Within the Wells Fargo cross-selling scandal of 2016, financial institution staff are reported to have created a number of million fraudulent financial savings and checking accounts within the identify of Wells Fargo purchasers. Whereas the preliminary blame fell on particular person department staff and managers, it later got here out that high-level administration had been pushing them to cross-sell, or promote a number of merchandise to prospects. A poisonous gross sales tradition progressively developed at Wells Fargo, the place aggressive and unrealistic gross sales targets might make or break careers. These incentives pushed staff to open accounts prospects didn’t need and even learn about. Wells Fargo paid about $3 billion in fines and authorized settlements for this fraud and suffered authorized and reputational harm.
I work with a crew of researchers within the SEI’s CERT Division who advocate a extra holistic method to addressing insider threat, one that comes with constructive deterrence to affect worker habits. Optimistic deterrence is a set of evidence-based workforce practices selling the mutual pursuits of staff and their group in ways in which scale back insider threat. This method relies on greater than 20 years of expertise in learning insider threat, a database of greater than 3,000 instances, and a considerable scientific literature on organizational habits. On this weblog publish, I talk about the significance of augmenting conventional insider risk controls with constructive deterrence and a strategic roadmap developed on the CERT Division for incorporating constructive deterrence in an insider threat administration program (IRMP).
Optimistic Deterrence
To encourage staff to behave in the most effective pursuits of the group, IRMPs have sometimes relied on command-and-control methods that stress staff to behave within the pursuits of the group by way of extrinsic controls on their habits, comparable to guidelines, insurance policies, technical constraints, monitoring, and response. We’ve discovered, nonetheless, that extreme or unique reliance on command and management can scale back workforce goodwill and exacerbate the chance of insider-caused hurt to a company. In distinction, a positive-deterrence method promotes inner behavioral drivers that encourage staff to wholeheartedly behave in ways in which scale back insider threat.
Optimistic deterrence leverages workforce administration practices to set off intrinsic drivers, reasonably than depend on exterior controls. Optimistic deterrence mixed with command-and-control approaches can scale back insider incident charges over command and management alone.
Optimistic deterrence practices can take three main varieties:
- Organizational assist is the extent to which the group values staff’ contributions and cares about their well-being. Related observe areas embrace performance-based rewards and recognition, worker help packages, and truthful worker grievance mediation and determination.
- Job engagement is the extent to which staff are excited by and absorbed of their work. Related observe areas embrace job crafting and strengths-based administration.
- Connectedness at work is the extent to which staff belief, really feel near, and wish to work together with their co-workers. Related observe areas embrace crew constructing and job rotation.
For insider threat administration, such positive-deterrence practices defend towards intentional insider acts by lowering worker frustration and disgruntlement, a typical motivator of insider sabotage, theft, espionage, or different detrimental behaviors spurred by poisonous administration. This text focuses particularly on organizational assist as perceived by the workforce as that is the place probably the most proof from earlier analysis exists that important advantages accrue. Extra not too long ago we’ve got advocated using bundling, which I’ll describe under, to include constructive deterrence in an IRMP. Bundling exploits complementary constructive deterrence and command and management actions the place will increase in a single exercise elevate the marginal advantage of others. I’ll present a couple of examples within the fourth observe within the subsequent part.
5 Operational Practices for Incorporating Optimistic Deterrence in Insider Danger Administration
The paper Lowering Insider Danger By means of Optimistic Deterrence, which I coauthored with Carrie Gardner and Denise M. Rousseau, outlines 5 operational practices that assist organizations incorporate constructive deterrence into their IRMP. The determine under illustrates the roadmap for constructive deterrence in insider risk threat administration.
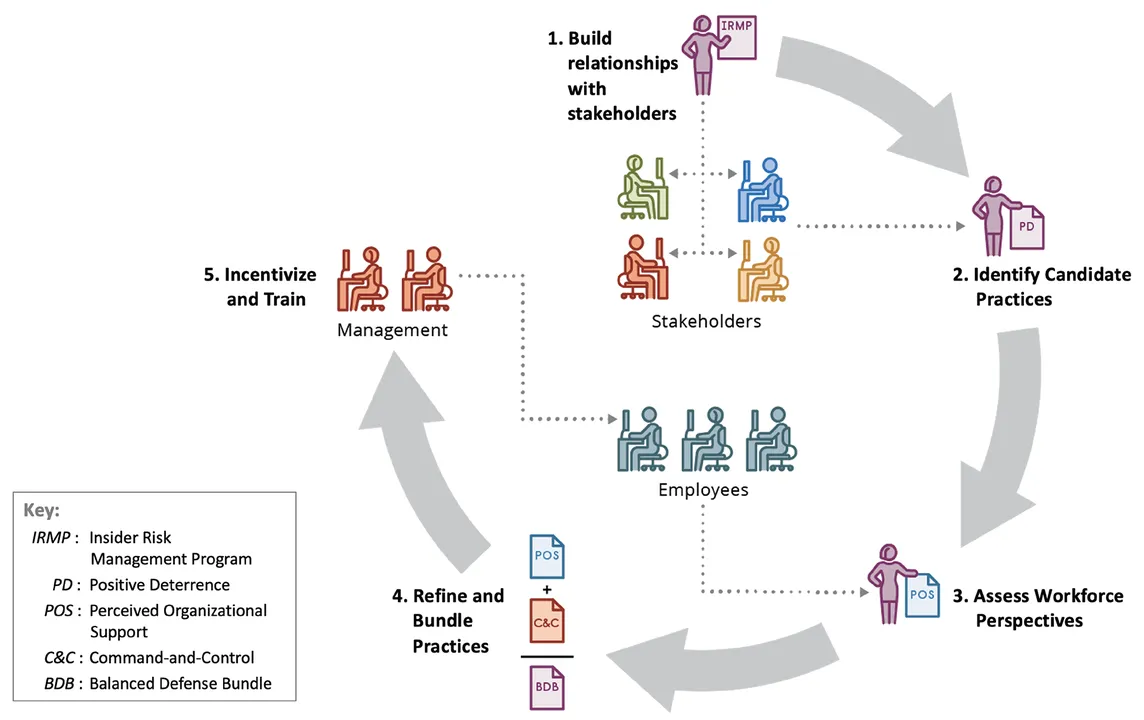
Determine 1: The roadmap illustrated above and detailed under could be tailored as wanted. Ongoing evaluation and refinement are important to make sure efficient implementation.
1. Construct high quality relationships with organizational stakeholders, together with line managers and members of human sources (HR) groups. Organizations can promote stakeholder buy-in to insider threat administration by advocating the worth of constructive deterrence for improved worker efficiency, greater retention, and fewer insider threat. Many points of constructive deterrence overlap with the work of line managers and HR groups. Line managers have to work with HR practitioners to create the supportive work settings that make constructive deterrence a actuality.
Proactive risk administration should be a part of total IRMP governance. The group’s management ought to keep away from tying the arms of the IRMP by limiting its scope to the command-and-control method. IRMPs should advocate broader recognition of how firm employment practices contribute to ranges of insider threat. Taking over constructive deterrence shouldn’t be the enlargement of scope it would first appear, nevertheless it does demand IRMP advocacy of supportive employment practices wherever insider threat exists. Such proactive risk administration requires assist and promotion from organizational leaders and different key stakeholders.
2. Work with stakeholders to determine and implement workforce administration practices that enhance perceived organizational assist. An worker’s constructive notion of the group and its practices reduces the chance of worker misbehavior. Listed here are some examples of workforce administration practices that enhance worker perceived organizational assist (POS):
- organizational justice (e.g., treating staff with dignity and compensating them
equitably contained in the group and according to business requirements) - performance-based rewards and recognition (e.g., utilizing clear standards for promotions and different rewards, basing them on efficiency and different contributions)
- sincere and respectful communication (e.g., setting clear expectations and providing common suggestions and mentoring)
- private {and professional} assist (e.g., providing worker help packages, selling worker improvement, and empowering staff on the job)
Meta-analytic analysis offers substantial proof that these points of POS lead to a discount of staff’ counterproductive work behaviors in addition to quite a lot of different helpful outcomes: organizational dedication and belief, job satisfaction, and intention to stick with the group. Social Change Principle establishes that people reciprocate their employer’s therapy of them, whether or not that therapy is perceived pretty much as good or dangerous. Optimistic reciprocity, which is in power when staff have sturdy POS, is when staff act within the pursuits of the group as a type of compensation or to ascertain an obligation for favorable therapy by the group. However, detrimental reciprocity includes misbehaviors of staff attributable to perceived mistreatment when POS is missing.
3. Frequently search out and assess worker views concerning the IRMP and the work atmosphere, redesigning practices accordingly. Organizations profit enormously from surveys and focus teams that preserve them updated on how staff really feel about their working atmosphere typically and IRMP practices particularly. Federal authorities organizations can reap the benefits of outcomes from the annual Federal Worker Viewpoint Survey after which conduct extra in-depth follow-on assessments to probe numerous points (e.g., POS or IRMP practices). Non-public organizations can leverage beforehand carried out worker local weather and job satisfaction surveys in a lot the identical approach. Since even small pockets of problematic administration practices or supervisory behaviors can enhance insider threat, analyzing worker suggestions requires drilling down into staff detrimental responses no matter how properly the group carried out total.
4. Bundle constructive deterrence with command-and-control practices to stability organizational protection. Balanced protection bundles assemble command-and-control and positive-deterrence practices that work properly collectively. Working properly can imply that the benefits of practices in a single space counter the disadvantages of practices in one other. Analysis demonstrates that constructive deterrence moderates the connection between organizational energy and the worker frustration that contributes to office deviance. As well as, proof means that constantly carried out organizational controls, with clear messaging and supportive coaching, reinforces reasonably than undermines the constructive relationship promoted by organizational assist. Motivational focus idea may also help determine the suitable stability of prevention and promotion methods at a person or crew degree. Instance balanced protection bundles embrace the next:
- combining practices that empower staff with people who implement worker monitoring—Proof means that worker empowerment can mitigate the dissatisfaction related to monitoring.
- bundling sanctions for rule violations with confidential grievance procedures to assist guarantee organizational justice—Proof means that sticks, reasonably than carrots, solely go up to now in lowering insider threat and that giving staff a “voice” for his or her disagreements helps to disarm probably unstable conditions.
- guaranteeing investigations contemplate disconfirming in addition to confirming proof to extend perceptions of equity —Proof means that if investigators take into consideration either side of an incident, they contemplate situational in addition to particular person components, thus lowering affirmation bias and bettering organizational justice.
- These practices aren’t new for many organizations, however explicitly contemplating their mixture in insider threat administration is new. Importantly, associating IRMPs with the introduction of positive-deterrence practices into workforce administration can enhance worker goodwill towards each the IRMP and the group.
5. Incentivize and practice administration to ship positive-deterrence practices successfully. Optimistic-deterrence administration practices require supervisor coaching to bolster wanted change in administration habits (e.g., supervisor supportiveness). A company’s administration tradition could have to shift to accommodate such behavioral modifications. The easiest way to instill such change is to (1) align supervisors’ targets and incentives with the observe’s intent and (2) practice supervisors on tips on how to execute a brand new observe successfully. This course of progressively helps supervisors internalize the values and beliefs which might be in line with new behaviors, selling the required cultural change.
Future Work in Insider Danger
Bundled command-and-control approaches and constructive deterrence strategies ought to complement one another. Complementarity is created when totally different practices contribute to a typical end result, presumably by way of totally different psychological and social mechanisms. Proof signifies that organizations exploiting complementarities present a profit to the group that’s “greater than the sum of its components.”
Whereas there’s a lot analysis on complementarity within the organizational science literature, there’s little or no analysis within the space the contribution of particular practices and even much less straight associated to cybersecurity or insider threat. I recommend that researchers ought to conduct empirical research on particular workforce administration practices and balanced protection bundles, comparable to these described on this article, and suggest others for lowering insider threat and bettering organizational efficiency.
Practitioners could wish to think about using this publish’s constructive deterrence implementation roadmap, or particular person practices from it, inside their very own organizations. Balanced protection bundles could function a place to begin for desirous about what stability means in a given group. Such an method may also help decrease insider threat and staff’ detrimental perceptions of the command and management. It sends a message of advocacy to organizations’ workforces and dedication to worker well-being. Such a message is efficacious to all staff, significantly those that are turned off by packages targeted strictly on discovering insider wrongdoing. As a complement to command-and-control, constructive deterrence creates a piece atmosphere that reinforces the bond between the group and its workforce, contributing to the well-being of each.

