Actual-time analytics is utilized by many organizations to help mission-critical selections on real-time knowledge. The actual-time journey sometimes begins with reside dashboards on real-time knowledge and shortly strikes to automating actions on that knowledge with purposes like instantaneous personalization, gaming leaderboards and sensible IoT techniques. On this publish, we’ll be specializing in constructing reside dashboards and real-time purposes on knowledge saved in DynamoDB, as we now have discovered DynamoDB to be a generally used knowledge retailer for real-time use circumstances.
We’ll consider just a few standard approaches to implementing real-time analytics on DynamoDB, all of which use DynamoDB Streams however differ in how the dashboards and purposes are served:
1. DynamoDB Streams + Lambda + S3
2. DynamoDB Streams + Lambda + ElastiCache for Redis
3. DynamoDB Streams + Rockset
We’ll consider every strategy on its ease of setup/upkeep, knowledge latency, question latency/concurrency, and system scalability so you possibly can decide which strategy is finest for you primarily based on which of those standards are most essential to your use case.
Technical Issues for Actual-Time Dashboards and Functions
Constructing dashboards and purposes on real-time knowledge is non-trivial as any resolution must help extremely concurrent, low latency queries for quick load instances (or else drive down utilization/effectivity) and reside sync from the information sources for low knowledge latency (or else drive up incorrect actions/missed alternatives). Low latency necessities rule out instantly working on knowledge in OLTP databases, that are optimized for transactional, not analytical, queries. Low knowledge latency necessities rule out ETL-based options which improve your knowledge latency above the real-time threshold and inevitably result in “ETL hell”.
DynamoDB is a completely managed NoSQL database offered by AWS that’s optimized for level lookups and small vary scans utilizing a partition key. Although it’s extremely performant for these use circumstances, DynamoDB is just not a sensible choice for analytical queries which usually contain massive vary scans and sophisticated operations comparable to grouping and aggregation. AWS is aware of this and has answered prospects requests by creating DynamoDB Streams, a change-data-capture system which can be utilized to inform different companies of latest/modified knowledge in DynamoDB. In our case, we’ll make use of DynamoDB Streams to synchronize our DynamoDB desk with different storage techniques which are higher fitted to serving analytical queries.
Amazon S3
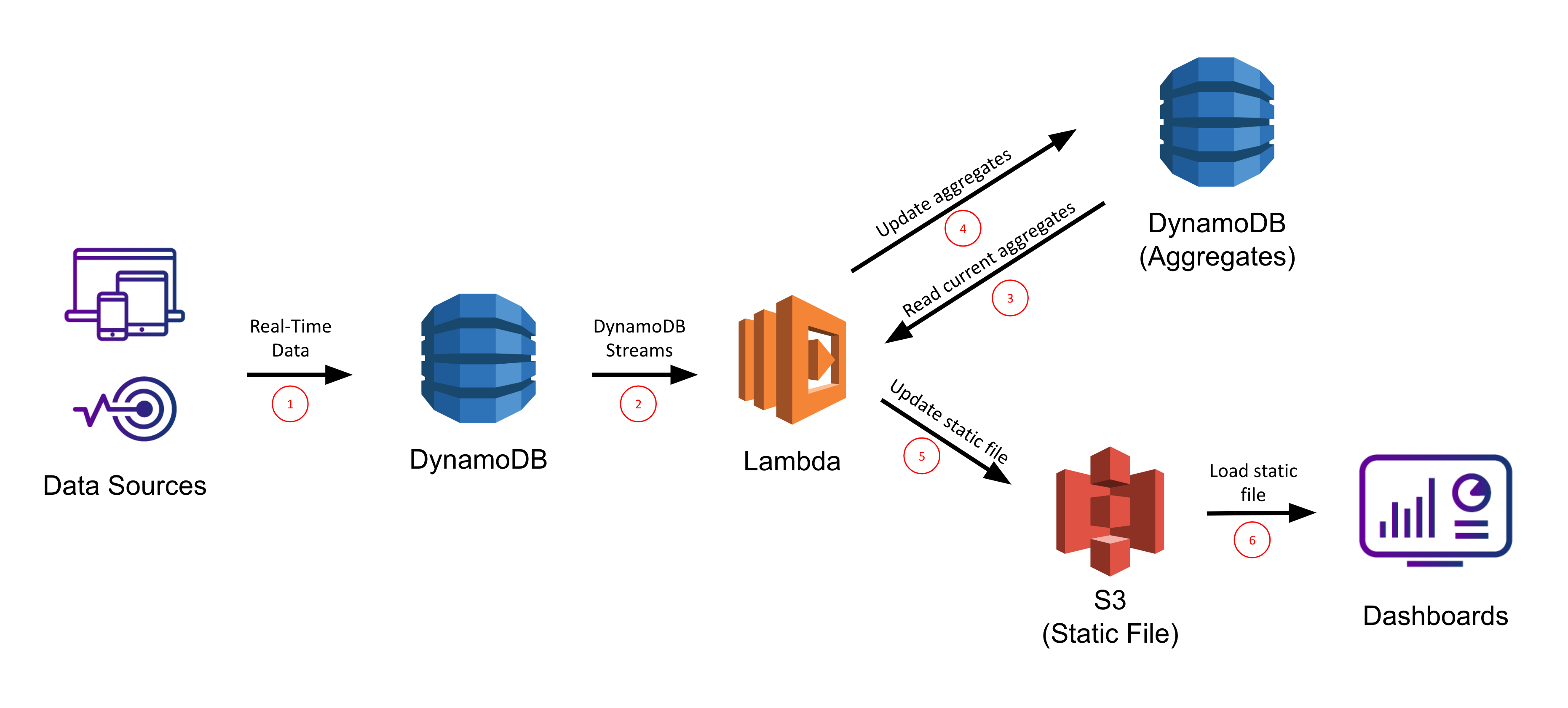
The primary strategy for DynamoDB reporting and dashboarding we’ll contemplate makes use of Amazon S3’s static web site internet hosting. On this situation, modifications to our DynamoDB desk will set off a name to a Lambda perform, which is able to take these modifications and replace a separate combination desk additionally saved in DynamoDB. The Lambda will use the DynamoDB Streams API to effectively iterate by means of the latest modifications to the desk with out having to do a whole scan. The mixture desk will likely be fronted by a static file in S3 which anybody can view by going to the DNS endpoint of that S3 bucket’s hosted web site.
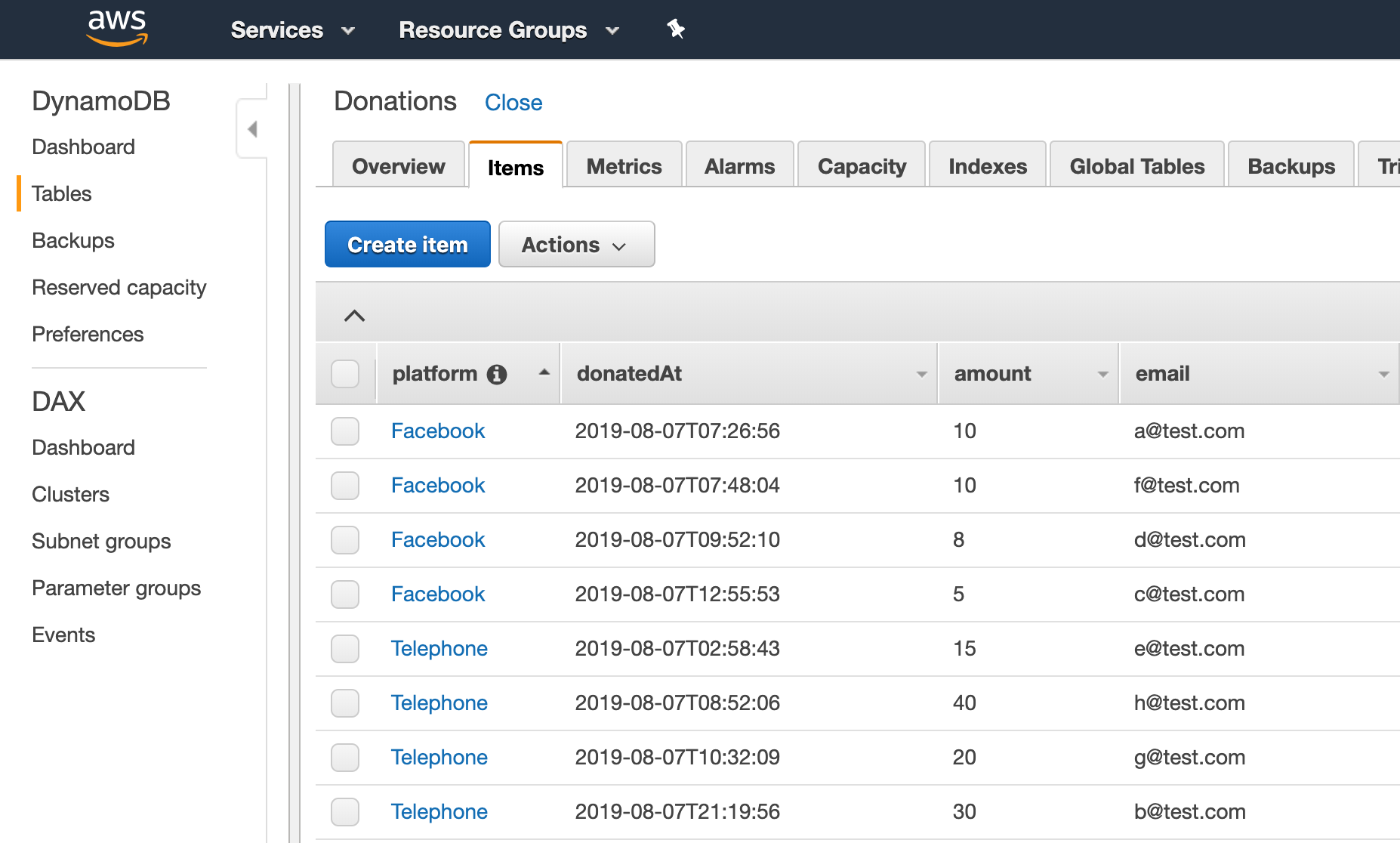
For instance, let’s say we’re organizing a charity fundraiser and need a reside dashboard on the occasion to indicate the progress in the direction of our fundraising objective. Your DynamoDB desk for monitoring donations would possibly seem like
On this situation, it could be cheap to trace the donations per platform and the whole donated thus far. To retailer this aggregated knowledge, you would possibly use one other DynamoDB desk that might seem like
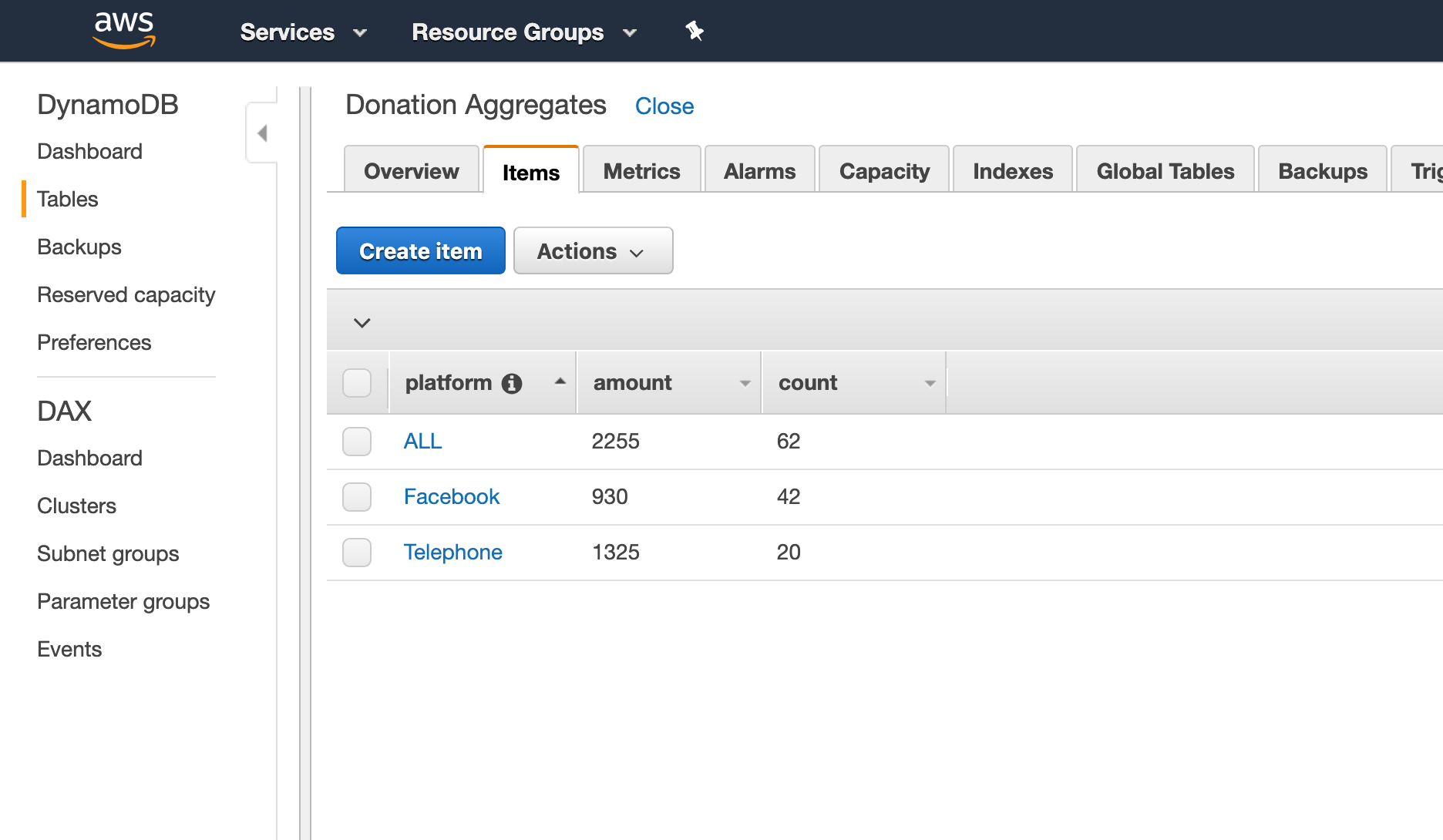
If we hold our volunteers up-to-date with these numbers all through the fundraiser, they’ll rearrange their effort and time to maximise donations (for instance by allocating extra folks to the telephones since cellphone donations are about 3x bigger than Fb donations).
To perform this, we’ll create a Lambda perform utilizing the dynamodb-process-stream blueprint with perform physique of the shape
exports.handler = async (occasion, context) => {
for (const file of occasion.Information) {
let platform = file.dynamodb['NewImage']['platform']['S'];
let quantity = file.dynamodb['NewImage']['amount']['N'];
updatePlatformTotal(platform, quantity);
updatePlatformTotal("ALL", quantity);
}
return `Efficiently processed ${occasion.Information.size} information.`;
};
The perform updatePlatformTotal would learn the present aggregates from the DonationAggregates (or initialize them to 0 if not current), then replace and write again the brand new values. There are then two approaches to updating the ultimate dashboard:
- Write a brand new static file to S3 every time the Lambda is triggered that overwrites the HTML to mirror the most recent values. That is completely acceptable for visualizing knowledge that doesn’t change very regularly.
- Have the static file in S3 really learn from the DonationAggregates DynamoDB desk (which may be completed by means of the AWS javascript SDK). That is preferable if the information is being up to date regularly as it would save many repeated writes to the S3 file.
Lastly, we’d go to the DynamoDB Streams dashboard and affiliate this lambda perform with the DynamoDB stream on the Donations desk.
Professionals:
- Serverless / fast to setup
- Lambda results in low knowledge latency
- Good question latency if the mixture desk is saved small-ish
- Scalability of S3 for serving
Cons:
- No ad-hoc querying, refinement, or exploration within the dashboard (it’s static)
- Ultimate aggregates are nonetheless saved in DynamoDB, so you probably have sufficient of them you’ll hit the identical slowdown with vary scans, and so forth.
- Troublesome to adapt this for an present, massive DynamoDB desk
- Have to provision sufficient learn/write capability in your DynamoDB desk (extra devops)
- Have to determine all finish metrics a priori
TLDR:
- It is a good technique to rapidly show just a few easy metrics on a easy dashboard, however not nice for extra complicated purposes
- You’ll want to take care of a separate aggregates desk in DynamoDB up to date utilizing Lambdas
- These sorts of dashboards received’t be interactive because the knowledge is pre-computed
For a full-blown tutorial of this strategy take a look at this AWS weblog.
ElastiCache for Redis
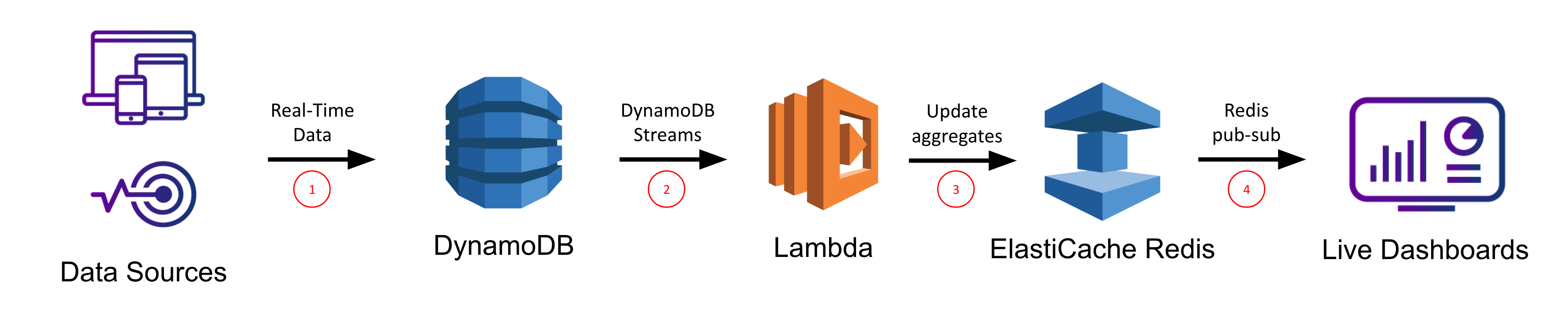
Our subsequent possibility for reside dashboards and purposes on high of DynamoDB includes ElastiCache for Redis, which is a completely managed Redis service offered by AWS. Redis is an in-memory key worth retailer which is regularly used as a cache. Right here, we are going to use ElastiCache for Redis very similar to our combination desk above. Once more we are going to arrange a Lambda perform that will likely be triggered on every change to the DynamoDB desk and that can use the DynamoDB Streams API to effectively retrieve latest modifications to the desk while not having to carry out a whole desk scan. Nonetheless this time, the Lambda perform will make calls to our Redis service to replace the in-memory knowledge buildings we’re utilizing to maintain monitor of our aggregates. We are going to then make use of Redis’ built-in publish-subscribe performance to get real-time notifications to our webapp of when new knowledge is available in so we are able to replace our utility accordingly.
Persevering with with our charity fundraiser instance, let’s use a Redis hash to maintain monitor of the aggregates. In Redis, the hash knowledge construction is much like a Python dictionary, Javascript Object, or Java HashMap. First we are going to create a brand new Redis occasion within the ElastiCache for Redis dashboard.
Then as soon as it’s up and operating, we are able to use the identical lambda definition from above and simply change the implementation of updatePlatformTotal to one thing like
perform udpatePlatformTotal(platform, quantity) {
let redis = require("redis"),
let consumer = redis.createClient(...);
let countKey = [platform, "count"].be a part of(':')
let amtKey = [platform, "amount"].be a part of(':')
consumer.hincrby(countKey, 1)
consumer.publish("aggregates", countKey, 1)
consumer.hincrby(amtKey, quantity)
consumer.publish("aggregates", amtKey, quantity)
}
Within the instance of the donation file
{
"electronic mail": "a@check.com",
"donatedAt": "2019-08-07T07:26:56",
"platform": "Fb",
"quantity": 10
}
This might result in the equal Redis instructions
HINCRBY("Fb:depend", 1)
PUBLISH("aggregates", "Fb:depend", 1)
HINCRBY("Fb:quantity", 10)
PUBLISH("aggregates", "Fb:quantity", 10)
The increment calls persist the donation info to the Redis service, and the publish instructions ship real-time notifications by means of Redis’ pub-sub mechanism to the corresponding webapp which had beforehand subscribed to the “aggregates” matter. Utilizing this communication mechanism permits help for real-time dashboards and purposes, and it offers flexibility for what sort of net framework to make use of so long as a Redis consumer is offered to subscribe with.
Be aware: You’ll be able to all the time use your personal Redis occasion or one other managed model apart from Amazon ElastiCache for Redis and all of the ideas would be the identical.
Professionals:
- Serverless / fast to setup
- Pub-sub results in low knowledge latency
- Redis could be very quick for lookups → low question latency
- Flexibility for selection of frontend since Redis purchasers can be found in lots of languages
Cons:
- Want one other AWS service or to arrange/handle your personal Redis deployment
- Have to carry out ETL within the Lambda which will likely be brittle because the DynamoDB schema modifications
- Troublesome to include with an present, massive, manufacturing DynamoDB desk (solely streams updates)
- Redis doesn’t help complicated queries, solely lookups of pre-computed values (no ad-hoc queries/exploration)
TLDR:
- It is a viable possibility in case your use case primarily depends on lookups of pre-computed values and doesn’t require complicated queries or joins
- This strategy makes use of Redis to retailer combination values and publishes updates utilizing Redis pub-sub to your dashboard or utility
- Extra highly effective than static S3 internet hosting however nonetheless restricted by pre-computed metrics so dashboards received’t be interactive
- All elements are serverless (when you use Amazon ElastiCache) so deployment/upkeep are simple
- Have to develop your personal webapp that helps Redis subscribe semantics
For an in-depth tutorial on this strategy, take a look at this AWS weblog. There the main target is on a generic Kinesis stream because the enter, however you should utilize the DynamoDB Streams Kinesis adapter together with your DynamoDB desk after which observe their tutorial from there on.
Rockset

The final possibility we’ll contemplate on this publish is Rockset, a real-time indexing database constructed for prime QPS to help real-time utility use circumstances. Rockset’s knowledge engine has sturdy dynamic typing and sensible schemas which infer discipline sorts in addition to how they modify over time. These properties make working with NoSQL knowledge, like that from DynamoDB, easy.
After creating an account at www.rockset.com, we’ll use the console to arrange our first integration– a set of credentials used to entry our knowledge. Since we’re utilizing DynamoDB as our knowledge supply, we’ll present Rockset with an AWS entry key and secret key pair that has correctly scoped permissions to learn from the DynamoDB desk we would like. Subsequent we’ll create a group– the equal of a DynamoDB/SQL desk– and specify that it ought to pull knowledge from our DynamoDB desk and authenticate utilizing the mixing we simply created. The preview window within the console will pull just a few information from the DynamoDB desk and show them to verify all the pieces labored appropriately, after which we’re good to press “Create”.
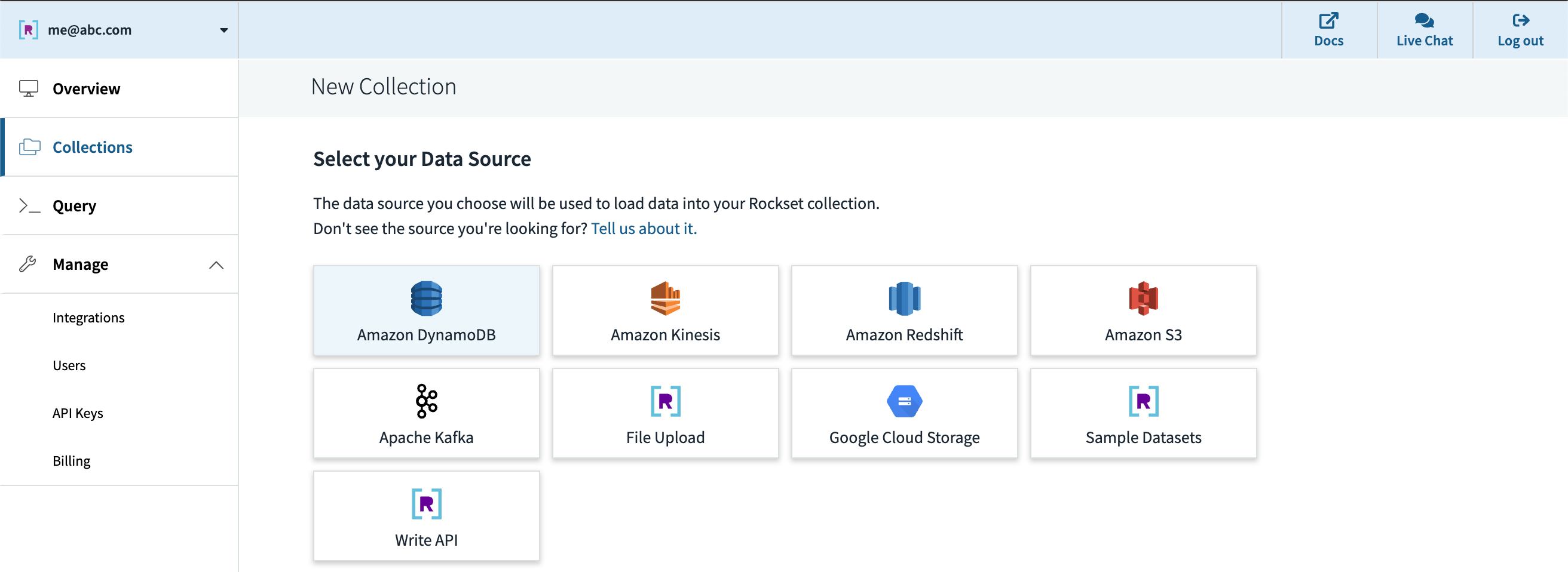
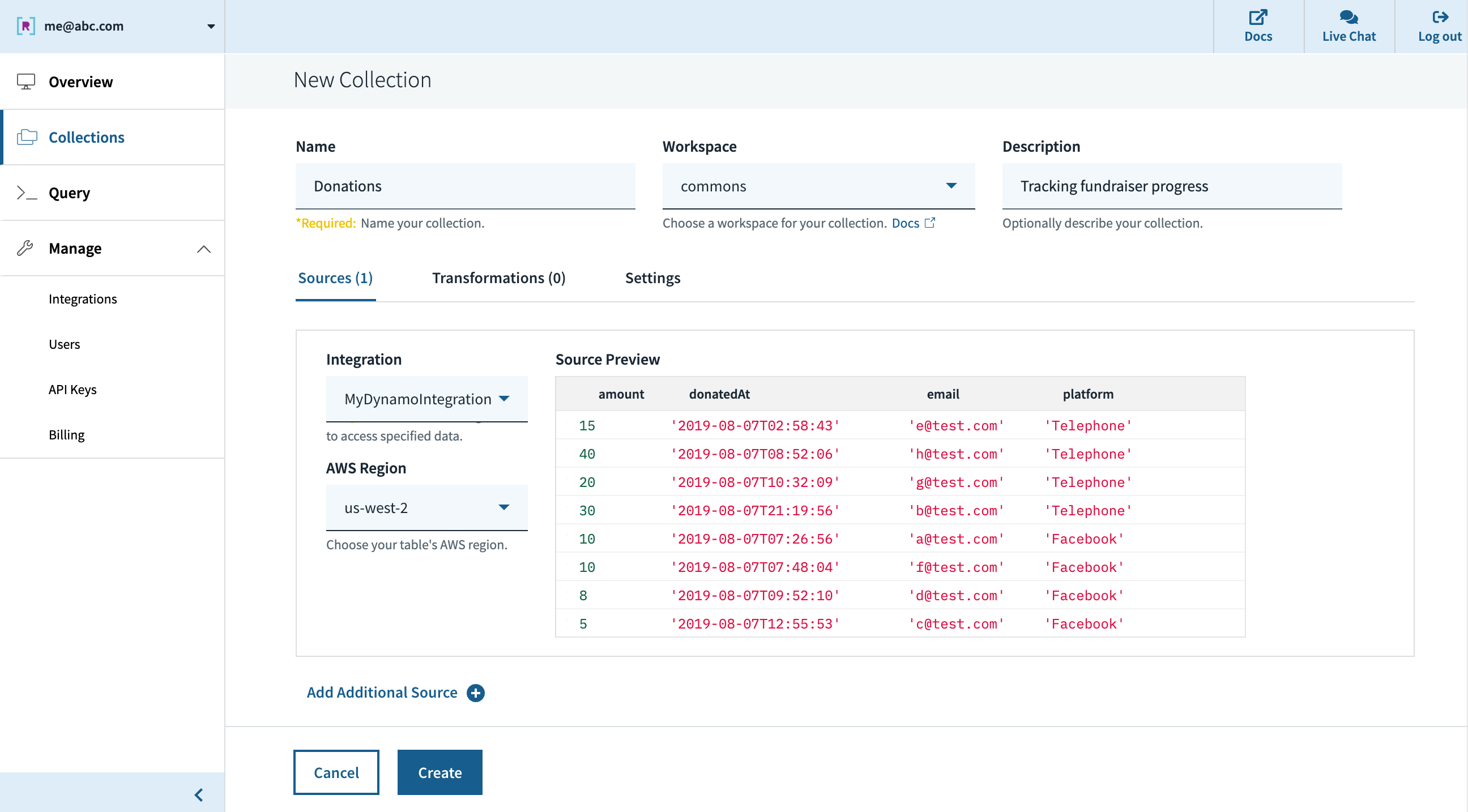
Quickly after, we are able to see within the console that the gathering is created and knowledge is streaming in from DynamoDB. We will use the console’s question editor to experiment/tune the SQL queries that will likely be utilized in our utility. Since Rockset has its personal question compiler/execution engine, there’s first-class help for arrays, objects, and nested knowledge buildings.
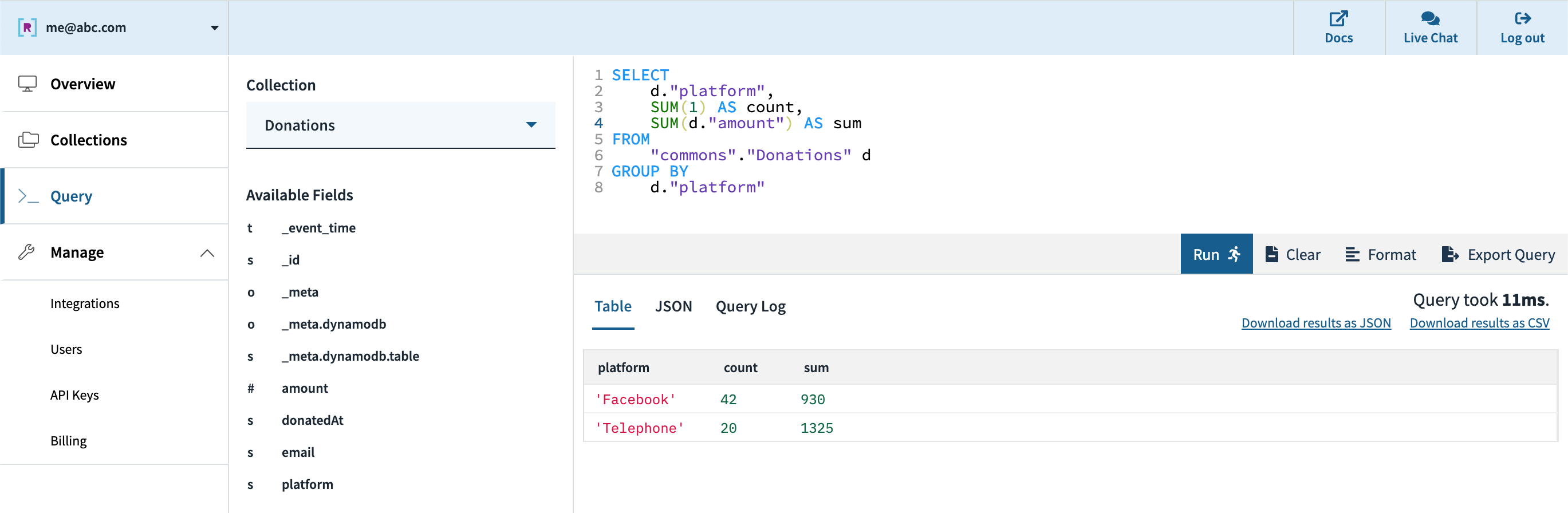
Subsequent, we are able to create an API key within the console which will likely be utilized by the appliance for authentication to Rockset’s servers. We will export our question from the console question editor it right into a functioning code snippet in a wide range of languages. Rockset helps SQL over REST, which implies any http framework in any programming language can be utilized to question your knowledge, and a number of other consumer libraries are offered for comfort as nicely.
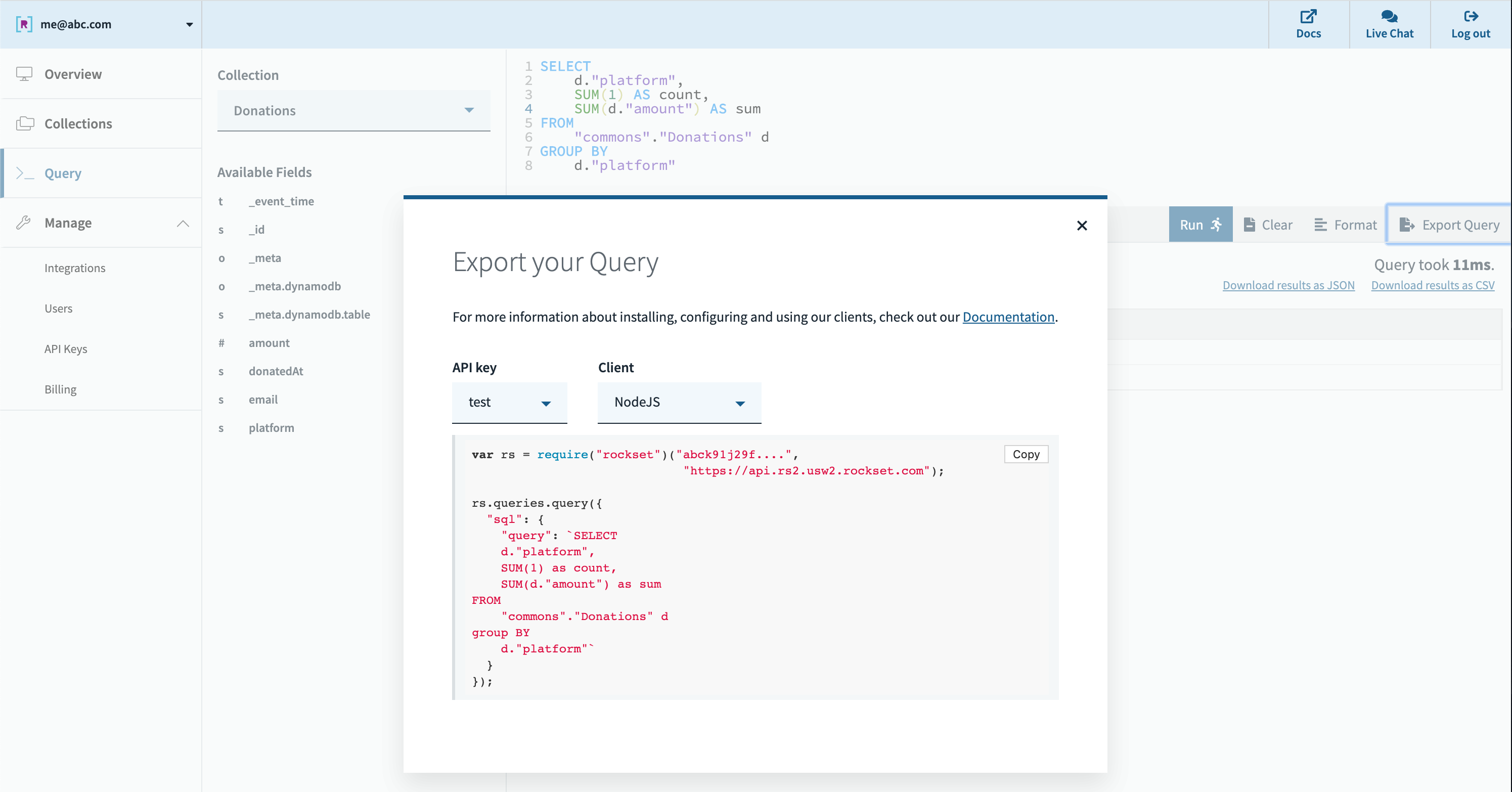
All that’s left then is to run our queries in our dashboard or utility. Rockset’s cloud-native structure permits it to scale question efficiency and concurrency dynamically as wanted, enabling quick queries even on massive datasets with complicated, nested knowledge with inconsistent sorts.
Professionals:
- Serverless– quick setup, no-code DynamoDB integration, and 0 configuration/administration required
- Designed for low question latency and excessive concurrency out of the field
- Integrates with DynamoDB (and different sources) in real-time for low knowledge latency with no pipeline to take care of
- Sturdy dynamic typing and sensible schemas deal with blended sorts and works nicely with NoSQL techniques like DynamoDB
- Integrates with a wide range of customized dashboards (by means of consumer SDKs, JDBC driver, and SQL over REST) and BI instruments (if wanted)
Cons:
- Optimized for energetic dataset, not archival knowledge, with candy spot as much as 10s of TBs
- Not a transactional database
- It’s an exterior service
TLDR:
- Think about this strategy you probably have strict necessities on having the newest knowledge in your real-time purposes, must help massive numbers of customers, or need to keep away from managing complicated knowledge pipelines
- Rockset is constructed for extra demanding utility use circumstances and will also be used to help dashboarding if wanted
- Constructed-in integrations to rapidly go from DynamoDB (and lots of different sources) to reside dashboards and purposes
- Can deal with blended sorts, syncing an present desk, and lots of low-latency queries
- Greatest for knowledge units from just a few GBs to 10s of TBs
For extra sources on learn how to combine Rockset with DynamoDB, take a look at this weblog publish that walks by means of a extra complicated instance.
Conclusion
We’ve coated a number of approaches for constructing real-time analytics on DynamoDB knowledge, every with its personal professionals and cons. Hopefully this will help you consider the perfect strategy to your use case, so you possibly can transfer nearer to operationalizing your personal knowledge!
Different DynamoDB sources:


