C. Scott Brown / Android Authority
TL;DR
- Google introduced a brand new program referred to as longevity GRF earlier this yr that makes it simpler for chipset distributors to assist their platforms for 7 years of Android updates.
- Chipsets beneath longevity GRF can use the identical vendor software program by means of 7 years of Android OS updates.
- Qualcomm’s Snapdragon 8 Elite is the primary chipset to be a part of the longevity GRF program.
No person needs to eliminate a wonderfully practical smartphone, however sadly, the cellphone replace insurance policies of many Android producers make it dangerous to maintain utilizing one after a number of years. Luckily, there’s a current development within the trade in the direction of extending software program assist, with a few of the greatest Android telephones now getting as much as 7 years of updates. Nonetheless, not many firms are providing this stage of assist, however Google is hoping to alter that with its new Longevity GRF program.
What’s GRF?
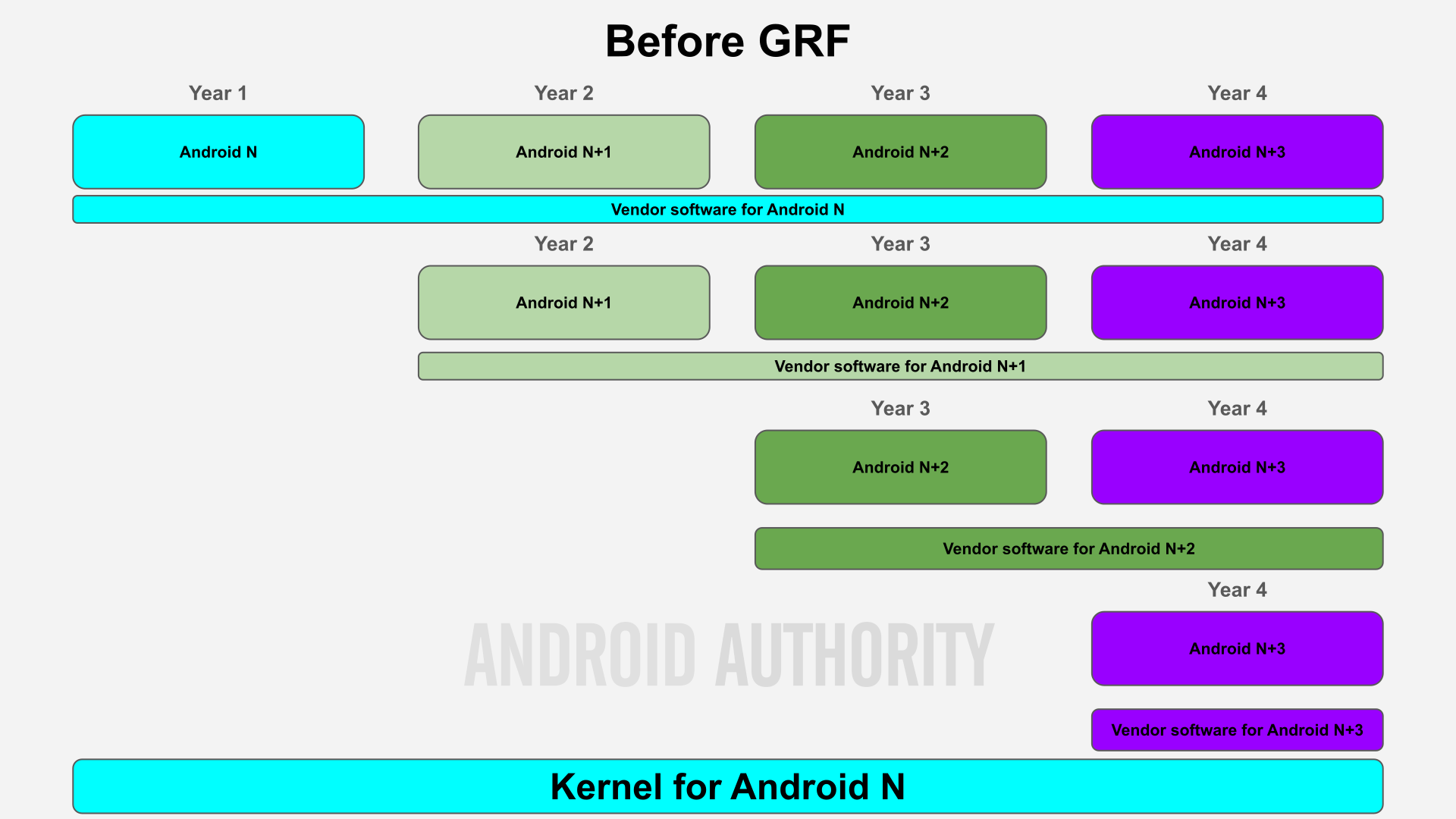
GRF, which stands for Google Necessities Freeze, is the title of a program that Google launched in 2020 to make it simpler for chipset distributors like Qualcomm and MediaTek to assist 3 years of Android OS updates. GRF makes good on the promise of Undertaking Treble, an architectural change that Google launched in 2017 that modularized Android to separate the OS framework from lower-level vendor and Linux kernel software program. The issue with Undertaking Treble is that whereas it made it simpler for OEMs to assist Android OS updates, it truly elevated the complexity for chipset distributors. It is because chipset distributors now needed to assist each units that launched with the unique model of Android that the chipset’s vendor software program was constructed for in addition to units that launched with newer variations of Android.
Mishaal Rahman / Android Authority
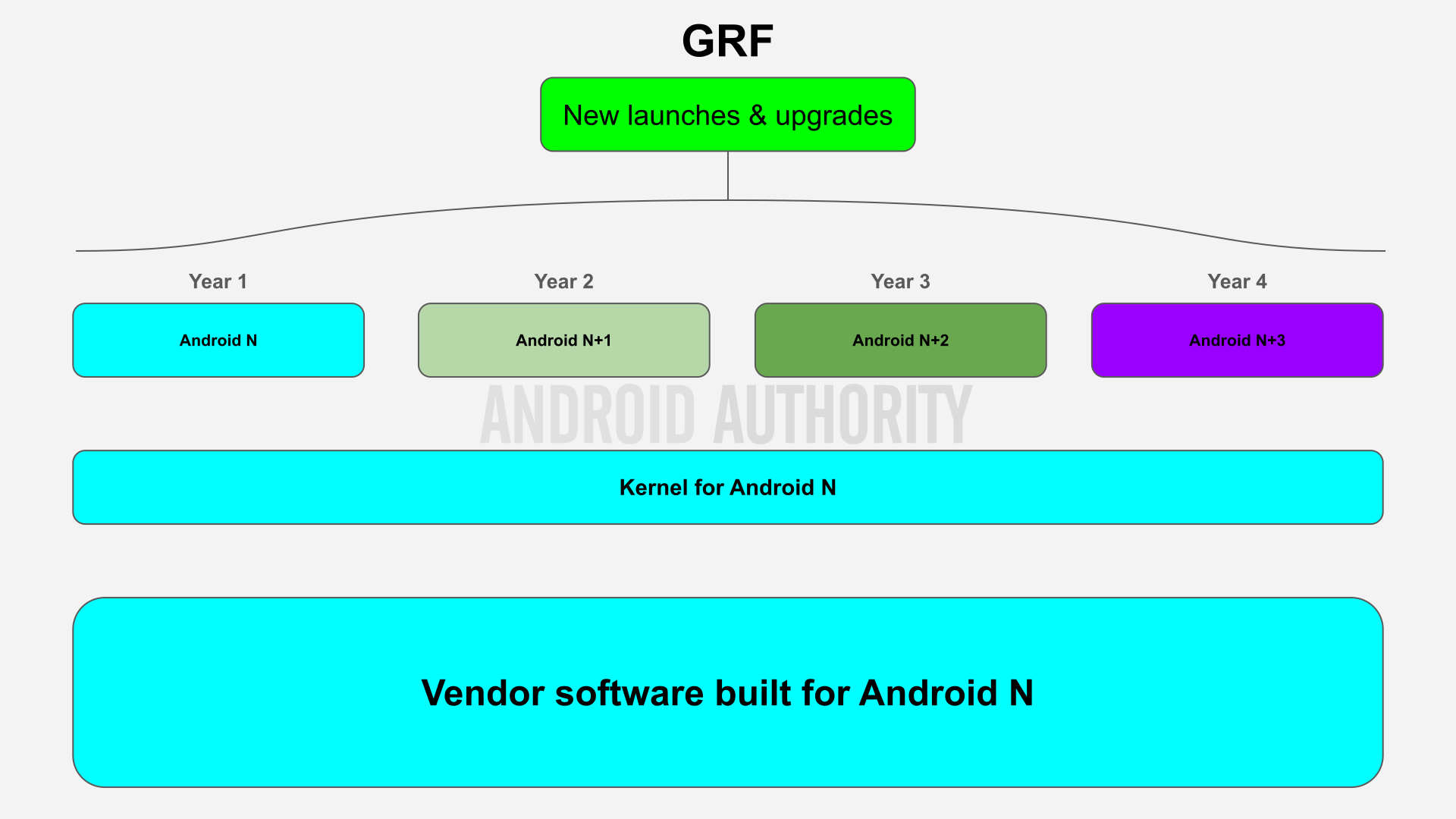
To resolve this, Google dedicated to freezing its vendor software program necessities so they’d not be retroactive, therefore the “Freeze” in Google Necessities Freeze. As an alternative of requiring OEMs to ship up to date vendor software program with every Android OS replace they wished to roll out, OEMs might now ship Android OS updates with the unique vendor software program that the chipset was constructed for.
Primarily, OEMs might reuse the chipset’s vendor software program throughout a number of variations of Android and nonetheless obtain certification from Google. This meant that chipset distributors like Qualcomm and MediaTek wouldn’t should replace their vendor software program to fulfill new vendor software program necessities for not less than 3 years after launch, lowering the engineering prices related to supporting a number of completely different mixtures of vendor software program and Android OS variations. Because of GRF, chipset distributors might save some huge cash by solely having to assist 4 Android OS/vendor software program mixtures versus 10 in the event that they wished to assist 3 years of updates.
Mishaal Rahman / Android Authority
What’s Longevity GRF?
You’ll discover, nevertheless, that GRF solely permits the seller software program to be reused for 3 Android model updates. At the start of this text, although, I discussed how Google needs to allow 7 years of Android model updates, one thing that isn’t enabled beneath the present GRF program phrases. If an OEM wished to ship a fourth, fifth, sixth, and even seventh Android OS model replace to a tool with a chipset that’s beneath GRF, the OEM must both pay the chipset vendor for prolonged assist or undertake the colossal engineering effort of updating the chipset’s vendor software program themselves to fulfill Google’s up to date vendor software program necessities for every subsequent launch.
It isn’t exceptional for an OEM to try this, as there are a number of Samsung units eligible for 7 main Android updates despite the fact that they’re utilizing chipsets which are beneath the GRF program, but it surely’s very troublesome and dear to take action. Google needs extra OEMs to assist 7 years of OS updates like Samsung and so they themselves do, although, which is why it created the brand new Longevity GRF program.
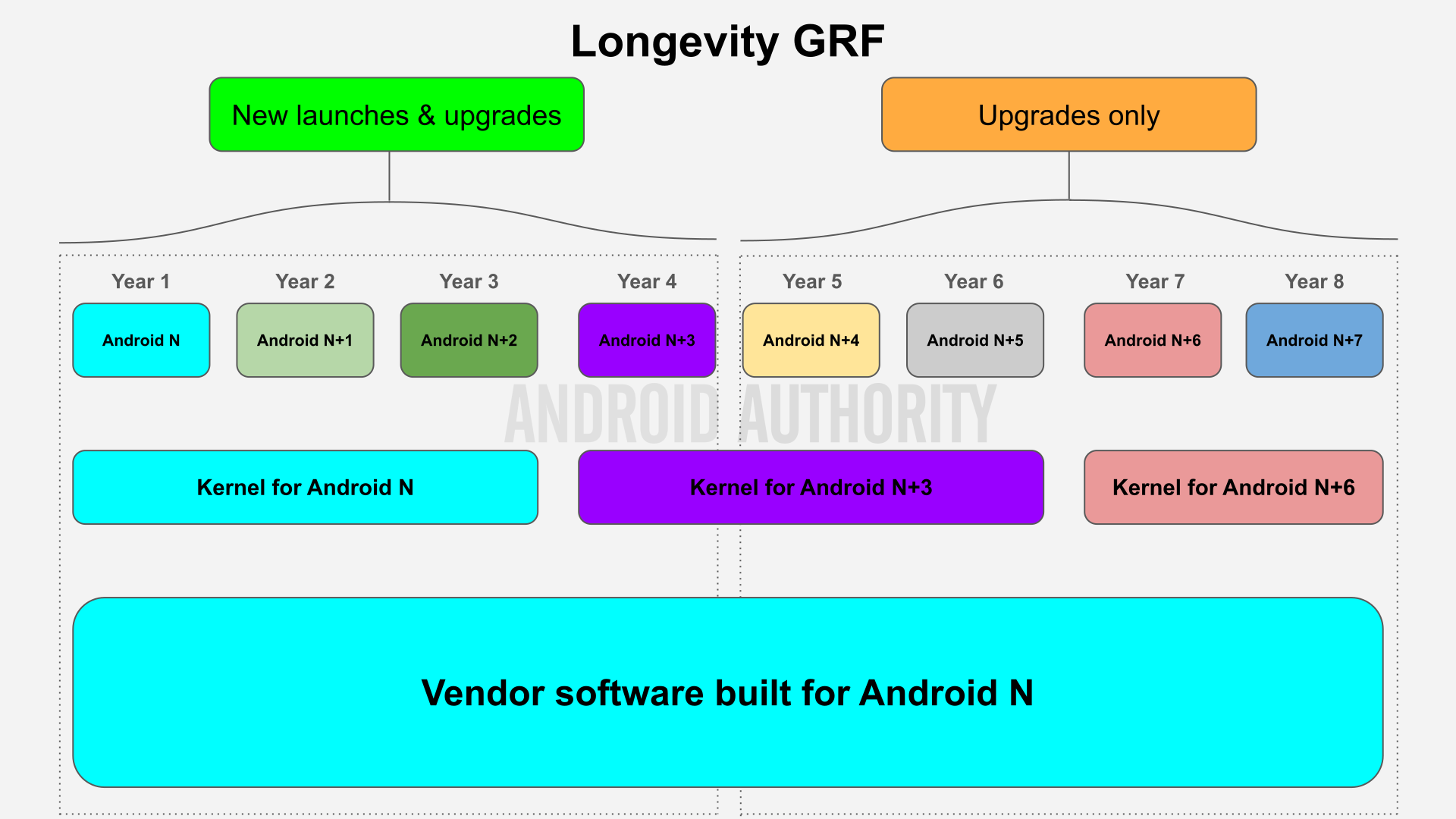
Longevity GRF permits for a chipset’s vendor software program to be reused for 7 Android model updates as a substitute of three. That signifies that a tool launching with a chipset whose vendor software program was constructed for, say, Android 15 can reuse that vendor software program when it updates to Android 16 by means of 22. The just lately introduced Qualcomm Snapdragon 8 Elite is the primary chipset beneath the Longevity GRF program, which signifies that all of the upcoming telephones powered by will probably be eligible to reuse the seller software program that Qualcomm initially constructed for it for 7 Android model updates after the chipset’s launch.
Nonetheless, there’s a catch: OEMs should improve the Linux kernel model after 3 years. A minor kernel replace gained’t suffice, both, as Google would require OEMs to ship a significant kernel model improve with the intention to obtain certification. The rationale for that is that Google is just committing to a four-year assist lifetime for its Linux kernel forks, beginning with kernel 6.6 which is the model that new chipsets constructed for Android 15 are required to launch with. If Google didn’t pressure OEMs to ship main kernel model upgrades, then OEMs must backport safety patches themselves to make sure they’re compliant with Android’s safety necessities. Backporting patches may be problematic, although, as a result of not each patch included in a Linux kernel launch is marked as a safety patch, so some essential patches could also be missed in the course of the backporting course of.
As well as, Google gained’t let OEMs ship new units operating Android variations which are 4 variations newer than what the seller software program was initially constructed for. That is so OEMs don’t ship units that’ll solely profit from 2 or 3 of the 7 Android model updates that Longevity GRF permits.
With all that in thoughts, right here’s what the Android assist lifecycle appears to be like like beneath Google’s Longevity GRF program.
Mishaal Rahman / Android Authority
Though Longevity GRF makes it simpler for OEMs and silicon distributors to assist 7 Android OS model upgrades, it additionally disincentivizes supporting new {hardware} options added in new variations of Android. For instance, the 2G toggle that Google added in Android 12 and the flashlight brightness API Google added in Android 13 each require updates to the seller software program to assist. That signifies that units upgrading to Android 12 or 13 with vendor software program frozen at Android 11 wouldn’t have the ability to assist both function. This was already an issue beneath GRF however will now be exacerbated by Longevity GRF because of the longer lifecycle that it covers.
Google introduced this Longevity GRF program at an occasion for OEMs earlier this yr, but it surely hasn’t publicly shared any particulars on it. I realized about it because of a supply who needs to stay nameless. The charts that I embedded on this article are recreations of charts that Google confirmed off to OEMs, so they need to precisely show how Longevity GRF impacts the Android assist lifecycle for chipsets coated beneath this system. Nonetheless, since Google hasn’t revealed this system publicly, there’s an opportunity I’m lacking some particulars. If I study any extra details about this system, I’ll be sure you replace this text.
