A brand new safety concern is placing WordPress-powered web sites in danger. Hackers are abusing the “Should-Use” plugins (MU-plugins) characteristic to cover malicious code and keep long-term entry on hacked web sites.
In earlier 2025, safety researchers at Sucuri seen cybercriminals utilizing the tactic, and so they say that it has been more and more used the approach within the months since.
In WordPress, MU-plugins are plugins which can be routinely enabled on a WordPress-powered web site and – as the outline suggests – should be used, and due to this fact cannot be deactivated via the WordPress admin interface.
These “must-use plugins” are positioned in a selected listing referred to as, imaginatively sufficient, mu-plugins throughout the wp-content folder. In contrast to common WordPress plugins, they is probably not listed alongside common plugins except the “should use” filter is chosen.
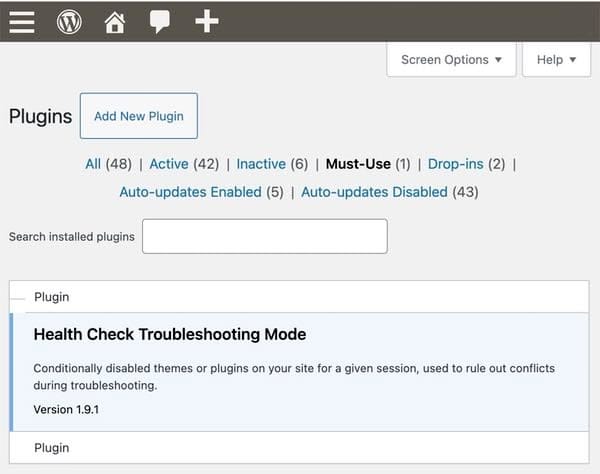
What makes a plugin “must-use”? Properly, any plugin that’s important for the positioning’s performance and shouldn’t be turned off. This will embody safety enhancements, efficiency optimisation, or multi-site administration options {that a} web site’s builders or directors have deemed crucial to stay energetic.
So there’s a good official purpose for a WordPress web site to have “must-use” plugins, though many WordPress customers could also be largely oblivious to their existence.
Based on researchers, an assault usually begins when hackers compromise a web site (usually through an out-of-date WordPress plugin, or weak password). As soon as an attacker has gained entry, they are going to plant a malicious PHP file into the mu-plugins folder, successfully giving it a persistent foothold on the web site.
Sucuri’s group say they’ve seen three malicious MU-plugins being deployed in in-the-wild assaults:
- redirect.php – Sends web site guests to a bogus browser replace web page that downloads malware.
- index.php – A backdoor which grants attackers distant entry to the compromised server.
- custom-js-loader.php – Replaces web site content material with spam hyperlinks or express pictures.
These hidden mu-plugins run the hackers’ code on each web page of the web site, and may reinfect a complete web site if nice care shouldn’t be taken to take away an an infection.
In an try and keep away from detection too quickly, the redirect plugin code avoids activating whether it is seen by one of many web site’s personal logged-in directors or a search engine bot.
After all, no one desires a hacker having a backdoor to their web site – granting an unauthorised social gathering admin-level management. A malicious attacker with such energy can steal information, create new admin accounts, or use your web site to unfold malware.
Moreover, it’s possible you’ll discover any visitors coming to your web site is redirected by the malicious mu-plugins planted by the cybercriminals elsewhere on the web, doing hurt to your enterprise and your model.
And it is dangerous information in your web site’s guests too. Anybody visiting an contaminated web site is placing their pc vulnerable to potential malware an infection.
The very best recommendation is to harden your WordPress web site, by guaranteeing that you simply use robust, distinctive passwords and have enabled two-factor authentication.
Moreover, monitor your web site for uncommon behaviour, and guarantee which can be conserving WordPress and any official plugins and themes your web site makes use of correctly up to date.
Lastly, when you suspect your WordPress-powered web site may very well be internet hosting malicious MU-plugins, look within the wp-content/mu-plugins folder. When you do not use MU-plugins it must be empty.

