That is the third submit in a sequence by Rockset’s CTO Dhruba Borthakur on Designing the Subsequent Era of Information Methods for Actual-Time Analytics. We’ll be publishing extra posts within the sequence within the close to future, so subscribe to our weblog so you do not miss them!
Posts printed thus far within the sequence:
- Why Mutability Is Important for Actual-Time Information Analytics
- Dealing with Out-of-Order Information in Actual-Time Analytics Purposes
- Dealing with Bursty Site visitors in Actual-Time Analytics Purposes
- SQL and Complicated Queries Are Wanted for Actual-Time Analytics
- Why Actual-Time Analytics Requires Each the Flexibility of NoSQL and Strict Schemas of SQL Methods
Builders, information engineers and web site reliability engineers could disagree on many issues, however one factor they will agree on is that bursty information site visitors is nearly unavoidable.
It’s nicely documented that net retail site visitors can spike 10x throughout Black Friday. There are various different events the place information site visitors balloons all of a sudden. Halloween causes client social media apps to be inundated with photographs. Main information occasions can set the markets afire with digital trades. A meme can all of a sudden go viral amongst youngsters.
Within the previous days of batch analytics, bursts of knowledge site visitors have been simpler to handle. Executives didn’t anticipate experiences greater than as soon as per week nor dashboards to have up-to-the-minute information. Although some information sources like occasion streams have been beginning to arrive in actual time, neither information nor queries have been time delicate. Databases might simply buffer, ingest and question information on an everyday schedule.
Furthermore, analytical programs and pipelines have been complementary, not mission-critical. Analytics wasn’t embedded into functions or used for day-to-day operations as it’s right this moment. Lastly, you may at all times plan forward for bursty site visitors and overprovision your database clusters and pipelines. It was costly, however it was secure.
Why Bursty Information Site visitors Is an Subject In the present day
These circumstances have fully flipped. Corporations are quickly remodeling into digital enterprises as a way to emulate disruptors corresponding to Uber, Airbnb, Meta and others. Actual-time analytics now drive their operations and backside line, whether or not it’s via a buyer suggestion engine, an automatic personalization system or an inside enterprise observability platform. There’s no time to buffer information for leisurely ingestion. And due to the huge quantities of knowledge concerned right this moment, overprovisioning will be financially ruinous for firms.
Many databases declare to ship scalability on demand to be able to keep away from costly overprovisioning and hold your data-driven operations buzzing. Look extra carefully, and also you’ll see these databases often make use of certainly one of these two poor man’s options:
- Guide reconfigurations. Many programs require system directors to manually deploy new configuration recordsdata to scale up databases. Scale-up can’t be triggered routinely via a rule or API name. That creates bottlenecks and delays which are unacceptable in actual time.
- Offloading complicated analytics onto information functions. Different databases declare their design offers immunity to bursty information site visitors. Key-value and doc databases are two good examples. Each are extraordinarily quick on the easy duties they’re designed for — retrieving particular person values or complete paperwork — and that velocity is basically unaffected by bursts of knowledge. Nevertheless, these databases are likely to sacrifice assist for complicated SQL queries at any scale. As an alternative, these database makers have offloaded complicated analytics onto utility code and their builders, who’ve neither the talents nor the time to always replace queries as information units evolve. This question optimization is one thing that every one SQL databases excel at and do routinely.
Bursty information site visitors additionally afflicts the numerous databases which are by default deployed in a balanced configuration or weren’t designed to segregate the duties of compute and storage. Not separating ingest from queries signifies that they straight have an effect on the opposite. Writing a considerable amount of information slows down your reads, and vice-versa.
This drawback — potential slowdowns brought on by rivalry between ingest and question compute — is frequent to many Apache Druid and Elasticsearch programs. It’s much less of a problem with Snowflake, which avoids rivalry by scaling up each side of the system. That’s an efficient, albeit costly, overprovisioning technique.
Database makers have experimented with totally different designs to scale for bursts of knowledge site visitors with out sacrificing velocity, options or price. It seems there’s a cost-effective and performant means and a pricey, inefficient means.
Lambda Structure: Too Many Compromises
A decade in the past, a multitiered database structure referred to as Lambda started to emerge. Lambda programs attempt to accommodate the wants of each huge data-focused information scientists in addition to streaming-focused builders by separating information ingestion into two layers. One layer processes batches of historic information. Hadoop was initially used however has since been changed by Snowflake, Redshift and different databases.
There’s additionally a velocity layer sometimes constructed round a stream-processing expertise corresponding to Amazon Kinesis or Spark. It offers prompt views of the real-time information. The serving layer — usually MongoDB, Elasticsearch or Cassandra — then delivers these outcomes to each dashboards and customers’ advert hoc queries.
When programs are created out of compromise, so are their options. Sustaining two information processing paths creates further work for builders who should write and keep two variations of code, in addition to higher danger of knowledge errors. Builders and information scientists even have little management over the streaming and batch information pipelines.
Lastly, a lot of the information processing in Lambda occurs as new information is written to the system. The serving layer is a less complicated key-value or doc lookup that doesn’t deal with complicated transformations or queries. As an alternative, data-application builders should deal with all of the work of making use of new transformations and modifying queries. Not very agile. With these issues and extra, it’s no surprise that the calls to “kill Lambda” hold rising 12 months over 12 months.
ALT: The Finest Structure for Bursty Site visitors
There’s a chic answer to the issue of bursty information site visitors.
To effectively scale to deal with bursty site visitors in actual time, a database would separate the features of storing and analyzing information. Such a disaggregated structure allows ingestion or queries to scale up and down as wanted. This design additionally removes the bottlenecks created by compute rivalry, so spikes in queries don’t decelerate information writes, and vice-versa. Lastly, the database have to be cloud native, so all scaling is automated and hidden from builders and customers. No must overprovision prematurely.
Such a serverless real-time structure exists and it’s referred to as Aggregator-Leaf-Tailer (ALT) for the way in which it separates the roles of fetching, indexing and querying information.
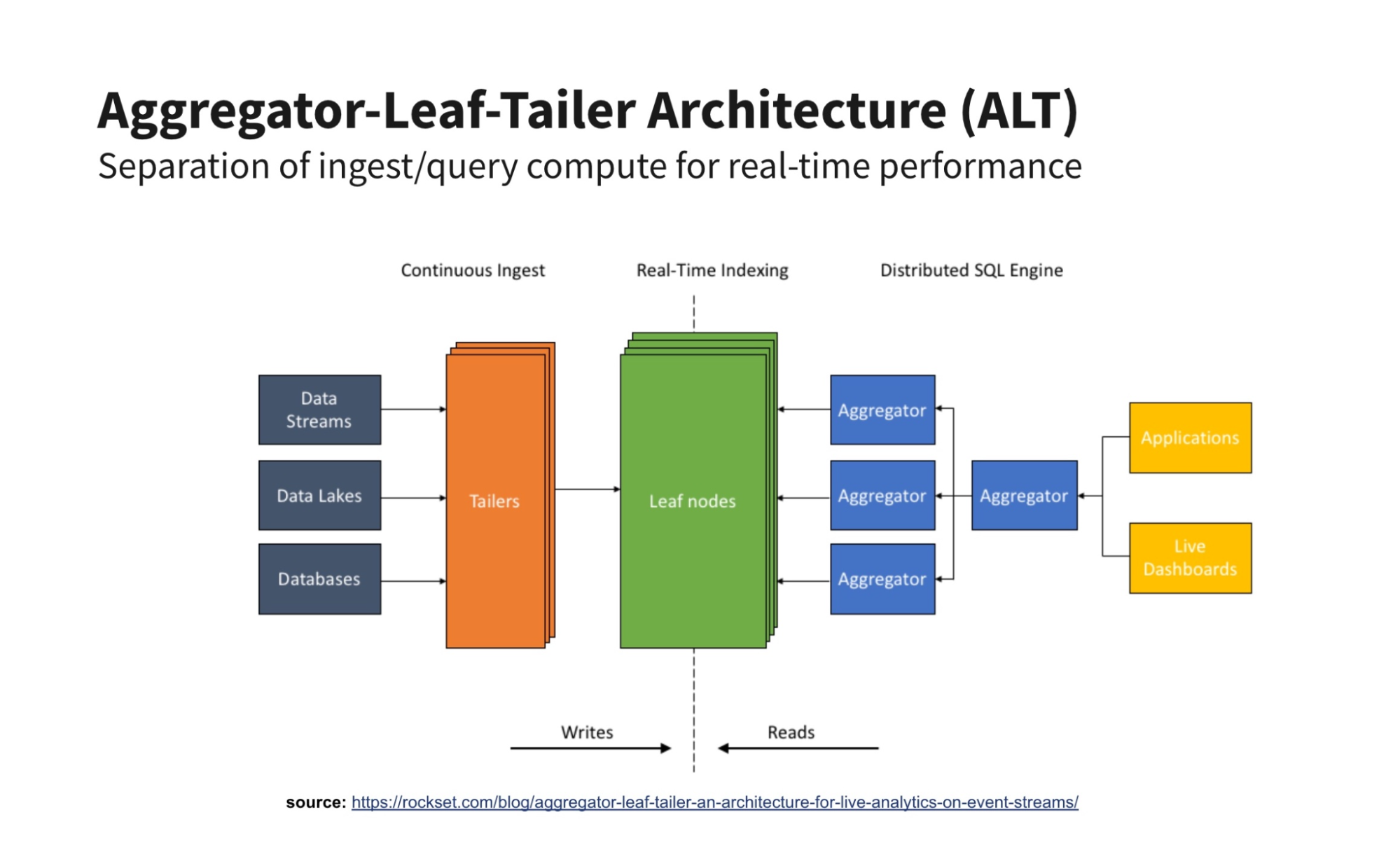
Like cruise management on a automotive, an ALT structure can simply keep ingest speeds if queries all of a sudden spike, and vice-versa. And like a cruise management, these ingest and question speeds can independently scale upward based mostly on utility guidelines, not handbook server reconfigurations. With each of these options, there’s no potential for contention-caused slowdowns, nor any must overprovision your system prematurely both. ALT architectures present one of the best worth efficiency for real-time analytics.
I witnessed the facility of ALT firsthand at Fb (now Meta) once I was on the crew that introduced the Information Feed (now renamed Feed) — the updates from your entire buddies — from an hourly replace schedule into actual time. Equally, when LinkedIn upgraded its real-time FollowFeed to an ALT information structure, it boosted question speeds and information retention whereas slashing the variety of servers wanted by half. Google and different web-scale firms additionally use ALT. For extra particulars, learn my weblog submit on ALT and why it beats the Lambda structure for real-time analytics.
Corporations don’t should be overstaffed with information engineers like those above to deploy ALT. Rockset offers a real-time analytics database within the cloud constructed across the ALT structure. Our database lets firms simply deal with bursty information site visitors for his or her real-time analytical workloads, in addition to remedy different key real-time points corresponding to mutable and out-of-order information, low-latency queries, versatile schemas and extra.
In case you are selecting a system for serving information in actual time for functions, consider whether or not it implements the ALT structure in order that it may well deal with bursty site visitors wherever it comes from.
Dhruba Borthakur is CTO and co-founder of Rockset and is accountable for the corporate’s technical path. He was an engineer on the database crew at Fb, the place he was the founding engineer of the RocksDB information retailer. Earlier at Yahoo, he was one of many founding engineers of the Hadoop Distributed File System. He was additionally a contributor to the open supply Apache HBase venture.
Rockset is the main real-time analytics platform constructed for the cloud, delivering quick analytics on real-time information with stunning effectivity. Study extra at rockset.com.

