A surge in ransomware teams in 2024 left corporations going through elevated assaults, at the same time as regulation enforcement ramped up investigations in opposition to well-known teams similar to LockBit, and dismantled in style cybercriminal providers, similar to phishing-as-a-service supplier LabHost and the encrypted messaging platform Ghost.
A pair of latest research outlines the state of play. General, greater than 75 ransomware teams had been actively compromising targets in 2024, in comparison with solely 43 the prior 12 months, in keeping with a current Rapid7 evaluation. Because of this, greater than half of organizations suffered a profitable assault, and nearly all of these impacted shut down some operations resulting in vital income loss, in keeping with a big survey of IT and cybersecurity practitioners performed by the Ponemon Institute.
So long as extortion continues to be worthwhile, organizations should take care of vital threats, says Trevor Dearing, director of essential infrastructure options at Illumio, a zero-trust safety agency and sponsor of the Ponemon report.
“When a few of these gangs had been taken down, there was a dip in exercise, however they get in a short time changed, and that is the problem,” he says. “It is a battle that’s is value combating and it does sluggish them down, however that is solely a part of the response we now have to have.”
The tempo of compromises seems to be solely accelerating, with about 15% extra ransomware assaults in 2024, in comparison with the earlier 12 months, in keeping with knowledge collected by each NCC Group and Rapid7. Their tallies differed barely, however trended in the identical path. And final month, the variety of profitable assaults claimed by ransomware teams averaged 18 per day, up from lower than 15 in December, in keeping with Rapid7’s knowledge.
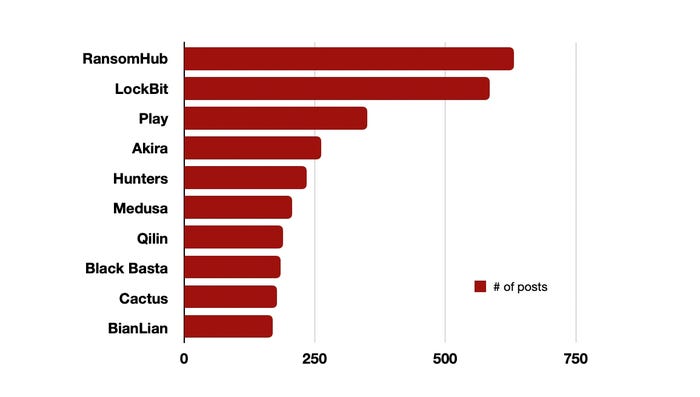
RansomHub, LockBit, and Play had been essentially the most prolific ransomware teams in 2024, as measured by the variety of breach posts. Supply: Creator primarily based on Rapid7 knowledge
General, cybercriminals compromised practically 6,000 victims, posting their info to public data-leak websites, with well-known ransomware teams — similar to RansomHub, LockBit, and Play — making tens of thousands and thousands of {dollars} every in ransom funds from victims, at the same time as fewer victims paid decrease common ransoms, the corporate discovered.
Laying Down the Legislation on Cybercrime
The ransomware positive aspects got here regardless of elevated regulation enforcement exercise. In September, European regulation enforcement disrupted the Ghost encrypted communications platform utilized by organized crime teams. In November, Canadian authorities arrested the hacker behind the compromise of 165 corporations’ Snowflake situations, who had demanded ransoms starting from $300,000 to $5 million. And, in December, Israeli regulation enforcement arrested a 51-year-old LockBit developer in Israel.
Whereas regulation enforcement efforts are having an affect on cybercriminal operations, their efforts look like fracturing the ecosystem, as extra teams and a better variety of suppliers provide cybercriminal providers, says Christiaan Beek, senior director of risk analytics for Rapid7.
“Legislation enforcement is actually combating laborious to tackle the most important teams [that are causing businesses] a number of issues, and we extremely applaud these initiatives,” he says. “However the cash is actually attracting folks, and particularly if you’re in sure international locations the place you are laborious to catch or protected by the federal government … then [becoming a ransomware operator] nearly appears like a protected choice.”
Paying Ransoms Is No Assure of Cyber Security
Estimates of the ransom quantities paid by corporations assorted considerably, with ransomware specialist Coveware estimating that the victims paid a median of $200,000 in Q3 2024, whereas a survey of greater than 2,500 corporations performed by the Ponemon Institute estimated the common ransom demanded to be $1.2 million.
And people figures don’t embody investigation and clear up prices, Illumio’s Dearing says.
“There was nearly a doubling within the [share of companies] that misplaced vital income, and that displays one thing that we’re seeing throughout the board — each from financially motivated ransomware attackers, nation-states, or hacktivists — they’re simply making an attempt to disrupt issues,” he says, including, “Organizations have to assume much more about incident response, about containing assaults, about making an attempt to guarantee that they really keep in enterprise if there’s an assault.”
The survey additionally discovered that paying a ransom not often solves the issue of misplaced knowledge nor ends the focusing on by attackers. Half of all corporations (51%) suffered a ransomware assault in 2024, however lower than half obtained a decryption key, and the attacker demanded extra money in a 3rd of circumstances. In the long run, solely 13% of corporations ultimately recovered all of their knowledge, in accordance the Ponemon Institute report.
Plan for Alternate Operations for Enterprise Continuity
Early detection and a plan to proceed operations within the face of disruption matter most in terms of minimizing the affect of a cyberattack. Of the businesses that didn’t pay a ransom, practically half had backups from which they might get well knowledge, whereas an analogous quantity deemed the info not essential sufficient to pay the ransom.
In one of the best case situation, corporations can shortly transfer to cloud operations — or one other plan for enterprise continuity — giving them one of the best likelihood of recovering with out drastic impacts, Rapid7’s Beek says.
“We noticed one firm flip the change, and all of a sudden the entire enterprise was operating on cloud sources whereas they had been restoring the day-to-day operations,” he says. “So the ransomware incident hardly impacted the enterprise.”
Corporations which have an absence of visibility into — and an absence of safety controls defending — their networks face essentially the most damaging disruption, says Illumio’s Dearing.
“Issues that permit lateral motion inside organizations — like unpatched techniques and weak passwords and open RDP ports — assist attackers,” he says. “So there’s an quantity of fundamentals that corporations have to take.”

