ESET researchers uncovered a crimeware marketing campaign that focused shoppers of three Czech banks. The malware used, which we’ve got named NGate, has the distinctive potential to relay information from victims’ cost playing cards, through a malicious app put in on their Android units, to the attacker’s rooted Android cellphone.
Key factors of this blogpost:
- Attackers mixed customary malicious methods – social engineering, phishing, and Android malware – right into a novel assault situation; we suspect that lure messages have been despatched to random cellphone numbers and caught prospects of three banks.
- Based on ESET Model Intelligence Service information, the group has operated since November 2023 in Czechia, utilizing malicious progressive net apps (PWAs) and WebAPKs. In March 2024 the group’s method improved by deploying the NGate Android malware.
- Attackers have been capable of clone NFC information from victims’ bodily cost playing cards utilizing NGate and relay this information to an attacker system that was then capable of emulate the unique card and withdraw cash from an ATM.
- That is the primary time we’ve got seen Android malware with this functionality getting used within the wild.
- Victims didn’t must root their units.
The first aim of this marketing campaign is to facilitate unauthorized ATM withdrawals from the victims’ financial institution accounts. This was achieved by relaying the close to discipline communication (NFC) information from the victims’ bodily cost playing cards, through their compromised Android smartphones through the use of the NGate Android malware, to the attacker’s system. The attacker then used this information to carry out ATM transactions. If this technique failed, the attacker had a fallback plan to switch funds from the victims’ accounts to different financial institution accounts.
We haven’t seen this novel NFC relay method in any beforehand found Android malware. The method relies on a software known as NFCGate, designed by college students on the Technical College of Darmstadt, Germany, to seize, analyze, or alter NFC visitors; subsequently, we named this new malware household NGate.
Overview
Victims downloaded and put in the malware after being deceived into pondering they have been speaking with their financial institution and that their system was compromised. In actuality, the victims had unknowingly compromised their very own Android units by beforehand downloading and putting in an app from a hyperlink in a misleading SMS message a few potential tax return. A brief description of this assault is on the market within the video under.
It’s vital to notice that NGate was by no means accessible on the official Google Play retailer.
NGate Android malware is expounded to the phishing actions of a menace actor that operated in Czechia since November 2023. Nonetheless, we consider these actions have been placed on maintain following the arrest of a suspect in March 2024.
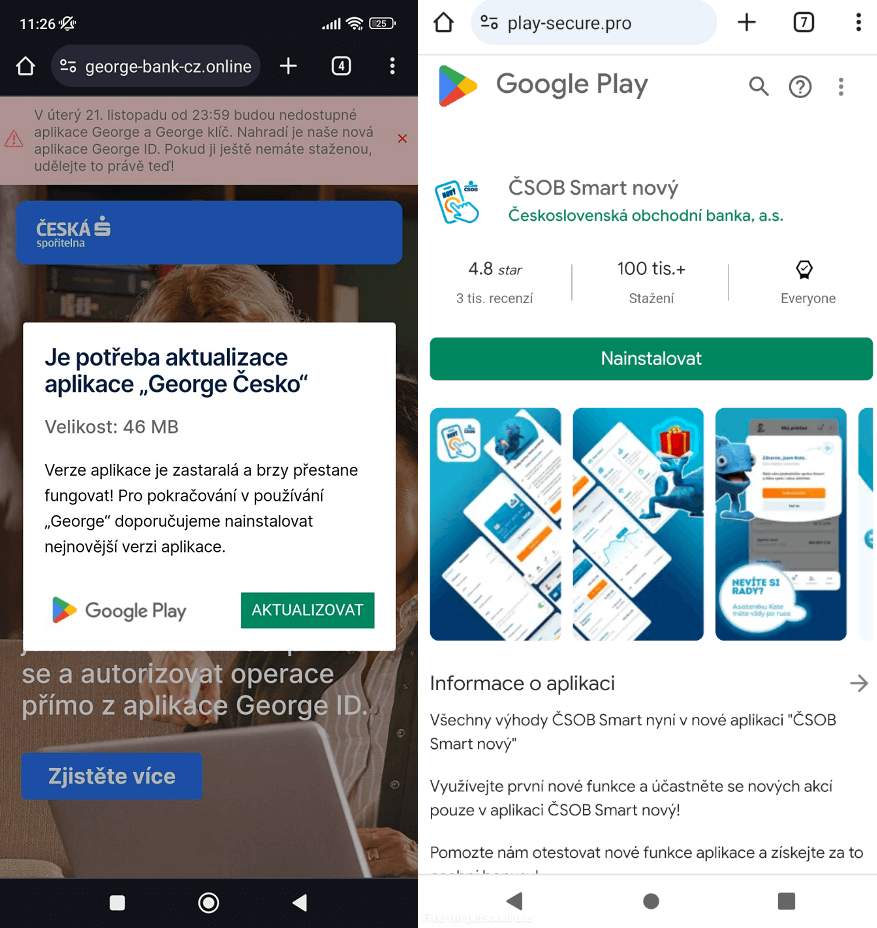
We first seen the menace actor focusing on shoppers of distinguished Czech banks beginning on the finish of November 2023. The malware was delivered through short-lived domains impersonating reputable banking web sites or official cell banking apps accessible on the Google Play retailer, as illustrated in Determine 1. These fraudulent domains have been recognized by way of the ESET Model Intelligence Service, which gives monitoring of threats focusing on a shopper’s model. Throughout the identical month, we reported our findings to our shoppers.
Victimology
Throughout our investigation, we recognized six completely different NGate apps particularly focusing on shoppers of three banks in Czechia between November 2023 and March 2024.
In a considerable breakthrough, the Czech police apprehended a 22-year-old, who had been stealing cash from ATMs in Prague. Upon arrest, the suspect had 160,000 Czech korunas in his possession, an quantity equal to over 6,000 euros (roughly US$6,500). The nationality of the arrested particular person has not been disclosed. Based on the Czech police, the cash recovered from the suspect was stolen from simply the final three victims, so it’s possible that the entire quantity stolen by the menace actor behind this scheme is significantly greater.
Evolution of assault situations
The attackers leveraged the potential of progressive net apps (PWAs), solely to later refine their methods by using a extra refined model of PWAs referred to as WebAPKs. Finally, the operation culminated within the deployment of NGate malware.
It is very important notice that in all the assault situations described right here, the sufferer’s system doesn’t should be rooted, solely the attacker’s system that emulates the obtained NFC visitors.
Progressive net apps
Initially, these fraudulent web sites misused PWA expertise. This expertise permits a person to put in an app from a web site through a supported browser; the set up will be triggered both routinely by way of a pop-up notification or manually by deciding on the Set up app possibility from the browser’s menu. On Android, supported browsers embody Chrome, Firefox, Edge, and Opera. As soon as put in, a brand new icon that includes a small browser brand within the backside proper nook is added to the smartphone’s dwelling display screen, mainly serving as a web site hyperlink. An instance is proven in Determine 2, the place we evaluate the icon of a PWA on the left facet with an icon of a normal app on the best facet.

PWAs are basically a sort of app, however not like conventional apps which are downloaded and put in from an app retailer, PWAs are accessed and used straight inside an internet browser. They’re constructed utilizing frequent net programming languages similar to HTML (for construction), CSS (for design), and JavaScript (for interactivity), that are the identical applied sciences used to create web sites. PWAs are identified for his or her compatibility and suppleness, as they’re designed to work on any system that has a standards-compliant net browser. Which means that a person, whether or not on a desktop pc, laptop computer, pill, or smartphone, can entry the identical PWA with no need to obtain a separate app for every system.
If a PWA is put in from a phishing web site, its icon is more likely to mimic that of a reputable banking utility, with the slight addition of a small browser icon. Upon launching this malicious PWA, a full-screen phishing web site is displayed that requests the person’s banking credentials.
WebAPKs
Subsequently, the menace actor improved on this assault situation, persevering with to focus on shoppers of the identical banks as earlier than however using a extra superior kind of PWA referred to as a WebAPK. WebAPKs are Android apps which are routinely generated by the Chrome browser when customers add a PWA to their Android system’s dwelling display screen. To tell apart between these two, PWAs are apps constructed utilizing net applied sciences, whereas WebAPKs use a expertise to combine PWAs as native Android apps. What’s completely different about WebAPKs is that they seem extra like native Android apps than typical PWAs, as a result of their icons do not need the small browser brand that PWA icons have. This absence of a browser brand can lead a person to mistakenly consider {that a} malicious WebAPK is a reputable app, as illustrated in Determine 3.

The distribution scheme stayed the identical – customers have been capable of obtain and set up a standalone app from phishing web sites, as a substitute of merely a PWA net shortcut. The WebAPK requires guide set up; nevertheless, the person will not be requested to grant express permission to put in apps from unknown sources or to permit the browser to put in unknown apps, as this isn’t a daily app. Due to that, customers may not remember that they’re putting in an app from an untrusted supply. Determine 4 exhibits an instance of what it seems like when customers go to a phishing web site that asks them to replace and set up a malicious WebAPK.
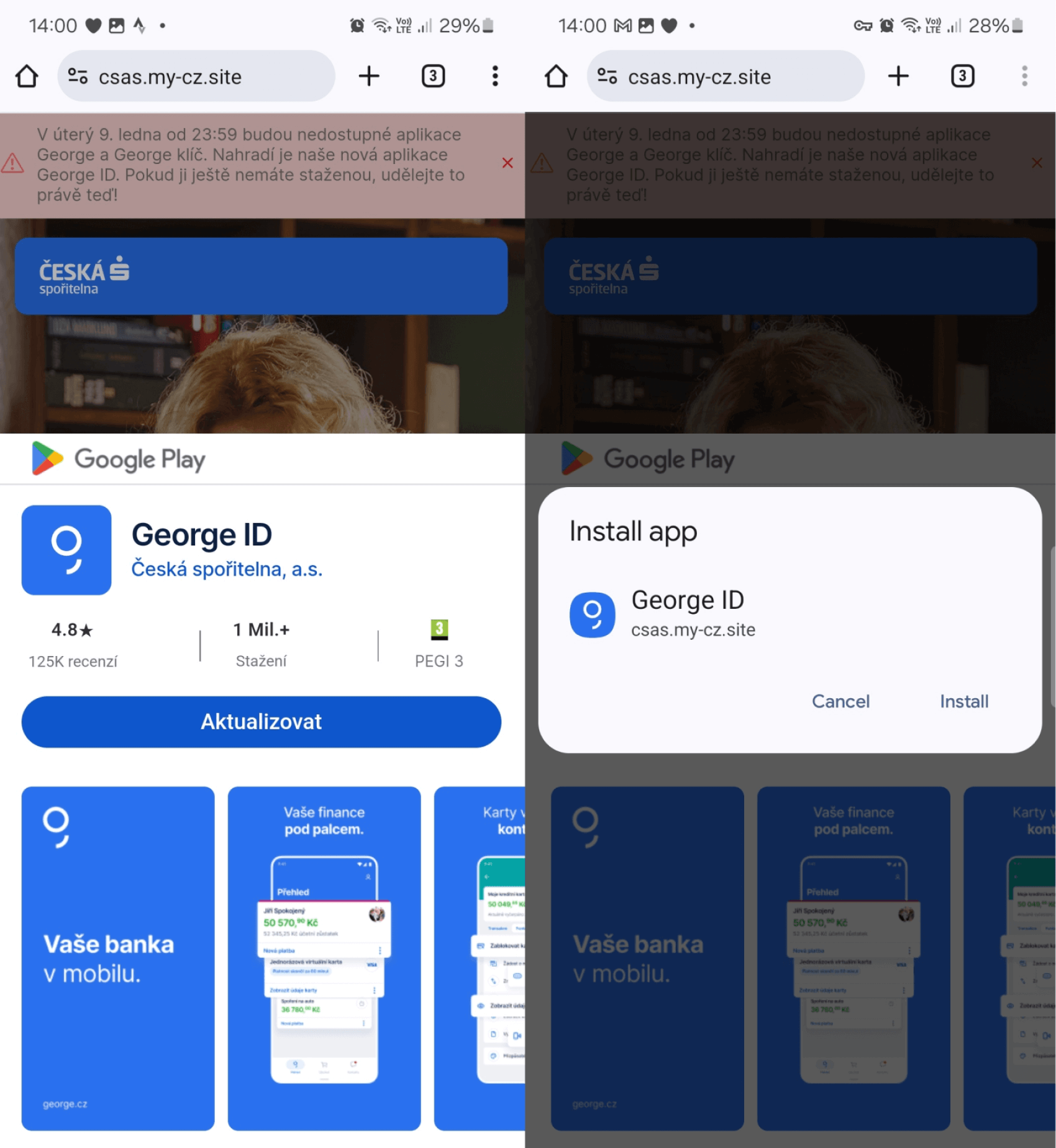
As soon as it’s put in and opened, the malicious app requests banking credentials. Extra particulars about phishing campaigns that use PWAs and WebAPKs have been mentioned in our earlier blogpost.
NGate malware
On March sixth, 2024 we found that NGate Android malware grew to become accessible on the identical distribution domains that have been beforehand used to facilitate phishing campaigns delivering malicious PWAs and WebAPKs.
After being put in and opened, NGate shows a pretend web site that asks for the person’s banking data, which is then despatched to the attacker’s server. Along with its phishing capabilities, NGate malware additionally comes with a software known as NFCGate, which is misused to relay NFC information between two units – the system of a sufferer and the system of a perpetrator. The NFCGate software was developed by college students from the Safe Cell Networking Lab on the Technical College of Darmstadt in Germany and is on the market on GitHub. NFCGate’s primary perform is to transmit an NFC sign from one Android system by way of a server to a different Android system that may mimic or emulate it, as depicted in Determine 5.
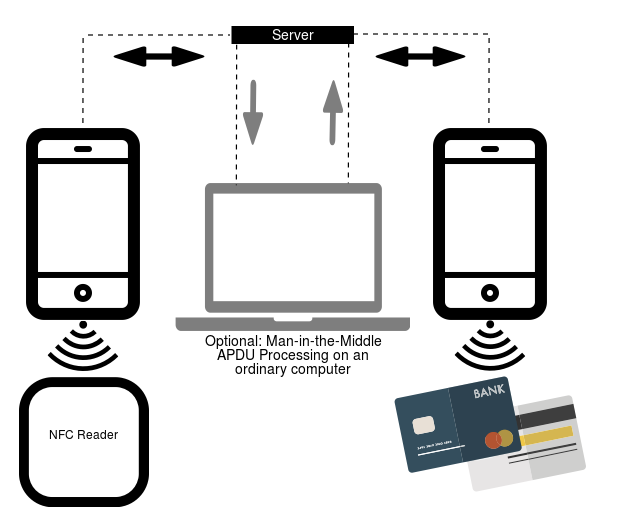
NFCGate is a software that may work together with NFC visitors on a tool. On the system the place NFCGate is put in, it might:
1. Seize NFC visitors from apps that use NFC.
2. Move alongside or relay this NFC information from one system to a different.
3. Mimic or replay information it has beforehand intercepted, on the opposite system.
A few of these options work solely on rooted units; nevertheless, relaying NFC visitors is feasible from non-rooted units as properly. The NGate malware misuses solely one in all NFCGate’s options. It doesn’t intervene with different information that’s accessible on the compromised system, and doesn’t attempt to mimic it. It abuses NFCGate solely to cross alongside NFC information from one system to a different.
Nonetheless, NGate additionally prompts its victims to enter delicate data like their banking shopper ID, date of delivery, and the PIN code for his or her banking card. It additionally asks them to activate the NFC function on their smartphone. Then, victims are instructed to position their cost card in the back of their smartphone till the malicious app acknowledges the cardboard.
What’s taking place behind the scenes is that the NFC information from the sufferer’s financial institution card is being despatched by way of a server to the attacker’s Android system. Basically, this permits the attacker to imitate the sufferer’s financial institution card on their very own system. This implies the attacker can now use this copied card information on their Android system to make funds and withdraw cash from an ATMs that use NFC.
Full assault situation with a backup answer
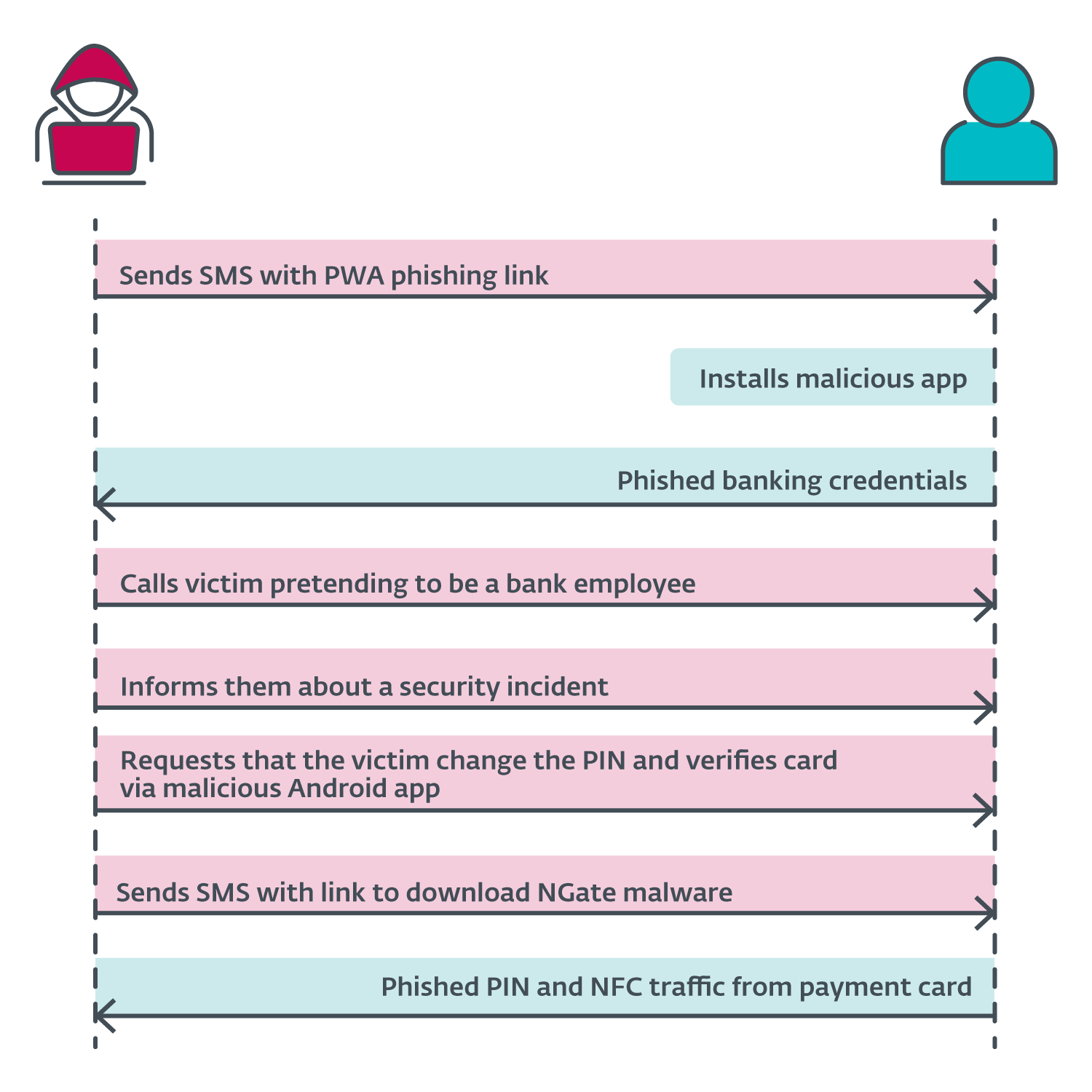
The announcement by the Czech police revealed the assault situation began with the attackers sending SMS messages to potential victims a few tax return, together with a hyperlink to a phishing web site impersonating banks. These hyperlinks almost certainly led to malicious PWAs. As soon as the sufferer put in the app and inserted their credentials, the attacker gained entry to the sufferer’s account. Then the attacker known as the sufferer, pretending to be a financial institution worker. The sufferer was knowledgeable that their account had been compromised, possible because of the earlier textual content message. The attacker was really telling the reality – the sufferer’s account was compromised, however this reality then led to a different lie.
To “shield” their funds, the sufferer was requested to vary their PIN and confirm their banking card utilizing a cell app – NGate malware. A hyperlink to obtain NGate was despatched through SMS. We suspect that throughout the NGate app, the victims would enter their previous PIN to create a brand new one and place their card in the back of their smartphone to confirm or apply the change.
Because the attacker already had entry to the compromised account, they may change the withdrawal limits. If the NFC relay technique didn’t work, they may merely switch the funds to a different account. Nonetheless, utilizing NGate makes it simpler for the attacker to entry the sufferer’s funds with out leaving traces again to the attacker’s personal checking account. A diagram of the assault sequence is proven in Determine 6.
Different doable assault situations
The utilization of NGate malware or a personalized model of NFCGate opens up the likelihood for extra assault situations, significantly in conditions the place the menace actor has bodily entry and will probably clone NFC tags or cost playing cards. To carry out and emulate the next doable assaults, the attacker requires a rooted and customised Android system.
Gaining entry through NFC tags
An NFC tag or token is a compact, contactless system that has the flexibility to retailer and switch information. These tags can serve quite a lot of functions, together with identification and information switch. NFC tags can be utilized as playing cards for public transportation, worker ID playing cards for entry management in buildings, wearable well being/affected person monitoring units, and so forth.
Each NFC tag has a novel ID (UID) and an information part the place keys are saved. When these tags are positioned close to a card reader, a handshake happens, verifying that the tag has the proper keys for authorization. Nonetheless, some readers solely confirm the UID of the token for authorization, bypassing the necessity for the keys. The UID is often 4 bytes lengthy.
Any non-rooted Android system can learn NFC tags that adjust to ISO/IEC 14443. Nonetheless, solely sure rooted Androids can emulate the UID of an NFC tag. Due to this fact, if a reader verifies solely the token UID, it’s doable to make use of NFCGate to relay and emulate the tag. If a reader requires additionally the keys (saved within the information part) for authentication, NFCGate is unable to repeat them, making it unattainable to clone an NFC tag in such a case.
Which means that an attacker, both with bodily entry to a supported NFC tag or by tricking a person to place the tag in the back of the smartphone the place this malicious app is put in, can duplicate the UID of the NFC entry token. This could then be used to emulate the UID and achieve entry to restricted areas, buildings, workplaces, and comparable areas.
Throughout our testing, we efficiently relayed the UID from a MIFARE Traditional 1K tag, which is often used for public transport tickets, ID badges, membership or pupil playing cards, and comparable use circumstances. Utilizing NFCGate, it’s doable to carry out an NFC relay assault to learn an NFC token in a single location and, in actual time, entry premises in a unique location by emulating its UID, as proven in Determine 7.
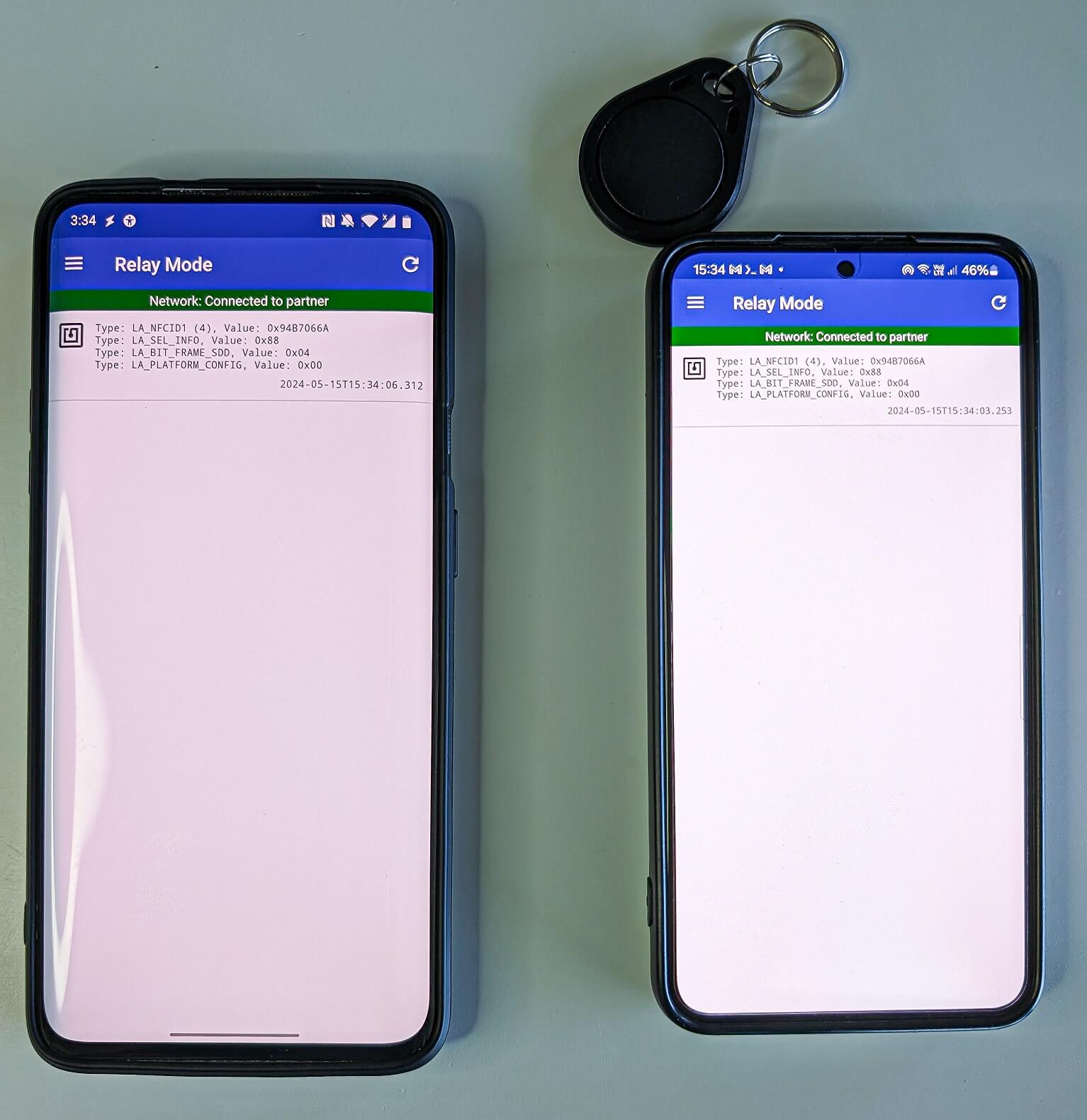
Nonetheless, after we tried to emulate the UID, NFCGate despatched completely different UIDs to the reader as a substitute of the relayed UID. We found that our testing system (OnePlus 7 Professional) is on the checklist of units that don’t assist UID cloning. Because of this, we used the NFC Card Emulator Professional (Root) app and manually entered the UID to efficiently clone it.
This assault situation is extremely focused, that means that the attacker must already know the place the token can be utilized.
Small contactless funds through cost playing cards
Along with the method utilized by the NGate malware, an attacker with bodily entry to cost playing cards can probably copy and emulate them. This system might be employed by an attacker making an attempt to learn playing cards by way of unattended purses, wallets, backpacks, or smartphone circumstances that maintain playing cards, significantly in public and crowded locations.
This situation, nevertheless, is mostly restricted to creating small contactless funds at terminal factors, relying on the restrict set by the financial institution that issued the cardboard, not for ATM withdrawals, because the latter would require the attacker to have the cardboard’s PIN.
One other theoretical situation entails cloning a cost card saved in smartphone pockets apps. It’s doable to relay the NFC sign from Android smartphones outfitted with pockets apps, similar to Google Pockets. Nonetheless, as of April 2024, Google requires customers to offer verification for each NFC cost. Due to this fact, even with an unlocked system, a person would nonetheless want to offer verification within the Google Pockets app earlier than making a cost. Equally, the Apple Pockets app additionally requests authorization earlier than processing a cost. These safety measures make it tougher to relay and emulate cost playing cards from the Google and Apple pockets apps, utilizing the NFCGate software.
Technical evaluation of NGate malware
Preliminary entry
Preliminary entry to the system is gained by deceiving the sufferer into putting in a malicious app, usually beneath the guise of a false assertion that there’s an overpayment of revenue tax that the sufferer can reclaim. This request is often delivered through SMS and we consider these messages have been despatched to random cellphone numbers. Sadly, we weren’t capable of purchase samples of those SMS messages, and no screenshots have been made publicly accessible by the Czech authorities.
Ought to victims obtain the app and enter their credentials, the attacker then initiates a cellphone name, posing as a financial institution worker. They inform the victims that their accounts have been compromised and advise them to vary their PINs and confirm their banking playing cards utilizing a unique app. This new app, supplied through one other SMS hyperlink, comprises the NGate malware. Not one of the malicious apps we analyzed have been accessible on Google Play.
We discovered two domains, mimicking the Czech Raiffeisenbank (as depicted in Determine 8) and the ČSOB financial institution, the place NGate was accessible for obtain. On the time of writing, none of them have been lively:
- raiffeisen-cz[.]eu
- app.mobil-csob-cz[.]eu
![Figure 8. One of the distribution websites (raiffeisen-cz[.]eu) for NGate malware](https://web-assets.esetstatic.com/wls/2024/8-2024/ngate/figure8.png)
Toolset
The NGate malware shows uniform traits throughout all six samples we analyzed. Every pattern shares the identical package deal identify (rb.system.com) and makes use of the identical hardcoded phishing URL that’s distinctively recognized with a novel ID (present in the important thing question parameter) to show particular net content material. All samples have been signed utilizing the identical developer certificates (SHA-1 fingerprint: 0C799950EC157BB775637FB3A033A502F211E62E). This constant sample throughout all six samples signifies a uniformity of their growth and deployment.
All the samples function the identical hardcoded phishing URL (https://shopper.nfcpay.staff[.]dev/?key=8e9a1c7b0d4e8f2c5d3f6b2); nevertheless, every app has a definite key related to it. This distinctive key corresponds to a particular banking phishing web site that’s exhibited to the potential sufferer. The given hyperlink serves solely as a redirection to the supposed phishing web site. From the samples analyzed, we have been capable of determine 5 distinct phishing web sites, particularly:
- rb.2f1c0b7d.tbc-app[.]life
- geo-4bfa49b2.tbc-app[.]life
- rb-62d3a.tbc-app[.]life
- csob-93ef49e7a.tbc-app[.]life
- george.tbc-app[.]life
The icon and identify of every pattern has been designed to imitate particular focused banking apps, additional enhancing their misleading look.
Upon initiation, the NGate malware presents the sufferer with a phishing web site inside a WebView. A WebView is actually a window or mini browser throughout the utility itself. It’s used to show net content material or net pages with out having to go away the applying or open a separate net browser. On this case, the web site requests the person’s private data, similar to shopper ID and date of delivery, as depicted in Determine 9.
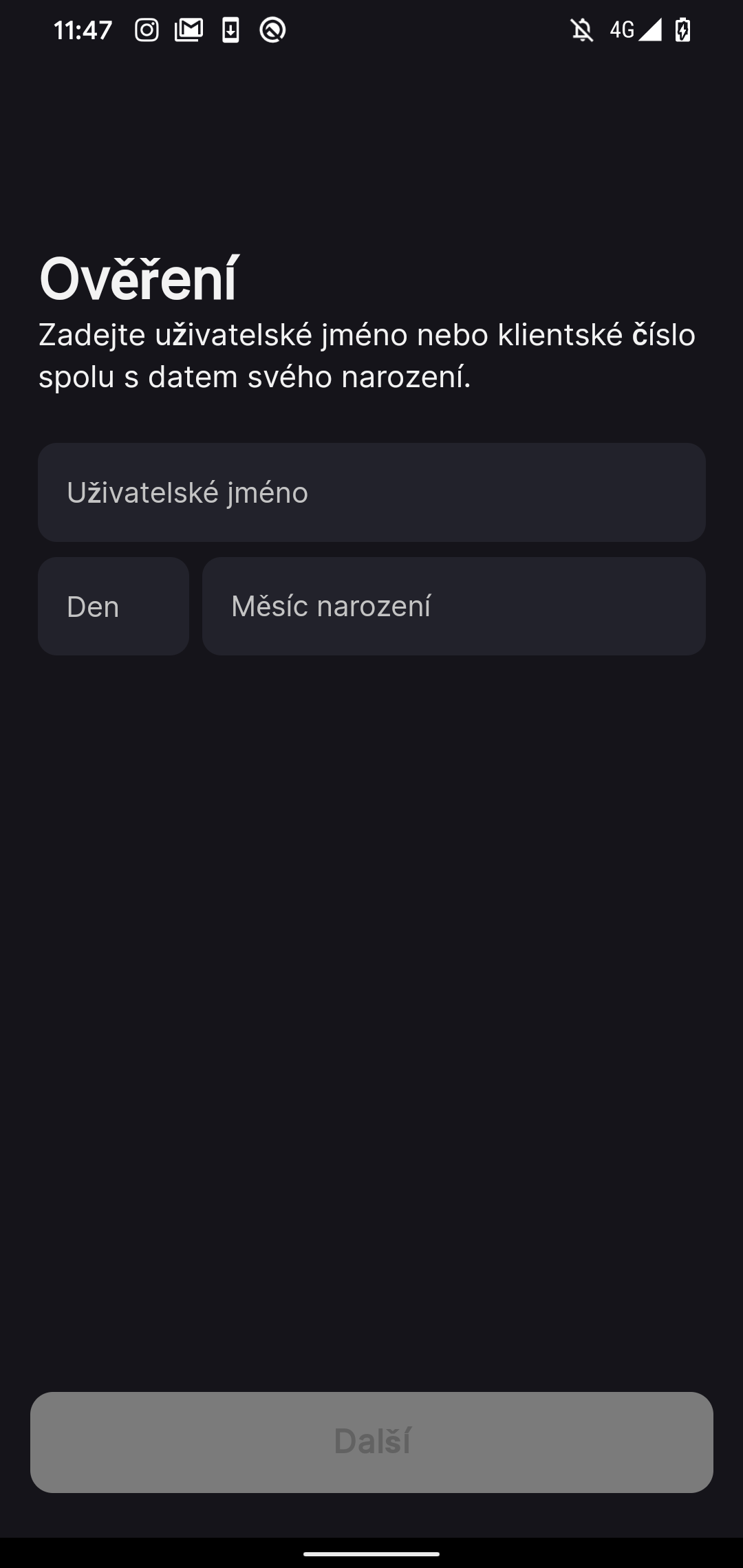
The misleading phishing web site guides the sufferer to not solely enter the PIN code for his or her banking card, but additionally to allow the NFC function on their system. The sufferer is then instructed to place their card on the bottom of their smartphone, setting the stage for an NFC relay assault.
In contrast to standard malware, NGate doesn’t obtain particular directions from a Command and Management (C&C) server. As a substitute, the compromised system is managed through the phishing web site. That is achieved by way of using a JavaScript interface that triggers sure Android capabilities. These capabilities embody retrieving details about the system such because the mannequin and the NFC standing, establishing a server to which the NFC visitors can be redirected, and initiating the NFC relay assault.
Determine 10 illustrates a code snippet of a perform that’s tasked with establishing an NFC relay server and enabling the system to learn after which ahead NFC visitors.
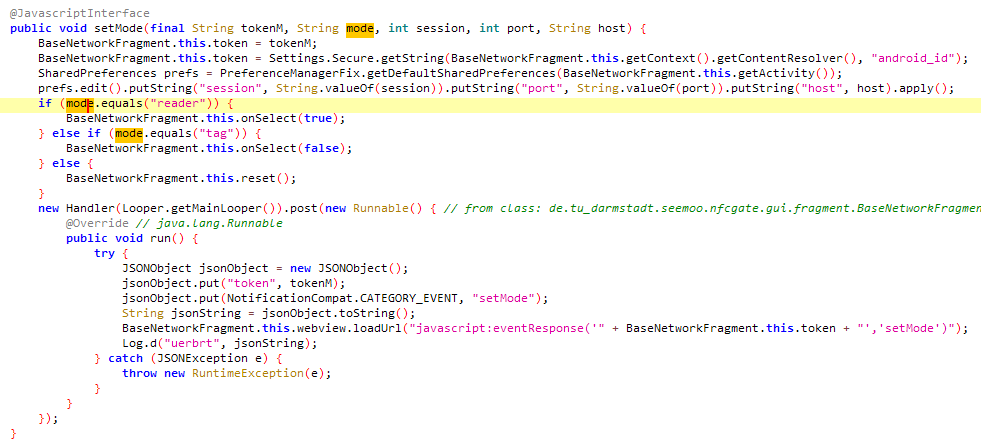
NGate makes use of two distinct servers to facilitate its operations. The primary is a phishing web site designed to lure victims into offering delicate data and able to initiating an NFC relay assault. The second is an NFCGate relay server tasked with redirecting NFC visitors from the sufferer’s system to the attacker’s. In our preliminary evaluation of the NGate samples, we discovered that the NFC server might be set primarily based on the response from the phishing web site. Nonetheless, in subsequent samples, these servers seemed to be hardcoded into the NGate malware.
If the sufferer follows all of the directions issued by NGate, it leads to the attacker being able to relay the NFC visitors from the sufferer’s cost card. This allows the attacker to make use of the sufferer’s monetary data to withdraw funds or make funds at contactless terminals.
Prevention
Making certain security from such advanced assaults requires using sure protecting steps towards ways like phishing, social engineering, and Android malware. These steps embody:
- Checking the web site’s authenticity. This may be performed by wanting on the URL to verify the web site isn’t a pretend model of a real one.
- Solely downloading apps from official sources, such because the Google Play retailer. This precaution considerably reduces the chance of unknowingly putting in dangerous software program.
- Holding cost card PIN codes secret. This vital data ought to be stored protected always.
- Utilizing safety apps on cell units that may cease probably undesirable software program and malware, like NGate, from being downloaded and put in. These safety apps add an additional layer of protection by repeatedly scanning and monitoring for threats.
- Turning off the NFC perform on units when it’s not wanted. This step helps to stop any unauthorized entry or information switch through NFC.
- Utilizing protecting circumstances or protectors for radio frequency identification (RFID) playing cards. By making a barrier that blocks undesirable RFID scans, these can cease anybody from stealing NFC information from the cardboard.
- Utilizing digital variations of bodily playing cards on smartphones. These digital playing cards are saved securely on the system and will be protected by further safety measures, similar to biometric authentication, making them a safer and extra handy different to conventional plastic playing cards.
Conclusion
ESET researchers have investigated a novel and distinctive assault situation that mixes well-known strategies, similar to phishing, with a brand new malware strategy of relaying NFC visitors from victims’ bodily cost playing cards to the attackers’ Android cell system. Earlier than transitioning to the brand new malware, which we named NGate, to relay NFC visitors, the attackers previously used PWA, then WebAPKs, to steal the banking credentials of their victims. This evolution showcases the attackers’ dedication and elevated effort in executing their fraudulent operations.
Whereas we’ve got recognized and totally examined one particular assault situation, it’s essential to notice that theoretically there might be further misuse circumstances. These might contain the cloning of bodily playing cards or accessing NFC tokens, which might probably amplify the menace and its impacts.
This crimeware marketing campaign was targeted on Czechia and is at the moment on maintain, possible because of the arrest of a suspected perpetrator. Nonetheless, the potential of its growth into different areas or nations can’t be dominated out. Moreover, the arrest of 1 participant with substantial money readily available gives tangible proof of the real-world penalties of those “digital” crimes. Due to this fact, it’s important to stay conscious of social engineering ways, keep cautious on-line, and use sturdy cell safety apps.
For any inquiries about our analysis revealed on WeLiveSecurity, please contact us at threatintel@eset.com.ESET Analysis presents non-public APT intelligence reviews and information feeds. For any inquiries about this service, go to the ESET Menace Intelligence web page.
IoCs
A complete checklist of Indicators of Compromise (IoCs) and samples will be present in our GitHub repository.
Recordsdata
|
SHA-1 |
Filename |
Detection |
Description |
|
7225ED2CBA9CB6C038D8 |
csob_smart_klic.apk |
Android/Spy.NGate.B |
NGate Android malware. |
|
66DE1E0A2E9A421DD16B |
csob_smart_klic.apk |
Android/Spy.NGate.C |
NGate Android malware. |
|
DA84BC78FF2117DDBFDC |
george_klic.apk |
Android/Spy.NGate.C |
NGate Android malware. |
|
E7AE59CD44204461EDBD |
george_klic-0304.apk |
Android/Spy.NGate.C |
NGate Android malware. |
|
103D78A180EB973B9FFC |
rb_klic.apk |
Android/Spy.NGate.A |
NGate Android malware. |
|
11BE9715BE9B41B1C852 |
rb_klic.apk |
Android/Spy.NGate.C |
NGate Android malware. |
Community
|
IP |
Area |
Internet hosting supplier |
First seen |
Particulars |
|
91.222.136[.]153 |
raiffeisen-cz[.]eu |
Internet hosting Ukraine LTD |
2024‑03‑05 |
NGate distribution web site. |
|
104.21.7[.]213 |
shopper.nfcpay.staff[.]dev |
Cloudflare, Inc. |
2024‑03‑03 |
Phishing web site. |
|
172.187.98[.]211 |
N/A |
Divya Quamara |
2024‑04‑07 |
NGate C&C server. |
|
185.104.45[.]51 |
app.mobil-csob-cz[.]eu |
Internet hosting Ukraine LTD |
2024‑03‑12 |
NGate distribution web site. |
|
185.181.165[.]124 |
nfc.cryptomaker[.]information |
Serverius |
2024‑02‑21 |
NGate C&C server. |
MITRE ATT&CK methods
This desk was constructed utilizing model 15 of the MITRE ATT&CK framework.
|
Tactic |
ID |
Title |
Description |
|
Preliminary Entry |
Phishing |
NGate has been distributed utilizing devoted web sites impersonating reputable providers. |
|
|
Credential Entry |
Enter Seize: GUI Enter Seize |
NGate tries to acquire victims’ delicate data through a phishing WebView pretending to be a banking service. |
|
|
Discovery |
System Data Discovery |
NGate can extract details about the system together with system mannequin, Android model, and details about NFC. |
|
|
Command and Management |
Software Layer Protocol: Net Protocols |
NGate makes use of a JavaScript interface to ship and execute instructions to compromised units. |
|
|
Non-Commonplace Port |
NGate makes use of port 5566 to speak with its server to exfiltrate NFC visitors. |
||
|
Out of Band Knowledge |
NGate can exfiltrate NFC visitors. |


