Synthesis and characterization of GBP@HA NPs
We ready and characterised GBP@HA NPs based mostly on our conceptual framework (Scheme 1a). As proven in Fig. 1a, the FT-IR Fig of BSA v = 1661 cm− 1, v = 1537 cm− 1 and v = 1239 cm− 1 are attributed to the amide (I) peak, amide (II) peak and amide (III) peak, respectively. Within the spectrum of G-BSA, v = 1655 cm− 1, v = 1542 cm− 1 and v = 1247 cm− 1 are amide I, II, III bands, respectively, glycosylation may cause the carboxyl group within the lactobionic acid molecule and the free amino group in BSA for amide response, so its amide I, II, III band modifications, 1135 cm− 1 in lactobionic acid corresponds to the -OH group enlargement vibration within the galactosyl group, and the height wavenumber in G-BSA is 1162 cm− 1, indicating the profitable synthesis of G-BSA.
Then analyze its crystal construction via XRD. XRD spectra (Fig. 1b) confirmed that the broad peaks of lactobionic acid and BSA confirmed that each have been amorphous, and bodily mixing had no impact on them, they usually have been nonetheless amorphous, whereas there have been apparent diffraction peaks at 31°(2θ) and 45°(2θ) within the spectra of G-BSA, indicating that G-BSA was crystalline, additional proving the profitable synthesis of G-BSA.
Analyze the synthesis technique of GBP@HA NPs via potential modifications. The potential change outcomes of Fig. 1c present that the zeta floor potential of G-BSA-polyphenol NPs throughout the synthesis of GBP@HA NPs is -30.97 ± 0.29 mV. As a result of EPL has a constructive cost and HA has a unfavourable cost, G-BSA-polyphenol NPs are encapsulated layer by layer via EPL and HA to type GBP@HA NPs. On this course of, GBP@EPL NPs are fashioned after EPL encapsulation, and the potential modifications from − 30.97 ± 0.29 mV to 21.50 ± 0.53 mV, after which via HA encapsulation, it lastly turns into − 22.23 ± 3.62 mV.
The round dichroism patterns of BSA, G-BSA and G-BSA-polyphenol NPs (Fig. 1d) have been verified and analyzed as proven in Desk S1 (Supplementary Materials), when BSA was modified by glycosylation, the content material of its α-helix construction elevated from 32.2%, the content material of β-fold elevated from 30.7 to 34.0%, and the content material of β-corner decreased from 6.2 to 2.6%, indicating that the content material of lactobonic acid glycosylation modified BSA The molecular secondary construction was affected, confirming the synthesis of G-BSA, however didn’t trigger vital modifications within the secondary construction. The binding of polyphenols to G-BSA additional impacts the construction of G-BSA, indicating that its binding could also be associated to hydrogen bonding, and trigger secondary structural modifications by affecting the intramolecular hydrogen bonding power of G-BSA.
We additionally examined the particle dimension distribution of GBP@EPL NPs and GBP@HA NPs, each of which confirmed a unimodal distribution. The particle dimension of GBP@EPL NPs was 367.57 ± 27.17 nm (Determine S1), with a PDI of 0.207. As proven in Fig. 1e, the particle dimension of GBP@HA NPs is 441.93 ± 17.27 nm with a PDI of 0.268. Each varieties of nanoparticles have good dispersibility and uniform distribution.
Stability and in vitro launch profiles of GBP@HA NPs
Transmission electron microscopy was used to look at the morphology of nanoparticles, as proven in Fig. 1f-h, and it may be noticed that the nanoparticles are common and uniformly spherical, and the particle dimension distribution is about 500 nm, which is in step with the particle dimension distribution detection outcomes. To judge the soundness of GBP@HA NPs, they have been incubated in pepsin-containing synthetic gastric juice and trypsin-containing synthetic small intestinal fluid, respectively, after which the morphology of GBP@HA NPs was noticed. Transmission electron microscopy confirmed that GBP@HA NPs have been nonetheless comparatively full spherical after 3 h incubation in synthetic gastric juice and synthetic small intestinal fluid, and there’s no vital change in particle dimension, so GBP@HA NPs had good stability in pepsin and trypsin, which was conducive to their easy reaching of the colon web site after oral administration.
The discharge curves of GBP@HA NPs below completely different pH situations are proven in Fig. 1i-j, and the cumulative launch charges of TA and EGCG in GBP@HA NPs inside 48 h at pH 1.5 are (30.84 ± 1.24) % and (29.96 ± 0.43) %, respectively, indicating that they’re extra steady and fewer launched below acidic situations. At pH 6.8, the cumulative launch charges of TA and EGCG elevated, (68.84 ± 0.68) % and (38.29 ± 1.40) %, respectively, and the cumulative launch charges reached (91.26 ± 0.42) % and (47.15 ± 0.90) % at pH 7.4, respectively, in contrast with the cumulative launch charges at pH 1.5 and pH 7.4. Due to this fact, GBP@HA NPs can successfully resist the acidic setting, preserve good stability when administered orally, and perform drug launch course of within the colon.
In vitro free radical scavenging capability of GBP@HA NPs
PTIO• is usually used ROS radicals, DPPH• and ABTS•, generally used reactive nitrogen species (RNS) radicals, and the antioxidant capability of GBP@HA NPs was preliminarily examined by free radical scavenging experiments. As proven in Fig. 1k-m, the scavenging price of GBP@HA NPs within the vary of fifty ∼ 500 µg/mL is greater than 60% for PTIO radicals, greater than 70% for DPPH radicals, and greater than 98% for ABTS radicals, and its clearance progressively will increase with the rise of focus, so GBP@HA NPs can successfully take away ROS and RNS, indicating that they might have good antioxidant perform. On the similar time, in response to the detection outcomes, 200 µg/mL was chosen for cell experiments.
Synthesis and characterization of GBP@HA NPs. (a) Infrared spectra of G-BSA. (b) XRD spectrum of G-BSA. (c) Potential modifications throughout the synthesis of GBP@HA NPs. (d) Round dichroic spectra of BSA, G-BSA, and G-BSA-polyphenol NPs. (e) Particle dimension distribution of GBP@HA NPs. (f) Observe the morphology of GBP@HA NPs via transmission electron microscopy (pH = 7) and GBP@HA NPs have been incubated in synthetic gastric juice at pH 1.5 (g) and synthetic intestinal juice at pH 6.8 (h) for 3 h earlier than morphological commentary. Launch curves of (i) TA and (j) EGCG in GBP@HA NPs below completely different pH situations (n = 3). The (okay) PTIO, (l) DPPH, and (m) ABTS free radical clearance charges of GBP@HA NPs. All knowledge are introduced as imply ± SD
In vitro and in vivo biocompatibility of GBP@HA NPs
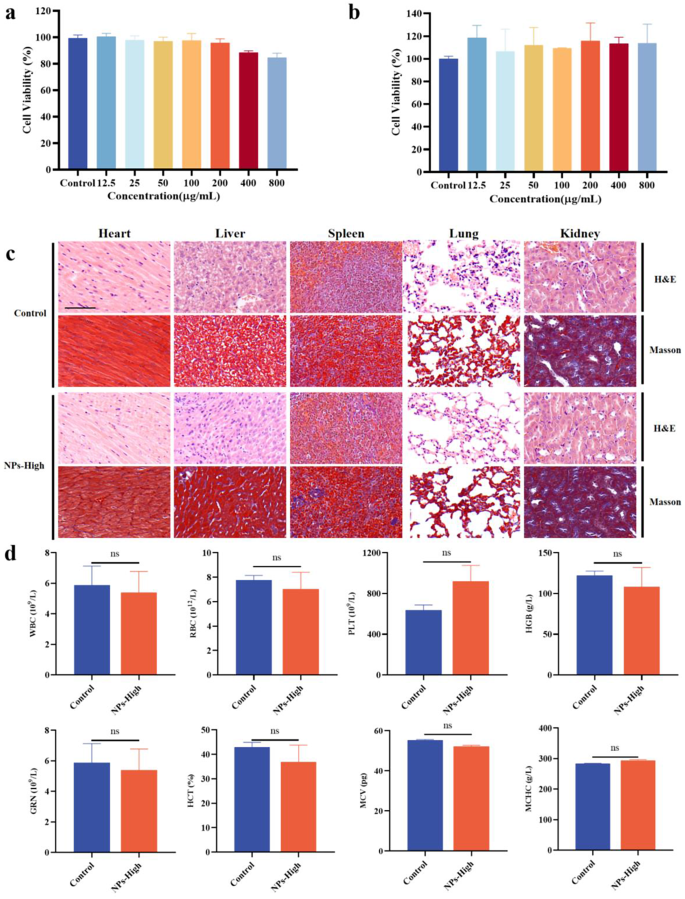
The security of a drug is essential to the applying of the drug. Due to this fact, the cytotoxicity of GBP@HA NPs in RAW 264.7 mouse macrophages and Caco-2 colorectal most cancers cells was first analyzed by MTT. As proven in Fig. 2a-b, at a focus of 12.5 ∼ 800 µg/mL, the survival price of RAW 264.7 macrophages and Caco-2 colorectal most cancers cells was above 80%, and there was no apparent cytotoxicity, which proved that GBP@HA NPs had good in vitro biocompatibility. As very best nanoparticles for oral administration, along with good therapeutic results, good biocompatibility can also be essential. On this examine, the center, liver, spleen, lungs and kidneys of mice repeatedly given excessive doses of GBP@HA NPs have been subjected to histopathological commentary by H&E staining and Masson staining, and the blood cells of mice have been analyzed and in contrast with regular mice.
As proven in Fig. 2c, cardiomyocytes are full and neatly organized, liver cells are regular and intently organized, the construction of white pulp and crimson pulp in spleen tissue is evident and regular, there isn’t a alveolar injury within the lungs, no inflammatory cells are produced, and the kidney tissue presents regular tubules and glomeruli, all with out inflammatory response. The blood cells of mice have been analyzed to detect white blood cells (WBC), crimson blood cells (RBC), platelets (PLT), hemoglobin (HGB), granulocytes (GRN), hematocrit (HCT), imply quantity of crimson blood cells (MCV), and imply hemoglobin focus (MCHC) within the blood of mice, and the outcomes of Fig. 2d confirmed that there was no vital distinction between the blood cells within the blood of mice within the NPs-Excessive group and people of regular mice. The above outcomes present that GBP@HA NPs don’t have any antagonistic results on the tissues and blood of mice, have good biocompatibility, and can be utilized as a secure supply system to play a therapeutic position.
Impact of various concentrations of GBP@HA NPs on cell viability after incubation with (a) RAW 264.7 cells and (b) Caco-2 cells for twenty-four h, respectively. (n = 3) (c) H&E staining and Masson staining of coronary heart, liver, spleen, lung, kidney of mice administered GBP@HA NPs mice (Scale bar: 200 μm). (d) Blood cell evaluation of mice administered GBP@HA NPs (n = 3; ns: No vital distinction). All knowledge are introduced as imply ± SD
Anti-inflammatory, antioxidant and mobile uptake properties of GBP@HA NPs
Cytokines play an irreplaceable position within the prevalence and growth of irritation, during which macrophages are intently associated to the manufacturing of cytokines [56]. The anti-inflammatory results of GBP@HA NPs in vitro have been analyzed by investigating the secretion of 4 inflame-related cytokines, TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6 and IL-10 by RAW 264.7 macrophages in numerous remedy teams. As proven in Fig. 3a, after the stimulation of LPS, the content material of pro-inflammatory components TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-6 elevated considerably, whereas the content material of anti-inflammatory issue IL-10 was considerably lowered. After remedy with blended polyphenols, G-BSA-polyphenol NPs and GBP@HA NPs, the pro-inflammatory components of every group have been lowered and the anti-inflammatory components have been elevated, amongst which the regulatory impact of GBP@HA NPs was probably the most vital, displaying good in vitro anti-inflammatory results.
We evaluated the power of GBP@HA NPs to restore oxidative stress injury attributable to H2O2 utilizing MTT assay. As proven within the Fig. 3b, H2O2 will trigger vital oxidative stress injury to cells, resulting in a big lower in cell survival price. Polyphenols can successfully restore oxidative stress injury and enhance cell survival charges to be just like regular cells. The formation of GBP@HA NPs has no vital impact on the restore impact of polyphenols, and may nonetheless considerably enhance cell survival charges.
ROS in cells was detected by DCFH-DA fluorescence probe. Determine 3c exhibits that, after LPS stimulation, intracellular fluorescence was considerably enhanced and ROS content material elevated considerably. The fluorescence in cells handled with EGCG and TA blended polyphenols, G-BSA-polyphenol NPs and GBP@HA NPs was considerably lowered, which proved that the expansion of ROS content material was inhibited. And We speculate that the antioxidant capability of G-BSA-polyphenol NPs and GBP@HA NPs primarily got here from pure polyphenols with good antioxidant impact, whereas the formation of G-BSA-polyphenol NPs and GBP@HA NPs can nonetheless preserve their antioxidant impact.
The focusing on of GBP@HA NPs to macrophages was evaluated in vitro by cell uptake experiments. Fluorescence photos confirmed that the fluorescence in regular macrophages with out LPS remedy was weak, indicating that fewer GBP@HA NPs have been ingested. And the fluorescence depth in LPS-induced inflammatory macrophages was considerably enhanced than that of regular macrophages, indicating that the uptake of GBP@HA NPs by inflammatory macrophages was considerably elevated, and GBP@HA NPs had good focusing on of inflammatory macrophages (Fig. 3d). To additional discover the focusing on of GBP@HA NPs, we pretreated inflammatory macrophages with a mix of lactobionic acid, HA, and lactobionic acid and HA, respectively, after which incubated with GBP@HA NPs, respectively. As proven within the Fig. 3d, the pretreatment of lactobionic acid and HA can weaken the fluorescence in inflammatory macrophages, and the combination pretreatment of lactobionic acid and HA considerably reduces the fluorescence to be near that of regular cells, which signifies that the great focusing on of GBP@HA NPs to inflammatory macrophages is expounded to the galactose group and HA contained in GBP@HA NPs. Galactose teams and HA selectively bind to macrophages galacto-type lectins (MGL) and CD44 proteins which can be extremely expressed on the floor of inflammatory macrophages, respectively, selling focused binding of GBP@HA NPs to inflammatory macrophages and entry.
(a) The contents of TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6 and IL-10 secreted by RAW 264.7 cells have been detected by ELISA (n = 3; *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001). (b) The restore capability of GBP@HA NPs for oxidative stress injury attributable to H2O2 was detected by MTT methodology in Caco-2 cells. (c) Detection of reactive oxygen species in RAW 264.7 cells utilizing DCFH-DA fluorescence probe (scale: 50 μm). (d) Uptake of GBP@HA NPs by RAW 264.7 cells (blue fluorescence: DAPI-stained nucleus; Inexperienced fluorescence: Rhodamine B labeled GBP@HA NPs; White scale: 50 μm; Inexperienced scale: 25 μm). All knowledge are introduced as imply ± SD
GBP@HA NPs alleviate acute UC
As proven in Fig. 4a, after free consuming of two.5% DSS aqueous resolution for 8 d, the mannequin group mice had extreme diarrhea, and the feces have been bloody mucus-like, the mobility was considerably lowered, and the coat shade was seen to the bare eye. It confirmed that the mouse ulcerative colitis mannequin was efficiently constructed. In Fig. 4b, the blood within the stool of mice in every group was noticed with bare eye, and it was seen that there have been apparent traces of blood within the stool on the anus of the mice within the mannequin group.
The burden of mice with colitis decreased considerably, and after remedy, the load of 5 teams of mice in polyphenol group, G-BSA-polyphenol group, NPs-Low group, NPs-Excessive group and 5-ASA group all recovered, amongst which the NPs-Excessive group had the perfect therapeutic impact, indicating that GBP@HA NPs may successfully improve the therapeutic impact of polyphenols, and the therapeutic impact was concentration-dependent (Fig. 4c). The DAI scores of mice in every group additionally demonstrated this outcome, with DSS-induced acute UC resulting in a big enhance within the DAI rating of the mice, and a lower in DAI in all remedy teams, in addition to the NPs-Excessive group (Fig. 4d). On the similar time, below the remedy impact of every group, the blood within the stool attributable to colitis in mice was additionally considerably improved (Fig. 4b). This outcome was additionally confirmed within the acute UC mannequin constructed via TNBS (Fig. S2a-c).
As well as, each DSS and TNBS induced mice developed signs of colitis, which developed colon congestion and swelling, weight achieve, and shortened colon size. As well as, as an essential part of the immune system, the inflammatory response may have an effect on the load of the thymus and pancreas, so colon size, thymus weight, and spleen weight are essential indicators of UC severity. As proven within the Fig. 4e-f and Fig. S2d-e, the colon of the mannequin group mice was swollen and the size was considerably shortened, whereas the excessive dose of GBP@HA NPs had a big protecting impact on the colon, and the protecting impact was higher than that of the polyphenol group and the G-BSA-polyphenol group. For spleen modifications attributable to colitis, all teams of mice improved after remedy, and performed alleviation impact on spleen enlargement attributable to irritation, and like different indicators, GBP@HA NPs additionally performed a concentration-dependent therapeutic impact (Fig. 4g-h). Due to this fact, we discovered that in contrast with unmodified polyphenols, GBP@HA NPs have therapeutic impact on DSS-induced colitis, and may successfully enhance the therapeutic impact of polyphenols, which is closest to that of regular mice.
Building of a mouse mannequin of ulcerative colitis and the therapeutic impact of GBP@HA NPs on UC. (a) Schematic diagram of experimental time. (b) Visible commentary of mouse fecal blood state of affairs picture. (c) Modifications in physique weight of mice. (d) DAI rating of mice. (e) Image of mouse colon. (f) Colon size in mice. (g) Image of mouse spleen. (h) Spleen index of mice. (i–l) The regulatory results of GBP@HA NPs on antioxidant-related enzymes MDA, SOD, CAT and GSH-PX in colon tissues of UC mice. (m–r) The regulatory impact of NPs on inflammatory associated components MPO, TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β and IL-10 in colon tissue of UC mice. (n = 6; *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001). All knowledge are introduced as imply ± SD
As well as, we evaluated the anti-inflammatory and antioxidant results of GBP@HA NPs in mice with acute UC [57, 58]. The antioxidant capability of GBP@HA NPs in vivo was analyzed by detecting the degrees of MDA, SOD, CAT and GSH-Px within the colons of mice in every group. As proven within the Fig. 4i, DSS-induced colitis led to a big enhance in MDA content material within the colon of mice, whereas the MDA content material in every remedy group decreased in contrast with it, amongst which the NPs-Low group and NPs-Excessive group have been considerably lowered and concentration-dependent. After testing, we discovered that colitis considerably brought about the discount of SOD, CAT and GSH-Px antioxidant enzymes, and the degrees of antioxidant enzymes have been considerably elevated after the remedy of polyphenols, G-BSA-polyphenols, low-dose GBP@HA NPs, high-dose GBP@HA NPs and 5-ASA, as proven within the Fig. 4j-l, the degrees of SOD enzymes within the NPs-Excessive group elevated considerably. The CAT ranges of NPs-Low group and NPs-Excessive have been considerably elevated, and the GSH-Px ranges of every remedy group have been considerably elevated, so GBP@HA NPs can successfully improve the antioxidant impact of polyphenols to advertise the advance of colitis. The experimental outcomes of TNBS induced acute UC in mice are in step with them (Fig. S2f-i).
To investigate the anti-inflammatory results of GBP@HA NPs in vivo, we examined the inflammation-related components MPO, TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β, and IL-10 in mouse colons (Fig. 4m). MPO is a useful marker and activation marker of neutrophils, and the prevalence of irritation is intently associated. As proven within the Fig. 4n-r, the content material of MPO in mice with DSS induced acute UC is considerably elevated in contrast with regular mice, and after drug remedy, the content material of every group exhibits a big downward pattern, and the G-BSA-polyphenol group, NPs-Low group, NPs-Excessive group and 5-ASA group are considerably lowered. The inflammatory components TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-1β have been considerably elevated when irritation occurred within the colon, however confirmed a big lower below the remedy impact of every group. And the content material of anti-inflammatory issue IL-10 in regular mice was greater than that within the mannequin group, the contents of the G-BSA-polyphenol group, NPs-Low group, NPs-Excessive group and 5-ASA group have been considerably greater than these within the mannequin group. The detection of inflammatory components within the colon of TNBS induced acute colitis mice additional confirms that GBP@HA NPs have a regulatory impact on inflammatory components and may play a task in decreasing MPO (Fig. S2j-n). The outcomes of those inflammation-related components confirmed that GBP@HA NPs had good anti-inflammatory results in vivo and considerably enhanced the anti-inflammatory results of polyphenols.
Histopathological analysis
The colons of DSS and TNBS induced acute colitis mice have been stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) and Masson for histopathological evaluation (Fig. 5 and Fig. S3a). As proven within the Fig. 5a, every layer of the intestinal wall of the colon of DSS-induced colitis mice had completely different levels of inflammatory cell infiltration, intestinal mucosal defects and crypt construction injury. The pathological accidents of mice within the remedy group have been improved to various levels, amongst which the G-BSA-polyphenol NPs group, NPs-Low group and NPs-Excessive group have been the closest to the conventional colon, and the histopathological scores of every group additionally confirmed this outcome. On the similar time, the collagen fibers of the tissue have been stained by Masson staining, which additional confirmed the pathological modifications within the colon tissue. As proven within the Masson staining picture, the colonic tissue construction of mice within the mannequin group was destroyed, accompanied by collagen deposition and fibrosis, and the remedy of every group had an inhibitory impact on colon tissue construction injury, collagen deposition and fibrosis, and promoted colon restoration, amongst which the G-BSA-polyphenol NPs group, NPs-Low group and NPs-Excessive group had the perfect remedy impact and was closest to regular tissue.
As well as, the evaluation of colon tissue by alcian blue staining can observe the mucus matrix of colon tissue. Intestinal cells secrete mucus to cowl the epithelial mucosal layer, forming the intestinal mucosal barrier, and the mucus comprises IgA and antimicrobial peptides that work collectively to defend in opposition to the invasion of dangerous commensal micro organism and pathogens. Determine 5b exhibits that colitis within the mannequin group results in the destruction of colonic tissue, a big discount in mucus secretion, and injury to the intestinal mucosal barrier. In contrast with the mannequin group, mucus secretion in colon tissues was considerably elevated in all remedy teams, and the G-BSA-polyphenol NPs group, NPs-Low group and NPs-Excessive group recovered to be near regular mice. Due to this fact, in contrast with pure polyphenols and 5-ASA, the modified GBP@HA NPs can successfully inhibit the pathological injury of the colon attributable to colitis and restore the intestinal mucosal barrier.
Histopathological commentary. (a) H&E staining and Masson staining of colon tissue in every group of mice. (b) Alcian blue staining of colon tissue in every group of mice. (c) Cy7 labeled GBP@HA NPs have been administered orally to regular group mice and UC mannequin group mice, and entire physique imaging was carried out utilizing IVIS know-how at 4 h, 6 h, 12 h, and 24 h. (d) The guts, liver, spleen, lungs, and kidneys, in addition to the digestive tract from the abdomen to the colon, have been collected to detect the fluorescence distribution of every web site. All knowledge are introduced as imply ± SD. (n = 3; *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001. Magnification: 20 ×; Scale: 200 μm)
Focusing on and biodistribution of GBP@HA NPs in colitis mice
Subsequent, we analyzed the in vivo distribution of GBP@HA NPs utilizing Cy7 fluorescent dye. Determine 5c exhibits that vital fluorescence was noticed in each regular mice and UC mannequin mice after administration, and the fluorescence decreased over time. Nonetheless, the fluorescence in regular mice decreased extra considerably. In line with the fluorescence distribution maps in numerous organs (Fig. 5d), throughout the 24-hour distribution course of, there was no fluorescence distribution within the liver, liver, spleen, lungs, and kidneys, however solely within the gastrointestinal tract. After 12 h, UC mice confirmed stronger fluorescence within the gastrointestinal tract than regular mice, and there was nonetheless vital fluorescence within the colon after 24 h, indicating that GBP@HA NPs have good colon focusing on capability.
Intestinal barrier restore and regulation of macrophage polarization
The presence of tight junctions between intestinal epithelial cells within the intestinal barrier is crucial and performs an irreplaceable position in sustaining the integrity of the intestinal barrier, and the expression of tight junction proteins between intestinal epithelial cells is affected when colitis happens, leading to modifications within the construction and performance of tight junctions, so the detection of tight junction proteins is a vital a part of evaluating the therapeutic impact of colitis. By twin immunofluorescence staining, we analyzed the 4 tight junction proteins ZO-1 and Occludin, Claudin-4, and E-Cadherin, respectively. The immunostaining outcomes (Fig. 6a-b and Fig. S3b) confirmed that the fluorescence of ZO-1, Occludin, Claudin-4 and E-Cadherin within the colon of regular mice was sturdy, which proved that the content material of tight junction protein was excessive and the intestinal barrier perform was intact. Nonetheless, the intestinal barrier perform of mice with colitis was impaired, tight junctions have been destroyed, the content material of associated proteins was considerably lowered, and the fluorescence depth was considerably weakened. By means of the remedy of GBP@HA NPs and 5-ASA, the fluorescence depth of the 4 proteins was enhanced in contrast with the mannequin group, that’s, the content material of the 4 proteins elevated, the intestinal barrier perform was restored. And the fluorescence depth of the GBP@HA NPs remedy group was additionally stronger than that of the 5-ASA group, which was near that of the conventional group, indicating that GBP@HA NPs can enhance the colon situation of mice and deal with colitis by repairing the intestinal barrier.
Macrophages, as immune cells that play an essential position within the intestinal immune barrier, can successfully assist preserve and regulate intestinal homeostasis [59]. Macrophages in numerous environments will be polarized into M1 (classical activation) and M2 (selective activation) two completely different phenotypes, M1 macrophages have pro-inflammatory results, within the technique of colitis prevalence and growth of M1 macrophages polarization will increase, inflicting an extra enhance in pro-inflammatory cytokines, whereas M2 has anti-inflammatory results, can promote the secretion of anti-inflammatory components, and is expounded to the decision of irritation [60]. On this examine, the markers iNOS (inducible nitric oxide synthase) and CD206 of M1 and M2 macrophages have been chosen as indicators for the analysis of macrophage polarization, as proven in Fig. 6c, iNOS (crimson fluorescence) expression was little or no, whereas CD206 (inexperienced fluorescence) expression was considerably greater than iNOS, indicating that macrophages in regular mice have been multipolarized to M2 sort. In distinction, iNOS expression was considerably greater than CD206 within the colon tissues of DSS-induced mice with colitis, indicating that colitis growth is intently associated to elevated polarization of M1-type macrophages. After remedy with GBP@HA NPs and 5-ASA, the expression of iNOS in mouse colon tissues decreased, and the expression of CD206 within the NPs-Excessive group elevated considerably in contrast with the mannequin group, indicating that regulating the M1 and M2 polarization of macrophages, decreasing M1 cells, and rising M2 cells is one other essential cause why GBP@HA NPs can successfully play a therapeutic position.
Examine on repairing impact of intestinal barrier and regulating macrophage polarization by GBP@HA NPs. (a) Immunofluorescence staining and quantitative evaluation of ZO-1 and Occludin within the colon (Blue fluorescence: DAPI-stained nucleus; Inexperienced fluorescence: ZO-1; Pink fluorescence: Occludin) (b) Immunofluorescence staining and quantitative evaluation of Claudin4 and E-Cadherin within the colon (Blue fluorescence: DAPI-stained nucleus; Inexperienced fluorescence: Claudin4; Pink fluorescence: E-Cadherin). (c) Immunofluorescence staining and quantitative evaluation of iNOS and CD206 within the colon (Blue fluorescence: DAPI stained nuclei; Inexperienced fluorescence: CD206; Pink fluorescence: iNOS) scale: 400 μm; magnification: 40 ×
GBP@HA NPs regulate the intestinal flora
Necessary influences of the intestine microbiota have been recognized in sustaining well being in addition to illness pathogenesis [61, 62]. On this examine, the intestinal micro organism within the feces of every group of mice have been analyzed. First, the richness and variety of the microbiota have been analyzed, primarily evaluating the α-diversity index: operational taxa (OTUs), Chao1 index and Simpson index. As proven in Fig. 7a, the OTUs and Chao1 indices of DSS-induced colitis mice have been considerably decrease than these of regular mice, indicating that colitis affected intestinal homeostasis and lowered the abundance of intestinal flora, whereas the Simpson index of colitis mice was considerably lowered, indicating a lower within the variety of intestinal flora in mice with colitis. After the remedy of polyphenols and GBP@HA NPs, the OTUs, Chao1 index and Simpson index of mice have been elevated, indicating their restoration impact on the abundance and variety of intestinal flora, amongst which GBP@HA NPs may promote the numerous enhance of OTUs, Chao1 index and Simpson index in mice with colitis, indicating its vital position in restoring the abundance and variety of intestinal flora.
An in depth evaluation of the microbiota was carried out on the phylum and genus ranges (Fig. 7b). The primary intestinal micro organism have been analyzed on the phylum and genus ranges, respectively. As proven in Fig. 7c, checks have been carried out on the genus stage, and the principle intestinal micro organism genera amongst them have been analyzed. Lactobacillus is probably the most considerable probiotic within the intestine, which is conducive to sustaining intestinal homeostasis and immune situations [63]. Akkermansia, a traditional human intestinal flora, not solely performs a metabolic protecting position in defending the integrity of intestinal epithelial cells and mucus layer, but additionally performs an anti-inflammatory position within the technique of irritation via regulatory T cells, endocannabinoid system and non-classical toll-like receptors [64]. Research have proven that enterotoxins produced by the genus Bacteroides are current within the human intestine throughout lively colitis and are intently related to colitis [65]. Klebsiella has a symbiotic relationship with people, serving to to interrupt down meals and produce the vitamins and power the physique wants. Nonetheless, when the immune system is broken or the intestinal barrier is broken, Klebsiella enter components of the physique aside from the gastrointestinal area, which may trigger an infection, oxidative stress and different antagonistic results [66]. As proven in Fig. 7d, within the intestines of regular mice, Lactobacillus and Akkermania glutinophilus have been considerable, Klebsiella and Bacteroides have been considerable, and the alternative was true in colitis mice. The regulatory impact of GBP@HA NPs modifications the flora abundance, which is near that of regular mice. Determine 7e-f exhibits that on the phylum stage, Bacteroidetes, Firmicutes, and Proteobacteria have the best abundance. In colitis mice, Bacteroidetes elevated whereas Firmicutes decreased. The Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes ratio (F/B), as an essential indicator reflecting the diploma of intestinal microbiota dysfunction, decreased in comparison with regular mice. After remedy with GBP@HA NPs, the F/B ratio of mice considerably elevated, confirming the position of GBP@HA NPs in regulating intestinal microbiota and inhibiting intestinal problems. The outcomes of principal coordinate evaluation (PCoA) (Fig. 7g) have been in step with it, and the space between the management group and the mannequin group was the farthest, indicating that the distinction between the 2 teams was the best. GBP@HA NPs remedy may scale back the distinction between the colitis mice and the management group, that’s, near regular mice. Due to this fact, GBP@HA NPs can successfully regulate intestinal flora and restore intestinal homeostasis.
The position of GBP@HA NPs in regulating intestine microbiota. (a) Examine the impact of GBP@HA NPs on the abundance and variety of intestine microbiota via OTUs, chao1 index, and Simpson index. (b) Warmth map of intestine microbiota on the phylum and genus ranges. (c) The relative abundance of intestine microbiota on the genus stage. (d) The relative abundance of essential genera within the intestine microbiota. (e) The relative abundance of intestine microbiota on the gate stage. (f) Ratio of Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes ratio (f/B). (g) Principal coordinate evaluation (PCoA) diagram of intestinal microbiota. (n = 6; *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001). All knowledge are introduced as imply ± SD
GBP@HA NPs alleviate power UC
Impressed by the therapeutic impact of GBP@HA NPs on acute UC, we additional explored its therapeutic impact in DSS induced power UC mouse mannequin (Fig. 8a). As proven within the Fig. 8b, the load of power UC mice induced by DSS was considerably lowered in comparison with regular mice. After 7 weeks of remedy, the polyphenol group, G-BSA-polyphenol group, NPs-Low group, NPs-Excessive group, and 5-ASA group all confirmed greater physique weight than UC mice, demonstrating weight restoration impact. Equally, every remedy group additionally demonstrated therapeutic results on colon size discount attributable to colitis, with the NPs-Excessive group returning to a stage near that of the conventional group (Fig. 8c-d). As proven within the Fig. 8e-f, GBP@HA NPs additionally has aid impact on spleen enlargement attributable to colitis, and the spleen quantity and index are considerably lowered. Subsequent, the inflammation-related components MPO, TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β and IL-10 within the colon of mice in every group of the power UC mannequin have been analyzed. As anticipated, GBP@HA NPs can successfully scale back the rise of MPO, TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β attributable to power UC, and enhance the extent of anti-inflammatory issue IL-10 (Fig. 8g-k).
The therapeutic impact of GBP@HA NPs on power UC. (a) Schematic diagram of experimental time. (b) Modifications in physique weight of mice. (c) Image of the mouse colon. (d) Mouse colon size. (e) Image of mouse spleen. (f) Mouse spleen index. (g-k) The regulatory impact of NPs on inflammatory associated components MPO, TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β and IL-10 in colon tissue of power UC mice. (n = 6; *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001). All knowledge are introduced as imply ± SD
The histopathological research carried out in power UC fashions have additional demonstrated the restore impact of GBP@HA NPs on UC-induced colon tissue injury. As well as, we carried out histopathological research. The H&E staining outcomes (Fig. 9a) point out that power UC may trigger extreme injury to colon tissue, inflicting issues akin to crypt injury and inflammatory cell infiltration. GBP@HA NPs additionally display good therapeutic results and successfully restore broken colon tissue. In the meantime, the Masson staining outcomes (Fig. 9a) point out that GBP@HA NPs can play a big therapeutic position in selling colon restoration in power UC induced collagen deposition and fibrosis within the colon. Due to this fact, GBP@HA NPs may play a wonderful position in inhibiting colonic pathological injury attributable to colitis and repairing the intestinal mucosal barrier in power UC.
To analyze whether or not GBP@HA NPs can alleviate colonic intestinal barrier injury attributable to power UC, we detected tight junction protein by immunofluorescence staining. As proven in Fig. 9b-c, GBP@HA NPs confirmed therapeutic impact on the discount of tight junction proteins ZO-1, Occludin, Claudin4 and E-Cadherin attributable to power UC, and the fluorescence of the 4 tight junction proteins was considerably enhanced, indicating a big enhance of their content material. The broken intestinal barrier is repaired. We additionally studied the regulatory impact of GBP@HA NPs on macrophage polarization by immunofluorescence staining.
Examine on repairing impact of intestinal barrier by GBP@HA NPs. (a) H&E staining and Masson staining of colon tissue in every group of mice. (Magnification: 20 ×) (b) Immunofluorescence staining and quantitative evaluation of ZO-1 and Occludin within the colon (blue fluorescence: DAPI-stained nucleus; Pink fluorescence: ZO-1; Inexperienced fluorescence: Occludin) (c) Immunofluorescence staining and quantitative evaluation of Claudin4 and E-Cadherin within the colon (blue fluorescence: DAPI-stained nucleus; Pink fluorescence: Claudin4; Inexperienced fluorescence: E-Cadherin). Scale: 400 μm; Magnification: 40 ×
The regulatory impact of GBP@HA NPs on metabolites
We used UPLC-Q-MS know-how to detect endogenous metabolites in mouse colon tissue, preliminarily screening differential metabolites associated to GBP@HA NPs assuaging colitis, and conducting a deeper exploration of their therapeutic mechanisms. As proven in Fig. 10a-d, the clean management group and mannequin group have been considerably separated, indicating a change within the metabolic stage of colonic tissue content material in mice after modeling. There was no aggregation between the mannequin group and the GBP@HA NPs group, indicating separation. This means that the metabolic stage of colonic content material in mice with colitis additionally modified after remedy with GBP@HA NPs. Determine 10e exhibits that colitis causes vital modifications in metabolites in mice, whereas remedy with GBP@HA NPs reduces the differential metabolites between colitis mice and regular mice. Metabolites akin to L-tryptophan, phenylacetylglycine, biochanin A, hepoxilin A3 and 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid within the colon of mannequin group mice have been considerably elevated in comparison with regular mice and L-Asparagine, glycitein, epiandrosterone, and L-Aspartic acid metabolites have been considerably downregulated (Fig. 10f). Additional pathway enrichment evaluation of differential metabolites between the GBP@HA NPs group and the mannequin group confirmed that the amino acid metabolism pathway is affected, and amino acids not solely present power, however their metabolites may take part in essential physiological actions (Fig. 10g-h). Cytoplasmic glutamate is essential for sustaining redox stability and avoiding oxidative stress in cells by producing glutathione (GSH). We additionally discovered that UC growth is related to the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) signaling pathway, a ligand-activated receptor within the nuclear hormone receptor household that performs an essential position in inflammatory responses and binds to the NF-κB subunit that regulates the expression of inflammatory components [67]. Due to this fact, based mostly on its therapeutic efficacy and metabolomics analysis, a deeper exploration of its potential mechanisms has been carried out.
(a) PLS-DA rating plot between the management group and the mannequin group below constructive ion mode. (b) PLS-DA rating plot between the management group and the mannequin group below unfavourable ion mode. (c) PLS-DA rating plot between GBP@HA NPs group and mannequin group in constructive ion mode. (d) PLS-DA rating plot between GBP@HA NPs group and mannequin group in unfavourable ion mode. (e) Differential metabolite statistics. Pink: enhance the quantity; Blue: Decreased quantity. (f) Z-score warmth map of differential metabolites. MetaboAnalyst was used to carry out KEGG pathway enrichment evaluation on differential metabolites between the GBP@HA NPs group and the mannequin group. (g) Distinction enrichment rating chart. (h) Scatter plot for differential metabolite enrichment evaluation
Potential mechanisms by which GBP@HA NPs alleviate colitis
Research have proven that oxidative stress attributable to oxidation and antioxidant imbalance within the physique impacts the prevalence and growth of UC [68]. The Keap1-Nrf2 signaling pathway is a key pathway in mobile oxidative stress, and the mRNA transcription and expression of Keap1 and Nrf2 within the colon tissues of every group of mice have been analyzed by qPCR and Western blotting [69, 70]. As proven within the Fig. 11a-b, below oxidative stress, the mRNA ranges of Keap1 and Nrf2 within the colon tissues of colitis mice have been considerably elevated in contrast with regular mice, and the remedy teams performed a regulatory position, in order that their relative expression ranges have been considerably lowered. Western blotting’s detection of Keap1 and Nrf2 proteins additionally confirmed this outcome, and the regulation of GBP@HA NPs was the obvious, and the NPs-Excessive group decreased to shut to the conventional group (Fig. 11c). Due to this fact, the highly effective regulation of Keap1-Nrf2 signaling pathway by GBP@HA NPs is a vital strategy to alleviate oxidative stress and exert antioxidant results.
Research have discovered that NF-κB controls many genes associated to irritation, so the activation of NF-κB signaling pathway can also be intently associated to the inflammatory response within the colon [71]. The detection of NF-κB mRNA expression stage confirmed that the expression stage of NF-κB mRNA in colonic cells was considerably elevated when colitis occurred, which was about 4 occasions that of regular mice and the G-BSA-polyphenol group and NPs-Excessive group have been considerably decrease than the mannequin group. On the similar time, the mRNA expression ranges of pro-inflammatory components TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6 and anti inflammatory issue IL-10 have been detected, as proven within the Fig. 11d-h, which was in step with the detection outcomes of Elisa. Lowered the elevated mRNA ranges of TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6 attributable to colitis, and elevated the expression of anti-inflammatory issue IL-10. As well as, Western blotting additionally introduced the expression of 4 inflammation-related components (Fig. 11i). As we imagined, below the regulation of GBP@HA NPs, TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6. The expression ranges have been considerably down-regulated, whereas the expression stage of IL-10 was considerably elevated. These outcomes recommend that GBP@HA NPs might successfully inhibit inflammatory response by regulating NF-κB signaling pathway.
With a view to additional discover the regulatory position of GBP@HA NPs on the cytopyrosis pathway, we analyzed the genes and proteins related to cytopyrosis. To begin with, immunofluorescence staining was utilized to the colon web site NLRP3 (crimson fluorescence), Caspase-1 (inexperienced fluorescence) and GSDMD (pink fluorescence) preliminary analysis. As proven within the Fig. 11n, below regular state the three proteins are much less, fluorescence depth is weak, and the DSS-induced colitis mice colon three fluorescence within the colon is considerably enhanced, indicating that the three essential proteins related to cell pyroptosis are considerably elevated, whereas the fluorescence of the GBP@HA NPs remedy group is considerably weakened, suggesting a detailed connection to the cytopyrosis pathway. Subsequent, qPCR evaluation outcomes confirmed that the mRNA ranges of NLRP3, Caspase-1 and GSDMD have been in step with the pattern proven by fluorescent staining, and the mRNA ranges of the three proteins have been considerably lowered after every group of drug administration (Fig. 11j-l). The Western blotting band additional confirmed this outcome (Fig. 11m). GBP@HA NPs exerted a robust inhibitory impact on the rise of NLRP3, Caspase-1 and GSDMD expression in colitis, just like that of regular mice. In abstract, GBP@HA NPs can downregulate NLRP3, Caspase-1, and GSDMD, thus possessing the potential to control the cell pyroptosis pathway and alleviate colitis.
Exploration of the position of GBP@HA NPs in regulating signaling pathways. (a-b) RT-qPCR measured the relative expression ranges of Keap1 and Nrf2 mRNA within the colon tissues of mice in every group. (c) Western blotting measured the expression of Keap1 and Nrf2 within the colon tissues of every group of mice. (d-h) RT-qPCR detected the relative expression ranges of mRNA in NF-κB p65, TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6 and IL-10 within the colon tissues of every group of mice. (i) Western blotting detected the expression of NF-κB p65, TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6 and IL-10 within the colon tissues of mice in every group. (j-l) RT-qPCR was used to detect the relative mRNA expression ranges of NLRP3, Caspase-1 and GSDMD in colon tissues of mice in every group. (m) Western blotting detected the expressions of NLRP3, Caspase-1 and GSDMD in colon tissues of mice in every group. (n) Immunofluorescence staining of NLRP3, Caspase-1, and GSDMD within the colon (Blue fluorescence: DAPI stained nuclei; Pink fluorescence: NLRP3; Inexperienced fluorescence: Caspase-1; Pink fluorescence: GSDMD; Scale: 100 μm; Magnification: 40 ×). (n = 3; *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001). All knowledge are introduced as imply ± SD