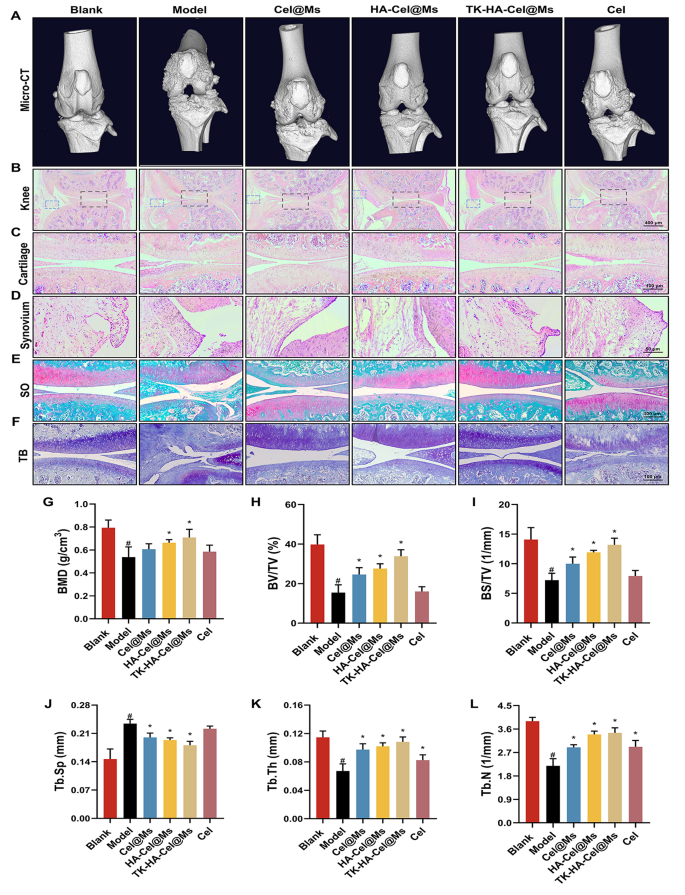
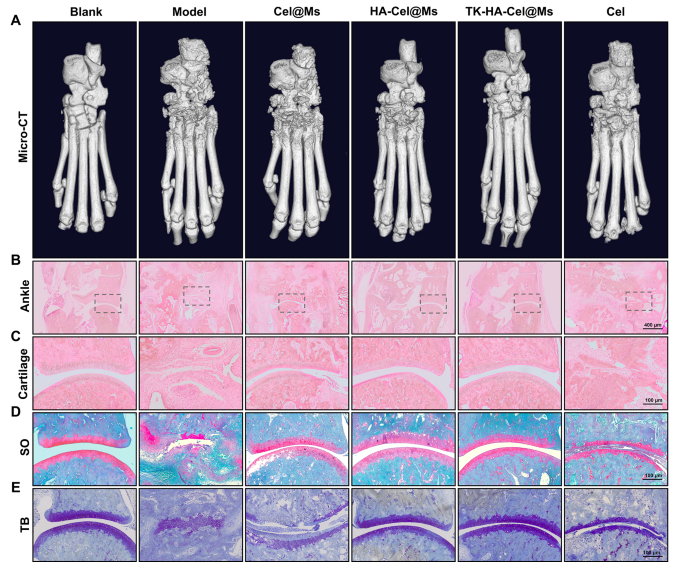
Bone destruction is a serious contributor to incapacity and lack of joint operate in RA and is modulated by numerous elements; it will probably function an necessary medical indicator for assessing the severity of arthritis [35, 36]. The knee and ankle joints of rats had been scanned utilizing X-ray and micro-computed tomography (micro-CT) to evaluate the bone injury after remedy in rats with CIA. As proven in Figs. 8A and 9A, and S5, the knee and ankle joints of saline-treated rats with RA confirmed extreme bone injury with tough surfaces and extreme bone destruction. Bone erosion was reversed to a sure extent in all remedy teams in contrast with the mannequin group. This resulted in improved bone high quality. The TK-HA-Cel@Ms group demonstrated essentially the most vital impact, with bone high quality closest to that of regular rats. The histomorphometric analyses of micro-CT photos had been additionally carried out to guage the extent of bone injury in numerous teams. Numerous parameters, reminiscent of BMD, BV/TV, BS/TV, Tb.Sp, Tb.Th, and Tb.N, had been analyzed. The outcomes confirmed that TK-HA-Cel@Ms considerably elevated BMD, BV/TV, BS/TV, Tb.Th, Tb.N, and decreased Tb.Sp in contrast with these in rats with CIA (Fig. 8G-L). All these parameters exhibited related tendencies, supporting the notion that TK-HA-Cel@Ms slowed the development of RA and prevented RA-mediated bone destruction and bone erosion.
Micro-CT evaluation and histology evaluation of the knee joints of rats. (A) Consultant micro-CT photos of the knee joints of rats; (B–D) HE staining of knee, cartilage and synovium sections of rats in every group; (E) Safranin O staining of cartilage sections of rats in every group; (F) Toluidine blue staining of cartilage sections of rats in every group; (G–L) BMD, BV/TV, BS/TV, Tb.Sp, Tb.Th and Tb.N from joints of rats in numerous group. Knowledge had been introduced as imply ± SD (n = 6). #, vs. Clean; *, vs. Mannequin. P < 0.05
Micro-CT evaluation and histology evaluation of the ankle joints of rats. (A) Consultant micro-CT photos of the ankle joints of rats; (B–C) HE staining of ankle and cartilage sections of rats in every group; (D) Safranin O staining of cartilage sections of rats in every group; (E) Toluidine blue staining of cartilage sections of rats in every group (n = 6). #, vs. Clean; *, vs. Mannequin. P < 0.05
The expression of macrophage floor markers in synovial tissues of CIA rats was detected by circulate cytometry. The outcomes, as proven in Fig. S6, confirmed that in contrast with the traditional group, the expression of CD86 in synoviocytes of rats within the mannequin group was considerably elevated, and the expression of CD206 was barely elevated, and all of the remedy teams decreased the expression of CD86, and elevated the expression of CD206 within the CIA rats, during which the remedy impact of TK-HA-Cel@Ms was the obvious, and the expression of CD86 was down-regulated almost 3-fold in contrast with the mannequin group, and the expression of CD206 was elevated by 3 instances in contrast with the mannequin group.
The histological evaluation was carried out to additional examine the protecting impact of TK-HA-Cel@Ms on the joints of the CIA rat mannequin. Figs. 8B-D, 9B, C present the outcomes of hematoxylin and eosin (HE) staining of the knee and ankle joints of rats in every group. The cartilage tissue of each knee and ankle joints of regular rats was structurally intact, and the joint surfaces had been easy and neat. In distinction, the joint area of rats with CIA confirmed cracks and deformations, with a lot of synovial hyperplasia and inflammatory cell infiltration. The knee and ankle joints of rats in every group had been stained with Safranin O and toluidine blue, respectively, to guage the protecting results of various formulations on inflammation-induced cartilage injury. The cartilages of the ankle and knee joints had been clearly stained, with no apparent discoloration of cell staining within the clean management group. In distinction, the cartilage tissue of the knee joint within the mannequin group confirmed mild staining; additionally, the joint floor was uneven, and the cartilage construction was disorganized (Figs. 8E, F, 9D, E). Nonetheless, the cartilage staining of rats in every micellar group was considerably darker than that within the mannequin group, and the impact was most evident within the TK-HA-Cel@Ms group. Furthermore, the rats within the TK-HA-Cel@Ms group confirmed higher morphological integrity and fewer erosive destruction of cartilage surfaces, which was the closest to that within the clean group, suggesting that the TK-HA-Cel@Ms had glorious bone safety and anti-synovial proliferation results.
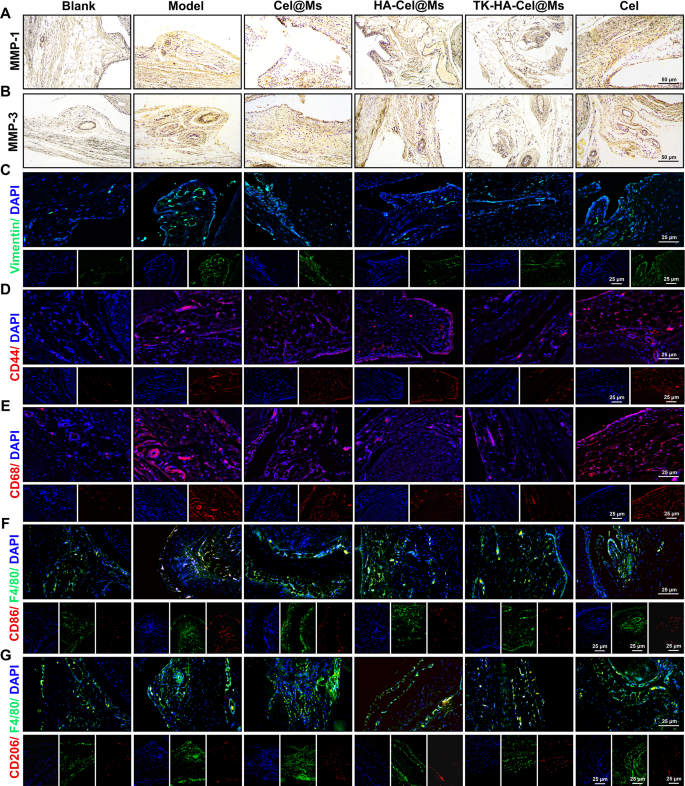
FLSs play a pivotal function in RA pathogenesis, secreting inflammatory cytokines and proteases reminiscent of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) and inflicting everlasting joint injury [37, 38]. As zinc-dependent endopeptidases, MMPs (e.g., MMP-1 and MMP-3) degrade numerous proteins within the extracellular matrix (ECM), trigger FLSs migration and invasion, and play an necessary function within the destruction of cartilage and bone [29, 39]. The immunohistochemistry outcomes of MMP-1 (Fig. 10A) and MMP-3 (Fig. 10B) in synovial sections confirmed a lot of MMP-1 and MMP-3 proteins expressed within the mannequin group in contrast with the clean management group. In distinction, the expression ranges of each proteins decreased within the different remedy teams. The TK-HA-Cel@Ms group had the bottom expression of MMP-1 and MMP-3 proteins, which inhibited FLSs migration and invasion, additional diminished cartilage injury and erosion, and guarded cartilage. We additionally selected vimentin, a marker of fibroblasts, to find out the proliferation of FLSs. As proven in Fig. 10C, the immunofluorescence outcomes of vimentin in synovial sections confirmed that the expression of vimentin was considerably diminished, and FLSs proliferation was inhibited within the TK-HA-Cel@Ms group.
Immunohistochemistry and immunofluorescence staining in synovium of rats. (A–B) Photographs of immunohistochemistry outcomes of MMP-1 and MMP-2 in synovium after remedy; (C–G) Photographs of immunofluorescence outcomes of vimentin, CD44, CD68, CD86 and CD206 in knee synovial tissues after remedy (n = 6)
Macrophages are activated throughout RA pathogenesis, and CD44 and CD68 receptors are extremely expressed on their floor [40, 41]. The immunofluorescence staining outcomes of CD44 and CD68 in synovial tissues are proven in Fig. 10D and E. The outcomes confirmed that CD44 and CD68 had been abundantly expressed within the synovium of the mannequin rats. Additionally, the TK-HA-Cel@Ms considerably inhibited the expression of CD44 and CD86 on the floor of the activated macrophages, successfully assuaging the inflammatory response.
Primarily based on the numerous in vitro macrophage phenotypic repolarization capacity of TK-HA-Cel@Ms, we additional investigated macrophage polarization in infected joints utilizing immunofluorescence. As proven in Fig. 10F and G, CD86 fluorescence depth considerably elevated and CD206 fluorescence depth barely elevated within the synovium of rats within the mannequin group in contrast with regular rats, suggesting the infiltration of a lot of M1 macrophages into the RA synovium. After remedy with TK-HA-Cel@Ms, the expression of CD86 was considerably diminished, whereas the expression of CD206 considerably elevated. This indicated that TK-HA-Cel@Ms promoted the repolarization of M1 macrophages to the M2 phenotype, which was in line with the outcomes of the in vitro research.
Security analysis in vivo
Regardless of numerous pharmacological actions of Cel reminiscent of anti-inflammatory results, modulation of macrophage polarization, and inhibition of FLSs proliferation, its potential toxicity stays a priority [42, 43]. Some research have reported that though efficient, Cel could cause injury to a number of organs or tissues and even loss of life [44]. Due to this fact, HE staining of main organs was carried out to watch the morphology of the center, liver, spleen, lungs, and kidneys to evaluate the in vivo toxicity of Cel. As noticed in Fig. S7, free Cel prompted mobile injury and inflammatory cell infiltration within the liver and kidney. The center, liver, spleen, lung, and kidney tissues of rats within the TK-HA-Cel@Ms group didn’t present any apparent histological abnormality or lesion, suggesting that TK-HA-Cel@Ms considerably diminished liver and kidney injury, thereby reducing the hepatorenal toxicity of Cel.