Characterization and efficiency evaluation of various hydrogels
The extracellular matrix (ECM) is a three-dimensional scaffolding construction composed of proteins and polysaccharides secreted by cells. It not solely supplies bodily help for cells, but additionally participates within the regulation of cell habits and performs a vital function in sustaining the conventional construction and performance of the pores and skin [38, 39]. On this examine, we designed a novel HAMA hydrogel that’s able to speedy gentle curing. It could possibly mimic the construction of pure ECM to supply attachment websites for cells, which facilitates cell proliferation and differentiation. As depicted in Fig. 1A and B, the HAMA and HA@TA-Okra hydrogel exhibited a uniformly distributed porous construction with pore diameters measured to be roughly 188 ± 31 μm and 150 ± 37 μm, respectively. Notably, the addition of TA and okra parts hardly modified the unique pore construction of HA@TA-Okra hydrogel. As noticed in Determine S1, the form of the 2 hydrogels reworked right into a three-dimensional construction after freeze-drying therapy. This three-dimensional construction not solely maintains the unique free and porous properties of the hydrogel, but additionally additional enhances its stability and utility vary. This property permits HAMA and HA@TA-Okra hydrogels not solely to advertise the absorption of wound exudate but additionally to effectively transport vitamins, Additional efficiency analysis of the hydrogels revealed that each HAMA and HA@TA-Okra hydrogels exhibited exceptional hydrophilicity, with contact angle measurements of roughly 1° and a pair of°, respectively (Fig. 1C and E). This attribute ensures environment friendly water absorption and retention, fostering a moist setting within the wound space, thereby accelerating the therapeutic course of.
Furthermore, HAMA and HA@TA-Okra hydrogels all boast distinctive injectability, permitting exact supply to the goal website in a liquid state, adopted by speedy solidification below UV gentle publicity to kind a steady three-dimensional construction (Fig. 1D). This property may meet the wants of wound restore of numerous shapes, as proven in Fig. 1F HA@TA-Okra hydrogel patterns of assorted shapes. This function simplifies surgical procedures and enhances the precision and adaptability of therapy. As proven in Fig. 1G, a major huge absorption band was noticed within the wavenumber vary of 3200–3500 cm− 1, which was attributed to the attribute vibration brought on by the hydroxyl (OH) teams wealthy in HAMA, TA and okra. Primarily based on spectroscopic evaluation, we inferred {that a} hydrogen bond interplay could also be fashioned between HAMA, TA and okra molecules. This interplay leads to a slight shift of the absorption peak of the hydroxyl stretching vibration mode in HA@TA-Okra to the low frequency path, accompanied by a rise in peak form complexity, reflecting the formation of a hydrogen bond community. Moreover, the FTIR spectra confirmed a brand new and extra advanced absorption attribute peak within the vary of 1700–1750 cm− 1, which could possibly be clearly attributed to the vibration of the ester bond (C = O-O-C) fashioned contained in the HA@TA-Okra hydrogel. In contrast with the usual peak form of a single methacrylate group, the absorption peak right here exhibits larger complexity. That is imagined to be because of the formation of assorted forms of ester bond buildings contained in the hydrogel, together with attainable spatial conformational variations and completely different bonding environments, which collectively contribute to the advanced spectral response on this band.
Within the in vitro degradation experiments, the degradation habits of HAMA, HA@TA, HA@Okra, and HA@TA-Okra hydrogels inside a PBS setting have been systematically evaluated. Particularly, the experimental knowledge unequivocally demonstrated that, by day 5, the degradation fee of all hydrogels attained roughly 40%, offering compelling proof for the creation of favorable situations for cell proliferation by partial degradation in the course of the preliminary levels (Fig. 1H). Because the experimental period progressed, the degradation fee steadily decelerated, plateauing at a comparatively steady vary of 60-80% after 25 days. This development underscores the distinctive controllability of HA@TA-Okra hydrogels by way of biodegradation charges and TA/okra launch profiles. We consider that HA@TA-Okra hydrogel its long-term degradation merchandise might primarily embrace phenolic and quinone degradation merchandise of hyaluronic acid fragments and tannins, in addition to small molecules reminiscent of sugars and amino acids in okra extract [40,41,42]. Most of those degradation merchandise are biocompatible and might be excreted from the physique in urine, feces, or breath. Nonetheless, additional scientific observations and validation are wanted to make sure its long-term security.
Characterization of HA@TA-Okra Hydrogels. (A) SEM picture of hydrogels. (B) Pore measurement evaluation of hydrogels. (C) Hydrogels contact angle field chart statistics. (D) HAMA and HA@TA-Okra Hydrogels fashioned by UV irradiation (405 nm, 30 s). (E) Contact angle of the hydrogels. (F) Injectability evaluation of HA@TA-Okra Hydrogels. (G) FTIR spectra of HAMA, HA@TA, HA@Okra, and HA@TA-Okra. (H) Degradation ratio of hydrogels. (I) Swelling ratio of hydrogels
Concerning swelling checks, as depicted in Fig. 1I, all examined hydrogels exhibited marked will increase in swelling ratios. Enlargement equilibrium was reached inside roughly 24 h, with swelling ratios starting from 310 to 335%. This discovering underscores the extremely steady cross-linked community construction of those hydrogels, enabling swift and environment friendly water absorption and retention. Moreover, current literature has definitively acknowledged [43] that top swelling charges are related to a well-developed porous community construction in hydrogels. Though our designed hydrogel has good light-curing and mechanical properties and stability, the long-term stability and storage situations of the hydrogel have to be additional investigated to make sure that the hydrogel maintains its properties unaffected throughout storage and transportation.
Biocompatibility, antioxidant potential, and antibacterial efficacy of HA@TA1.25/2.5/5 hydrogels
A scientific evaluation of the biocompatibility traits of HA@TA1.25/2.5/5 hydrogels have been carried out. As depicted in Fig. 2A, all teams exhibited a development of mobile proliferation over time. On the fifth-day time level, each HA@TA1.25 and HA@TA2.5 teams maintained a excessive stage of cell proliferation charges corresponding to the HAMA group (P > 0.05), strongly supporting their superior biocompatibility. Cell proliferation in HA@TA5 group was slower than that in HA@TA1.25 and HA@TA2.5 teams (P < 0.001). It might be because of the excessively excessive TA focus (5%) surpassing the secure threshold tolerable by cells.
Addressing the prevalent oxidative stress problem in contaminated wound environments, the DPPH radical scavenging assay was employed to quantitatively consider the in vitro antioxidant efficacy of HA@TA1.25/2.5/5 hydrogels. As evident in Fig. 2B, a marked improve in DPPH scavenging fee was noticed with the escalation of TA focus. Particularly, the HA@TA1.25 group achieved roughly 73% DPPH scavenging, whereas each HA@TA2.5 and HA@TA5 teams exhibited superior scavenging efficiencies exceeding 80%. This discovering underscores the potent antioxidant potential of TA’s polyphenolic construction [44,45,46] and additional confirms that modulating TA focus can successfully improve the antioxidant properties of the hydrogels. In distinction, the HAMA hydrogel carried out poorly within the DPPH scavenging take a look at, with a negligible scavenging fee of 4%.
In exploring the antibacterial properties of HA@TA1.25/2.5/5 hydrogels, consultant E. coli and S. aureus have been chosen as goal strains. As proven in Determine S2, though pure HAMA hydrogels lack direct antibacterial exercise, their distinctive three-dimensional community construction acts as a bodily barrier to some extent, limiting bacterial progress and proliferation. Upon the introduction of TA at adequate concentrations, the antibacterial efficacy of the hydrogels was considerably enhanced. The HA@TA2.5 hydrogel demonstrated near-complete inhibition (roughly 100%) towards each take a look at strains, an impact corresponding to that of the higher-concentration HA@TA5 group. Integrating cytocompatibility with antibacterial and antioxidant efficacy, the HA@TA2.5 (HA@TA for brief) was screened to maximise therapeutic results in sensible purposes.
Willpower of focus of okra extract
Among the many myriad of biomaterials, okra extract is a promising candidate for the event of pores and skin restore dressings attributable to its richness in terpenes, phenolics, and flavonoids, which have important antioxidant properties. On this examine, HAMA, HA@TA-Okra0.25, HA@TA-Okra0.5, HA@TA-Okra1, and HA@TA-Okra2 have been established to establish the optimum hydrogel formulation that greatest promotes cell progress and performance. As depicted in Fig. 2C, cell proliferation confirmed an growing development in all teams. Nonetheless, the outcomes on days 3 and 5 confirmed an inverse development in cell proliferation fee with growing focus of okra extract. As regards to related literatures, HA@TA-Okra0.5 hydrogel is chosen because the follow-up examine.
The biocompatibility, migration, and antibacterial capability of HA@TA-okra hydrogels
As a way to additional study the properties of HA@TA-Okra0.5 hydrogel (HA@TA-Okra for brief) and examine its particular results on cell habits, we used EdU cell proliferation assay. As proven in Fig. 2D and F, the outcomes unequivocally demonstrated that L929 cells retained proliferative exercise throughout all examined teams. The HAMA group exhibited the very best cell proliferation fee, attributed to the distinctive organic operate of hyaluronic acid in facilitating extracellular matrix transforming. The proliferation charges within the HA@TA, HA@Okra and HA@TA-Okra teams have been all barely decrease than HAMA group, the variations have been statistically insignificant, indicating that the introduction of TA and okra didn’t adversely have an effect on the proliferative capability of L929 cells.
Moreover, a scratch assay was carried out to evaluate the results of HAMA, HA@TA, HA@Okra, and HA@TA-Okra on cell migration potential. As illustrated in Fig. 2E, G and H, after incubation for 12 h, the therapeutic charges of HAMA, HA@TA, HA@Okra and HA@TA-Okra teams have been 19.95%, 22.36%, 25.46% and 27.93%, respectively, whereas these of the management group have been 9.5%. In distinction, the hydrogel group confirmed efficacy in selling cell migration. After 24 h, the migration fee of the management group was nonetheless decrease than that of the opposite hydrogel teams. The wound therapeutic charges of all hydrogel teams ranged from 50% ~ 65% with no important distinction between teams, additional substantiating the immense potential of hydrogel supplies in selling tissue regeneration and wound therapeutic.
The cytotoxicity and in vitro cell migration habits of hydrogels. (A) Cytotoxicity of L929 cells co-cultured with hydrogels extract medium containing completely different concentrations of TA for 1,3 and 5 days. (B) Willpower of DPPH clearance by HAMA and HA@TA1.25/2.5/5 hydrogels. (C) Cytotoxicity of L929 cells co-cultured with hydrogels extract medium for 1,3 and 5 days. (D) EdU fluorescence picture. (E) The migration potential of various hydrogel extracts after co-culture with L929 cells. (F) EdU statistical chart. Quantification of margin closure fee between completely different teams at (G) 12 h and (H) 24 h (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001)
The floor antibacterial take a look at outcomes introduced in Fig. 3A revealed each the HA@TA and HA@TA-Okra teams exhibited exceptional bactericidal charges exceeding 99% inside 4 h. This exceptional efficiency underscores the potent antibacterial efficacy of hydrogels containing TA. TA is wealthy in phenolic hydroxyl teams, which contribute to its efficient adsorption and accumulation on negatively charged bacterial cell partitions, thereby inhibiting bacterial progress and proliferation. This mechanism aligns carefully with earlier literature findings [47, 48]. To comprehensively consider the hydrogels’ antibacterial properties, a live-dead bacterial staining assay was carried out (Fig. 3B). The outcomes point out that E. coli and S. aureus within the management group have been nearly completely labeled with inexperienced fluorescence, indicating important bacterial exercise. In distinction, the HAMA group displayed a weak antibacterial impact, evidenced by sparse purple fluorescence, probably attributed to bodily confinement of micro organism by its construction. The HA@Okra group demonstrated a extra pronounced antibacterial impact, with a major discount in inexperienced fluorescence and a rise in purple fluorescence. The HA@TA and HA@TA-Okra teams nearly completely exhibited purple fluorescence, a powerful indication of their efficient bactericidal motion. The antibacterial fee statistics in Fig. 3C and D additional confirmed our observations. In contrast with HAMA group and HA@Okra group, HA@TA-Okra has a major antibacterial fee (P < 0.001), offering quantitative help for the antibacterial efficacy of the HA@TA-Okra hydrogels.
Willpower of antibacterial exercise of hydrogel towards E. coli and S. aureus in vitro. (A) Bacterial plate counting. (B) Stay/lifeless staining of E. coli and S. aureus handled with completely different hydrogels (inexperienced: stay micro organism, purple: lifeless micro organism). Statistics of antibacterial fee of various hydrogels towards (C) E. coli and (D) S. aureus. (**P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001)
Investigation into the antioxidant properties and detection of inflammatory cytokine secretion
Within the inflammatory response triggered by pores and skin damage, the buildup of immune cells on the damage website is commonly accompanied by an extreme launch of ROS. The average ranges of ROS play a pivotal function within the physique’s protection mechanisms, facilitating the preliminary therapeutic strategy of wounds [49, 50]. Nonetheless, its overaccumulation results in the formation of oxidative stress, subsequently damaging cells and impeding the graceful transition of wounds from the inflammatory to the proliferative section, finally affecting the progress therapeutic [51]. To judge the antioxidant functionality of HA@TA-Okra hydrogels, this examine designed and carried out experiments involving DPPH radical scavenging assays. As depicted in Fig. 4A, the HA@Okra group exhibited roughly a 25% enhancement in DPPH radical scavenging fee in comparison with the HAMA group, indicating that the incorporation of okra successfully bolstered the antioxidant baseline efficiency of the hydrogel. Nonetheless, the antioxidant properties of HA@Okra group have been considerably decrease than these of HA@TA-Okra group (P < 0.001), indicating that TA was the principle antioxidant in HA@TA-Okra hydrogel. Notably, upon the combination of TA into the system, each the HA@TA and HA@TA-Okra teams witnessed a considerable leap in scavenging charges, surpassing 90% (no important distinction between the 2 teams). This exceptional efficiency might be attributed to the plentiful ortho-phenolic hydroxyl teams in TA molecules, which act as environment friendly hydrogen donors, promptly responding to and neutralizing numerous forms of ROS, together with DPPH radicals, hydroxyl radicals, and superoxide anions [52].
To extra intuitively mirror the ROS scavenging efficacy of the hydrogels on the mobile stage, this examine employed DCFH-DA fluorescent probe expertise to quantitatively monitor ROS ranges inside RAW264.7 cells. The DCFH-DA probe permeates cell membranes, will get oxidized by ROS inside the cell, and produces DCF, which emits intense inexperienced fluorescence, enabling visible evaluation of intracellular ROS ranges. As proven in Fig. 4B and C, the HA@TA-Okra group (1.29 ± 0.31) exhibited considerably decreased inexperienced fluorescence depth in comparison with the constructive management group, which indicating its potent antioxidant exercise within the intracellular setting. In distinction, the cells of HAMA group (33.37 ± 5.56) displayed larger inexperienced fluorescence depth, indicating the manufacturing of considerable ROS below LPS stimulation, which the HAMA hydrogel didn’t considerably inhibit or scavenge. It’s price noting that ROS ranges within the HA@Okra group (14.73 ± 1.69) and the HA@TA group (7.85 ± 1.17) decreased reasonably however have been larger than these within the HA@TA-Okra group and decrease than these within the HAMA group, indicating that each okra extract and TA may improve the antioxidant exercise of HAMA hydrogel.
Macrophages, a pivotal element of the innate immune system, play a vital function in regulating tissue irritation by their dynamic polarization states. Particularly, M1 macrophages predominantly execute proinflammatory features, whereas M2 macrophages are inclined to secrete anti-inflammatory components to facilitate tissue restore and regeneration [53,54,55,56]. The immunomodulatory properties of HA@TA-Okra hydrogel on macrophages in vitro have been investigated by a collection of experiments. RAW 264.7 cells have been utilized as a mannequin to simulate their interplay with hydrogel extracts in vivo by co-incubating. LPS was employed as an inflammatory inducer to stimulate macrophage polarization towards the M1 phenotype and as a constructive management. The experimental outcomes (Fig. 4D-F) revealed that the experimental teams containing TA and okra parts exhibited important benefits in regulating inflammatory mediator expression in comparison with the LPS and HAMA teams (P < 0.001). Particularly, these experimental teams demonstrated a marked lower within the expression ranges of proinflammatory cytokines (reminiscent of TNF-α and IL-6) from M1 macrophages, accompanied by a considerable improve within the secretion of anti-inflammatory cytokines (reminiscent of IL-10) from M2 macrophages. Amongst them, the HA@TA-Okra hydrogel group was significantly outstanding in its anti-inflammatory results. This phenomenon could also be attributed to the synergistic enhancement of the anti-inflammatory mechanisms of TA and okra parts [56, 57]. The exact anti-inflammatory mechanisms of okra stay to be absolutely elucidated, preliminary proof signifies the potential utility of its extracts within the area of anti-inflammation [41].
Antioxidant and anti inflammatory actions of hydrogels in vitro. (A) Willpower of DPPH clearance by completely different hydrogels. (B) Represents ROS fluorescence depth. (C) Intracellular ROS detection below completely different hydrogels (Inexperienced fluorescence signifies ROS). The secretion of (D) TNF-α and (E) IL-6 (F) IL-10 by RAW264.7 cells on completely different samples have been quantitatively analyzed. (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001)
In vitro blood compatibility of HA@TA-okra hydrogels
The blood compatibility of HAMA, HA@TA, HA@Okra and HA@TA-Okra hydrogels have been methodically assessed on this examine. Deionized water and PBS have been served as constructive and destructive controls, respectively. As depicted in Fig. 5A and B, the hemolysis charges of all hydrogel teams have been markedly under the 5% threshold stipulated by the ASTM F756-2008 normal. This end result underscores the distinctive security and compatibility of all hydrogels inside a blood setting.
BCI is a key coagulation analysis index, the decrease the BCI worth, the higher the coagulation impact. As proven in Fig. 5C and D, in comparison with the gauze teams, all hydrogel teams exhibited considerably decreased BCI values, indicative of their superior coagulation skills. The HA@Okra and HA@TA-Okra hydrogel teams demonstrated even decrease BCI values (21.38% and 21.79%, respectively). In contrast with HAMA group, HA@Okra and HA@TA-Okra teams had higher coagulation impact (P < 0.05). This recommended that the incorporation of okra parts might improve the coagulation properties of the hydrogels by activating platelets, selling platelet adhesion and coagulation issue launch [32]. Moreover, erythrocyte aggregation at wound surfaces is crucial within the formation of an efficient hemostatic barrier [58]. The SEM photos (Fig. 5E) confirmed that erythrocytes and platelets adhered nicely and maintained a traditional morphology on the floor of the hydrogels, which additional confirmed their good blood compatibility.
Blood biocompatibility and coagulation properties. (A) Hemolysis take a look at pictures of various hydrogels. (B) Hemolysis fee. (C) Blood absorption images after gauze and completely different hydrogels contacted blood and soaked in PBS for 1 min. (D) BCI statistical outcomes. (E) SEM photos of blood cell and platelet adhesion on completely different hydrogels. (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001)
In vivo hemostatic properties
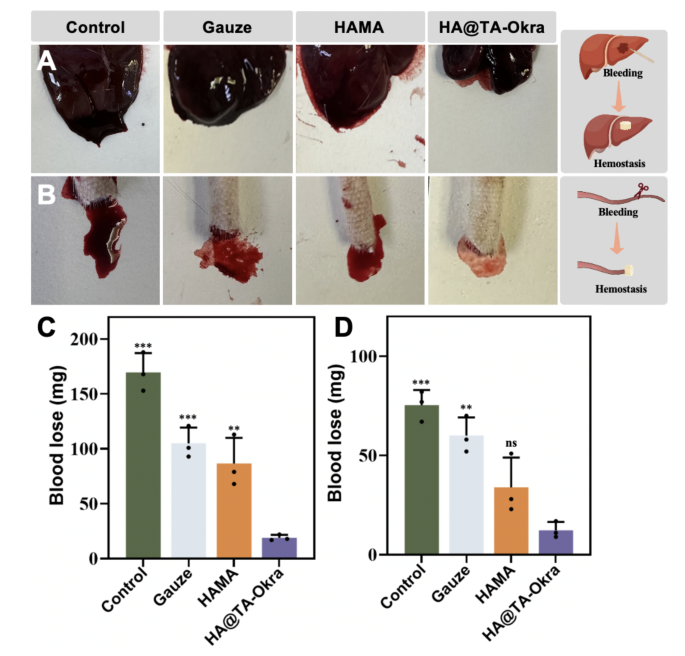
By the above collection of in vitro experiments, we selected the HA@TA-Okra hydrogel with comparatively greatest efficiency for the following in vivo experiments. To additional substantiate the hemostatic efficacy of the HA@TA-Okra hydrogels in genuine physiological settings, hemostasis experiments have been designed and carried out on two bleeding fashions: rat liver incision and tail amputation. As illustrated in Fig. 6A and C, within the liver incision mannequin, blood loss was considerably decrease within the HA@TA-Okra hydrogel group (19 ± 5 mg) than within the different teams, adopted by the HAMA group (86 ± 23 mg). This discovering highlights the strong blood absorption capability of HAMA substrates attributable to their three-dimensional porous construction. Okra parts might confer a exceptional enhancement of HAMA coagulation properties by growing coagulation issue exercise and optimizing platelet operate [32]. Primarily based on Fig. 6B and D, it may be discovered that within the tail amputation mannequin, the quantity of bleeding within the HAMA group was larger than that within the HA @ TA-Okra group. This can be attributable to that though the HAMA group has a steady three-dimensional porous construction, the porous three-dimensional construction is saturated when the quantity of bleeding is massive, and the residual blood quantity can’t be excessively absorbed. After loading okra, it may possibly improve platelet adhesion, trigger platelets to kind thrombus to dam the wound, and initially obtain hemostasis.
The hemostatic properties of various hydrogels in vivo. Photographs of various hydrogel hemostatic properties utilizing (A) liver incision and (B) tail amputation fashions. Blood lack of completely different hydrogels within the (C) liver incision and (D) tail amputation fashions. (** P < 0.01, *** P < 0.001)
Wound therapeutic in a full-thickness pores and skin defect mannequin in rats
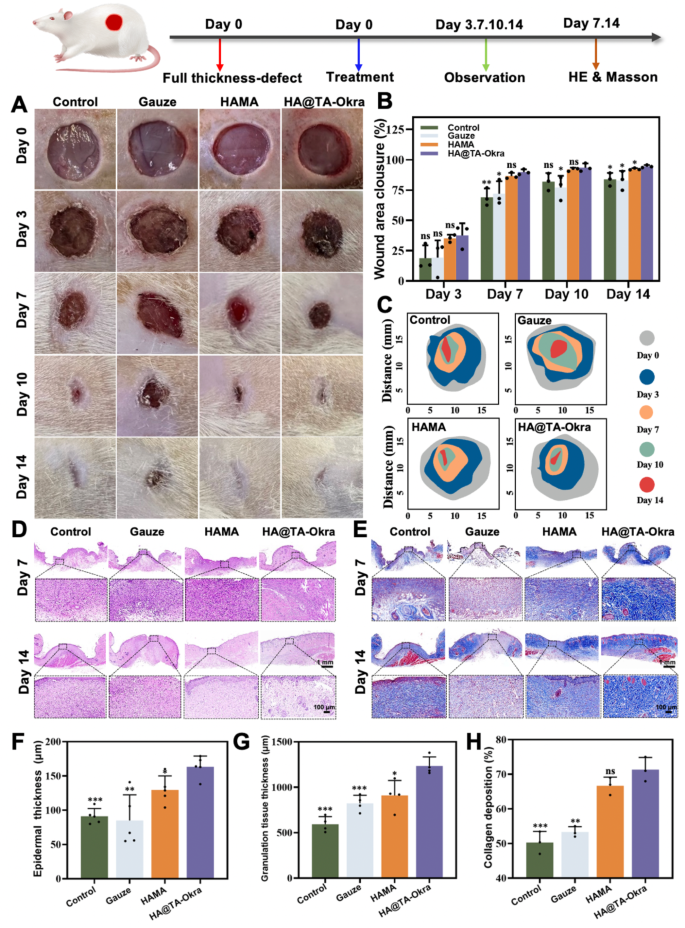
Investigating the therapeutic potential of HA@TA-Okra hydrogel in tissue restore by a rat mannequin of full-thickness pores and skin defects. As depicted in Fig. 7A and B, the HA@TA-Okra hydrogel group confirmed a pronounced therapeutic trajectory with a progressive discount in wound space. In the course of the early stage of therapeutic (day 7), the HA@TA-Okra hydrogel group confirmed a major discount in wound space in comparison with the opposite teams. As therapeutic progressed (Day 14), the injuries of the hydrogels within the HAMA and the HA @ TA-Okra group have been smaller than these within the management and the gauze group. HAMA and HA @TA-Okra hydrogels can fill the wound, keep away from the invasion of exterior bacterial microorganisms, and speed up the wound therapeutic fee. As well as, the wound therapeutic impact of HA @ TA-Okra group was statistically completely different from that of the opposite three teams (P < 0.05), indicating that the hydrogel with TA and okra had a greater impact on wound restore. Quantitative evaluation of wound therapeutic charges (Fig. 7C) illustrated the exceptional benefits of HA@TA-Okra hydrogel in accelerating wound restore.
To additional elucidate the therapeutic mechanism, we collected specimens from every group on day 7 and day 14 and used H&E staining and Masson staining for histological analysis. The outcomes of H&E staining (Fig. 7D, F and G) confirmed that the dermis and granulation tissue layers of HA@TA-Okra group have been considerably thicker than these of management and gauze teams on the day 14, indicating that HA@TA-Okra had a constructive impact on pores and skin tissue regeneration and transforming. The primary element of hyaluronic acid is the extracellular matrix, which may improve collagen deposition, epithelial formation and wound angiogenesis. In contrast with the HAMA group, the thickness of the dermis and granulation tissue layer of the HAMA hydrogel loaded with efficient anti-inflammatory and hemostatic parts was larger, and the therapeutic impact was higher (P < 0.05). Furthermore, Masson staining evaluation (Fig. 7E and H) confirmed that the collagen deposition fee was 71% within the HA@TA-Okra group, which was considerably larger than the 50% within the management group (P < 0.001), 53% within the gauze group (P < 0.01) and 66% within the HAMA group. This discovery strongly helps the pivotal function of HA@TA-Okra hydrogel in enhancing collagen fiber synthesis and deposition.
HA@TA-Okra promotes full-thickness pores and skin defect wound therapeutic. (A) Consultant images of wounds in several teams after 0,3,7,10 and 14 days of therapy. (B) Quantification of wound space in every group. (C) The wound therapy sample of various teams. (D) H&E and (E) Masson staining photos of wound defects on day 7 and day 14 in several teams. (F) Pores and skin thickness statistics. (G) Granulation tissue thickness statistics. (H) Collagen share statistics. (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001)
Analysis of therapeutic efficacy in S. aureus-infected wounds
This examine aimed to systematically assess the therapeutic potential of HA@TA-Okra hydrogel on contaminated wounds by developing a full-thickness pores and skin defect mannequin in rats contaminated with S. aureus. As depicted in Fig. 8A and B, each the HAMA and HA@TA-Okra teams considerably accelerated the wound therapeutic course of in the course of the steady therapeutic interval, with the HA@TA-Okra teams exhibiting significantly exceptional efficiency. In the course of the preliminary section of therapy (Day 3), the HA@TA-Okra teams achieved a wound closure fee of 56%, far surpassing the 20% noticed within the management teams (P < 0.05) and the 4% within the gauze group (P < 0.001). To delve into the antibacterial impact in additional depth, we additional analyzed bacterial viability within the wounds on day 3 (Fig. 8C and D). The outcomes indicated an entire inhibition of bacterial viability within the HA@TA-Okra teams, whereas bacterial viability was near 100% within the management and gauze teams. Bacterial viability additionally decreased considerably in HAMA group (about 10%). This discovering highlights the synergistic antibacterial impact of TA and okra parts within the HA@TA-Okra teams. Because the therapy progressed, all teams demonstrated an growing development in wound therapeutic. The HA@TA-Okra teams continued to exhibit essentially the most pronounced therapeutic results on days 7 and 10, reaching wound closure charges of 84% and 91%, respectively. By day 14, wounds on this group have been nearly utterly healed (roughly 98%), showcasing its distinctive therapeutic functionality. The experimental outcomes confirmed that the therapeutic fee of HA@TA-Okra hydrogel was accelerated from the day 3, and the therapeutic fee on the day 10 and 14 was considerably larger than that of the management group (P < 0.05). The therapeutic fee of gauze group was the bottom from the day 3 to 14. This can be as a result of though gauze, as a conventional wound dressing, can merely defend the wound and block the invasion of micro organism, it’s simple to dehydrate the wound and cling to the wound. When altering the dressing, it’s simple to trigger mechanical re-injury of the brand new tissue of the wound, which is straightforward to trigger wound bleeding. Primarily based on the above evaluation of the change in wound space with therapy time, the superior wound restore potential of HA@TA-Okra hydrogel was confirmed.
To achieve insights into histological modifications throughout wound therapeutic, pores and skin samples have been collected on days 3, 7 and 14 post-surgery and subjected to H&E staining and Masson staining evaluation. On the day 3, it was discovered that whether or not H&E or Masson staining, the dermis, granulation tissue and collagen manufacturing of broken pores and skin have been within the early stage of progress. Amongst them, the irritation stage of HA@TA-okra teams have been decrease than that of different teams, which can be associated to the nice antibacterial and antioxidant properties of its contained substances. On day 7, wounds within the management and gauze teams have been closely coated with inflammatory cells, hindering new dermis formation (P < 0.05). Though full epithelialization was not achieved within the HAMA and HA@TA-Okra teams, the numerous discount in inflammatory cell infiltration favored wound therapeutic. By day 14, all hydrogel-treated wounds exhibited full epidermal protection. The HA@TA-Okra group displayed regeneration of pores and skin appendages, reminiscent of hair follicles and sebaceous glands, indicative of the very best re-epithelialization end result (Fig. 8E, G and H). Moreover, we selected collagen deposition as an indicator of wound therapeutic high quality. On day 14, Masson staining revealed sparse collagen deposition within the management group and plentiful collagen accumulation within the hydrogel-treated group. Furthermore, the collagen fibers within the HA@TA-Okra group have been extra orderly organized, resembling the structural traits of regular pores and skin tissue (Fig. 8F and I). In contrast with the HA@TA-Okra group, the collagen within the management and gauze teams was not neatly organized and the content material was much less (P < 0.05). This discovering demonstrates the numerous benefit of HA@TA-Okra hydrogel in selling collagen synthesis.
HA@TA-Okra promotes infectious wound therapeutic. (A) Contaminated mannequin wound footage after 0,3,7,10 and 14 days of therapy. (B) Quantification of wound space in every group. (C) Photographs of contaminated pores and skin S. aureus on the day 3. (D) Bacterial colony rely statistics. (E) H&E and (F) Masson staining photos of wound defects in several teams on day 7 and day 14. (G) Pores and skin thickness statistics. (H) Granulation tissue thickness statistics. (I) Collagen share statistics. (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001)
Lastly, the experimental animals have been analyzed for histopathology of main organs and routine blood checks to comprehensively consider the biosafety of HA@TA-Okra hydrogel. The outcomes indicated that there have been no apparent pathological modifications within the coronary heart, liver, spleen, lungs and kidneys of the animals in all therapy teams (Fig. 9A-D). Moreover, hematological parameters reminiscent of purple blood cells, platelets, and hemoglobin remained inside regular ranges within the HA@TA-Okra teams, suggesting good biocompatibility and in vivo security of this hydrogel.
Though hydrogels have proven promising antimicrobial and pro-healing results in vitro and in animal experiments, it’s nonetheless a problem to make sure the suitability of hydrogels for various wound varieties in precise scientific purposes. For instance, for advanced wounds reminiscent of deep burns or power ulcers, extra personalised therapy protocols and finer hydrogel designs could also be required.
Immunofluorescence evaluation
On this examine, immunofluorescence evaluation was carried out on wound pores and skin at day 14, specializing in elucidating the expression profiles of two pivotal immunomodulatory components: tumor TNF-α and IL-10. Immunofluorescence photos (Fig. 10A and B) confirmed the expression of TNF-α and IL-10 in several therapy teams. Evaluation of the quantitative outcomes (Fig. 10C) demonstrated that the HA@TA-Okra group exhibited the bottom stage of TNF-α expression, indicative of its efficacy in mitigating extreme inflammatory responses. In distinction, whereas the HAMA teams additionally demonstrated comparatively decrease TNF-α expression, its impact was barely inferior to that of the HA@TA-Okra teams. Conversely, the management and gauze teams manifested considerably elevated TNF-α expression (P < 0.001), reflecting a excessive inflammatory state, probably attributable to the absence of efficient immune modulation. Alternatively, the expression stage of IL-10 in HA@TA-Okra group (Fig. 10D) was considerably larger than that in management and gauze teams (P < 0.001). The elevated expression of IL-10 could also be carefully associated to its distinctive antibacterial properties and enhanced antioxidant capability.
(A) Immunofluorescence staining of TNF-α (inexperienced) and DAPI (blue) in regenerated pores and skin tissue. (B) Immunofluorescence staining of IL-10 (inexperienced) and DAPI (blue) in regenerated pores and skin tissue. Immunofluorescence statistical plots of (C) TNF – α and (D) IL-10. (***P < 0.001)