Identification and characterization of PGEVs
PGEVs had been remoted from recent PG by ultracentrifugation and sucrose gradient centrifugation technique. Pushed by the sucrose gradient, the PGEVs had been deposited primarily on the 30%/45% interface. TEM was employed to character the morphology of the PGEVs (Fig. 1A). The TEM pictures clearly revealed that the PGEVs had been typical spherical nanovesicles. Two strategies had been used to detect the particle dimension of the PGEVs. The nanoflow cytometry outcomes demonstrated that the imply diameter of the PGEVs was 73.0 nm and the median diameter was 64.8 nm (Fig. 1B). The nanocoulter counter measured that the imply dimension and median dimension of the PGEVs had been 74.0 nm and 74.0 nm, respectively (Fig. 1C). The zeta potential is a major parameter for evaluating the soundness of nanoparticles. In accordance with the outcomes from the nanocoulter counter, the zeta potential of PGEVs was − 19.23 mV (Fig. S1), which was conducive to their medical software in vivo. PEVs often comprise proteins and RNAs. The SDS-PAGE gel electrophoresis was carried out to detect the protein distribution in PGEVs. The outcomes revealed that the molecular weights of the main proteins ranged from 30 kDa to 130 kDa (Fig. 1D). The agarose gel electrophoresis outcomes demonstrated that the nucleic acids inside PGEVs had been primarily small RNAs, as confirmed by the entire degradation of those nucleic acids after therapy with RNase (Fig. 1E). As well as, the PD content material in PGEVs (17.1 µg/mL) was detected via HPLC (Fig. S2).
Identification and characterization of PGEVs. (A) TEM pictures of PGEVs, scale bar: 200 nm. Measurement distribution of PGEVs detected by nanoflow cytometry (B) and nanocoulter counter (C). (D) SDS-PAGE gel electrophoresis of PGEVs. The proteins in PGEVs had been separated through 15% SDS-PAGE and stained with Coomassie blue dye. (E) Agarose gel electrophoresis of PGEVs. The RNA extracted from PGEVs was handled with or with out RNase and run on a 1.5% agarose gel. Lipid compositions (F) and protein abstract (G) of PGEVs. GO secondary classification statistical charts (H) and KEGG annotated statistical charts (I) of proteins in PGEVs
Lipidomic evaluation was carried out to establish the lipid composition of PGEVs. As proven in Fig. 1F and Desk S1, the main lipid elements in PGEVs had been triglyceride (TG, 35.6%), diacylglycerol (DG, 11.4%) and ceramide (Cer, 10.6%). In accordance with earlier report, Cer is an important part recognized for its position in facilitating or inducing membrane curvature throughout the formation and secretion of EVs [31]. The presence of Cer in PGEVs proved the pure secretion of PGEVs from PG. A substantial proportion of phospholipids, together with lysophosphatidylcholine (LPC, 4.1%), phosphatidylethanolamine (PE, 3.7%), phosphatidylglycerol (PG, 2.8%) and phosphatidylcholine (PC, 2.7%), had been detected in PGEVs, which was per the truth that PEVs are enriched in phospholipids. Phospholipids play an important position in selling the neural cell differentiation and activating the neutrophils and macrophages. Moreover, they take part in regulating immune responses, together with their recognition by TLRs and the activation of immune cells [32]. These outcomes prompted us to invest the potential participation of PGEVs in immunomodulatory processes. Moreover, monogalactosyldiacyglycerol (MGDG) and digalactosyldiacylglycerol (DGDG) accounted for two.3% and a couple of.2% of the entire lipids in PGEVs, respectively, which had been often utilized to stabilize phospholipids throughout freeze-thawing and freeze-drying [33]. MGDG is especially notable for its sturdy binding affinity to the asialoglycoprotein receptor (ASGPR) that extremely expressed on the floor of tumor cells, which makes it helpful for enhancing the focused supply of bioactive molecules to tumor websites [34]. Phosphatidic acid (PA), constituting 1.7% of the entire lipids in PGEVs, participates in numerous organic features and processes, together with cell proliferation, transformation and differentiation. It additionally influences the uptake of PEVs by inducing cytoskeleton rearrangement [35]. Moreover, the above lipids present in PGEVs are amphiphilic, that are essential for sustaining the structural integrity and stability of those vesicles. The evaluation of lipid composition contributes to elucidating the origin and performance of PGEVs.
Proteomic evaluation was carried out to investigate the compositions of proteins in PGEVs. The outcomes revealed the presence of 5296 proteins in PGEVs (Fig. 1G), together with aquaporin-like proteins, ribosomal proteins, transmembrane proteins, and the plasma membrane. The warmth shock proteins 70 and 90 (HSP 70 and HSP 90), in addition to glutathione transferase and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH), had been detected in PGEVs, which have been incessantly reported in earlier research on PEVs [36]. RNA-binding proteins comparable to argonaute (AGO) had been additionally recognized in PGEVs. AGO proteins, in affiliation with small RNAs (sRNAs), are concerned in gene silencing through complementary sequences, probably influencing the packaging of small RNAs in PGEVs. This discovering recommend that PGEVs, as useful vesicles, could take part in cargo transportation inside the PG [37]. The organic features of the above proteins had been analyzed via GO database (Fig. 1H). They had been labeled into three classes: organic course of, mobile part and molecular operate. As well as, KEGG evaluation displayed that the proteins in PGEVs had been related primarily with the organismal system, metabolism, genetic info processing, environmental info processing and mobile elements (Fig. 1I). General, these outcomes revealed that PGEVs contained considerable lipids and proteins.
Stability and mobile uptake of PGEVs in vitro
Amongst all routes of administration, oral administration is considered essentially the most handy technique due to its minimal requirement for added labor or tools, low value and excessive affected person compliance. Nonetheless, the cruel circumstances within the gastrointestinal tract (GIT), characterised by sturdy abdomen acidity and energetic digestive enzymes, presents important challenges for the oral administration of biomaterials. PGEVs had been incubated with PBS, 10% FBS, SIF or SGF for numerous durations to guage their stability in GIT. Adjustments of their particle dimension and dimension distribution had been detected utilizing nanoflow cytometry, as introduced in Fig. 2A-D and Fig. S3. The particle dimension of PGEVs remained secure in PBS, 10% FBS and SGF in any respect time factors. Nonetheless, a slight lower in particle dimension was noticed in SIF after 48 h of incubation. These findings indicated that PGEVs had been in a position to keep their integrity and resist digestion whereas passing via the GIT for no less than 24 h.
For efficient tumor therapy, it’s essential that tumor cells effectively internalize PGEVs, because the energetic elements of pure nanoparticles exert their therapeutic results primarily inside the cells. To evaluate the mobile uptake of PGEVs, DiI-labeled PGEVs (DiI-PGEVs) had been incubated with 4T1 and A549 cells, and their internalization was noticed utilizing fluorescence microscopy. As indicated in Fig. 2E and F, the internalization of PGEVs was noticed to be time-dependent. After 6 h of incubation, the numerous proportions of each 4T1 cells and A549 cells exhibited purple fluorescence, indicative of DiI-PGEVs. The internalization effectivity of PGEVs was additional quantified utilizing stream cytometry. Determine 2G-I additionally confirmed that the internalization effectivity of DiI-PGEVs by 4T1 and A549 cells improved with rising incubation time. After 6 h of incubation, the odds of DiI-PGEVs taken up by 4T1 and A549 cells had been 72.2% and 81.3%, respectively. Earlier analysis has indicated that the effectivity of nanoparticle uptake is influenced by the presence of particular cell floor receptors [38]. Subsequently, the distinction within the uptake effectivity of PGEVs between 4T1 cells and A549 cells could also be attributed to their heterogeneous floor compositions. Moreover, Uncooked 264.7 macrophages had been additionally handled with DiI-PGEVs for various durations. The outcomes (Fig. S4) demonstrated the environment friendly uptake of DiI-PGEVs by Uncooked 264.7 cells, with preferential localization within the cytomembrane.
Stability and mobile uptake of PGEVs in vitro. Adjustments within the imply particle sizes and median sizes of PGEVs after incubation in PBS (A), 10% FBS (B), SIF (C) or SGF (D) at 37 °C for 1 h, 3 h, 6 h, 12 h, 24 h, or 48 h. Consultant fluorescence pictures of DiI-PGEVs handled 4T1 cells (E) and A549 cells (F) for 1 h, 3 h, or 6 h, scale bar: 50 μm. The uptake effectivity of DiI-PGEVs in 4T1 cells (G) and A549 cells (H) was examined utilizing stream cytometry and the corresponding quantitative evaluation (I)
Anti-tumor exercise of PGEVs in vitro
The anti-tumor exercise of PGEVs in vitro was decided via the CCK-8 assay. As demonstrated in Fig. 3A and B, PGEVs inhibited the 4T1 and A549 cell proliferation in each concentration- and time-dependent manners, with notable inhibitory results at 50 µg/mL and 100 µg/mL. After 48 h co-incubation, the viabilities of 4T1 cells had been 55.2% and 45.6% for PGEVs at 50 µg/mL and 100 µg/mL, and the viabilities of A549 cells had been 73.0% and 60.2% for PGEVs at 50 µg/mL and 100 µg/mL. The info indicated that the PGEVs possessed a larger capability to suppress the proliferation of 4T1 cells (a TNBC cell line) than A549 cells (a lung most cancers cell line). Moreover, we carried out CCK-8 experiments to guage the impact of PD on the survival charges of 4T1 cells and A549 cells to match the efficacy of PGEVs with that of free PD. The outcomes indicated that the PD focus of 24.6 µg/mL was obligatory to attain a survival fee of roughly 50% for 4T1 cells and 60% for A549 cells (Fig. S5). Notably, the PD focus in 100 µg/mL of PGEVs was a mere 0.342 µg/mL, which recommend that the impact of free PD at 24.6 µg/mL was corresponding to that of PGEVs containing solely 0.342 µg/mL PD. Moreover, we examined the impact of PGEVs on Uncooked 264.7 cells utilizing CCK-8 assay, which indicated that slight cytotoxicity was detected in Uncooked 264.7 macrophages even at 100 µg/mL of PGEVs. Notably, PGEVs exerted slight promotion impact on Uncooked 264.7 macrophages at a low focus of 12.5 µg/mL, indicating their potential helpful results and wonderful biocompatibility (Fig. 3C).
To evaluate the pro-apoptotic potential of PGEVs on tumor cells, we carried out apoptosis assay by stream cytometry. As indicated in Fig. 3D-F, there was only a few apoptotic cells within the management teams with out PGEVs therapy. In distinction, after co-culture with PGEVs for 48 h, considerably elevated percentages of apoptotic cells had been noticed in each 4T1 and A549 cells, particularly 4T1 cells. The proportion of apoptotic cells, encompassing each early and late levels of apoptosis, was 41% in 4T1 cells and 20.4% in A549 cells. Moreover, the apoptosis fee of Uncooked 264.7 cells handled with PGEVs was comparatively low, as illustrated in Fig. S6. The plate colony formation assay is an efficient technique for evaluating cell proliferation means. Subsequently, we additional validated the inhibitory impact of PGEVs on 4T1 cells and A549 cells utilizing clone formation assay. As depicted in Fig. 3G, therapy with PGEVs at 50 µg/mL and 100 µg/mL led to clearly fewer colonies fashioned by each 4T1 and A549 cells in comparison with untreated cells.
It’s typically believed that top degree of oxidative stress can induce cytotoxicity and apoptosis in tumor cells [39]. To research the mechanisms driving the pro-apoptotic impact of PGEVs on tumor cells, we measured the degrees of intracellular ROS in 4T1 and A549 cells following PGEV therapy using the DCFH-DA probe. As proven in Fig. 3H and I, therapy with PGEVs led to a marked improve in ROS ranges in each 4T1 and A549 cells. The fluorescence alerts from DCF had been predominantly localized inside the cells and exhibited a concentration-dependent enhancement in depth. The elevated intracellular ROS manufacturing induced by PGEVs therapy could disrupt important mobile substances concerned in tumor cell metabolism, finally triggering apoptosis. Moreover, we carried out ROS quantitative evaluation by detecting DCF fluorescence depth of the stained cells with a microplate reader. The outcomes displayed that the ROS ranges in PGEVs-administrated 4T1 cells and A549 cells had been 12.0-fold and eight.9-fold larger than these of their respective management cells (Fig. S7), which additional indicated that PGEVs therapy considerably promoted oxidative stress in most cancers cells. Notably, larger accumulation of ROS was noticed in PGEVs-treated 4T1 cells than in A549 cells. This differential ROS response may very well be a essential issue contributing to the decrease viability and better apoptosis fee noticed in 4T1 cells than in A549 cells upon PGEVs therapy.
Anti‑tumor exercise of PGEVs in vitro. Cytotoxicity of PGEVs in 4T1 cells (A), A549 cells (B) and Uncooked 264.7 cells (C) submit administration of PGEVs at concentrations starting from 12.5 µg/mL to 100 µg/mL for twenty-four h and 48 h. *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001 vs. management group (24 h), ##p < 0.01, ###p < 0.001 vs. management group (48 h). (D) Apoptosis of 4T1 cells and A549 cells after handled with PGEVs at 50 µg/mL and 100 µg/mL for 48 h, as detected by stream cytometry and (E, F) the corresponding quantitative evaluation. (G) Plate colony formation of 4T1 cells and A549 cells after therapy with PGEVs. Fluorescence pictures of 4T1 cells (H) and A549 cells (I) stained with DCFH-DA after handled with 50 µg/mL and 100 µg/mL PGEVs for 48 h, scale bar: 50 μm
TAMs polarization induced by PGEVs in vitro
Just lately, researchers have more and more centered on TAMs to rebuild the immunosuppressive TME, thereby enhancing the immunotherapy effectivity of TNBC. TAMs may be labeled into tumoricidal M1-TAMs and protumoral M2-TAMs [40]. Throughout the preliminary stage of tumorigenesis, M1-TAMs are the dominant phenotype and primarily answerable for killing tumor cells. Nonetheless, as tumors progress, the cytokines launched from tumor cells promote the transition of M1-TAMs to M2-TAMs, which facilitate tumor progress and angiogenesis. M2-TAMs are prevalent in a majority of stable tumors and contribute considerably to the immunosuppressive setting inside the TME [41]. Subsequently, reprogramming TAMs from protumoral M2-TAMs to tumoricidal M1-TAMs provides a promising technique to reverse the immunosuppressive TME and improve the effectiveness of TNBC remedy. On this examine, we employed a transwell co-culture system to simulate TAMs and assess the macrophage reprogramming impact of PGEVs in vitro. Intimately, PGEVs handled Uncooked 264.7 cells had been seeded within the higher chamber and co-cultured with 4T1 or A549 cells within the decrease chamber. Whole RNA was extracted from Uncooked 264.7 cells, and qRT-PCR experiment was proceeded to detect the gene expressions of M1 markers (iNOS, TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-12) and M2 marker (CD206). The info revealed that therapy with PGEVs considerably upgraded the expressions of iNOS, TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-12 (Fig. 4A-D) and downgraded the expression of CD206 (Fig. 4E). Concretely, within the 4T1/Uncooked 264.7 co-culture system, PGEVs (50 µg/mL) considerably enhanced the expression ranges of iNOS, TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-12 by 46.2, 13.8, 28.7 and 4.9 occasions and decreased the expression of CD206 by 0.45 occasions compared to the management group group. Equally, within the A549/Uncooked 264.7 co-culture system, PGEVs on the identical focus led to 21.1-fold, 4.1-fold, 51.1-fold and 5.2-fold adjustments within the expression ranges of iNOS, TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-12, and 0.68-fold change within the expression degree of CD206, in contrast with these within the management group. Furthermore, the concentrations of the standard pro-inflammatory cytokines TNF-α and IL-6 and the anti-inflammatory cytokines IL-4 and IL-10 within the co-cultured Uncooked 264.7 cell supernatant had been examined via ELISA kits. The outcomes displayed that the concentrations of TNF-α and IL-6 had been remarkably elevated following therapy with PGEVs at 50 µg/mL in each 4T1/A549 and Uncooked 264.7 cell co-culture methods (Fig. 4F and G). Nonetheless, no important distinction was noticed within the concentrations of IL-4 and IL-10 (Fig. 4H and I). The above findings collectively indicated that PGEVs therapy successfully promoted the polarization of TAMs towards M1 phenotype.
Subsequent, the Uncooked 264.7 cells within the transwell system had been labeled with the M1 marker protein CD86, and the share of CD86+ macrophages was quantitatively measured utilizing stream cytometry to evaluate the impact of PGEVs on macrophage phenotypic conversion. As indicated in Fig. 4J-M, Uncooked 264.7 cells had been polarized by PGEVs, leading to CD86+ share of 55.6% within the 4T1/Uncooked 264.7 system and 42.8% within the A549/Uncooked 264.7 system. To additional confirm the impact of PGEVs on macrophage polarization, we decided the expression of the M1 marker proteins CD86 and iNOS in Uncooked 264.7 cells by immunofluorescence staining. As proven in Fig. 4N and O, in contrast with management group, PGEVs therapy resulted in larger fluorescence intensities of CD86 and iNOS in Uncooked 264.7 cells, which was per the outcomes from stream cytometry. These findings illustrated that PGEVs therapy may polarize TAMs to M1 phenotype within the microenvironments of each 4T1 and A549 cells.
Polarization of TAMs induced by PGEVs in vitro. The mRNA expression ranges of the M1 markers iNOS (A), TNF-α (B), IL-6 (C) and IL-12 (D) and M2 marker CD206 (E) in PGEVs handled Uncooked 264.7 cells co-cultured with 4T1 cells or A549 cells had been evaluated by qRT-PCR, these mRNA expressions had been normalized to these of GAPDH. Professional-inflammatory cytokines TNF-α and IL-6 launched from PGEVs handled Uncooked 264.7 cells co-cultured with 4T1 cells (F) and A549 cells (G) had been detected by ELISA. Anti-inflammatory cytokines IL-4 and IL-10 launched from PGEVs handled Uncooked 264.7 cells co-cultured with 4T1 cells (H) and A549 cells (I) had been detected by ELISA. Consultant stream cytometry plots and percentages of CD86+ cells (M1 marker) of PGEVs handled Uncooked 264.7 cells co-cultured with 4T1 cells (J, Ok) and A549 cells (L, M). Immunofluorescence staining for the M1 marker proteins CD86 (N) and iNOS (O) in PGEVs-treated Uncooked 264.7 cells co-cultured with 4T1 cells or A549 cells, scale bar: 100 μm
It’s typically believed that the discharge of pro-inflammatory cytokines comparable to TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-12 from polarized macrophages can induce most cancers cell dying. Herein, we evaluated the viability of most cancers cells within the decrease chamber via CCK-8 assay. As indicated in Fig. S8, PGEVs therapy clearly inhibited the proliferation of each 4T1 and A549 cells. Compared to the management group, the viability of 4T1 cells decreased to 41.1% at PGEVs focus of fifty µg/mL, whereas the viability of the A549 cells was 54.8% on the identical PGEVs focus. The above outcomes indicated that polarized TAMs by PGEVs can suppress most cancers cell progress, significantly within the TNBC cell line 4T1.
Biodistribution of PGEVs in vivo
In scientific most cancers therapy, i.v. injection is a generally used method that delivers medicine instantly into the bloodstream, permitting for swift onset of their results. However, oral administration ensures secure absorption through the gastrointestinal tract and maintains a comparatively sustained blood focus. It’s cost-effective, because it doesn’t require specialised infusion units or medical personnel involvement, providing the next psychological acceptance in sufferers. Since these two strategies possess their very own benefits, we comparatively assessed the in vivo biodistribution of PGEVs via each oral administration and that i.v. injection. The PGEVs labeled with fluorescent dye DID (DiD-PGEVs) had been orally or i.v. administered to the mice. Mice given PBS served as management group. The DiD fluorescence alerts from the mice had been tracked at totally different intervals and noticed via an animal in vivo imaging system.
Determine 5A exhibited that substantial DiD fluorescence was predominantly detected on the belly areas of the mice in each oral and that i.v. administration teams and steadily enhanced inside 3 h, with the mice within the i.v. administration group exhibiting stronger fluorescence (Fig. 5B). Then the alerts in belly areas step by step weakened after 6 h of administration and had been barely noticed by 48 h within the oral therapy group. Nonetheless, sturdy alerts endured intensely in i.v. injection group even after injection for 48 h. On the designated time, the mice had been executed, and their foremost organs, brains and intestines had been harvested for fluorescence statement. Nearly all of the fluorescence from DiD-PGEVs was detected within the livers and kidneys of each orally and that i.v. handled mice (Fig. 5C-F). In contrast with these within the livers and kidneys, the fluorescence alerts within the lungs had been a lot weaker in each PGEVs therapy teams (Fig. S9). There have been negligible accumulation of DiD-PGEVs within the hearts and spleens at any time factors, as little or no fluorescence was detected in these organs from each teams. Notably, DiD-PGEVs quickly accrued within the mind after each administration strategies. Inside 1 h of oral and that i.v. administration, the DiD-PGEVs successfully traversed the blood-brain barrier (BBB) and efficiently focused mind areas. The strongest fluorescence depth on the mind websites occurred at 12 h after each oral and that i.v. therapy. Particularly, within the i.v. injection group, the sign within the mind endured even at 48 h post-administration. The above observations recommend that after getting into the circulatory system in vivo, DiD-PGEVs may be rapidly captured primarily by the liver and kidney and demonstrated a sturdy capability to penetrate the BBB. Moreover, following oral administration, sustained and intense DiD fluorescence alerts had been noticed within the intestinal tract of the mice and step by step pale after 24 h (Fig. 5G and Fig. S10). Within the i.v. injection group, the fluorescence sign of DiD-PGEVs was comparatively weaker than that within the oral group and tended to attenuate after 12 h of injection. Minimal alerts could originate from meals residues inside the gastrointestinal tract in PBS group. Subsequently, we verified that PGEVs can stay secure in gastric and intestinal fluids and exhibit gastrointestinal absorption traits in vivo.
In abstract, the biodistribution of PGEVs in vivo differed between the oral and that i.v. administration routes. The info indicated that almost all of the PGEVs had been absorbed by the liver and kidney and will throughout the BBB to achieve mind websites. They might persist within the GIT, thereby permitting the encapsulated contents to cross the intestinal barrier and enter the circulatory system successfully.
The biodistribution of PGEVs in vivo. (A) Biodistribution of PBS, PGEVs (oral) and PGEVs (i.v.) in mice after therapy for 1 h, 3 h, 6 h, 12 h, 24 h and 48 h. (B) The quantitative outcomes of the mice in numerous therapy teams. Biodistribution of PBS (C), PGEVs (oral) (D) and PGEVs (i.v.) (E) in foremost organs from totally different therapy teams. (F) The quantitative outcomes of the primary organs from totally different handled mice after 24 h. (G) Biodistribution of PBS, PGEVs (oral) and PGEVs (i.v.) in intestinal tract
Biosafety in vivo
Within the biosafety analysis system of nanodrugs, monitoring the influence of medication on the physique weight of mice initially gives insights into potential antagonistic results. If a drug is extremely poisonous, important adjustments in mouse physique weight could happen following administration. Herein, the physique weights of the mice after oral administration and that i.v. injection of PGEVs had been recorded to evaluate their biosafety. As depicted in Fig. S11, oral or i.v. injection of PGEVs at totally different doses didn’t considerably have an effect on the physique weights of the mice, intently resembling the developments noticed within the management group. The liver and kidneys are important organs that take part within the immune response, metabolism and cleansing inside the physique. Medicine and their metabolites can probably impose burdens and even induce toxicity on these organs. Scientific analysis signifies that medicine with potential toxicity to the liver and kidney considerably constrain their widespread software. AST and ALT are essential enzymes which can be primarily concentrated within the liver. Irregular serum ranges of those enzymes point out liver damage. BUN and CREA are the ultimate metabolites of protein and nitrogenous natural matter, that are excreted via the kidneys. Elevated or decreased ranges of those substances point out kidney injury or dysfunction. The above indices, together with ALT, AST, BUN and CREA, are generally utilized in scientific settings for the analysis of hepatorenal toxicity. Our examine revealed that steady oral and that i.v. administration of PGEVs, even at excessive focus didn’t considerably have an effect on any of those 4 indicators compared to the management group (Fig. 6A-D). Furthermore, we carried out histological evaluations utilizing H&E staining to evaluate the impacts of PGEVs on 5 foremost organs (coronary heart, liver, spleen, lung and kidney) and the mind. As introduced in Fig. 6E, no morphological abnormalities or tissue injury had been noticed in these organs and brains following oral or i.v. administration of PGEVs at totally different concentrations. These findings additional underscore the favorable biosafety profile of PGEVs.
In vivo anti-tumor effectivity of PGEVs
Inspired by the superior leads to vitro, we investigated the anti-tumor impact and mechanism of PGEVs towards TNBC in vivo in a subcutaneous xenograft TNBC mouse mannequin. Previous to evaluating the anti-tumor effectivity of PGEVs, the tumor accumulation of PGEVs had been assessed in tumor-bearing mice. PGEVs had been labeled with the fluorescence dye DiD and orally given or i.v. injected into the tumor-bearing mice. Then, the mice had been executed at totally different intervals, and the primary organs and tumors had been imaged with an animal in vivo imaging system. As illustrated in Fig. 7A, DiD-PGEVs step by step accrued at tumor websites whatever the two totally different drug administration strategies. The fluorescence alerts from DiD-PGEVs elevated steadily at tumor websites 24 h after oral administration and 12 h after i.v. injection. Notably, the strongest fluorescence sign within the tumors was noticed after 48 h of administration through each the oral and that i.v. routes. Moreover, intense fluorescence alerts had been detected within the livers, kidneys and brains for each administration strategies, and a substantial depth maintained for 48 h.
Anti-tumor efficacy of PGEVs in vivo. (A) Biodistribution of DiD-PGEVs in foremost organs and tumors after oral administration and that i.v. injection for 12 h, 24 h and 48 h in tumor-bearing mice. (B) Schematic illustration of the anti-tumor experimental protocol. (C-G) Particular person tumor sizes of management, PGEVs (oral, low), PGEVs (oral, excessive), PGEVs (i.v., low) and PGEVs (i.v., excessive)-treated mice. Common tumor progress curves (H), tumor weights (I), and consultant tumor pictures (J) within the totally different therapy teams. Consultant pictures of tumor sections after immunofluorescence staining with TUNEL (Ok), Ki67 (L) and CD31 (M)
For investigating the therapeutic impact of PGEVs, the mice with TNBC tumors had been handled with the management, PGEVs (oral, low), PGEVs (oral, excessive), PGEVs (i.v., low) or PGEVs (i.v., excessive) each two days (Fig. 7B). The tumor volumes and physique weights of the totally different handled mice had been measured each two days. Determine 7C-G illustrated the adjustments within the tumor volumes of the mice within the totally different teams. The tumors within the management group quickly progressed, whereas all PGEVs remedies successfully inhibited tumor progress to various levels. In contrast with these within the management group, the common tumor volumes on the finish of the totally different remedies (Fig. 7H) had been 1.33-, 2.14-, 1.44- and a couple of.39-fold smaller in PGEVs (oral, low), PGEVs (oral, excessive), PGEVs (i.v., low) and PGEVs (i.v., excessive) teams, respectively. Notably, though the PGEVs (i.v., excessive) therapy resulted in a larger tumor inhibition fee than that of PGEVs (oral, excessive) therapy, there was no important distinction between the 2 teams. The imply tumor weights in each PGEVs (oral, excessive) group and PGEVs (i.v., excessive) group had been decrease than these within the different teams (Fig. 7I). Moreover, the alterations in tumor sizes (Fig. 7J) aligned with the adjustments noticed in each tumor volumes and weights. The physique weights of the mice remained comparatively secure throughout the 5 teams (Fig. S12). Moreover, TUNEL staining and Ki67 immunofluorescence staining had been proceeded to evaluate the pro-apoptotic and proliferation-inhibitory results of PGEVs on tumors in vivo. In comparison with the PGEVs (oral, low) and PGEVs (i.v., low) teams, the PGEVs (oral, excessive) and PGEVs (i.v., excessive) teams exhibited larger purple fluorescence of TUNEL, indicating their sturdy pro-apoptotic results on TNBC (Fig. 7Ok). The expression degree of Ki67 represents the diploma of cell proliferation. A excessive degree of Ki67 expression signifies a excessive fee of tumor proliferation and aggressiveness. Compared to the management group, totally different levels of Ki67 fluorescence (yellow) had been detected in all PGEVs therapy teams, with the weakest alerts noticed within the PGEVs (oral, excessive) and PGEVs (i.v., excessive) teams, suggesting the marked lower within the variety of proliferative cells in these teams (Fig. 7L). Moreover, the antiangiogenic exercise of PGEVs was assessed through CD31 (angiogenesis marker) immunofluorescence staining. As demonstrated in Fig. 7M, the expression ranges of CD31 (orange fluorescence) within the PGEVs (oral, excessive) and PGEVs (i.v., excessive) teams had been considerably decrease in contrast with these within the management, PGEVs (oral, low) and PGEVs (i.v., low) teams, which demonstrated a major discount in CD31+ blood vessels related to tumors and underscored the angiogenesis inhibition capability of PGEVs. Collectively, the above outcomes confirmed the efficient therapeutic impact of PGEVs on TNBC tumors in vivo whatever the oral or i.v. route of administration.
Systemic immune response induced by PGEVs in vivo
We aimed to additional perceive the mechanisms underlying the extremely profitable TNBC therapy outcomes of PGEVs. Herein, the immune cells inside tumors had been analyzed to guage the regulatory influence of PGEVs on the TME in vivo. Firstly, on the finish of the remedies, tumors from the assorted teams had been harvested, and stream cytometry was used to investigate the proportions of M1-TAMs and cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) inside the tumors. Antibodies towards F4/80 and CD86 had been used to label M1 macrophages. In contrast with the management group, we discovered various will increase within the proportions of CD86+F4/80+ cells in all PGEVs therapy teams. Remedy with PGEVs (oral, excessive) considerably elevated the share of CD86+F4/80+ cells to 22.5%, a degree corresponding to that noticed in PGEVs (i.v., excessive) therapy group (26.1%) (Fig. 8A and Fig. S13). The outcomes revealed that PGEVs promoted the reprogramming of TAMs to M1 sort. CTLs contribute to anti-tumor immunity by instantly killing tumor cells or by regulating the exercise of different immune cells. Circulate cytometry was used to measure the share of CD3+CD8+ cells, which displays the infiltration of CTLs within the tumors. As introduced in Fig. 8B and Fig. S14, the odds of CD3+CD8+ cells in tumors had been markedly elevated following remedies with PGEVs (oral, excessive, 21.8%), PGEVs (i.v., low, 16.2%) and PGEVs (i.v., excessive, 24.5%), whereas such infiltration was largely absent in mice subjected to regulate (1.12%) or PGEVs (oral, low, 3.33%) group. We then assessed the expressions of the cytotoxic components IFN-γ and Granzyme B (GzmB) in tumor, which contribute to advertise the activation and improve the killing operate towards tumor cells of CTLs. In contrast with these within the management group, each PGEVs (oral, excessive) and PGEVs (i.v., excessive) considerably elevated the expression ranges of those components (Fig. 8C and D), suggesting that PGEVs enhanced the cytotoxicity of CTLs towards tumors. Moreover, we explored the mechanism via which PGEVs boosted the cytotoxic exercise of CTLs. We measured the protein expression of PD-1 on the tumor tissues after totally different remedies via immunofluorescence staining. PD-1 is an immune checkpoint protein that’s expressed totally on T cells. By exploiting PD-1 signaling, tumors induce exhaustion or dysfunction of T cells to evade immune surveillance and develop uncontrollably, thus selling tumor development [42]. The immunofluorescence staining outcomes clearly demonstrated that each orally and that i.v handled PGEVs diminished the expression of PD-1 on tumors, (Fig. 8E), which can be answerable for the improved cytotoxicity of CTLs towards tumor cells.
In vivo immune response analysis. Consultant stream cytometry plots of CD86+F4/80+ cells (A) and CD3+CD8+ cells (B) in tumors from mice after therapy with Management, PGEVs (oral, low), PGEVs (oral, excessive), PGEVs (i.v., low) and PGEVs (i.v., excessive). qRT-PCR evaluation of the relative mRNA expression ranges of IFN-γ (C) and GzmB (D) in tumors after totally different remedies. (E) Immunofluorescence staining pictures of PD-1+ cells in tumors from mice after totally different remedies. Immunofluorescence staining pictures of CD206+CD86+ (F), CD3+CD8+ (G) and Foxp3+ (H) cells in tumors from the mice after totally different remedies. Cytokine ranges of TNF-α (I), IL-6 (J) and IFN-γ (Ok) within the serum of mice from totally different teams
To additional make clear the regulatory impact of PGEVs on the TME on the tissue degree, tumor tissues had been collected, and an immunofluorescence staining experiment was carried out to evaluate the immune response in vivo. The outcomes of immunofluorescence staining for CD86 (M1-TAMs marker) and CD206 (M2-TAMs marker) (Fig. 8F and Fig. S15) clearly demonstrated that M2-TAMs had been dominant within the management group since they introduced the strongest inexperienced fluorescence from CD206 and the bottom purple fluorescence from CD86. Within the PGEVs (oral, excessive) and PGEVs (i.v., excessive) teams, the inexperienced fluorescence depth diminished whereas the purple fluorescence depth elevated, suggesting that PGEVs therapy successfully promoted the polarization of TAMs to the M1 phenotype. CTLs are recognized for his or her means to kill tumor cells. As depicted in Fig. 8G and Fig. S16, the outcomes of immunofluorescence staining for CD3 and CD8 demonstrated that the PGEVs (oral, excessive) and PGEVs (i.v., excessive) teams exhibited the very best abundance of CD3+ and CD8+ cells. The elevated infiltration of CD3+/CD8+ T cells is necessary for restraining tumor progress in mice. Foxp3 is well known as essentially the most particular marker for Tregs, that are pivotal goal for therapeutic intervention as a result of their functionality to suppress T cell proliferation and effector cytokines manufacturing. Consequently, evaluating the expression of Foxp3 inside tumors provides necessary insights into tumor development and prognosis. Moreover, we carried out immunofluorescence staining experiment to evaluate the expression of Foxp3. In Fig. 8H, the expression of Foxp3 diminished after PGEVs (oral, excessive) and PGEVs (i.v., excessive) remedies in comparison with the management group, whereas no important adjustments had been detected within the PGEVs (oral, low) and PGEVs (i.v., low) teams.
Cytokines are essential for activating and regulating the immune response. Adjustments within the host immune standing result in corresponding alterations within the ranges of cytokines in vivo. Herein, we detected the degrees of cytokines (TNF-α, IL-6 and IFN-γ) related to anti-tumor immune responses in mouse serum through ELISA assay. TNF-α and IL-6 are important mediators that activate innate immune cells, IFN-γ is answerable for inducing adaptive cell-mediated immunity, that are essential for a sturdy immune response in tumor immunotherapy. The concentrations of TNF-α, IL-6 and IFN-γ in mice serum clearly elevated following PGEVs (i.v., low) and PGEVs (i.v., excessive) remedies (Fig. 8I-Ok). Though PGEVs (oral, low) and PGEVs (oral, excessive) administration additionally led to elevated cytokine concentrations of TNF-α, IL-6 and IFN-γ, they had been decrease than these noticed in PGEVs (i.v., excessive) group. This was most likely as a result of the consequences of oral administration and that i.v. injection differ considerably when it comes to drug absorption, distribution, and metabolism. I.v. administration permits medicine to bypass the digestive absorption course of and enter instantly into the bloodstream. In distinction, oral administration requires drug absorption via the GIT, medicine work together with the intestine microbiota, probably altering their composition and performance.
Modulation of the intestine microbiota by PGEVs
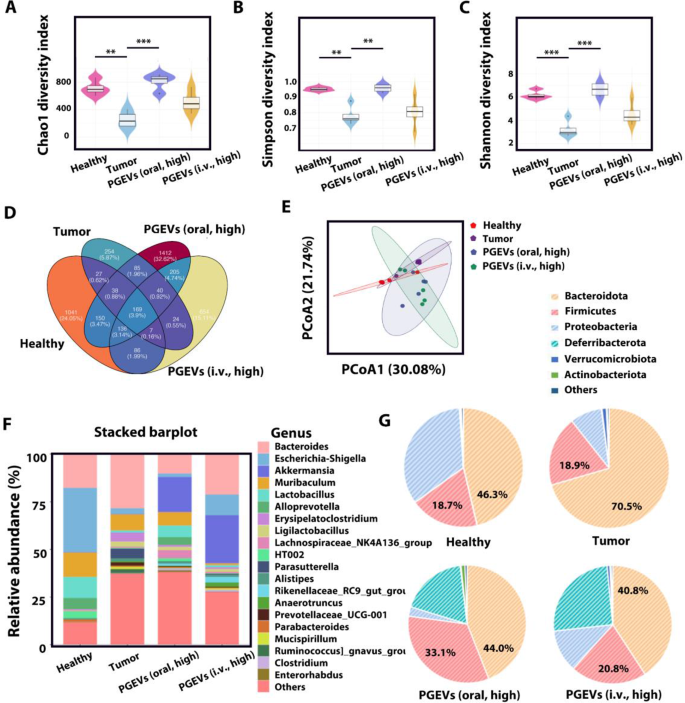
Analysis on the intestine microbiota is changing into more and more very important in personalised tumor therapy [43]. Understanding the person’s intestine microbiota may optimize drug therapy methods, reduce negative effects, and improve tumor therapeutic outcomes. The intestine microbiota constitutes a fancy ecosystem inside the GIT, and rising proof signifies that the intestine microbiota is extremely related to the initiation, development, and therapeutic response of varied tumors, together with TNBC [44]. Dysbiosis refers to adjustments within the variety and composition of the intestine microbiota, which can compromise the integrity of the intestinal barrier, probably leading to elevated intestinal permeability and the translocation of pathogenic micro organism. In our work, we carried out 16S rRNA gene sequencing to comparatively analyze the microbial compositions of feces from mice in numerous teams. Alpha variety (Chao1, Shannon and Simpson indices) displays the species abundance and variety of the intestine microbiota. A better Chao1 index signifies elevated flora abundance, and better Shannon and Simpson indices point out elevated flora variety. Augmenting the abundance and variety of the intestine microbiota in mice is useful for impeding tumor growth. As depicted in Fig. 9A-C, in comparison with the wholesome management group, the Chao1, Simpson and Shannon indices had been decrease within the tumor management group. Following PGEVs (oral, excessive) and PGEVs (i.v., excessive) therapy, Chao1, Simpson and Shannon indices elevated in comparison with these of the tumor management group. The Chao1, Simpson, and Shannon indices had been larger within the PGEVs (oral, excessive) group in comparison with the PGEVs (i.v., excessive) group. The Venn diagram successfully illustrates the variety of shared and distinctive species, highlighting the similarity and overlap amongst totally different teams. The info (Fig. 9D) revealed that PGEVs (oral, excessive) therapy resulted in a notable improve in operational taxonomic items (OTUs), totaling 2235 strains, comprising 196 strains shared throughout all teams and 1412 strains distinctive to this therapy, which was consistent with the development noticed within the Chao1, Simpson and Shannon indices. Principal coordinate evaluation (PCoA) reveals the similarities in microbiota composition throughout totally different teams, with the gap between any two teams reflecting variations alongside the PCoA axes. The leads to Fig. 9E demonstrated that there have been sure variations between the tumor management group and the wholesome management group.
Intestine microbiota modulating impact of PGEVs. Alpha variety had been introduced as violin diagrams of the Chao1 (A), Shannon (B) and Simpson (C) indices. (D) Venn diagram of widespread and distinctive bacterial species in mice from totally different therapy teams. (E) PCoA plots of the intestine microbiota. The genus (F) and phylum (G) ranges of intestine microbiota compositions in numerous handled mice
Moreover, the composition of intestine microbiota on the genus degree was analyzed (Fig. 9F). In comparison with the wholesome management group, the relative abundance of the dangerous micro organism Bacteroides elevated within the tumor management group. Following oral or i.v. injection of PGEVs, the relative abundance of Bacteroides decreased, and the PGEVs (oral, excessive) therapy resulted in a a lot decrease relative abundance of Bacteroides than that in PGEVs (i.v., excessive) group. As helpful micro organism, Lactobacillus have been reported to alleviate galactose-induced liver damage via lowering liver irritation, thus enhancing the intestinal barrier and regulating microbiome metabolism [45]. The tumor management group exhibited a decrease relative abundance of Lactobacillus. In distinction, the PGEVs (oral, excessive) group introduced a rise in Lactobacillus abundance, and such phenomenon was inconspicuous in PGEVs (i.v., excessive) group. Determine 9G introduced the intestine microbiota composition labeled on the phylum degree. The dominant phylum of the totally different therapy teams had been Bacteroidota, Firmicutes and Proteobacteria. Within the gut, Firmicutes and Bacteroidota are the predominant species of gram-positive and gram-negative micro organism, respectively. Alterations of their ratio point out intestine dysbiosis. Greater Firmicutes/Bacteroidota ratio was detected within the PGEVs (oral, excessive) group and PGEVs (i.v., excessive) group than within the tumor management group, demonstrating that PGEVs therapy maintained the stability of the intestine microbiota. General, PGEVs therapy possessed the potential to extend the abundance and variety of the intestine microbiota and proper microbiota problems, which was helpful for suppressing tumor growth.