
Researchers at Stanford College and UC Berkeley lately introduced the model 1.0 launch of LOTUS, an open supply question engine designed to make LLM-powered information processing quick, simple, and declarative. The mission’s backers say growing AI functions with LOTUS is as simple as writing Pandas, whereas offering efficiency and pace boosts in comparison with current approaches.
There’s no denying the nice potential to make use of massive language fashions (LLMs) to construct AI functions that may analyze and motive throughout massive quantities of supply information. In some circumstances, these LLM-powered AI apps can meet, and even exceed, human capabilities in superior fields, like drugs and legislation.
Regardless of the huge upside of AI, builders have struggled to construct end-to-end programs that may take full benefit of the core technological breakthroughs in AI. One of many large drawbacks is the dearth of the suitable abstraction layer. Whereas SQL is algebraically full for structured information residing in tables, we lack unified instructions for processing unstructured information residing in paperwork.
That’s the place LOTUS–which stands for LLMs Over Tables of Unstructured and Structured information–is available in. In a brand new paper, titled “Semantic Operators: A Declarative Mannequin for Wealthy, AI-based Analytics Over Textual content Knowledge,” the pc science researchers–together with Liana Patel, Sid Jha, Parth Asawa, Melissa Pan, Harshit Gupta, and Stanley Chan–focus on their strategy to fixing this large AI problem.
The LOTUS researchers, who’re suggested by legendary pc scientists Matei Zaharia, a Berkeley CS professor and creator of Apache Spark, and Carlos Guestrin, a Stanford professor and creator of many open supply tasks, say within the paper that AI growth presently lacks “high-level abstractions to carry out bulk semantic queries throughout massive corpora.” With LOTUS, they’re looking for to fill that void, beginning with a bushel of semantic operators.
“We introduce semantic operators, a declarative programming interface that extends the relational mannequin with composable AI-based operations for bulk semantic queries (e.g., filtering, sorting, becoming a member of or aggregating data utilizing pure language standards),” the researchers write. “Every operator could be carried out and optimized in a number of methods, opening a wealthy area for execution plans just like relational operators.”
These semantic operators are packaged into LOTUS, the open supply question engine, which is callable by way of a DataFrame API. The researchers discovered a number of methods to optimize the operators pace up processing of frequent operations, similar to semantic filtering, clustering and joins, by as much as 400x over different strategies. LOTUS queries match or exceed competing approaches to constructing AI pipelines, whereas sustaining or bettering on the accuracy, they are saying.
“Akin to relational operators, semantic operators are highly effective, expressive, and could be carried out by quite a lot of AI-based algorithms, opening a wealthy area for execution plans and optimizations below the hood,” one of many researchers, Liana Patel, who’s a Stanford PhD scholar, says in a publish on X.
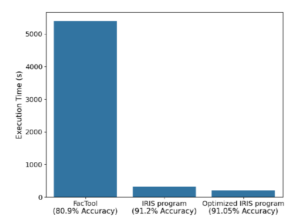
Comparability of state-of-the-art fact-checking instruments (FacTool) vs a brief LOTUS program (center) and the identical LOTUS program carried out with declarative optimizations and accuracy ensures (proper). (Supply: “Semantic Operators: A Declarative Mannequin for Wealthy, AI-based Analytics Over Textual content Knowledge”)
The semantic operators for LOTUS, which is obtainable for obtain right here, implement a spread of features on each structured tables and unstructured textual content fields. Every of the operators, together with mapping, filtering, extraction, aggregation, group-bys, rating, joins, and searches, are based mostly on algorithms chosen by the LOTUS group to implement the actual perform.
The optimization developed by the researchers are simply the beginning for the mission, because the researchers envision all kinds being added over time. The mission additionally helps the creation of semantic indices constructed atop the pure language textual content columns to hurry question processing.
LOTUS can be utilized to develop quite a lot of totally different AI functions, together with fact-checking, multi-label medical classification, search and rating, and textual content summarization, amongst others. To show its functionality and efficiency, the researchers examined LOTUS-based functions towards a number of well-known datasets, such because the FEVER information set (truth checking), the Biodex Dataset (for multi-label medical classification), the BEIR SciFact (for search and rating), and the ArXiv archive (for textual content summarization).
The outcomes show “the generality and effectiveness” of the LOTUS mannequin, the researchers write. LOTUS matched or exceeded the accuracy of state-of-the-art AI pipelines for every process whereas working as much as 28× quicker, they add.
“For every process, we discover that LOTUS applications seize top quality and state-of-the-art question pipelines with low growth overhead, and that they are often mechanically optimized with accuracy ensures to attain larger efficiency than current implementations,” the researchers wrote within the paper.
You’ll be able to learn extra about LOTUS at lotus-data.github.io
Associated Objects:
Is the Common Semantic Layer the Subsequent Massive Knowledge Battleground?
AtScale Claims Textual content-to-SQL Breakthrough with Semantic Layer
A Dozen Questions for Databricks CTO Matei Zaharia


