Regulating NETs ranges would possibly emerge as a novel therapeutic method for sepsis
On the medical degree, this research enrolled sufferers identified with sepsis in accordance with Sepsis 3.0 standards, in addition to wholesome volunteers. The detection outcomes confirmed that the degrees of CitH3-DNA and MPO-DNA complexes, which had been particular biomarkers of NETs, had been considerably elevated within the peripheral blood of septic sufferers (Fig. 1A-B). Concurrently, the degrees of inflammatory cytokines IL-1β and TNF-α had been additionally considerably elevated within the peripheral blood of septic sufferers (Fig. 1C-D). Furthermore, there was a big correlation between NET biomarkers and inflammatory cytokines (Fig. 1E-H). Additional analysis had revealed a big correlation between the rise in NETs ranges and the elevation of SOFA scores in addition to APACHE II scores (Fig. 1I-L). Due to this fact, based mostly on the aforementioned outcomes, we might conclude that there was an in depth correlation between neutrophil extracellular traps ranges and sepsis. Consequently, regulating the degrees of NETs might characterize a novel therapeutic technique for the therapy of sepsis.
NETs and inflammatory components in peripheral blood had been elevated in sufferers with sepsis. (A-B) The MPO-DNA and CitH3-DNA concentrations within the plasma from management and sufferers with sepsis had been decided (n = 20). (C-D) ELISA to detect the concentations of cytokine IL-1β and TNF-α in management and sepsis group (n = 20). (E-H) Pearson correlation evaluation of IL-1β, TNF-α and MPO-DNA and CitH3-DNA, respectively. (I-L) Pearson correlation evaluation of SOFA, APACHE II rating and MPO-DNA and CitH3-DNA, respectively. All the information in A-D are introduced because the imply ± SD. P < 0.05 point out important variations
Astragaloside IV achieved important protecting results for each CLP-induced and LPS-induced sepsis mice
Within the quest to find new medicine able to modulating NETs ranges for the therapy of sepsis, we’ve screened varied bioactive parts from conventional natural medicines. Amongst these parts, Astragaloside IV-As is a small molecular saponin extracted from the roots of Astragalus membranaceus, a key energetic constituent of the herb, famend for its potent anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic properties. In subsequent experimental research, As has demonstrated promising potential in regulating NETs and treating septic mice.
The structural components of As is proven in Determine S1. To discover the potential position of As within the therapy of sepsis, we established two sepsis fashions: a bacterial sepsis mannequin (induced by CLP) and endotoxemic shock mannequin (induced by LPS). For the primary 3 days earlier than mannequin institution, we administered the drug to mice as soon as day by day through intraperitoneal injection at a dose of 20 mg/kg. After mannequin institution, we collected peripheral blood samples from mice at 12 h and tissue samples from lung, liver, and kidney at 24 h. We additionally constantly monitored the survival standing of mice and plotted a 7-day survival curve (Fig. 2A). To find out the optimum therapeutic dose of As, we carried out an in vivo research with dose gradients starting from 0 to 40 mg/kg. Via H&E staining and lung damage scoring, we noticed important pathological harm in lung tissues of CLP mannequin mice together with bleeding, edema, inflammatory cell infiltration, and tissue disorganization. After therapy with As, these accidents had been alleviated to some extent, particularly within the group handled with a dose of 20 mg/kg the place lung damage enchancment was most important (Fig. 2B-C). Afterwards, we additional investigated the therapeutic impact of As on sepsis utilizing a dose of 20 mg/kg. Firstly, within the CLP mannequin mice, we analyzed and plotted the 7-day survival curve. The outcomes confirmed that the 7-day survival charge of mice within the CLP + Mock group was 35.0% (7/20), whereas it was 50.0% (10/20) within the CLP + As group, indicating that As therapy improved the 7-day survival charge of CLP mice (Fig. 2D). Subsequent, to discover the impact of As therapy on systemic inflammatory response in CLP mice, we measured ranges of inflammatory components in peripheral blood utilizing ELISA. The outcomes confirmed that in comparison with the Sham + Mock group, ranges of TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-6 had been considerably elevated within the CLP + Mock group mice, whereas they had been decrease within the CLP + As group than within the CLP + Mock group, indicating that As therapy diminished ranges of inflammatory components in peripheral blood of CLP mice (Fig. 2E-G). To additional examine the results of As therapy on the organ harm in CLP-induced septic mice, we utilized H&E staining and assessed the severity of lung damage within the mice by lung damage scoring and the protein focus in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) (Determine S2, Fig. 2H-I). Moreover, we measured the degrees of ALT and AST via blood biochemical checks to judge the extent of liver damage (Fig. 2J-Ok). Equally, the severity of kidney damage was assessed by figuring out the degrees of creatinine and blood urea nitrogen (BUN) within the serum (Fig. 2L-M). The outcomes confirmed that in comparison with Sham + Mock group, detailed lung damage scores in addition to liver and kidney harm had been aggravated in CLP + Mock group mice; whereas As therapy alleviated main organ harm severity in CLP mice (Fig. 2H-M). The identical outcomes had been noticed in LPS-induced mouse fashions (Fig. 2N-Q). Due to this fact, we concluded that As therapy not solely improved the short-term survival charge of septic mice, but in addition successfully diminished their systemic inflammatory response and harm to main organs.
Astragaloside alleviated the harm of vital goal organs in septic mice. (A) Schematic illustration of the animal experimental through which Astragaloside was IP injected 3 days earlier than the mice had been subjected to CLP or LPS IP injection and the animals had been euthanized after 12 h, 1 days or 7 days. (B) H&E staining to look at the pathological construction of lung tissue in CLP mice handled with completely different concentrations of As. The field confirmed a 200X magnification of the placement (n = 5). Scale bars = 50 μm. (C) Smith rating of lung tissue to find out the optimum performing focus of As (n = 5). (D) Survival curves of mice in several therapy teams (n = 20). (E-G) ELISA was used to detect the degrees of the TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-6 within the plasma of mice in Sham + Mock, Sham + As, CLP + Mock and CLP + As teams (n = 5). (H-I) lung damage index Smith rating and BALF protein focus and (J-Ok) liver damage index ALT and AST concentrations and (L-M) kidney damage index creatine and BUN concentrations within the plasma from mice in Sham + Mock, Sham + As, CLP + Mock and CLP + As teams had been decided (n = 5). (N) Survival curves of mice in Con + Mock, Con + As, LPS + Mock and LPS + As teams (n = 20). (O-Q) ELISA was used to detect the degrees of the TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-6 within the plasma of mice in Con + Mock, Con + As, LPS + Mock and LPS + As teams (n = 5). The info are expressed as imply ± SD. P < 0.05 point out important variations
Astragaloside IV successfully diminished the excessive ranges of NETs attributable to sepsis
Following a complete evaluation of the therapeutic results of As on sepsis, we intend to delve deeper into the underlying mechanisms of its potential therapy. Within the research depicted in Fig. 1, we noticed that the degrees of NETs within the peripheral circulation of sufferers with sepsis had been considerably increased than these within the wholesome management group. Furthermore, the degrees of NETs had been positively correlated with the depth of the physique’s inflammatory response. This discovery underscores the pivotal position of NETs within the etiology and development of sepsis. Constructing on this basis, we plan to look at the influence of As on the degrees of NETs in sepsis sufferers and discover the mechanisms behind its therapeutic motion.
We labeled neutrophils with ly6G and used immunohistochemical staining to research the lung tissues of CLP mice, we noticed a big enhance in neutrophil infiltration within the CLP + Mock group in comparison with the Sham + Mock group. Within the CLP + As group of mice that acquired As therapy, the diploma of this neutrophil infiltration was diminished (Fig. 3A-B). Subsequently, the degrees of NETs biomarkers – CitH3-DNA complexes and MPO-DNA complexes in peripheral blood samples from CLP-induced septic mice had been detected by ELISA. The outcomes confirmed that As therapy successfully diminished the elevated ranges of NETs induced by CLP (Fig. 3C-D). Moreover, an identical lower impact was additionally noticed within the LPS-induced sepsis mannequin (Fig. 3E-F). Moreover, immunofluorescence outcomes confirmed that in contrast with the Sham + Mock group, the fluorescence ranges of CitH3 and MPO within the lung tissues of mice within the CLP + Mock group had been considerably elevated, whereas the fluorescence ranges of CitH3 and MPO within the CLP + As group had been diminished (Fig. 3G-I).
Astragaloside alleviated NETs in mice with sepsis. (A-B) The variety of neutrophils in lung tissue was detected by Ly6G immunohistochemistry in Sham + Mock, CLP + Mock, Sham + As and CLP + As teams. The field confirmed a 200X magnification of the placement. Scale bars = 50 μm. (C-F) The MPO-DNA and CitH3-DNA concentrations within the plasma from mice after sepsis induction by CLP or LPS handled with or with out 20 mg/kg As. (G-I) Consultant photographs and statistical outcomes of immunofluorescence staining of MPO and CitH3 in lung tissue sections from Sham + Mock, CLP + Mock, Sham + As and CLP + As teams. Scale bars = 50 μm. The info are expressed as means ± SD, n = 5 per group. P < 0.05 point out important variations
Synthesizing the aforementioned findings, we had totally validated via in vivo experiments that As might scale back the degrees of NETs in septic mice. Nevertheless, to additional affirm the results of As, extra in vitro validation is required. To find out the optimum in vitro therapeutic dosage of As, we carried out in vitro research utilizing a spread of concentrations, particularly a gradient of 0, 10, 20, 30, and 40 µg/mL. The research discovered that As at concentrations of 10 µg/mL and 20 µg/mL had no important impact on the proliferation of MLE12 cells, whereas As at concentrations of 30 µg/mL and 40 µg/mL exhibited a sure inhibitory impact on the proliferation of MLE12 cells (Determine S3). Primarily based on these findings, we chosen the 20 µg/mL dosage of As to additional discover its regulatory impact on NETs via in vitro experiments. We utilized two kinds of neutrophils (PBNs and dHL60), subjecting them to corresponding therapies. After 24 h, we collected the cell tradition supernatants and carried out assays for inflammatory cytokines and NETs (Fig. 4A). The outcomes indicated that underneath LPS stimulation, PBNs produced increased ranges of inflammatory cytokines, together with TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-6, whereas therapy with As diminished the excessive expression of those cytokines (Fig. 4B-D). The experimental outcomes of dHL60 cells had been in keeping with these of PBNs (Fig. 4E-G). Moreover, we measured the NETs biomarkers within the supernatants, together with CitH3-DNA complexes and MPO-DNA complexes. The findings confirmed that underneath LPS stimulation, the degrees of NETs produced by PBNs considerably elevated, and therapy with As equally diminished the excessive ranges of NETs induced by LPS (Fig. 4H-I). The outcomes of dHL60 cells additionally demonstrated a constant development (Fig. 4J-Ok). Primarily based on the outcomes from each in vitro and in vivo experiments, we might conclude that As might scale back the elevated ranges of NETs induced by sepsis.
Astragaloside inhibited NETs and inflammatory response in vitro. (A) Diagram of neutrophil tradition supernatant assortment through which PBNs or dHL60 cells had been added with or with out LPS or As for twenty-four h after which amassing cell tradition supernatant to detect cytokins or for subsequent experiments. (B-G) Concentrations of TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6 launched into PBNs and dHL60 cell tradition supernatants had been detected by ELISA in Con + Mock, LPS + Mock, Con + As and LPS + As teams. (H-Ok) Concentrations of CitH3-DNA and MPO-DNA in tradition supernatants of PBNs and dHL60 cells with completely different therapies had been decided. The info are expressed as imply ± SD, n = 5 per group. P < 0.05 point out important variations
Astragaloside IV regulated the discharge of NETs by focusing on IκBα to inhibit the NF-κB signaling pathway
Subsequent, we used community pharmacology to seek for doable targets of As motion on sepsis. We used key phrase “Sepsis” to seek for sepsis-related genes in OMIM, CTD, GeneCards and GEO databases. Venne diagram confirmed DEGs that| log2 FC| ≥1.0 and FDR < 0.05 in GSE54514 and genes in OMIM, CTD (scores > 20) and GeneCards (scores > 20) databases (Fig. 5A). We included genes that appeared no less than twice. A complete of 374 genes had been recognized as goal genes related to sepsis. Subsequent, the Smile model of As was obtained on Pubchem, and the Smile model was imported into SwissTargetPrediction and SuperPred databases to acquire a complete of 266 therapeutic targets of As after eradicating duplicate targets. Virtually 31 goal genes of As within the therapy of sepsis had been obtained by intersection of the 2 (Fig. 5B). The 31 goal genes had been enter into the string database, and Cytoscape software program was used to assemble the PPI community. A complete of seven Hub targets had been obtained, together with TLR4, NFκB1, SRC, AKT1, HIF1A, CASP3 and STAT3 (Fig. 5C).
TLR4, sensing of LPS, probably the most potent pathogen-associated molecular sample of gram-negative micro organism, prompts NF-κB and Irf3, which induces inflammatory cytokines and interferons that set off an intense inflammatory response, which is essential for the pathogenesis of sepsis [18]. Given the significance of NF-κB signaling within the pathogenesis of sepsis, we examined the expression of NF-κB pathway associated proteins in neutrophils. Western blotting evaluation revealed that LPS therapy considerably elevated the phosphorylation ranges of IKKα, IκBα, and P65 in whole proteins, and in addition elevated the extent of P65 in nuclear proteins. Nevertheless, therapy with As diminished the degrees of p-IκBα and p-P65 in whole proteins, in addition to the extent of P65 in nuclear proteins. Apparently, there appeared no important impact on the p-IKKα ranges (Fig. 5D-H). Due to this fact, As might inhibit the NF-κB signaling pathway in neutrophils throughout sepsis. On condition that As therapy didn’t have an effect on the extent of p-IKKα, however considerably influenced the p-IκBα and the translocation of P65 into the nucleus, we hypothesized that As would possibly regulate the NF-κB signaling pathway by focusing on the IκBα.
Astragaloside regulated NETs via NF-κB signaling. (A) Venn diagram evaluation of sepsis-related genes predicted by the GeneCards, CTD, OMIM and GEO databases. (B) Venn diagram evaluation of sepsis-related genes and targets of Astragaloside predicted by SuperPred and SwissTargetPrediction databases. (C) PPI community evaluation of goal genes of Astragaloside and sepsis by Cytoscape. The colour adjustments step by step from yellow to purple; the nearer to the purple goal gene, the extra vital it’s. (D-H) Consultant protein bands and statistical values for Nuclear P65 and whole p-p65, p65, IKKα, p-IKKα, IκBα and p-IκBα. The info are expressed as imply ± SD, n = 3 per group. P < 0.05 point out important variations
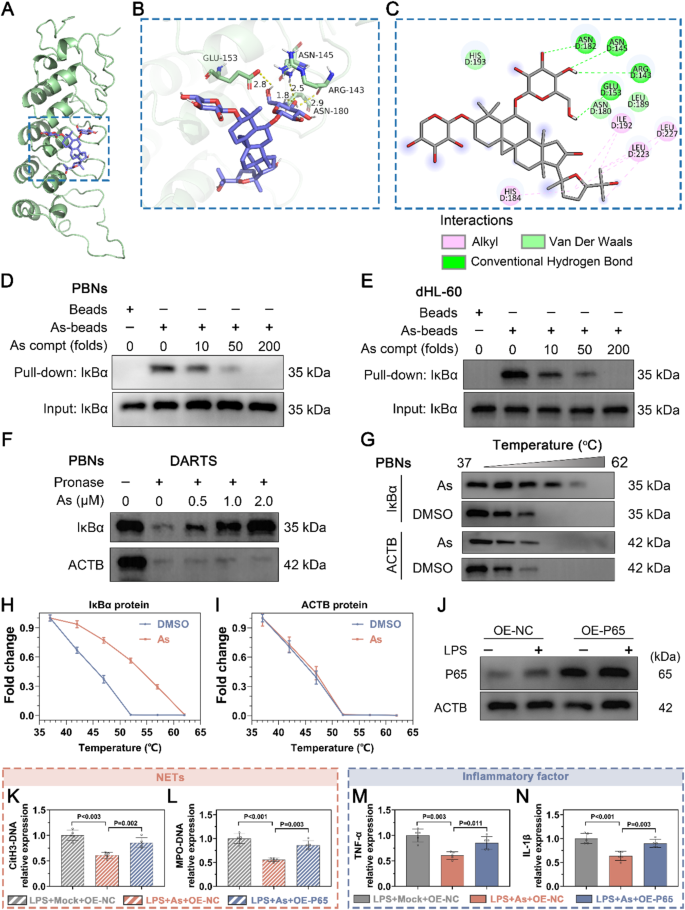
Docking simulation know-how is a handy and efficient technique for learning the interactions between small molecules and their goal websites. On this research, we employed the Vina 1.1.2 software program to conduct a molecular docking research of the binding between As and the IκBα. Our evaluation yielded a binding mode diagram of As with the IκBα, the place the small molecule As was nestled inside a central groove of the protein (Fig. 6A). As shaped hydrogen bonds with amino acid residues GLU-153, ASN-145, ARG-143, and ASN-182 on the protein. Moreover, As engaged in hydrophobic interactions with residues ILE-192, LEU-227, LEU-223, and HIS-184 on the protein (Fig. 6B-C). The docking rating is a crucial indicator of the binding vitality between a small molecule and a protein, with a rating beneath − 5 kcal/mol usually suggesting a powerful binding affinity. On this research, the docking rating for the As-IκBα protein complicated was − 6.264 kcal/mol (Desk S3), indicating that the binding mode was believable and that As had potential organic exercise towards IκBα.
Astragaloside IV might bind to IκBα. (A-B) Consultant photographs of the docking mode of As binding to IκBα. (C) The potential connection websites between As and IκBα. (D-E) PBNs cells and their lysates had been incubated with As-biotin, adopted by pull-down assay utilizing streptavidin beads. The outcomes confirmed immunoblot evaluation of the IκBα protein. (F) After incubation with As, the lysates of PBNs cells had been handled with proteinase Ok. The outcomes demonstrated immunoblot evaluation of each IκBα and ACTB proteins. (G) CETSA assay to substantiate binding of As to IκBα. (H-I) introduced consultant blot and protein outcomes. (J) Consultant blots of P65 overexpression in PBN cells. (Ok-N) PBN cells had been transfected with P65 overexpression or NC plasmid for twenty-four h and added with or with out As together with LPS to steady cultivation for twenty-four h, then the focus of NETs and inflammatory components within the supernatant had been detected. (Ok-L) Concentrations of CitH3-DNA and MPO-DNA from three teams. (M-N) Concentrations of TNF-α and IL-1β from three teams. The info are expressed as imply ± SD, (n = 3 for D-J, n = 5 for Ok-N). P < 0.05 point out important variations
To discover the interplay between As and IκBα, we synthesized biotin-labelled As probe (biotin-As) for pull-down evaluation. The outcomes confirmed that IκBα was considerably pulled down by As-beads, and this course of might be blocked by an extra of As (Fig. 6D-E). Moreover, we discovered that in Drug Affinity Responsive Goal Stability (DARTS) evaluation, As particularly focused IκBα to inhibit the proteolytic exercise of trypsin (Fig. 6F). Equally, in CETSA, As considerably prevented the degradation of IκBα protein, however had no impact on the ACTB protein (Fig. 6G-I).
In an effort to confirm the mechanism by which As regulated the extent of NETs by inhibiting the NF-κB signaling pathway, we carried out a collection of rescue experiments. We transfected P65 overexpression plasmids into PBNs cells and confirmed profitable overexpression of P65 via Western blotting evaluation (Fig. 6J and Determine S4). As proven in Fig. 6Ok-L, As therapy might scale back LPS-induced excessive ranges of NETs, together with CitH3-DNA complexes and MPO-DNA complexes, whereas overexpression of P65 might block this discount impact of As. In the meantime, we discovered that As therapy additionally diminished excessive ranges of LPS-induced TNF-α and IL-1β, whereas overexpression of P65 might counteract this anti-inflammatory impact of As (Fig. 6M-N). Due to this fact, As certainly might regulate the discharge of NETs by inhibiting NF-κB signaling pathway. The above outcomes confirmed that As focused IκBα to suppress the activation of NF-κB signaling, thereby regulating the degrees of NETs in sepsis.
Neutrophils handled with Astragaloside IV down-regulated tissue cells oxidative stress and loss of life
Organ damage typically includes the co-involvement of epithelial cells, endothelial cells and immune cells. It had been confirmed that elevated NETs typically exert poisonous results on different cells. Subsequent, we collected the supernatant of PBNs cell tradition after 24 h of therapy from every group and used it for conditioned tradition of MLE12 cells (Fig. 7A). Concurrently, the supernatant from dHL60 cell was collected for conditioned tradition of HUVEC. Commentary of MLE12 cell loss of life utilizing a dwell/lifeless cell staining assay clearly confirmed a big enhance within the variety of lifeless cells within the LPS + Mock group, whereas the variety of lifeless cells decreased after therapy with As (LPS + As group) (Fig. 7B). Moreover, the CCK-8 assay outcomes indicated that cell proliferation was markedly inhibited within the LPS + Mock group, and there was a restoration in cell proliferation capability after therapy with As (LPS + As group) (Fig. 7C-D).
As handled neutrophils inhibited apoptosis and oxidative stress of lung epithelial cells. (A) Schematic illustration of neutrophil supernatant treating tissue cells. Neutrophils with completely different therapies had been cultured for twenty-four h after which changed with contemporary medium. After continued tradition for twenty-four h, supernatant was collected by centrifuge after which used as conditioned medium (CM). HUVEC or MLE12 cells had been added into CM and contemporary medium of 1:1 for tradition for twenty-four h to detect oxidative stress and apoptosis, and to detect cell proliferation for twenty-four–72 h. (B) Consultant staining of dwell and lifeless cell staining of MLE12 cells. The field reveals a 400X magnification of the placement. Scale bars = 100 μm–50 μm. (C-D) CCK-8 assay to detect cell proliferation of HUVEC and MLE12 cells in several teams. (E) DCFH-DA-stained MLE12 cells had been examined through stream cytometry, which additionally represented the ROS content material within the cells. Within the consultant photographs of stream, the vertical coordinate represented the variety of cells and the horizontal coordinate represented the fluorescence depth of DCFH-DA. (F) Quantitative values of DCFH-DA fluorescence depth. (G-J) The degrees of GSH, SOD, CAT and MDA in MLE12 cells, which represented oxidative stress, had been measured. The info are expressed as imply ± SD, n = 5 per group. P < 0.05 point out important variations
To research whether or not As mitigated tissue cell harm in sepsis by regulating NETs, we carried out a collection of rescue experiments. Initially, PAD4 overexpression plasmids had been transfected into PBNs cells, and the profitable overexpression of PAD4 was confirmed utilizing Western blotting know-how (Determine S5A-B). As proven in Determine S5C-F, overexpression of PAD4 attenuated the inhibitory impact of AS on CitH3-DNA, MPO-DNA, TNF-α, and IL-1β. Moreover, we collected the supernatant from PBNs and dHL60 cells within the LPS + Mock + OE-NC group, LPS + As + OE-NC group, and LPS + As + OE-PAD4 group to deal with MLE12 and HUVEC cells. CCK-8 assay outcomes confirmed that the cell proliferation charge of the LPS + As + OE-NC group was increased than that of the LPS + Mock + OE-NC group, whereas the cell proliferation charge of the LPS + As + OE-PAD4 group was decrease than that of the LPS + As + OE-NC group (Determine S5G-H). In view of the regulatory impact of NF-κB on NETs, we additional handled HUVEC and MLE-12 cells with neutrophil CM overexpressing P65. The CCK-8 experiment additional proved our conclusion, through which the cell proliferation charge of the LPS + As + OE-P65 group was considerably decrease than that of the LPS + As + OE-NC group (Determine S6A-B).
To additional discover the underlying mechanisms of neutrophils harm tissue cells, we continued to deal with MLE-12 cells with CM. Determine 7E-F confirmed considerably enhance of ROS ranges in LPS + Mock MLE12 cells, which was diminished in LPS + As group. Subsequently, to evaluate the harm to the cells’ antioxidant capability, glutathione (GSH), superoxide dismutase (SOD), and catalase (CAT) had been measured in MLE12 cells after conditional tradition handled in every group. The outcomes indicated that the conditional tradition of the LPS + Mock group led to a lower in GSH ranges and a discount in SOD and CAT enzyme actions inside MLE12 cells, whereas the conditional tradition following As therapy (LPS + As group) partially restored these indicators (Fig. 7G-I). Lastly, we analyzed the extent of lipid peroxidation inside the cells by measuring the content material of malondialdehyde (MDA). The outcomes confirmed that the conditional tradition of the LPS + Mock group considerably elevated the extent of MDA inside MLE12 cells, whereas the conditional tradition following As therapy (LPS + As group) diminished these ranges (Fig. 7J). In abstract, As, modulating the degrees of NETs, alleviated the oxidative stress-induced harm and loss of life.
Preparation and characterization of ZIF-8, As@Z, and As@ZM
In an effort to enhance the steadiness and bioavailability of As, it was pressing to develop new supplies based mostly on As. Metallic-organic frameworks (MOFs) are supplies composed of metallic ions, clusters, or natural linkers. Within the area of drug supply, MOFs, as rising carriers, have demonstrated their excessive drug-loading capability, ease of floor modification, and the flexibility to realize managed drug launch. Zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 (ZIF-8), a member of the zeolitic imidazolate frameworks (ZIFs), is primarily composed of zinc ions and 2-methylimidazole (2-MIM). On this research, we utilized ZIF-8 as a service for the supply of astragaloside IV (As), and coated the outermost layer with a neutrophil membrane. Utilizing this technique, we ready three kinds of nanoparticles: ZIF-8, As-loaded ZIF-8 (As@ZIF-8, abbreviated as As@Z), and neutrophil membrane-coated As@Z (As@ZIF-8/Neutrocyte membrane, abbreviated as As@ZM). The preparation course of of those nanoparticles was depicted in Fig. 8A. The structural components of As was displayed in Determine S1. Throughout the synthesis of As@ZM, we noticed via the encapsulation effectivity (LE) and encapsulation charge (EE) check outcomes that the dosage of 20 mg/mL of As achieved the optimum ranges of LE and EE, thus being chosen as the popular dosage for subsequent synthesis (Determine S7). The morphology of ZIF-8 and As@ZM was noticed utilizing SEM (Fig. 8B). The outcomes confirmed that ZIF-8 exhibited a hexagonal construction with sharp edges, whereas As@ZM nanoparticles appeared extra rounded, tending in the direction of a spherical or elliptical form. Additional remark utilizing TEM (Fig. 8C) revealed that As@ZM had a typical core-shell construction with a mean coating thickness of roughly 20 nm. We additional measured the zeta potential and hydrated particle dimension of ZIF-8, As@Z, and As@ZM nanoparticles. The outcomes confirmed that the zeta potential of ZIF-8 was 22.02 mV, whereas that of As@ZM was − 18.48 mV (Fig. 8D). The lower in potential might be attributed to the negatively charged nature of the cell membrane, and this decrease detrimental potential was helpful for the nanoparticles to keep up suspension, dispersion, and stability within the bloodstream. The hydrated particle dimension elevated from 201.56 nm for ZIF-8 to 227.62 nm for As@ZM (Fig. 8E), with this enhance in particle dimension primarily because of the coating of the outer cell membrane. The presence of cell membrane proteins in As@ZM was additional confirmed by SDS-PAGE. The outcomes indicated that As@ZM displayed a protein spectrum similar to that of the neutrophil membrane, suggesting that As@ZM nanoparticles had been efficiently encapsulated by the neutrophil membrane (Fig. 8F). Thermogravimetric evaluation (TGA) confirmed a gradual enhance within the natural element content material of ZIF-8, As@Z, and As@ZM (Fig. 8G). Moreover, we monitored the adjustments in hydrated particle dimension of the nanoparticles in PBS over a 7-day interval. The outcomes confirmed that the particle sizes of ZIF-8, As@Z, and As@ZM nanoparticles solely barely decreased over the 7-day remark interval (Fig. 8H), indicating that the ready nanoparticles had excessive physicochemical stability in PBS answer. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) evaluation additional confirmed the presence of carbon (C), nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), sulfur (S), oxygen (O), and zinc (Zn) in As@ZM (Fig. 8I). Primarily based on these experimental outcomes, we might conclude that ZIF-8, As@Z, and As@ZM nanoparticles had been efficiently ready, they usually all exhibited good physicochemical stability.
Preparation and characterization of ZIF-8, As@Z, and As@ZM. (A) Schematic illustration of the synthesis of As@ZM. (B) SEM photographs of ZIF-8 and As@ZM (low magnification scale bar: 500 nm, excessive magnification scale bar: 100 nm). (C) TEM photographs of As@ZM (low magnification scale bar: 200 nm, excessive magnification scale bar: 50 nm). (D) Zeta potentials of the completely different nanoparticles and (E) hydrated particle sizes. (F) SDS-PAGE protein evaluation of the Neutrophil membrane, As@Z, and As@ZM. (G) Thermogravimetric evaluation (TGA) curves of ZIF-8, As@Z, and As@ZM. (H) Adjustments in hydrated particle dimension of ZIF-8, As@Z, and As@ZM over 7 days. (I) XPS spectrum of R@ZQC. All the information in D, E, and H are introduced because the imply ± SD, n = 5 per group. P < 0.05 point out important variations
As@ZM exhibited good biocompatibility, the flexibility to particularly goal neutrophils, and managed launch traits of As
Good biocompatibility is all the time thought-about a basic requirement for the biomedical purposes of nanomaterials. To guage the biocompatibility of the biomimetic nanoparticles (As@ZM) we ready, we co-cultured As@ZM nanoparticles at varied focus gradients (10, 20, 30, 40 µg/mL) with diluted mouse blood to evaluate whether or not As@ZM would trigger hemolysis. The experimental outcomes confirmed that at a focus of 20 µg/mL, the hemolysis charge attributable to As@ZM nanoparticles was 2.47% (± 1.38%), which was not considerably completely different from the hemolysis charge of the detrimental management group. This indicated that As@ZM nanoparticles at concentrations of 20 µg/mL and beneath basically didn’t trigger hemolysis and exhibited good biocompatibility (Fig. 9A-B). Moreover, we administered As@ZM nanoparticles at various focus gradients (10, 20, 30, 40 mg/kg) through tail vein injection into mice and picked up the principle organs (coronary heart, liver, and kidneys) for H&E staining after two weeks. The outcomes confirmed no pathological adjustments in these main organs in any respect examined concentrations, additional confirming the wonderful in vivo security profile of As@ZM nanoparticles (Fig. 9C).
As@ZM exhibited good biocompatibility, the flexibility to particularly goal neutrophils, and managed launch traits of As. (A-B) Consultant pictures of diluted blood samples after varied therapies, together with quantitative evaluation of the hemolysis charge. (C) H&E staining photographs of main organs similar to the guts, liver, and kidney two weeks publish completely different therapies (Scale bar: 100 μm). (D) Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy (CLSM) photographs of varied cell traces incubated with FITC-labeled As@Z nanoparticles or As@ZM nanoparticles for 4 h (Scale bar: 50 μm). (E) Three hours after the mice underwent sham surgical procedure or CLP surgical procedure, they had been injected with anti-Ly6G antibody (purple) and FITC-labeled nanoparticles (inexperienced) through the tail vein. Thirty minutes later, the lung tissues of the mice had been collected for fluorescence detection. (F) Consultant two-dimensional depth histogram from Figur 9E. The y-axis represents the depth of inexperienced pixels above zero (FITC-labeled nanoparticles). The x-axis represents the depth of purple pixels above zero (neutrophils). (G) In vitro launch profile of As from As@Z and As@ZM handled with PBS inside 48 h. All the information in B, and E are introduced because the imply ± SD, n = 5 per group. P < 0.05 point out important variations
After confirming the profitable synthesis of As@ZM nanoparticles with secure physicochemical properties and good biocompatibility, we additional explored the potential benefits of As@ZM nanoparticle therapy over the only use of As therapy. We first investigated the focusing on of As@ZM nanoparticles to neutrophils. The outcomes exhibit that, in comparison with the PBS management group, each RAW 264.7 and PBNs cells exhibit elevated fluorescence depth after incubation with As@Z and As@ZM (Fig. 9D). Notably, for RAW 264.7 cells, the fluorescence depth is analogous between the As@Z and As@ZM therapy teams. Nevertheless, PBNs cells handled with As@ZM present considerably increased fluorescence depth in comparison with these handled with As@Z (Fig. 9D), confirming the particular focusing on of neutrophils by As@ZM in vitro.
Moreover, we’ve carried out immunofluorescence staining of lung tissues to confirm the focusing on capacity of As@ZM to neutrophils in vivo. The purple fluorescence alerts (representing neutrophils stained with Ly6G) within the lung tissues of all sham-operated mice are virtually similar. Equally, the purple fluorescence alerts within the lung tissues of all mice present process CLP surgical procedure are comparable. Importantly, the purple fluorescence is markedly elevated within the CLP group in comparison with the sham group, indicating enhanced neutrophil infiltration within the lung tissues of CLP mice. Crucially, the inexperienced fluorescence depth within the CLP + As@ZM group is considerably increased than that within the CLP + As@Z group (Fig. 9E). Additional evaluation reveals minimal colocalization between neutrophils and As@Z nanoparticles, whereas a excessive diploma of colocalization is noticed between neutrophils and As@ZM (Fig. 9F and S8). These findings additional substantiate the focusing on capacity of As@ZM to neutrophils in vivo.
Moreover, we analyzed the discharge traits of As from As@Z and As@ZM nanoparticles. The discharge of As was successfully managed via the encapsulation by the ZIF-8 service and the neutrophil membrane (Fig. 9G). This helped to cut back the fluctuations within the blood focus of As in mice, sustaining the blood focus inside an efficient and low facet impact vary for an extended interval, thereby bettering the therapeutic impact whereas decreasing unintended effects. We additional investigated the particular results of nanoparticles on the steadiness and bioavailability of As. The soundness of As within the nanoparticles was assessed by measuring the retention charge after long-term storage (30 days at 25 °C underneath pure mild), high-temperature therapy (50–90 °C), and UV mild publicity. The outcomes indicated that the steadiness of As was improved in each As@Z and As@ZM nanoparticles, with As@ZM exhibiting much more important enhancement (Determine S9 A-C). Moreover, we evaluated the bioavailability of As in mice after intravenous injection of As, As@Z, and As@ZM nanoparticles. The outcomes confirmed that the AUC0-t for As was 12.19 ± 1.01 (µg/mL)·h, whereas the AUC0-t for As@Z and As@ZM had been 14.94 ± 0.58 and 18.02 ± 0.88 (µg/mL)·h, respectively (Determine S9D, Desk S4). This means that the bioavailability of As@Z and As@ZM was 1.26 and 1.48 instances that of As alone.
Primarily based on the above experimental outcomes, we might conclude that we had efficiently synthesized As@ZM nanoparticles, which exhibited secure physicochemical properties and good biocompatibility. In contrast with the therapy utilizing As alone, As@ZM nanoparticles exhibit a number of benefits similar to focusing on neutrophils, regulating the discharge of As, considerably enhancing the steadiness of As, and successfully bettering the bioavailability of As. These traits endow them with potential broad prospects for medical software.
The therapeutic efficacy of As@ZM nanoparticles within the therapy of sepsis was superior to that of monotherapy with As
After an in-depth investigation of the biocompatibility and distinctive benefits of As@ZM nanoparticles, we additional explored their therapeutic results on a sepsis mouse mannequin. CLP mouse had been administered with drug or nanoparticles through tail vein injection as soon as day by day for 3 days previous to the surgical procedure at a dosage of 20 mg/kg. Peripheral blood was collected from the mice 12 h post-surgery, and lung, liver, and kidney tissues had been harvested 24 h post-surgery. Mouse survival was constantly monitored and recorded, and a 7-day survival curve was plotted (Fig. 10A). Initially, we analyzed and plotted the 7-day survival curve of the mice. The outcomes confirmed that the 7-day survival charge of the mice within the CLP surgical procedure group handled with As alone was 50.0% (10/20), whereas the survival charge within the As@ZM therapy group reached 65.0% (13/20), demonstrating that As@ZM was simpler in bettering the 7-day survival charge of CLP-induced septic mice than As monotherapy (Fig. 10B). In the meantime, IF and ELISA outcomes indicated that As@ZM was simpler in inhibiting NETs ranges and cytokines in CLP-induced septic mice than As monotherapy (Fig. 10C-H). The extent of organ harm in CLP-induced septic mice (lung, liver, kidney) was assessed utilizing H&E staining, lung damage scoring, protein content material in BALF, ALT, AST, creatinine, BUN, and different indicators. The outcomes additional confirmed that As@ZM was simpler in decreasing organ harm in comparison with As monotherapy (Fig. 10I-J, Determine S10A-E). Moreover, we carried out in vitro experiments to evaluate the therapeutic potential of As@ZM nanoparticles towards cell harm induced by NETs. CCK-8 assay outcomes indicated that As@ZM nanoparticles had been simpler in restoring the proliferative vitality of MLE12 cells than the therapy with As alone (Determine S11). Contemplating the aforementioned experimental outcomes, we might conclude that, because of the glorious biocompatibility and distinctive therapeutic benefits of As@ZM nanoparticles, their efficacy in treating sepsis was considerably enhanced in comparison with the usage of As alone.
The therapeutic efficacy of As@ZM nanoparticles within the therapy of sepsis was superior to that of monotherapy with As. (A) Schematic diagrams of animal mannequin institution, pattern assortment, and therapy processes with As, As@Z, and As@ZM. (B) Survival curves of mice over 7 days (n = 20). (C) Immunofluorescence method was used to detect key parts of NETs, together with MPO and CitH3, in mouse lung tissue. (D-E) ELISA was employed to measure the degrees of NETs biomarkers in mouse peripheral blood, particularly CitH3-DNA complexes and MPO-DNA complexes. (F-H) ELISA was additionally used to detect the degrees of inflammatory cytokines in mouse peripheral blood, together with TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6. (I) Evaluation of organ harm in main organs (lung, liver, kidney) of mice by H&E staining. (J) Lung tissue harm scores derived from the evaluation of H&E stained photographs of mouse lung tissue. All the information in D, E, F, H, I, and J are introduced because the imply ± SD, (n = 20 for B, n = 5 for C-J). P < 0.05 point out important variations