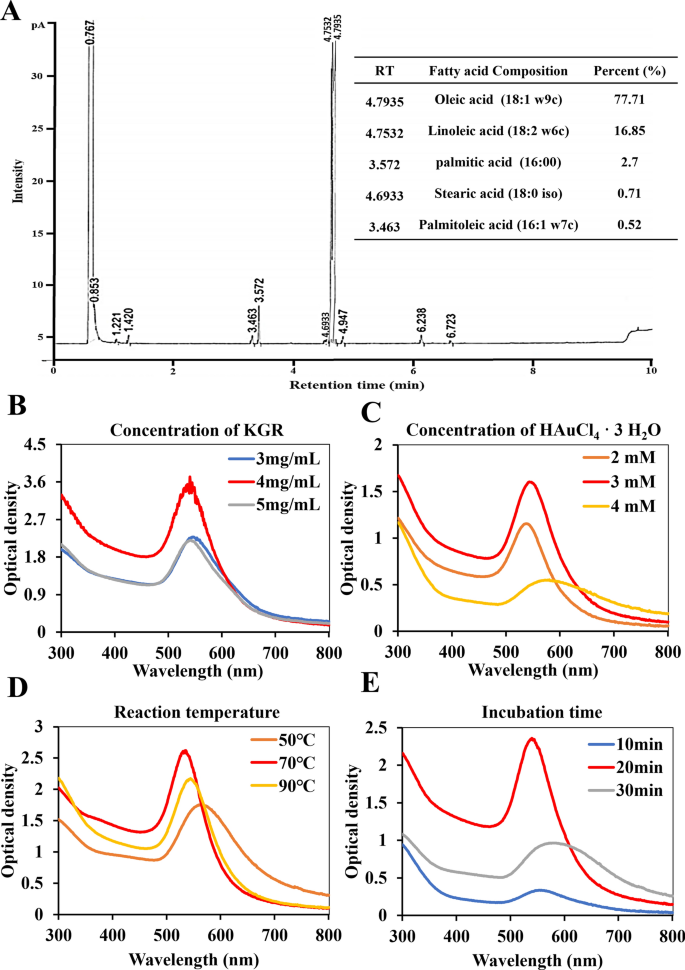
Fatty acid composition of GSO
In our research, we initially analyzed the fatty acid composition of the extracted GSO utilizing GC evaluation to establish the precise varieties of natural compounds current. As illustrated in Fig. 1A, the principal compounds discovered inside GSO embrace Oleic acid, Linoleic acid, Palmitic acid, Stearic acid, and Palmitoleic acid. Among the many natural compounds in GSO, oleic acid constitutes a predominant portion at 77.71%. The second most plentiful compound is linoleic acid, constituting 16.85% of the composition. In our outcomes, minor constituents of saturated fatty acids, together with Palmitic acid (2.7%) and Stearic acid (0.71%), are current in GSO. Regardless of the potential influence on levels of cholesterol with extreme consumption, GSO is mostly thought-about secure for consumption because of the comparatively low quantities current. Moreover, GSO accommodates a really small quantity of palmitoleic acid (0.52%). Based mostly on these findings, we discovered that the extracted GSO was wealthy in unsaturated fatty acids.
Fatty acid evaluation and synthesis of KGR-GNP: A Ginseng seed oil (GSO) fatty acid composition was recognized by way of GC evaluation. The GSO accommodates oleic acid at 77.71%, linoleic acid at 16.85%, palmitic acid at 2.7%, stearic acid at 0.71%, and palmitoleic acid at 0.52%. B–E The optimization course of for KGR-GNP synthesis is introduced with variations in KGR focus (3 to five mg/mL), Au focus (2 to 4 mM), temperatures (50 to 90 °C), and incubation time (10 to 30 min)
Optimization, synthesis and physiochemical characterization of KGS-NE
Optimization of KGR-GNP
KGR-GNP was synthesized utilizing the bio-reduction methodology outlined within the supplementary experimental part. Briefly, KGR was utilized as a decreasing agent, and the concentrations of 4 mg/mL for KGR and three mM of HAuCl4·3H2O, at 70 °C for 20 min, had been optimized to attain the formation of KGR-GNP. The optimum outcomes for the synthesis of KGR-GNP are introduced in Fig. 1B-E and Desk S3. As proven in Fig. 2A, the UV–Vis spectroscopy reveals the synthesized KGR-GNP absorbance peak at 547 nm, which was confirmed utilizing TEM imaging as proven in Fig. 2B.
Physicochemical characterization of KGS-NE. A The ultimate optimized situations for synthesizing KGR-GNP had been as follows: KGR (4 mg/mL), Au (3 mM), Temperature (70 °C), and incubation time (20 min), with absorbance measured at λ max 547 nm. B Transmission electron microscope (TEM) picture of KGR-GNP. C TEM picture highlighting KGR-GNP (pink arrow) encapsulated by KGS-NE (orange arrow). D Vitality-dispersive X-ray (EDX) spectrum confirming the presence of Au in KGS-NE. E Enhanced darkfield microscope (EFM) depicting KGR-GNP contained in the KGS-NE by way of particle reflection. F Chosen space diffraction (SAED) shows the crystalline construction of KGS-NE at (111), (200), (220), and (311). G Fourier-transform infrared (FT-IR) spectrum-derived infrared absorption spectrum for confirming the practical teams of KGS-NE
Encapsulation of nanoparticle utilizing GSO
As proven in Determine S1, the optimized GSO at totally different ratios demonstrated that the 8% ratio had the bottom zeta potential, indicating the best stability at roughly − 42.54 mV. Consequently, we intentionally selected a 4:2 ratio of Tween 80 and Span 80 to attain a focused HLB worth of 11.43 for the surfactant mix, which is inside the desired vary for O/W nanoemulsion [28]. Furthermore, the loading efficacy of silydianin into KGS-NE was 94.3 ± 2.6%. The encapsulation content material was excessive, above 90%, as anticipated in nanoemulsion programs, owing to the hydrophobic nature of silydianin. Some research have reported that the encapsulation worth decreases because the drug focus will increase, suggesting saturation of the system [29,30,31]. The presence of the floor modification monolayer was proven within the TEM picture (Fig. 2C), indicating that the KGR-GNP was additionally efficiently encapsulated by the GSO. Nanoemulsions encapsulated had been denoted as KGS-NE. Numerous methods had been employed to verify the encapsulation of nanoparticles into KGS-NE. Initially, the EDX spectrum, SAED sample, and EDX had been utilized to establish the presence of nanoparticles. We noticed the best Au aspect peak at 2.1 keV with a number of factors and the looks of a Cu peak at 8 keV was attributed to the copper grid utilized within the EDX evaluation (Fig. 2D) [32]. Moreover, the DFM picture (Fig. 2E) revealed particle reflections (indicated by pink arrows) and the SAED sample (Fig. 2F) reveals crystallographic buildings (111, 200, 220, and 311), offering additional affirmation of the presence of nanoparticles [33]. FT-IR spectrometry was employed to investigate the presence of practical teams within the KGS-NE (Fig. 2G). Major peaks had been noticed at 2922.09 cm−1, which corresponded to alkene C–H stretching. In the meantime, peaks noticed at two totally different wavelengths, i.e., 1740.24 cm−1, indicated the presence of aldehyde C=O stretching. Moreover, peaks had been noticed at 1098.07 cm−1, suggesting the presence of C–O stretching within the secondary alcohol.
Stability evaluation
Determine 3A presents the Z-average dimension ranges of KGS-NE together with quantity, quantity, and depth distribution at 202.7 nm, 87.6 nm, and 62.5 nm. The functionalization of KGS-NE confirmed that the particle dimension was 153.7 nm, PDI worth of 0.25. Furthermore, the zeta potential (Fig. 3B) of the KGS-NE was − 44.78 mV, indicating that the KGS-NE is steady. We noticed the modifications within the synthesized KGS-NE saved at numerous temperatures over 6 months. As proven in Fig. 3C and D, our findings point out that the dimensions and stability of KGS-NE stays excessive at 4 °C for as much as 6 months in comparison with storage at different temperatures. Since KGS-NE is meant for oral administration, it’s important to show its stability in gastrointestinal fluids. The soundness of KGS-NE was evaluated over time in simulated gastric fluid (SGF, composed of 0.2% w/v NaCl in 0.7% v/v HCl, pH 1.2) and simulated intestinal fluid (SIF, consisting of 0.05 M potassium dihydrogen phosphate and 0.02 M sodium hydroxide, pH 7.0). The outcomes indicated that KGS-NE remained steady in each media, with no important change in particle dimension noticed (Determine S2). These outcomes present {that a} steady KGS-NE was efficiently synthesized as an O/W nanoemulsion with increased stability.
Sturdiness and stability evaluation. A Dynamic gentle scattering (DLS) depicting the depth, quantity, and quantity distribution of KGS-NE. B Zeta potential (mV) of the synthesized KGS-NE. C, D Evaluation of Polydispersity Index (PDI), zeta potential, and zeta common over a 1 to 6-month time interval
KGS-NE inhibits HCoV-OC43 an infection: insights from cell viability, RNA sequencing, and pathway evaluation
HCoV-OC43, belonging to the equivalent viral genus as SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2, demonstrates comparable signs to these elicited by SARS-CoV-2 [34]. We preliminarily examined the cytotoxicity and viral inhibition results of KGR-GNP, silydianin, GSO-NE, and KGS-NE in opposition to HCoV-OC43. As proven in Determine S3, the non-toxic concentrations of KGR-GNP, silydianin, and GSO-NE had been chosen. Nevertheless, KGR-GNP, silydianin, and GSO-NE didn’t present higher exercise than KGS-NE within the non-toxic focus. Subsequently, in additional experiments, we centered on finding out the antiviral impact of KGS-NE. In an extra research, we first examined the antiviral exercise of KGS-NE in Vero-E6 cells contaminated with HCoV-OC43 to discover its efficacy in opposition to the virus. In Fig. 4A, a cell viability assay was carried out on Vero E6 cells. The MTT assay outcomes revealed that KGS-NE didn’t present important cytotoxicity till the focus reached 10 μg/mL, and the IC50 worth of KGS-NE in Vero E6 cells was decided to be 24.92 μg/mL (Fig. 4B). Furthermore, as proven in Fig. 4C, totally different concentrations of KGS-NE had been used to quantitatively analyze its impact on HCoV-OC43 N gene manufacturing. The outcomes demonstrated that KGS-NE remedies dose-dependently suppressed HCoV-OC43 replication, with viral RNA ranges decreased by 98% at 0.5 μg/mL. This outcome indicated that KGS-NE displays antiviral results in HCoV-OC43-infected Vero E6 cells. Subsequently, we carried out an RNA sequencing evaluation of the differentially expressed genes (DEGs) concerned within the Vero E6 cells. This evaluation aimed to discover the potential of KGS-NE on antiviral and anti inflammatory results and its underlying mechanism. As proven in Fig. 4D, therapy with KGS-NE resulted within the DEGs of 145 down-regulated and 178 up-regulated important genes, as in comparison with the HCoV-OC43 an infection group. The DEGs knowledge was used to indicate the distribution of genes that had been differentially expressed with a fold change of higher than 1.2 or lower than 0.8, and a p-value lower than 0.05.
Impact of KGS-NE therapy on Vero E6 cells contaminated by human coronavirus OC43 (HCoV-OC43). A, B Cell viability in Vero E6 cells handled with KGS-NE, together with the dedication of IC50 worth. C RNA ranges in HCoV-OC43-infected Vero E6 cells handled with KGS-NE. D Visualization of up-and down-regulated Differential Gene Expressions (DEGs) utilizing a volcano plot. E Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway evaluation indicating important signaling pathways. F Heatmap illustration of DEGs concerned within the ABC transporters signaling pathway. G Gene Ontology (GO) evaluation of organic processes (BP), mobile part (CC), and molecular interactions (MF)
The Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) enrichment bubble plots had been utilized to summarize the correlation between important pathways. Determine 4E and Desk S4 supplied the KEGG mapping of serious genes and their corresponding fold enrichment values. Our research recognized a number of important signaling pathways, amongst which ABC transporters exhibited the best enrichment rating, indicating that the ABC transporter’s signaling pathway would possibly function the first regulator. Furthermore, as proven in Fig. 4F, the genes related to the ABC transporters are visualized by way of a heatmap. This heatmap illustrates the regulation of ABC genes, together with their subfamilies, underneath the affect of KGS-NE therapy and HCoV-OC43 an infection. The outcome reveals that the ABC transporters household gene rules had been reversed by KGS-NE therapy. Notably, the ABC transporters subfamily F had considerably reverse regulation amongst these teams. Subsequently, the noticed differential regulation of ABCF2 and ABCF3 genes may very well be indicative of the crucial operate between the host and the virus. The downregulation after therapy suggests a possible constructive response to the intervention by KGS-NE.
Moreover, complete Gene Ontology (GO) enrichment analyses had been carried out to judge the organic capabilities of all recognized DEGs. The GO evaluation, encompassing Organic Processes (BP), Mobile Element (CC), and Molecular Operate (MF), is introduced in Fig. 4G. Inside BP, essentially the most considerably enriched genes had been related to catabolic and metabolic pathways. In CC, peroxisomes and microbodies exhibited the same variety of genes with notable enrichment scores. MF, ATPase-coupled transmembrane, Major lively transmembrane, and ATPase exercise demonstrated the best important enrichment scores. Notably, when evaluating BP, CC, and MF the MF reveals the best variety of enrichment scores. The GO fold enrichment values of signaling pathways had been introduced in Tables S5, S6, and S7. Collectively, the Gene Ontology (GO) outcomes present a complete depiction of the molecular intricacies influenced by KGS-NE therapy together with a considerable influence on mobile processes associated to vitality metabolism and energy-dependent transmembrane transport and ATP hydrolysis.
KGS-NE attenuates lung tissue injury in SARS-CoV-2 spike RBD protein induction in mice
Utilizing SARS-CoV-2 spike RBD protein in mice permits for immune response research and particular investigations with out inflicting a full COVID-19 an infection in mice, as they aren’t naturally vulnerable to SARS-CoV-2. This strategy aids in understanding immune responses, growing vaccines, and exploring virus-host cell interactions. After confirming the antiviral efficacy of KGS-NE in Vero E6 cells, extra validation of its results was evaluated utilizing the SARS-CoV-2 spike RBD protein. To discover the in vivo immune response potential of KGS-NE, mice had been orally administered KGS-NE for 2 days (pre-infection). Subsequently, on the third day, after a 5 h interval from the oral administration of KGS-NE, mice had been intratracheally inoculated with SARS-CoV-2 spike RBD. As depicted in Fig. 5A, the therapy routine was maintained for the following 4 days (post-infection), totaling six days of the therapy. Following KGS-NE therapy, the severity of acute lung harm was evaluated within the mice at 7 dpi. Histological evaluation (Fig. 5B) of lung tissues by way of H&E staining revealed that RBD protein led to the infiltration of inflammatory cells and thickening of alveolar partitions, indicating extreme injury to lung tissues. Furthermore, the inflammatory rating signifies that oral administration of KGS-NE was capable of inhibit these situations and mitigate the adversarial results of RBD protein in a dose-dependent method. The noticed restoration was roughly 56% on the highest dose of 40 mg/kg. The outcomes counsel that administration with KGS-NE alleviates lung harm induced by the RBD protein.
Impact of KGS-NE in SARS-CoV-2 spike receptor binding area (RBD) protein-induced C57BL/6 mice. A Schematic illustration of mice therapy teams. Mice had been categorized into 5 teams: Group 1: Sham group; Group 2: RBD spike protein-induced group; Group 3: RBD spike protein-induced with KGS-NE (10 mg/kg) therapy group; Group 4: RBD spike protein-induced with KGS-NE (20 mg/kg) therapy group; and Group 5: RBD spike protein-induced with KGS-NE (40 mg/kg) therapy group. B Histopathology staining was carried out to find out the pathology within the lungs, and the inflammatory rating was calculated. C IF staining of ACE2, CD68, and Iba-1 the place the depth is proven within the bar graph. Crosshatch marks point out important variations between sham and SARS-CoV-2 RBD, and asterisks point out important variations between SARS-CoV-2 RBD and every group. *, # p < 0.05, **, ## p < 0.01, and ***, ### p < 0.001
Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) is a central part of the renin-angiotensin system, essential for blood strain and fluid homeostasis. Within the context of SARS-CoV-2, the RBD protein binds to ACE2 (Angiotensin-Changing Enzyme 2) as the first mechanism for mobile entry, contributing to the event of lung harm [35]. Subsequently, we investigated whether or not KGS-NE prompts the immune response by affecting the binding of RBD protein to ACE2. Based mostly on the IF staining outcomes proven in Fig. 5C, the RBD protein enhanced the degrees of ACE2 expression. In distinction, KGS-NE administration suppressed ACE2 expression by 72%, even at a low focus of 10 mg/kg. As well as, Ionized calcium-binding adapter molecule 1 (Iba1) and Cluster of Differentiation 68 (CD68) each are generally used markers in IF to establish the presence of macrophages, which is important to the immune response of the lungs. Our IF staining outcomes for Iba-1 and CD68 present that the expression was increased within the group handled with RBD protein than within the sham group indicated. After the administration of KGS-NE, it suppressed the Iba-1 and CD68 expression. These outcomes counsel that KGS-NE may stop acute lung harm attributable to the RBD protein by way of the modulation of ACE2, Iba-1, and CD68. This might point out a possible mitigation of an overactive or dysregulated immune response, thereby decreasing the chance of extreme irritation or tissue injury.
Furthermore, the expression of ACE2, Iba-1, and CD68 was additional confirmed by way of immunoblotting. As depicted in Fig. 6A and B, RBD induction dramatically upregulated the expression of ACE2, Iba-1, and CD68 proteins. Conversely, KGS-NE administration considerably inhibited this upregulation. These collective outcomes strengthen the influence of KGS-NE on immune regulators (ACE2, Iba-1, and CD68), highlighting its potential in modulating immune responses linked to RBD-induced protein expression. Along with the noticed influence on ACE2, Iba-1, and CD68 expression, the pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-6 and IL-1β) had been additionally evaluated. This evaluation may improve our understanding of KGS-NE immunomodulatory results in response to RBD induction. Our outcomes present that these proteins had been considerably overexpressed by RBD induction, whereas treating with KGS-NE suppressed these expressions. Notably, IL-1β protein expression was suppressed by roughly 89% on the highest dose in comparison with the an infection group. Nuclear issue kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NF-κB) serves as an important transcriptional activator of cytokines implicated within the innate immune response, equivalent to IL-6 and IL-1β. Past its distinguished position in innate immunity, NF-κB additionally performs important capabilities within the adaptive immune system. On this research, we assessed the expression of NF-κB protein upon RBD induction. The outcomes point out a big upregulation of NF-κB by RBD induction, and KGS-NE exhibited a dose-dependent suppression of its expression. These findings assist KGS-NE numerous immunomodulatory influence on key cytokines within the immune response.
Results of KGS-NE on inflammatory regulators. A Demonstrates that KGS-NE therapy suppressed ACE2, Iba-1, CD68, IL-6, p-NF-κB/NF-κB by way of protein expression. B A bar graph represents the protein expression analyzed utilizing Picture J. Crosshatch marks point out important variations between sham and SARS-CoV-2 RBD, whereas asterisks point out important variations between SARS-CoV-2 RBD and every group. *, # p < 0.05, **, ## p < 0.01, and ***, ### p < 0.001
KGS-NE modulates antiviral and anti inflammatory results in SARS-CoV-2-infected Syrian hamsters
Syrian hamster was chosen because the experimental animal mannequin to judge the feasibility of KGS-NE to inhibit SARS-CoV-2. The Syrian hamsters are small mammals which were broadly used as a mannequin for an infection with respiratory viruses, together with SARS-CoV-2, influenza viruses, and adenoviruses. On this research, we carried out an evaluation to analyze the influence of KGS-NE on SARS-CoV-2-induced pneumonia. The evaluation was carried out using a Syrian hamster mannequin subjected to intranasal an infection with SARS-CoV-2, adopted by therapeutic intervention using various dosage ranges of KGS-NE. KGS-NE was orally administered (1–6 dpi) after SARS-CoV-2 an infection, as proven in Fig. 7A. The burden loss and virus replication variety of hamsters had been assessed at 4 dpi and seven dpi, respectively. As depicted in Fig. 7B and C, hamsters contaminated with SARS-CoV-2 exhibited a lower in physique weight. Nevertheless, the dose-dependent administration of KGS-NE may alleviate the results of SARS-CoV-2 an infection. Additional, the lungs of the hamsters had been dissected to look at the impact of KGS-NE therapy in opposition to SARS-CoV-2 an infection.
Impact of KGS-NE in SARS-CoV-2 contaminated Syrian hamsters. A Schematic illustration of Syrian hamster therapy teams. (B, C Physique weight modifications in grams and share after infecting SARS-CoV-2 and KGS-NE administration. D, E RT-PCR was used to estimate the viral load of RdRp and E gene. Crosshatch marks point out important variations between sham and SARS-CoV-2 RBD, whereas asterisks point out important variations between SARS-CoV-2 RBD and every group. *, # p < 0.05, **, ## p < 0.01, and ***, ### p < 0.001
The RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) and envelope (E) genes are important targets for the detection and analysis of SARS-CoV-2 infections [36]. Subsequently, we evaluated the RNA copy variety of the SARS-CoV-2 particular sequence whereas concentrating on the RdRp and E genes to find out whether or not KGS-NE can stop the replication of SARS-CoV-2 in lung tissue. As proven in Fig. 7D and E, the expression of RdRp and E genes elevated considerably within the SARS-CoV-2 an infection, whereas the administration of KGS-NE barely suppressed the expression of RdRp and E genes.
As proven in Fig. 8A, irritation was noticed within the lungs of SARS-CoV-2-infected hamsters, and these abnormalities had been suppressed by administration of KGS-NE. Particularly, lung congestion and swelling escalated over time in SARS-CoV-2-infected hamsters. In distinction, the KGS-NE group demonstrated the flexibility to cut back this congestion and swelling in a dose- and time-dependent method. As well as, as proven in Fig. 8B, H&E staining was carried out on the lung tissue of hamsters to judge the pathological modifications in lung tissue attributable to SARS-CoV-2 an infection. Pathological lung tissue irritation (pink arrow), equivalent to alveolar injury, vascular modifications, fibrosis, and morphological disruption, was noticed in SARS-CoV-2 an infection and was dose-dependently attenuated by KGS-NE administration.
Impact of KGS-NE on lung morphological modifications in Syrian hamsters contaminated with SARS-CoV-2. A Morphology of the dissected lungs in 4 and seven dpi together with the load. B Histopathology (H&E) staining carried out to evaluate lung pathology and calculate the inflammatory rating. Crosshatch marks point out important variations between sham and SARS-CoV-2 an infection, and asterisks point out important variations between SARS-CoV-2 an infection and every group. *, # p < 0.05, **, ## p < 0.01, and ***, ### p < 0.001
To substantiate the inhibitory results of KGS-NE on the inflammatory response induced by SARS-CoV-2, a qRT-PCR examination was carried out to scrutinize the regulatory influence of KGS-NE on the gene expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines, together with NF-κB, IL-1β, IL-6, MCP-1, and TNF-α (Fig. 9). The outcomes unveiled an elevation within the ranges of pro-inflammatory cytokines equivalent to NF-κB, IL-1β, IL-6, MCP-1, and TNF-α in hamsters contaminated with SARS-CoV-2, indicative of an augmented immune response and an inflammatory cascade initiated by viral an infection. The intrusion of the coronavirus triggers the activation of the host immune system, prompting mobile synthesis of those pro-inflammatory components as a defensive measure in opposition to an infection. In distinction, administration of KGS-NE demonstrated a capability to down-regulate the gene expression related to pro-inflammatory cytokines, signifying its potential to attenuate the heightened inflammatory response induced by viral an infection. Moreover, KGS-NE exhibited a considerable discount within the gene expression of ACE2 in hamster lung tissue. At 4 days post-infection (dpi), there was a 46% discount, and at 7 dpi, there was a 58% discount, demonstrating a time-dependent and dose-dependent method. This remark means that KGS-NE could attenuate mobile susceptibility to viruses by diminishing ACE2 gene expression, thereby decelerating the method of virus invasion into host cells. Moreover, as proven in Determine S4, KEGG pathway evaluation recognized important expression of ABC transporter genes, significantly ABCF2 and ABCF3, which had been confirmed by way of qRT-PCR evaluation. In abstract, these findings collectively endorse the potential of KGS-NE to modulate immune responses and alleviate pulmonary irritation in hamsters throughout SARS-CoV-2 an infection.
Impact of KGS-NE on lung irritation in Syrian hamsters contaminated with SARS-CoV-2. A–F mRNA expression of inflammatory cytokines (IL-6, IL-1β, TNF-α and MCP1), and suppression of ACE2 and NF-κB in KGS-NE administrated group. Crosshatch marks point out important variations between sham and SARS-CoV-2 an infection, and asterisks point out important variations between SARS-CoV-2 an infection and every group. *, # p < 0.05, **, ## p < 0.01, and ***, ### p < 0.001
In vivo toxicity evaluation of KGS-NE administration
The toxicity evaluation of medication within the serum and liver is crucial as a result of these organs take part in drug metabolism and elimination [37]. On this research, the toxicity of KGS-NE was investigated by way of oral administrations of various concentrations (10–80 mg/kg) to C57BL/6 mice aged eight weeks for 14 days (Fig. 10A). The impact of KGS-NE therapy on the physique weight of the mice was evaluated, and the outcomes (proven in Fig. 10B) point out no important change within the physique weight. Liver histology was assessed by way of H&E staining (Fig. 10C). Regular liver tissue usually shows cords of hepatocytes with a central vein and sinusoids, and hepatocyte nuclei are usually spherical or oval with distinguished nucleoli. H&E staining confirmed hepatocyte swelling, necrosis, and irritation, suggesting liver illness or poisonous harm. Nevertheless, within the current research, KGS-NE (80 mg/kg) didn’t induce any of those modifications, indicating that its non-toxicity to the liver. ALT and AST ranges had been quantified to judge liver operate and establish liver harm, whereas ALP and LDH ranges had been investigated as potential indicators of liver illness. The outcomes are introduced in Fig. 10D. The enzyme actions had been comparable within the non-treatment group, indicating that extended KGS-NE administration didn’t induce important toxicity. Usually, these outcomes counsel that the administration of KGS-NE doesn’t have an effect on liver injury. Furthermore, to deal with issues in regards to the immune response, we assessed the proportion of immune cells in mice. Particularly, we analyzed the impact of KGS-NE on RAW 264.7 macrophage cells, specializing in cell proliferation. As proven in Determine S5, the outcomes confirmed no important modifications in cell proliferation after therapy with KGS-NE (40 mg/kg), indicating that KGS-NE doesn’t have poisonous results on immune cells. General, these findings show that KGS-NE is secure with respect to liver operate and immune cell well being.
In vivo toxicity analysis of KGS-NE in C57BL/6 mice. A Schematic illustration of KGS-NE administration in C57BL/6 mice. B Modifications in physique weight throughout experimental interval had been insignificant; C Histopathological (H&E) examination of liver tissue confirmed no indications of harm following saPGS-NE administration. D Serum exams for liver operate markers, together with ALT, ALP, AST, and LDH, confirmed no proof of toxicity. Crosshatch marks point out important variations between every group. *, # p < 0.05, **, ## p < 0.01, and ***, ### p < 0.001