The power to get the adjustments that occur in an operational database like MongoDB and make them obtainable for real-time purposes is a core functionality for a lot of organizations. Change Knowledge Seize (CDC) is one such strategy to monitoring and capturing occasions in a system. Wikipedia describes CDC as “a set of software program design patterns used to find out and observe the information that has modified in order that motion may be taken utilizing the modified knowledge. CDC is an strategy to knowledge integration that’s based mostly on the identification, seize and supply of the adjustments made to enterprise knowledge sources.“ Companies use CDC from operational databases to energy real-time purposes and varied microservices that demand low knowledge latency, examples of which embody fraud prevention techniques, sport leaderboard APIs, and customized advice APIs. Within the MongoDB context, change streams supply a means to make use of CDC with MongoDB knowledge.
Organizations will typically index the information in MongoDB by pairing MongoDB with one other database. This serves to separate operational workloads from the read-heavy entry patterns of real-time purposes. Customers get the additional advantage of improved question efficiency when their queries could make use of the indexing of the second database.
Elasticsearch is a typical alternative for indexing MongoDB knowledge, and customers can use change streams to impact a real-time sync from MongoDB to Elasticsearch. Rockset, a real-time indexing database within the cloud, is one other exterior indexing choice which makes it straightforward for customers to extract outcomes from their MongoDB change streams and energy real-time purposes with low knowledge latency necessities.
Rockset Patch API
Rockset lately launched a Patch API methodology, which allows customers to stream advanced CDC adjustments to Rockset with low-latency inserts and updates that set off incremental indexing, quite than an entire reindexing of the doc. On this weblog, I’ll focus on the advantages of Patch API and the way Rockset makes it straightforward to make use of. I’ll additionally cowl how Rockset makes use of it internally to seize adjustments from MongoDB.
Updating JSON knowledge in a doc knowledge mannequin is extra sophisticated than updating relational knowledge. In a relational database world, updating a column is pretty easy, requiring the person to specify the rows to be up to date and a brand new worth for each column that must be up to date on these rows. However this isn’t true for purposes coping with JSON knowledge, which could have to replace nested objects and parts inside nested arrays, or append a brand new component at a specific level inside a nested array. Conserving all these complexities in thoughts, Rockset’s Patch API to replace current paperwork is predicated on JSON Patch (RFC-6902), an internet commonplace for describing adjustments in a JSON doc.
Updates Utilizing Patch API vs Updates in Elasticsearch
Rockset is a real-time indexing database particularly constructed to sync knowledge from different sources, like MongoDB, and routinely construct indexes in your paperwork. All paperwork saved in a Rockset assortment are mutable and may be up to date on the area stage, even when these fields are deeply nested inside arrays and objects. Profiting from these traits, the Patch API was carried out to assist incremental indexing. This implies updates solely reindex these fields in a doc which are a part of the patch request, whereas retaining the remainder of the fields within the doc untouched.
In distinction, when utilizing Elasticsearch, updating any area will set off a reindexing of the complete doc. Elasticsearch paperwork are immutable, so any replace requires a brand new doc to be listed and the previous model marked deleted. This ends in further compute and I/O expended to reindex even the unchanged fields and to put in writing whole paperwork upon replace. For an replace to a 10-byte area in a 10KB doc, reindexing the complete doc could be ~1,000x much less environment friendly than updating the only area alone, like Rockset’s Patch API allows. Processing a lot of updates can have an antagonistic impact on Elasticsearch system efficiency due to this reindexing overhead.
For the aim of retaining in sync with updates coming by way of MongoDB change streams, or any database CDC stream, Rockset may be orders of magnitude extra environment friendly with compute and I/O in comparison with Elasticsearch. Patch API offers customers a method to reap the benefits of environment friendly updates and incremental indexing in Rockset.
Patch API Operations
Patch API in Rockset helps the next operations:
- add – Add a price into an object or array
- take away – Take away a price from an object or array
- substitute – Replaces a price. Equal to a “REMOVE” adopted by an “ADD”.
- take a look at – Assessments that the required worth is ready within the doc at a sure path.
Patch operations for a doc are specified utilizing the next three fields:
- “op”: One of many patch operations listed above
- “path”: Path to area in doc that must be up to date. The trail is specified utilizing a string of tokens separated by
/. Path begins with/and is relative to the foundation of the doc. - “worth”: Non-compulsory area to specify the brand new worth.
Each doc in a Rockset assortment is uniquely recognized by its _id area and is used together with patch operations to assemble the request. An array of operations specified for a doc is utilized so as and atomically in Rockset. If one in every of them fails, the complete patch operation for that doc fails. That is necessary for making use of patches to the proper doc, as we are going to see subsequent.
Use Patch API
Now I’ll walkthrough an instance on how you can use the Patch API utilizing Rockset’s python consumer. Think about the next two paperwork current in a Rockset assortment named “FunWithAnimals”:
{
"_id": "mammals",
"animals": [
{ "name": "Dog" },
{ "name": "Cat" }
]
},
{
"_id": "reptiles",
"animals": [
{ "name": "Snake" },
{ "name": "Alligator"}
]
}
Now let’s say I need to take away a reputation from the record of mammals and likewise add one other one to the record. To insert Horse on the finish of the array (index 2), I’ve to supply path /animals/2. Additionally to take away Canine from index 0, path /animals/0 is offered. Equally, I wish to add one other title within the record of reptiles as effectively. – character will also be used to point finish of an array. Thus, to insert Lizard at finish of array I’ll use the trail /animals/-.
Utilizing Rockset’s python consumer, you possibly can apply this patch like under:
from rockset import Consumer
rs = Consumer()
c = rs.Assortment.retrieve('FunWithAnimals')
mammal_patch = {
"_id": "mammals",
"patch": [
{ "op": "add", "path": "/animals/2", "value": {"name": "Horse"} },
{ "op": "remove", "path": "/animals/0" }
]
}
reptile_patch = {
"_id": "reptiles",
"patch": [
{ "op": "add", "path": "/animals/-", "value": {"name": "Lizard"} }
]
}
c.patch_docs([mammal_patch, reptile_patch])
If the command is profitable, Rockset returns an inventory of doc standing information, one for every enter doc. Every standing incorporates a patch_id which can be utilized to verify if patch was utilized efficiently or not (extra on this later).
[{'collection': 'FunWithAnimals',
'error': None,
'id': 'mammals',
'patch_id': 'b59704c1-30a0-4118-8c35-6cbdeb44dca8',
'status': 'PATCHED'
},
{'collection': 'FunWithAnimals',
'error': None,
'id': 'reptiles',
'patch_id': '5bc0696a-d7a0-43c8-820a-94f851b69d70',
'status': 'PATCHED'
}]
As soon as the above patch request is efficiently processed by Rockset, the brand new paperwork will seem like this:
{
"_id": "mammals",
"animals": [
{ "name": "Cat" },
{ "name": "Horse" }
]
},
{
"_id": "reptiles",
"animals": [
{ "name": "Snake" },
{ "name": "Alligator"},
{ "name": "Lizard"}
]
}
Subsequent, I wish to substitute Alligator with Crocodile if Alligator is current at array index 1. For this I’ll use take a look at and substitute operations:
reptile_patch = {
"_id": "reptiles",
"patch": [
{ "op": "test", "path": "/animals/1", "value": {"name": "Alligator"} },
{ "op": "replace", "path": "/animals/1", "value": {"name": "Crocodile"} }
]
}
c.patch_docs([reptile_patch])
After the patch is utilized, doc will seem like under.
{
"_id": "reptiles",
"animals": [
{ "name": "Snake" },
{ "name": "Crocodile"},
{ "name": "Lizard"}
]
}
As I discussed earlier than, the record of operations specified for a doc is utilized so as and atomically in Rockset. Let’s see how this works. I’ll use the identical instance above (changing Crocodile with Alligator) however as a substitute of utilizing take a look at for path /animals/1 I’ll provide /animals/2.
reptile_patch = {
"_id": "reptiles",
"patch": [
{ "op": "test", "path": "/animals/2", "value": {"name": "Crocodile"} },
{ "op": "replace", "path": "/animals/1", "value": {"name": "Alligator"} }
]
}
c.patch_docs([reptile_patch])
The above patch fails and no updates are achieved. To see why it failed, we might want to question _events system assortment in Rockset and search for the patch_id.
from rockset import Consumer, Q, F
rs = Consumer()
q = Q('_events', alias="e")
.choose(F['e']['message'], F['e']['label'])
.the place(F['e']['details']['patch_id'] == 'adf7fb54-9410-4212-af99-ec796e906abc'
)
end result = rs.sql(q)
print(end result)
Output:
[{'message': 'Patch value does not match at `/animals/2`', 'label': 'PATCH_FAILED'}]
The above patch failed as a result of the worth didn’t match at array index 2 as anticipated and the subsequent substitute operation wasn’t utilized, guaranteeing atomicity.
Capturing Change Occasions from MongoDB Atlas Utilizing Patch API
MongoDB Atlas offers change streams to seize desk exercise, enabling these adjustments to be loaded into one other desk or duplicate to serve real-time purposes. Rockset makes use of Patch API internally on MongoDB change streams to replace information in Rockset collections.
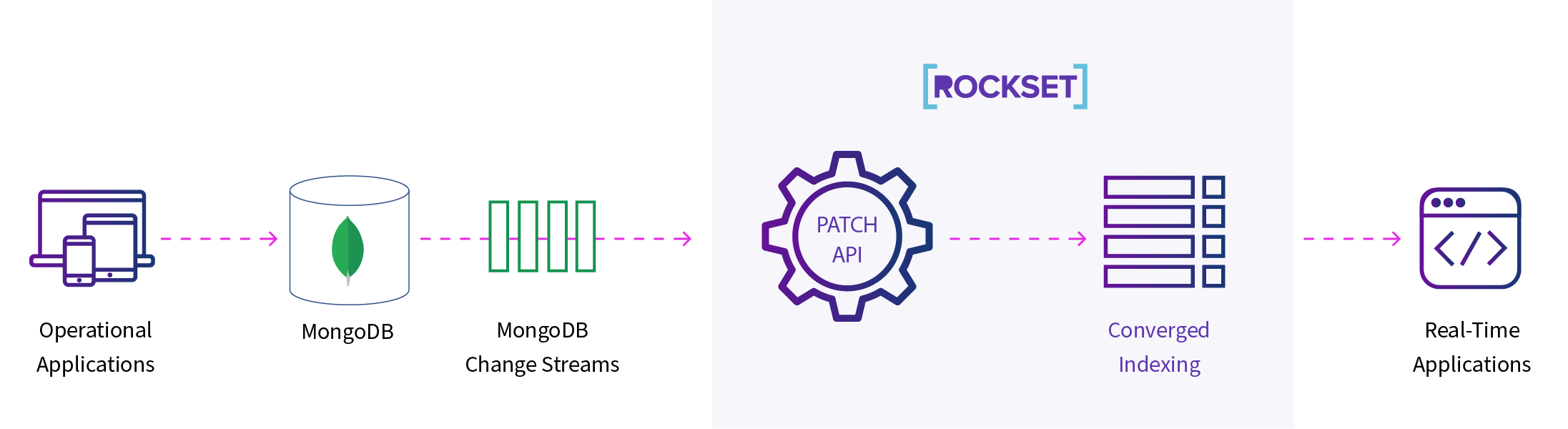
MongoDB change streams permit customers to subscribe to real-time knowledge adjustments in opposition to a set, database, or deployment. For Rockset-MongoDB integration, we configure a change stream in opposition to a set to solely return the delta of fields throughout the replace operation (default habits). As every new occasion is available in for an replace operation, Rockset constructs the patch request utilizing the updatedFields and removedFields keys to index them in an current doc in Rockset. MongoDB’s _id area is mapped to Rockset’s _id area to make sure updates are utilized to the proper doc. Change streams will also be configured to return the complete new up to date doc as a substitute of the delta, however reindexing every thing can lead to elevated knowledge latencies, as mentioned earlier than.
An replace operation on a doc in MongoDB produces an occasion like under (utilizing the identical instance as earlier than).
{
"_id" : { <BSON Object> },
"operationType" : "replace",
...
"updateDescription" : {
"updateDescription" : {
"updatedFields" : {
"animals.2" : {
"title" : "Horse"
}
},
"removedFields" : [ ]
},
...
"clusterTime" : <Timestamp>,
...
}
Rockset’s Patch API for the above CDC occasion will seem like:
mongodb_patch = {
"_id": "<serialized _id>",
"patch": [
{ "op": "add", "path": "/animals/2", "value": {"name": "Horse"} }
]
}
The _id within the CDC occasion is serialized as a string to map to _id in Rockset.
The connector from MongoDB to Rockset will deal with creating the patch from the MongoDB replace, so the usage of the Patch API for CDC from MongoDB is clear to the person. Rockset will write solely the particular up to date area, with out requiring a reindex of the complete doc, making it environment friendly to carry out quick ingest from MongoDB change streams.
Abstract
With growing knowledge volumes, companies are constantly searching for methods to chop down processing time for real-time purposes. Utilizing a CDC mechanism at the side of an indexing database is a typical strategy to doing so. Rockset provides a completely managed indexing resolution for MongoDB knowledge that requires no sizing, provisioning, or administration of indexes, in contrast to another like Elasticsearch.
Rockset offers the Patch API, which makes it easy for customers to propagate adjustments from MongoDB, or different databases or occasion streams, to Rockset utilizing a well-defined JSON patch net commonplace. Utilizing Patch API, Rockset offers decrease knowledge latency on updates, making it environment friendly to carry out quick ingest from MongoDB change streams, with out the requirement to reindex whole paperwork. Patch API is accessible in Rockset as a REST API and likewise as a part of totally different language purchasers.
Different MongoDB and Elasticsearch sources:

