India continues to see a surge in cybercrime affecting each residents and companies, with cyber fraud towards residents leaping 51% over the previous yr and cyberattackers concentrating on companies in volumes considerably larger than world averages.
Total, Indian residents filed greater than 1.7 million cybercrime complaints in 2024, up from 1.1 million complaints in 2023, in accordance with the most recent information from India’s Nationwide Cyber Reporting Platform (NCRP) launched in early February. Whereas a lot of these cyber scams got here from home sources, about 45% of the cyberattacks got here from cybercriminal havens in Cambodia, Myanmar, and Laos, in accordance with the report.
The issue underscores the darkish facet of accelerating entry to on-line providers. Whereas the nation is digitizing a lot of its authorities providers — giving residents simpler entry — crime has adopted on-line, President Droupadi Murmu mentioned throughout a speech to Parliament on Jan. 31.
“[I]n an more and more digital society, cybersecurity has change into an important situation of nationwide significance,” Murmu mentioned. “Digital fraud, cybercrime, and rising applied sciences like deepfakes pose challenges to our social, financial, and nationwide safety.”
India’s residents aren’t the one targets of cybercriminals — enterprise websites more and more face on-line assaults. Cyber-risks and digital/know-how dangers are essentially the most urgent issues for firms in India, with companies within the area prioritizing these points greater than their world counterparts, in accordance with PricewaterhouseCoopers’ “2025 International Digital Belief Insights — India Version.”
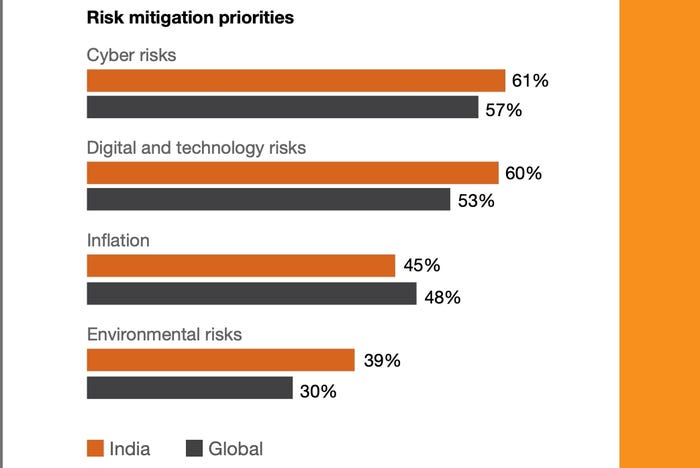
Supply: PricewaterhouseCoopers, “2025 International Digital Belief Insights — India Version”
“Over the subsequent 12 months, Indian organizations are prioritizing the mitigation of three key dangers: cyberthreats, digital vulnerabilities and inflation,” PwC India acknowledged within the report. “This focus highlights the crucial want for strong cybersecurity, dependable technological infrastructure, and methods to counter rising prices and guarantee resilience and sustained development.”
Companies See Totally different Menace Profile
In contrast with different areas of the world, India is seeing a better quantity of assaults. The common web site in India sees about 6.9 million undesirable requests — also known as “assaults” by distributors — yearly, with 26% extra assaults per website in contrast with the worldwide common, in accordance with Indusface. Denial-of-service assaults are additionally extra frequent towards Indian targets, in contrast with the worldwide common, says Venky Sundar, founder and president for the Americas at Indusface.
The menace actors have gone mobile-first, with API servers for cellular functions focused with 43% extra requests per host in contrast with web sites, he says.
There’s “a shift in assault methods in direction of disrupting cellular and linked providers,” Sundar says. “Cybercrime is more and more concentrating on external-facing APIs related to cellular apps quite than simply conventional internet platforms.”
The assaults are cut up pretty evenly between home sources and world ones, he provides. Total, about half of the malicious site visitors concentrating on firm websites and API servers are home, with a lot of the remainder coming from 4 nations: US, France, UK, and Singapore.
The federal government is at the moment taking steps to make life tougher for attackers. The Reserve Financial institution of India (RBI), for instance, has created unique Web domains for banks (financial institution.in) and for non-bank monetary establishments (fin.in), which might be run by the Institute for Improvement and Analysis in Banking Expertise (IDRBT). India additionally handed its first privateness and data-protection legislation in 2023, and drafted implementation guidelines final month, which collectively outline the rights of Indian residents and necessities for firms dealing with information.
India and the US additionally just lately signed a memorandum of understanding (MoU) that enables the 2 nations to cooperate on intelligence gathering, the change of knowledge on cybercrime instances, and collaborative coaching. India has additionally fought to rescue and repatriate its residents from pressured labor camps for legal syndicates in Cambodia, Myanmar, and Laos, the place they’re pressured to conduct quite a lot of on-line scams.
But the nation nonetheless faces a scarcity of cybersecurity professionals. In September, the federal government introduced an effort to practice 5,000 “cyber commandos” over the subsequent 5 years, to assist nationwide and state governments with cyber investigations.
Coaching residents in cybersecurity can have extra advantages, President Murmu mentioned in her remarks to Parliament.
“My authorities has taken quite a few measures to manage these cyber threats, creating alternatives for employment within the area of cybersecurity for the youth [and] is repeatedly working to make sure competence in cybersecurity,” she mentioned, noting that the nation has reached Tier 1 standing within the Worldwide Telecommunication Union’s International Cybersecurity Index.

