ESET researchers have mapped the latest actions of the CosmicBeetle risk actor, documenting its new ScRansom ransomware and highlighting connections to different well-established ransomware gangs.
CosmicBeetle actively deploys ScRansom to SMBs in varied components of the world. Whereas not being high notch, the risk actor is ready to compromise attention-grabbing targets.
CosmicBeetle changed its beforehand deployed ransomware, Scarab, with ScRansom, which is regularly improved. We’ve got additionally noticed the risk actor utilizing the leaked LockBit builder and attempting to leech off LockBit’s repute by impersonating the notorious ransomware gang each in ransom notes and leak web site.
Apart from LockBit, we imagine with medium confidence that CosmicBeetle is a brand new affiliate of RansomHub, a brand new ransomware gang lively since March 2024 with quickly rising exercise.
On this blogpost, we look at CosmicBeetle’s actions throughout the previous 12 months and analyze the connections to different well-established ransomware gangs. We additionally present perception into ScRansom.
Key factors of the blogpost:
- CosmicBeetle stays lively in 2024, regularly enhancing and distributing its customized ransomware, ScRansom.
- We offer an evaluation of ScRansom, emphasizing that it’s inconceivable to revive some encrypted information.
- CosmicBeetle has been experimenting with the leaked LockBit builder and has been attempting to abuse its model.
- CosmicBeetle could also be a latest affiliate of the ransomware-as-a-service actor RansomHub.
- CosmicBeetle exploits years-old vulnerabilities to breach SMBs everywhere in the world.
Overview
CosmicBeetle, lively since at the least 2020, is the title ESET researchers assigned to a risk actor found in 2023. This risk actor is most identified for the utilization of its customized assortment of Delphi instruments, generally referred to as Spacecolon, consisting of ScHackTool, ScInstaller, ScService, and ScPatcher. In August 2023, ESET researchers revealed their insights into CosmicBeetle. Shortly earlier than publishing, new customized ransomware we named ScRansom appeared that we imagine, with excessive confidence, is expounded to CosmicBeetle. We’ve got since discovered additional causes to extend our confidence of this relation and imagine that ScRansom is now that group’s ransomware of selection, changing the beforehand utilized Scarab ransomware.
On the time of that publication in 2023, we had not noticed any exercise within the wild. That, nonetheless, modified shortly thereafter. CosmicBeetle has since been spreading ScRansom to SMBs, primarily in Europe and Asia.
ScRansom just isn’t very refined ransomware, but CosmicBeetle has been in a position to compromise attention-grabbing targets and trigger nice hurt to them. Principally as a result of CosmicBeetle is an immature actor within the ransomware world, issues plague the deployment of ScRansom. Victims affected by ScRansom who determine to pay needs to be cautious. Whereas the decryptor itself works as anticipated (on the time of writing), a number of decryption keys are sometimes required and a few information could also be completely misplaced, relying on how CosmicBeetle proceeded throughout encryption. We go into extra particulars later on this blogpost. In step with our expertise relating to CosmicBeetle, an attention-grabbing research of immature ransomware teams just lately revealed by GuidePoint Safety reveals corresponding outcomes.
CosmicBeetle partially tried to handle, or slightly cover, these points by impersonating the just lately disrupted LockBit, most likely essentially the most notorious ransomware gang of the previous few years. By abusing the LockBit model title, CosmicBeetle hoped to higher persuade victims to pay. CosmicBeetle additionally utilized the leaked LockBit Black builder to generate its customized samples with a ransom word in Turkish.
Lately, now we have investigated an attention-grabbing case that leads us to imagine that CosmicBeetle could also be a brand new affiliate of RansomHub. RansomHub is a reasonably just lately emerged ransomware-as-a-service gang that shortly gained the general public’s eye when Notchy, the infamous affiliate of the BlackCat ransomware gang who claimed duty for the assault on Change Healthcare, complained that BlackCat stole Notchy’s ransom cost and can due to this fact be partnering with the rival gang RansomHub as an alternative.
This blogpost paperwork the evolution of ScRansom for the previous 12 months and CosmicBeetle’s strategy to compromising victims. We additionally dive deeper into the risk actor’s relations to different ransomware gangs.
Attribution
We imagine with excessive confidence that ScRansom is the latest addition to CosmicBeetle’s customized toolset. On this part, we clarify our reasoning.
ESET telemetry reveals a number of instances the place ScRansom deployment overlaps with different instruments generally utilized by CosmicBeetle. Moreover, a ZIP archive uploaded to VirusTotal comprises two embedded archives, every one most likely containing samples from an intrusion. Each archives comprise ScRansom, ScHackTool, and different instruments generally utilized by CosmicBeetle, additional supporting our suspicions.
There’s plenty of code similarity between ScRansom and former CosmicBeetle tooling, specifically:
- Delphi because the programming language of selection,
- IPWorks library for encryption,
- equivalent Turkish strings within the code,
- utilizing areas after colons in strings, which earned the Spacecolon toolset its title, and
- GUI similarity with ScHackTool.
All of those similarities additional strengthen our attribution. Though Zaufana Trzencia Strona analysts just lately revealed a blogpost about CosmicBeetle the place they attributed CosmicBeetle to an precise particular person – a Turkish software program developer, ESET researchers don’t suppose this attribution is correct. That attribution is predicated on the customized encryption scheme utilized in ScHackTool (not ScRansom). Particularly, they discovered a malicious pattern (SHA‑1: 28FD3345D82DA0CDB565A11C648AFF196F03D770) that comprises this algorithm and is signed by a Turkish software program improvement firm VOVSOFT with a strange-looking headquarters.
However the talked about pattern doesn’t belong to VOVSOFT; it’s really a malicious patched model of Disk Monitor Gadget, one in all many merchandise developed by VOVSOFT signed correctly (SHA-1: 2BA12CD5E44839EA67DE8A07734A4E0303E5A3F8). Furthermore, the digital signature was copied from the professional model and easily appended to the patched model, ensuing within the malicious pattern apparently being signed, however not having a legitimate signature.
Curiously, ScHackTool’s encryption scheme is used within the professional Disk Monitor Gadget too. Zaufana Trzencia Strona analysts found that the algorithm possible originates from this Stack Overflow thread from 13 years in the past. Because the creator of the publish, MohsenB, has been an lively person of Stack Overflow since 2012 – and, primarily based on profile footage, just isn’t the VOVSOFT developer himself – it’s possible that this algorithm was tailored by VOVSOFT and, years later, CosmicBeetle stumbled upon it and used it for ScHackTool.
Preliminary entry and victimology
CosmicBeetle usually makes use of brute-force strategies to breach its targets. Apart from that, the next vulnerabilities are being exploited by the risk actor:
SMBs from all types of verticals everywhere in the world are the most typical victims of this risk actor as a result of that’s the phase most definitely to make use of the affected software program and to not have sturdy patch administration processes in place. CosmicBeetle’s leak web site is, as we are going to show shortly, very unreliable and inconsistent; due to this fact we confer with ESET telemetry. Determine 1 demonstrates CosmicBeetle’s victims in accordance with ESET telemetry.
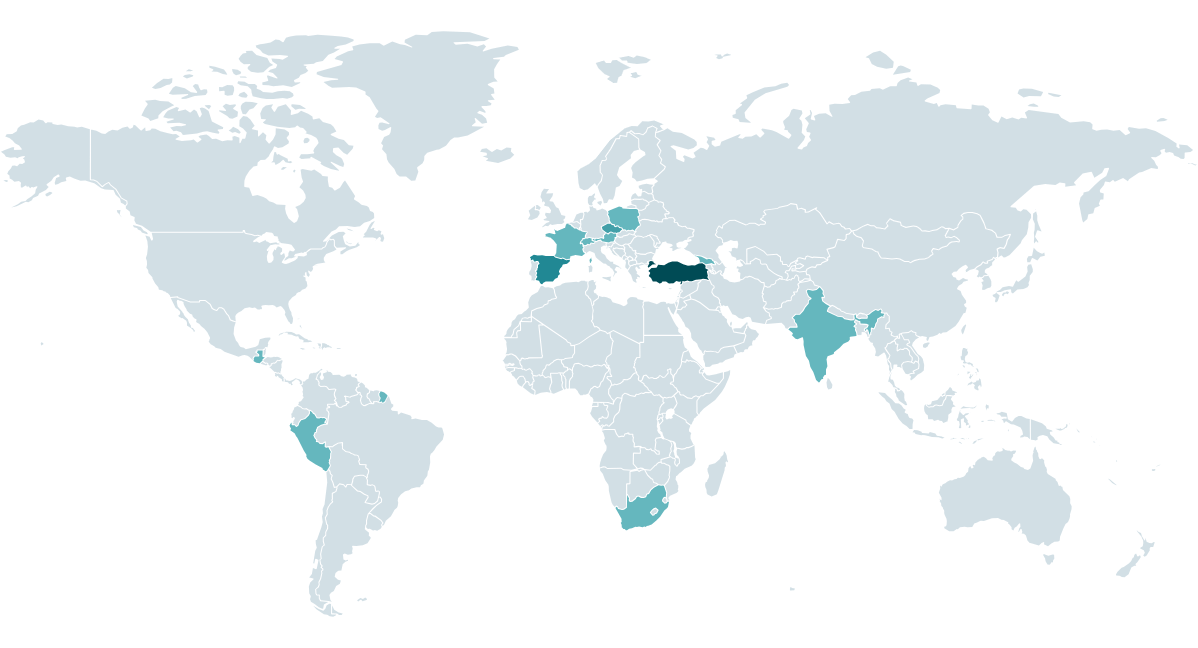
We noticed assaults on SMBs within the following verticals:
- manufacturing,
- prescription drugs,
- authorized,
- training,
- healthcare,
- expertise,
- hospitality leisure,
- monetary companies, and
- regional authorities.
Model
Most ransom notes dropped by ScRansom don’t assign a reputation to the ransomware. CosmicBeetle depends primarily on e mail and qTox, an immediate messaging utility utilized by many ransomware gangs, primarily on account of its utilization of the Tox protocol. The Tox protocol offers peer-to-peer end-to-end encrypted communication.
The one title CosmicBeetle selected for its customized ransomware is, paradoxically, NONAME, because the risk actor briefly branded the ransomware, which we focus on within the following part. As a result of chaotic nature of the branding, for the aim of this blogpost, we are going to proceed to confer with the ransomware as ScRansom.
LockBit copycat
In September 2023, CosmicBeetle determined to arrange a devoted leak web site (DLS) on Tor, which it named NONAME. This web site, illustrated in Determine 2, is a rip-off of LockBit’s leak web site (see Determine 3).
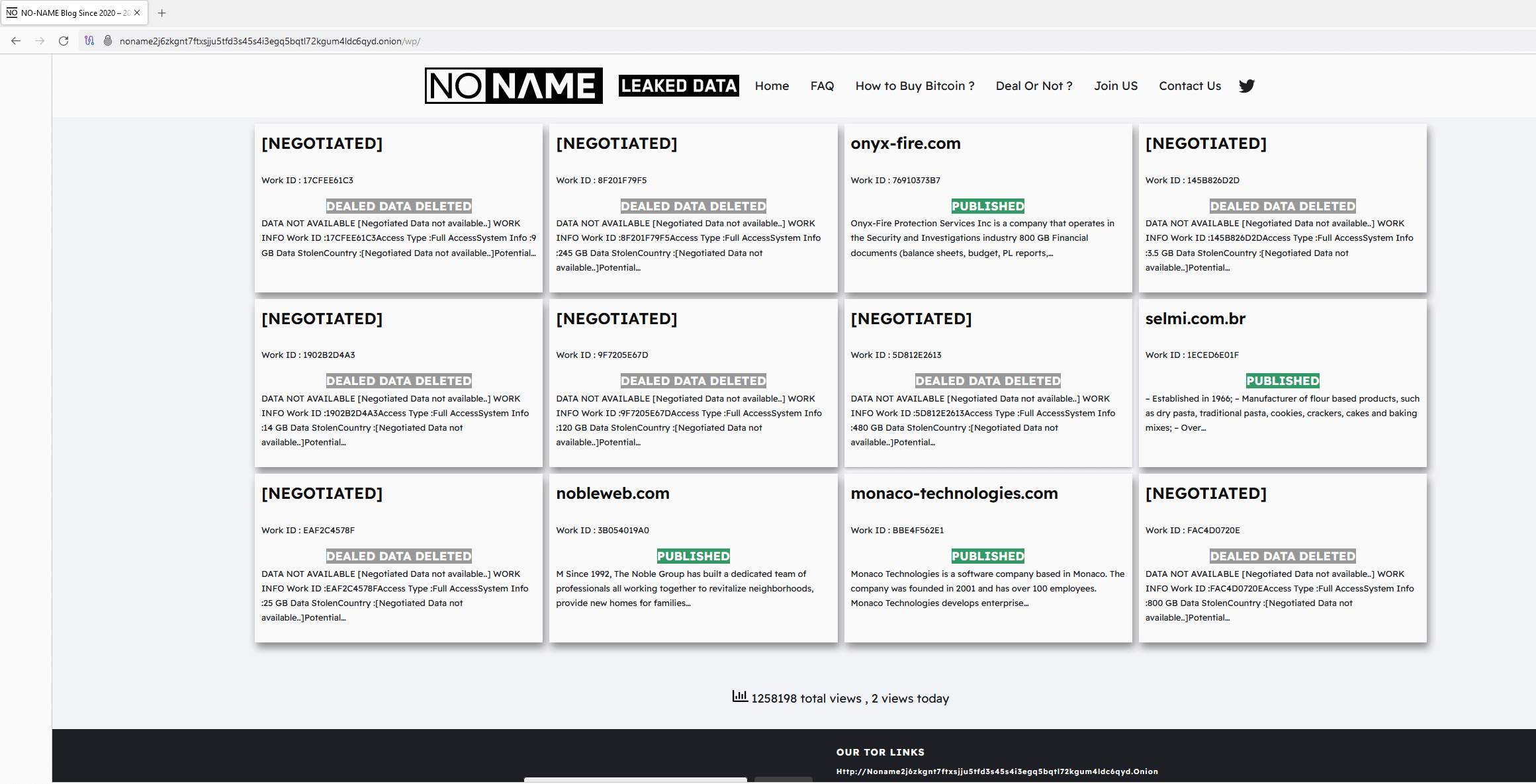
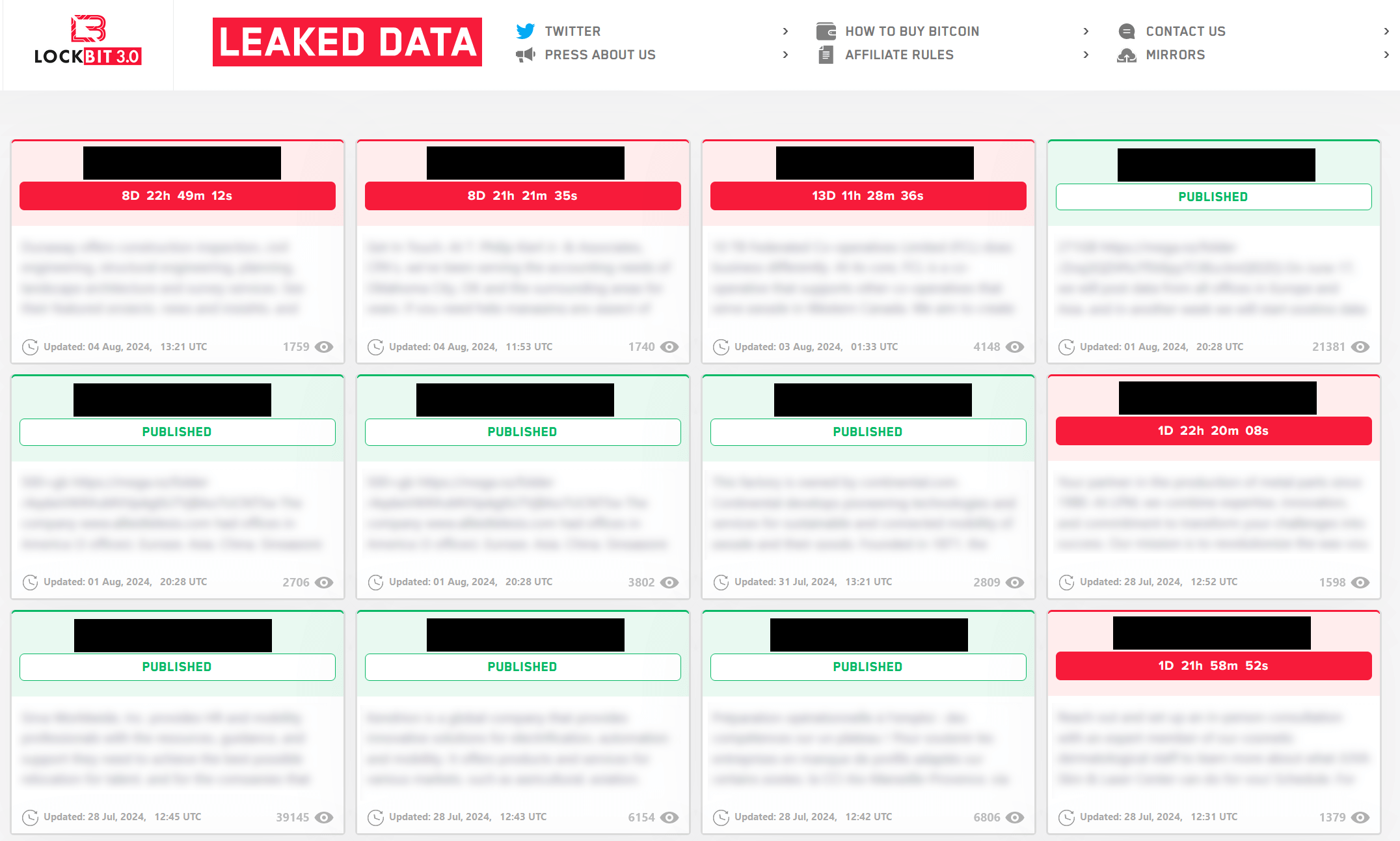
Whereas just a few graphical adjustments have been made, the inspiration continues to be clear. Furthermore, the design just isn’t the one similarity with LockBit. All the victims seen in Determine 2 have been really compromised by LockBit, not ScRansom. This may be verified through the use of DLS monitoring companies, reminiscent of RansomLook. All the victims have been posted on LockBit’s leak web site, most of them in September 2023, shortly earlier than the NONAME DLS appeared. The Work ID string is added to extend the phantasm of being associated to ScRansom, as that is how victims are recognized in ransom notes.
In early November 2023, CosmicBeetle determined to maneuver even additional and determined to impersonate LockBit fully. They did so by registering the area lockbitblog[.]information and utilizing the identical strategy as for the NONAME DLS, solely this time, they included the LockBit brand as properly (see Determine 4). Then, for a time, ScRansom’s ransom notes linked to this web site. The identical inspiration is seen and the graphical similarity to the NONAME DLS (Determine 2) is simple.
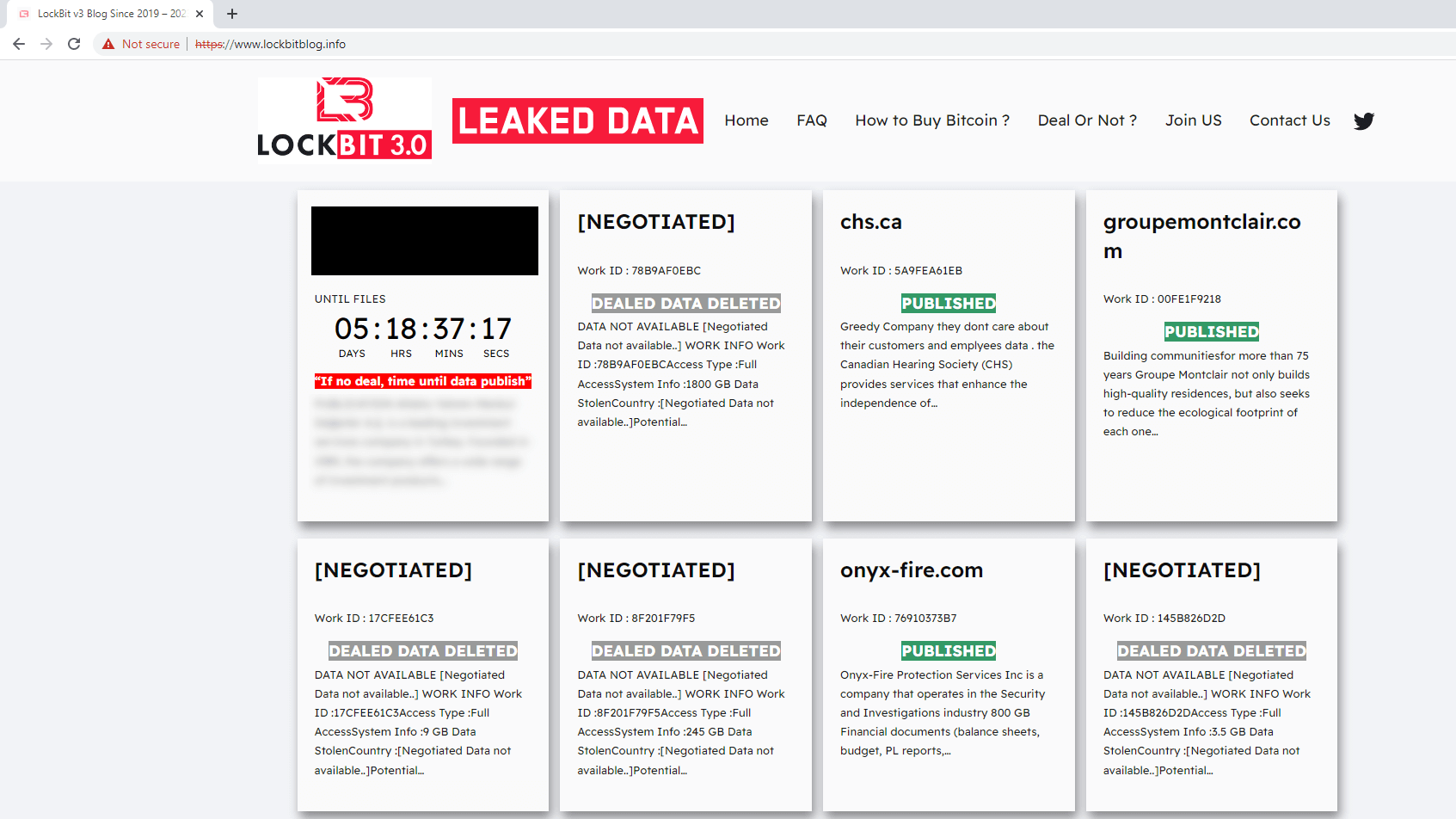
A pattern constructed utilizing the leaked LockBit 3.0 builder was uploaded to VirusTotal in August 2024 from Türkiye. What makes this pattern distinctive is that it makes use of a ransom message (see Determine 5) in Turkish and the qTox ID it mentions is one we conclusively linked to CosmicBeetle. ESET telemetry corroborates this connection, as now we have investigated a case the place deployment of LockBit overlapped with CosmicBeetle’s toolset.
|
I’ve encrypted your information and for the charge you’ll pay, I’ll reconnect to your system, decrypt it and ship it to you. We wish you to know that you just can not get your information again with identified information restoration strategies. These strategies will solely trigger you to lose time. If a return just isn’t made inside 48 hours, the password used within the system will probably be deleted and your information won’t ever be returned. Your disks are encrypted with Full disk encryption, unauthorized intervention will trigger everlasting information loss! Don’t imagine the pc guys who say they won’t open even if you happen to pay them or the folks round you who say they’ll take your cash and never offer you your information I’ve sufficient references to belief you I have no idea you, so there isn’t a level in having dangerous emotions in the direction of you or doing you hurt, I’ll hook up with your server as quickly as doable to revive your information. I can even clarify the best way to safe your system after this course of in order that such incidents won’t ever occur to you once more. Private Key e-mail 1 : sunucuverikurtarma@gmail[.]com Backup e-mail : serverdatakurtarma@mail[.]ru QTOX : A5F2F6058F70CE5953DC475EE6AF1F97FC6D487ABEBAE76915075E3A53525B1D863102EDD50E |
Determine 5. Ransom word that comprises a TOX ID utilized by CosmicBeetle, dropped by a LockBit pattern. Textual content was machine translated from Turkish.
Relation to RansomHub
Utilizing leaked builders is a standard observe for immature ransomware gangs. It permits them to abuse the model of their well-established rivals whereas additionally offering them with a ransomware pattern that often works correctly. The LockBit connection, nonetheless, just isn’t the one one now we have noticed.
In June, we investigated an incident involving ScRansom. From our telemetry, we have been in a position to collect the next:
- On June 3rd, 2024 CosmicBeetle tried to compromise a producing firm in India with ScRansom.
- After failing, CosmicBeetle tried quite a lot of process-killing instruments to take away EDR safety, specifically:
- On June 8th, 2024, RansomHub’s EDR killer was executed on the identical machine.
- On June 10th, 2024, RansomHub was executed on the identical machine.
The way in which RansomHub’s EDR killer was executed could be very uncommon. It was manually extracted by way of WinRAR from an archive saved at C:UsersAdministratorMusic1.0.8.zip and executed. Such execution could be very uncommon for RansomHub associates. However, utilizing the Music folder and manually extracting and executing payloads actually is typical CosmicBeetle habits.
To our data, there are not any public leaks of RansomHub code or its builder (although RansomHub itself might be primarily based on code purchased from Knight, one other ransomware gang). Due to this fact, we imagine with medium confidence that CosmicBeetle enrolled itself as a brand new RansomHub affiliate.
Technical evaluation
Just like the remainder of CosmicBeetle’s customized arsenal, ScRansom is written in Delphi. The earliest samples we have been in a position to get hold of have been compiled on the finish of March 2023, although, to the very best of our data, in-the-wild assaults didn’t begin earlier than August. ScRansom is below ongoing improvement.
The GUI is typical for Delphi purposes, although not a lot for ransomware. All ScRansom samples comprise a structured GUI. The older samples, often named “Static” by the builders, require person interplay to really encrypt something. Whereas this will appear a complication, it could be one of many the reason why ScRansom evaded detection for a while, as operating such samples in evaluation sandboxes doesn’t show any malicious exercise.
Launching such an encryptor requires the risk actor to have entry to the sufferer’s display screen and be capable to manipulate their mouse. This isn’t the primary time CosmicBeetle has used this strategy – ScHackTool can also be a device that must be executed on the sufferer’s machine and requires guide interplay. We’re not totally positive how CosmicBeetle achieves this aim, however guessing from the opposite instruments used, we imagine utilizing VPN entry with beforehand stolen credentials and RDP is essentially the most possible state of affairs.
CosmicBeetle additionally has experimented with a hardly ever seen variant named “SSH”. The encryptor logic is equivalent to the opposite variants, however as an alternative of encrypting native information, it encrypts information over FTP.
Newer builds make the most of automation, although solely by simulating clicking the right buttons from code. These automated builds, named “Auto” by the builders, are often bundled inside an MSI installer along with small instruments or scripts to delete shadow copies. The GUI is hidden by default; its most up-to-date model is illustrated in Determine 6.
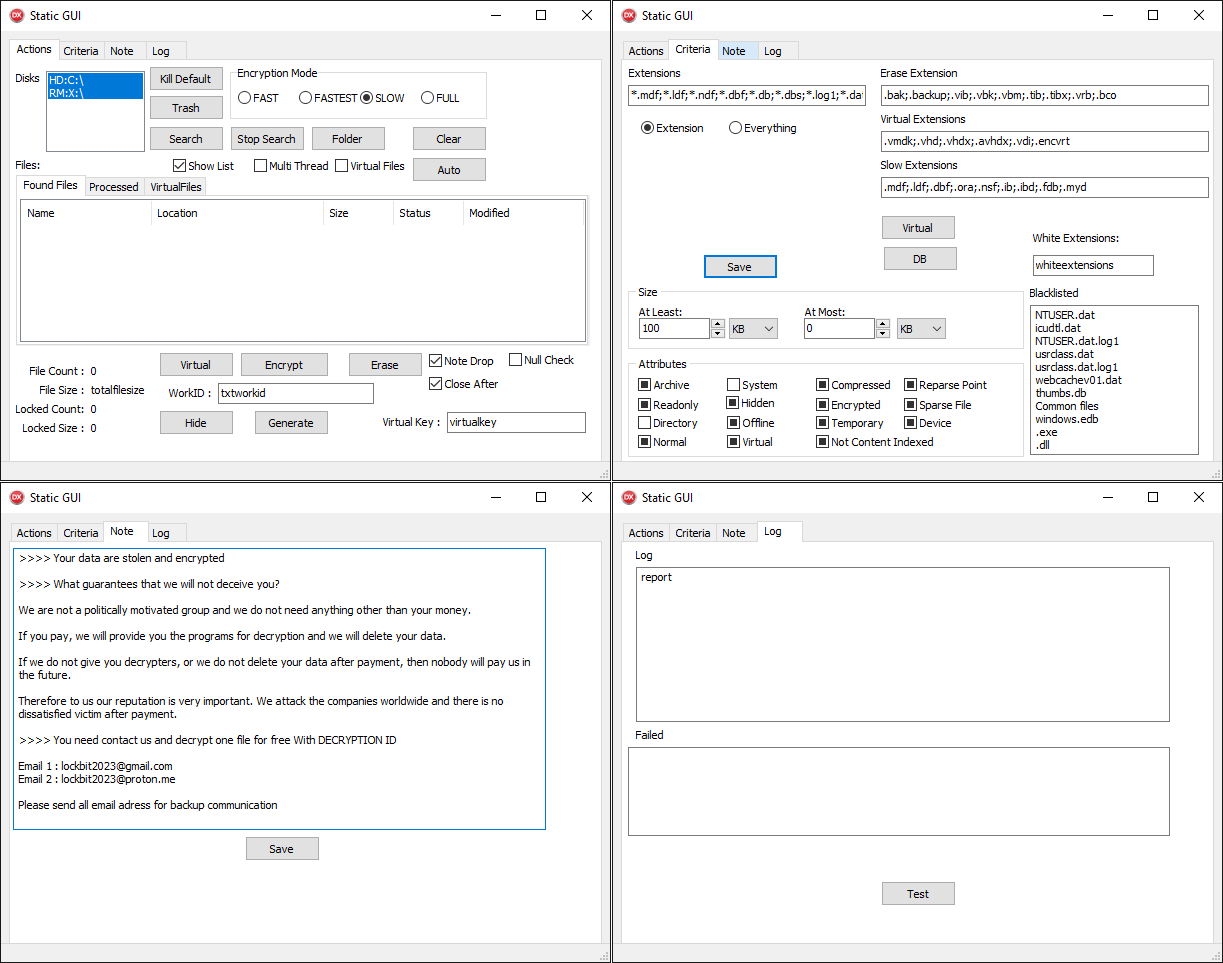
A posh GUI with plenty of buttons, a few of which do nothing, is typical for CosmicBeetle. Whereas the GUI with 4 tabs appears complicated, the performance is definitely very easy. ScRansom encrypts information on all fastened, distant, and detachable drives primarily based on a hardcoded checklist of extensions (see Appendix A: Focused file extensions) – this checklist might be modified by way of the textual content field labeled Extensions.
ScRansom employs partial encryption – solely components of the file are encrypted. 5 encryption modes are supported:
- FAST
- FASTEST
- SLOW
- FULL
- ERASE
The primary 4 modes merely differ in how the ransomware decides what parts of the file to encrypt. Their utilization appears to nonetheless be partially in improvement, as not all the modes are used. The final mode, ERASE, is necessary, nonetheless – when utilized, chosen parts of focused information are usually not encrypted however their contents are changed with a continuing worth, rendering these information unrecoverable. Which mode is utilized for a given file is decided both by way of the radio buttons within the Actions tab or by way of the inclusion of its extension within the Standards tab. The extensions checklist labeled Digital Extensions triggers a special encryption perform that, nonetheless, is equivalent to the common one. As you most likely guessed, White Extensions ought to outline an inventory of extensions excluded from encryption, although this characteristic just isn’t carried out.
Apart from encrypting, ScRansom additionally kills varied processes and companies (see Appendix B: Processes killed and Appendix C: Providers killed). Lately, a brand new Delphi pattern was break up off from ScRansom into an element that we named ScKill, whose sole function is to kill processes. ScRansom additionally employs debug-like options like loading an inventory of extensions to encrypt from an ext.txt file and ransom word content material from a word.txt file.
Encryption
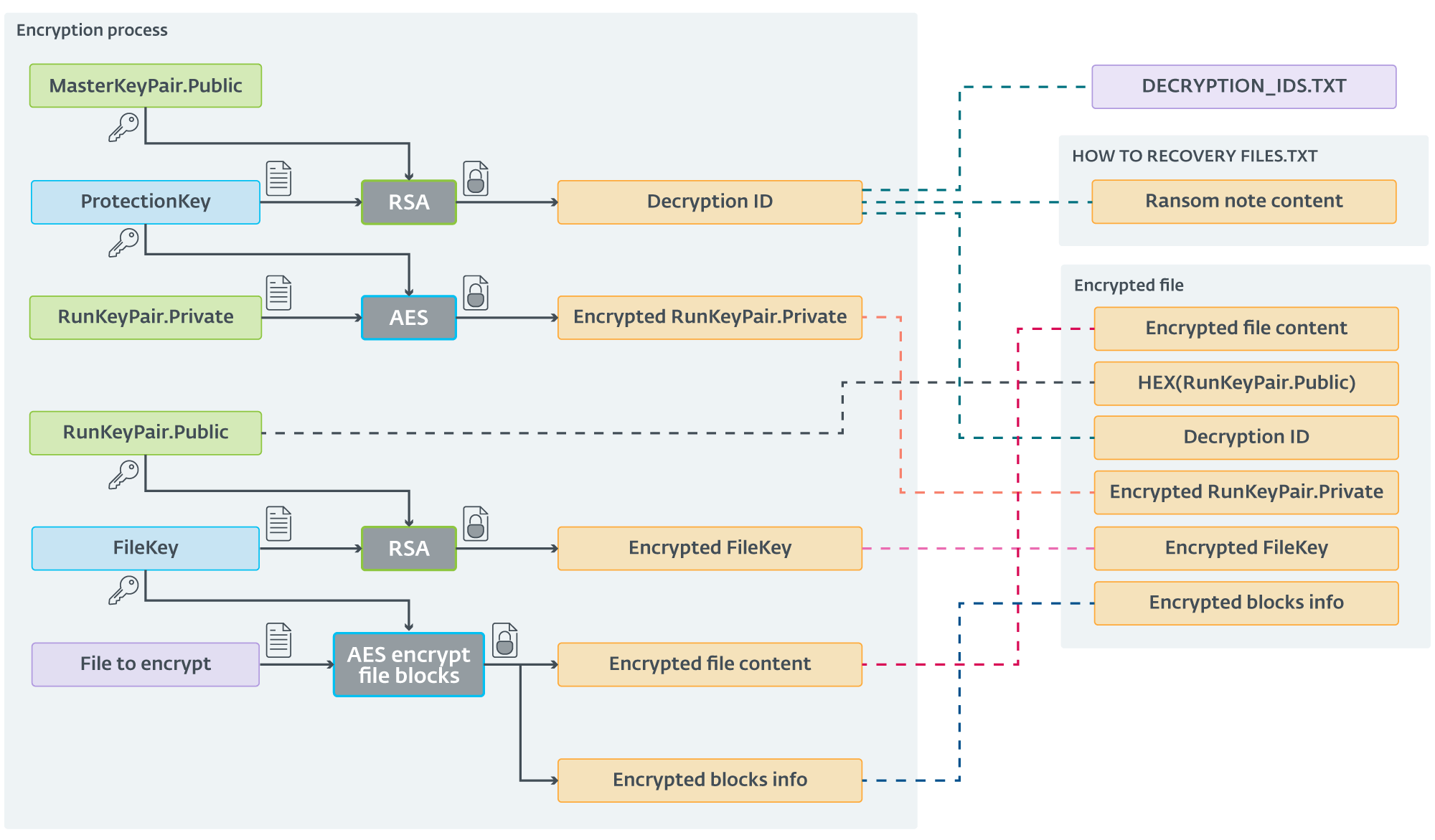
Preliminary ScRansom samples utilized easy symmetric encryption utilizing AES-CTR-128. Since December 2023, the encryption scheme has been up to date. The brand new scheme is sort of (unnecessarily) complicated. ScRansom, in the beginning, generates an AES key we are going to name ProtectionKey, and an RSA-1024 key pair we are going to name RunKeyPair.
Each ScRansom pattern utilizing this new scheme comprises a hardcoded public RSA key from a pair we are going to name MasterKeyPair. This public key’s encrypted utilizing RSA into what CosmicBeetle calls Decryption ID.
For each file, an AES-CTR-128 key that we are going to name FileKey is generated. Parts of the file are then encrypted utilizing AES with FileKey. When ScRansom finishes encrypting a file, it appends information to its finish, particularly:
- The string TIMATOMA (or TIMATOMAFULL if the entire file was encrypted).
- The string TBase64EncodingButton12ClickTESTB64@#$% (TESTB64 in older builds), encrypted by AES utilizing FileKey.
- The next entries, delimited by $ (a greenback signal):
- Hex-encoded RunKeyPair.Public,
- Decryption ID,
- RunKeyPair.Personal, encrypted utilizing AES-CTR-128 with ProtectionKey, and
- FileKey, encrypted utilizing RSA with RunKeyPair.Public.
- Details about encrypted blocks begin and their size (absent if the total file is encrypted).
Lastly, Decryption ID is saved right into a textual content file named DECRYPTION_IDS.TXT and in addition written within the ransom word named HOW TO RECOVERY FILES.TXT. Decryption ID is completely different every time the encryptor is executed. On subsequent execution(s), the Decryption IDs are appended to the DECRYPTION_IDS.TXT file, however not up to date within the ransom word.
The filename (together with extension) is then base64 encoded and the .Encrypted extension appended. Regardless of the complexity of the entire course of, now we have summarized it in Determine 7.
Decryption
We have been in a position to get hold of a decryptor carried out by CosmicBeetle for this latest encryption scheme. CosmicBeetle doesn’t present its victims with the MasterKeyPair.Personal key however with the already decrypted ProtectionKey (that must be entered within the discipline labeled CPriv Aes Key). Moreover, the decryptor expects the Decryption ID, which is ineffective, because the non-public key just isn’t supplied; certainly, the decryptor ignores its worth. The GUI of the decryptor is illustrated in Determine 8.
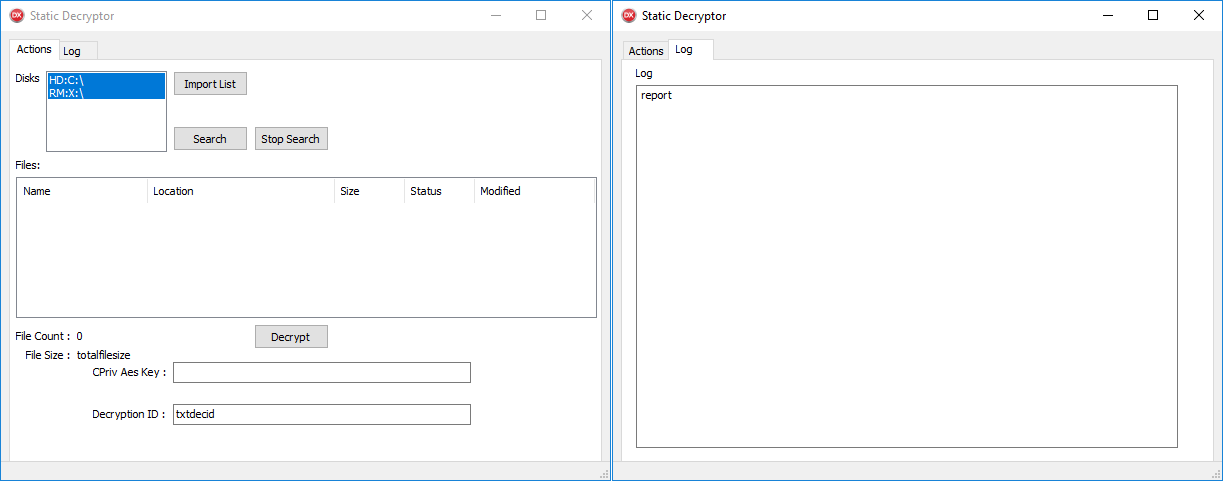
If the right ProtectionKey is entered, the decryptor works as anticipated. If victims determine to pay the ransom, they should acquire all Decryption IDs from all the machines the place ScRansom was executed. CosmicBeetle then wants to supply a special ProtectionKey for all the Decryption IDs. Victims then must manually run the decryptor on each encrypted machine, enter the right ProtectionKey (or strive all of them), click on the Decrypt button and anticipate the decryption course of to complete.
Furthermore, from collaboration with one of many victims, we realized that ScRansom was executed greater than as soon as on some machines, resulting in much more Decryption IDs. This sufferer collected 31 completely different Decryption IDs, requiring 31 ProtectionKeys from CosmicBeetle. Even with these, they have been unable to totally get well all of their information. Assuming the encrypted information weren’t tampered with, this can be the results of lacking some Decryption IDs, CosmicBeetle not offering all the required ProtectionKeys, or ScRansom destroying some information completely through the use of the ERASE encryption mode. This decryption strategy is typical for an immature ransomware risk actor.
Seasoned gangs desire to have their decryption course of as straightforward as doable to extend the probabilities of right decryption, which boosts their repute and will increase the chance that victims pays. Sometimes (like within the case of the leaked LockBit Black builder), a decryptor is constructed along with an encryptor. When distributed to the sufferer, no extra person effort is required, as the secret’s already contained within the binary. Moreover, one key’s enough to decrypt all encrypted information, no matter the place they’re within the sufferer’s community.
Conclusion
On this blogpost, now we have analyzed CosmicBeetle’s exercise over the previous 12 months. The risk actor continues to be deploying ransomware, although it switched from Scarab to a brand new customized household we name ScRansom. Most likely as a result of obstacles that writing customized ransomware from scratch brings, CosmicBeetle tried to leech off LockBit’s repute, probably to masks the problems within the underlying ransomware and in flip to extend the prospect that victims pays.
We additionally noticed CosmicBeetle attempting to deploy LockBit samples constructed utilizing the leaked builder, although solely briefly, earlier than switching again to ScRansom. The risk actor places efforts into continuous improvement of ScRansom, altering encryption logic and including options.
Lately, we noticed the deployment of ScRansom and RansomHub payloads on the identical machine solely every week aside. This execution of RansomHub was very uncommon in comparison with typical RansomHub instances now we have seen in ESET telemetry. Since there are not any public leaks of RansomHub, this leads us to imagine with medium confidence that CosmicBeetle could also be a latest affiliate of RansomHub.
ScRansom undergoes ongoing improvement, which isn’t an excellent sign up ransomware. The overcomplexity of the encryption (and decryption) course of is vulnerable to errors, making restoration of all information uncertain. Profitable decryption depends on the decryptor working correctly and on CosmicBeetle offering all obligatory keys, and even in that case, some information might have been destroyed completely by the risk actor. Even within the best-case state of affairs, decryption will probably be lengthy and sophisticated.
For any inquiries about our analysis revealed on WeLiveSecurity, please contact us at threatintel@eset.com.ESET Analysis gives non-public APT intelligence reviews and information feeds. For any inquiries about this service, go to the ESET Risk Intelligence web page.
IoCs
Information
| SHA-1 | Filename | Detection | Description |
| 4497406D6EE7E2EF561C |
auto.exe | Win32/Filecoder.Spacecolon.A | Auto variant of ScRansom. |
| 3C32031696DB109D5FA1 |
Project1.exe | Win32/Filecoder.Spacecolon.B | Auto variant of ScRansom. |
| 26D9F3B92C10E248B7DD |
New.exe | Win32/Filecoder.Spacecolon.A | Static variant of ScRansom. |
| 1CE78474088C14AFB849 |
Project1.exe | Win32/Filecoder.Spacecolon.B | Auto encryptor variant of ScRansom, Turkish ransom word. |
| 1B635CB0A4549106D8B4 |
Project1.exe | Win32/Filecoder.Spacecolon.A | Static SSH encryptor variant of ScRansom. |
| DAE100AFC12F3DE211BF |
Project1.exe | Win32/Filecoder.Spacecolon.A | Decryptor variant of ScRansom (oldest). |
| 705280A2DCC311B75AF1 |
Rarlab_sib.msi | Win32/Filecoder.Spacecolon.A | MSI file with embedded ScRansom, ScKill, BAT script to cease companies, and BAT script to delete shadow copies. |
Community
| IP | Area | Internet hosting supplier | First seen | Particulars |
| 66.29.141[.]245 | www.lockbitblog |
Namecheap, Inc. | 2023-11-04 | Pretend LockBit leak web site. |
Ransom word fragments
E-mail addresses
- decservice@ukr[.]internet
- nonamehack2024@gmail[.]com
- tufhackteam@gmail[.]com
- nonamehack2023@gmail[.]com
- nonamehack2023@tutanota[.]com
- lockbit2023@proton[.]me
- serverrecoveryhelp@gmail[.]com
- recoverydatalife@gmail[.]com
- recoverydatalife@mail[.]ru
Tox IDs
- 91E3BA8FACDA7D4A0738ADE67846CDB58A7E32575531BCA0348EA73F6191882910B72613F8C4
- A5F2F6058F70CE5953DC475EE6AF1F97FC6D487ABEBAE76915075E3A53525B1D863102EDD50E
- F1D0F45DBC3F4CA784D5D0D0DD8ADCD31AB5645BE00293FE6302CD0381F6527AC647A61CB08D
- 0C9B448D9F5FBABE701131153411A1EA28F3701153F59760E01EC303334C35630E62D2CCDCE3
Tor hyperlinks
- http://nonamef5njcxkghbjequlibwe5d3t3li5tmyqdyarnrsryopvku76wqd[.]onion
- http://noname2j6zkgnt7ftxsjju5tfd3s45s4i3egq5bqtl72kgum4ldc6qyd[.]onion
- http://7tkffbh3qiumpfjfq77plcorjmfohmbj6nwq5je6herbpya6kmgoafid[.]onion
MITRE ATT&CK methods
This desk was constructed utilizing model 15 of the MITRE ATT&CK framework.
| Tactic | ID | Identify | Description |
| Reconnaissance | T1595.002 | Energetic Scanning: Vulnerability Scanning | CosmicBeetle scans its targets for an inventory of vulnerabilities it may exploit. |
| T1590.005 | Collect Sufferer Community Info: IP Addresses | CosmicBeetle scans the web for IP addresses weak to the vulnerabilities it may exploit. | |
| Useful resource Improvement | T1583.001 | Purchase Infrastructure: Domains | CosmicBeetle registered its personal leak web site area. |
| T1587.001 | Develop Capabilities: Malware | CosmicBeetle develops its customized toolset, Spacecolon. | |
| T1588.002 | Receive Capabilities: Software | CosmicBeetle makes use of a big number of third-party instruments and scripts. | |
| T1588.005 | Receive Capabilities: Exploits | CosmicBeetle makes use of publicly out there PoCs for identified exploits. | |
| T1588.001 | Receive Capabilities: Malware | CosmicBeetle most likely obtained ransomware from RansomHub and the leaked LockBit 3.0 builder. | |
| Preliminary Entry | T1190 | Exploit Public-Going through Software | CosmicBeetle positive factors preliminary entry by exploiting vulnerabilities in FortiOS SSL-VPNand different public-facing purposes. |
| Execution | T1204 | Person Execution | CosmicBeetle depends on person execution for a few of its instruments, although that is often performed by the risk actor by way of RDP. |
| T1059.003 | Command and Scripting Interpreter: Home windows Command Shell | CosmicBeetle executes varied BAT scripts and instructions. | |
| T1059.001 | Command and Scripting Interpreter: PowerShell | CosmicBeetle executes varied PowerShell scripts and instructions. | |
| Persistence | T1136.001 | Create Account: Native Account | CosmicBeetle usually creates an attacker-controlled administrator account. |
| Protection Evasion | T1078 | Legitimate Accounts | CosmicBeetle abuses legitimate accounts whose credentials it efficiently obtains. |
| T1140 | Deobfuscate/Decode Information or Info | ScRansom samples defend public RSA keys by encryption. | |
| Credential Entry | T1110.001 | Brute Power: Password Guessing | CosmicBeetle makes use of RDP and SMB brute-force assaults. |
| T1212 | Exploitation for Credential Entry | CosmicBeetle exploits identified vulnerabilities to acquire credentials. | |
| Affect | T1485 | Information Destruction | CosmicBeetle renders some encrypted information unrecoverable. |
| T1486 | Information Encrypted for Affect | CosmicBeetle encrypts delicate information on compromised machines. |
Appendix A: Focused file extensions
This configuration is hardcoded in each ScRansom pattern and is topic to frequent change. The next sections comprise the latest configuration on the time of writing.
Filename masks to encrypt
| *._ms *.0001 *.001 *.002 *.003 *.004 *.005 *.006 *.007 *.008 *.1* *.2* *.3* *.3dm *.3dmbak *.3ds *.4* *.5* *.6* *.7* *.7z *.8* *.9* *.a01 *.a02 *.a03 *.a06 *.accdb *.ACD *.adm *.afi *.ai *.alt *.arc *.arc *.archive *.ard *.asm *.avhdx *.avi *.axf *.b1 *.bac *.backup *.bak *.BBCK *.BBCK3 *.bck *.bco *.bdmp *.bi4 *.bik *.bin *.bkf *.bkp |
*.bkup *.mix *.field *.bpf *.btr *.bup *.c1 *.cbd *.cbu *.cdr *.cdx *.cfgbak *.cgd *.sofa *.csv *.ctf *.d0 *.d1 *.d2 *.d3 *.d4 *.da1 *.da2 *.da3 *.da4 *.hazard *.dat *.db *.db1 *.db2 *.dbc *.dbdmp *.dbf *.dbs *.dbw *.df *.dft *.diff *.dmp *.doc *.docx *.dwg *.dxf *.dxt5_2d *.ebk *.edb *.edp *.elg *.eml *.encvrt *.fbf *.fbk *.fbw *.fdb *.fmp12 |
*.fp5 *.fp7 *.frm *.ful *.full *.fxl *.gan *.gbk *.gdb *.gho *.ghs *.hbp *.hlp *.hrl *.ib *.ibd *.idx *.imd *.indd *.itdb *.iv2i *.jet *.jpg *.L5X *.lbl *.ldb *.ldf *.llp *.log *.log1 *.lst *.mat *.max *.mdb *.mdbx *.mdf *.mmo *.mov *.mp4 *.mrimg *.msg *.mtx *.myd *.myi *.nb7 *.nbf *.ndf *.ndk *.ndx *.nsf *.nsg *.ntf *.nx1 *.nyf *.obk |
*.oeb *.ol2 *.outdated *.one *.ora *.ost *.ostx *.ova *.pak *.par *.pbd *.pcb *.pdb *.pod *.ppt *.pptx *.pqb *.pri *.prt *.psd *.psm *.pst *.pstx *.ptb *.qba *.qbb *.qbm *.qbw *.qic *.qrp *.qsm *.qvx *.rar *.uncooked *.rbf *.rct *.rdb *.redo *.rfs *.rman *.rpd *.rpo *.rpt *.rtf *.sai *.saj *.seq *.sev *.sic *.sko *.skp *.SLDASM *.SLDDRW *.SLDLFP |
*.SLDPRT *.sldprt *.sldrpt *.slp *.sna *.sna *.spf *.spl *.sql *.sqlaudit *.sqlite *.sqlite3 *.srd *.step *.stm *.stp *.tar *.tar.gz *.tga *.tgz *.tib *.tibx *.tif *.tiff *.tmp *.trc *.trn *.tuf *.upd *.usr *.vbk *.vbm *.vct *.vcx *.vhd *.vhdx *.vib *.vix *.vmdk *.vmsd *.vmsn *.vmx *.vmxf *.vob *.vrb *.vswp *.wim *.wt *.xls *.xlsm *.xlsx *.zip *ibdata |


