Heuristic static evaluation (SA) instruments are a important element of software program growth. These instruments use sample matching and different heuristic methods to investigate a program’s supply code and alert customers to potential errors and vulnerabilities. Sadly, SA instruments produce a excessive variety of false positives: they will produce one alert for each three traces of code. By our evaluation, it could take a person greater than 15 person-years to manually restore all of the alerts in a typical giant codebase of two million traces of code. Presently, most software program engineers filter alerts and solely repair those they deem most crucial, however this method dangers overlooking actual points. False positives create a barrier to the adoption and utility of heuristic SA instruments, rising the potential of safety vulnerabilities.
Our new open supply software Redemption leverages automated code restore (ACR) know-how to routinely restore SA alerts in C/C++ supply code. By lowering the variety of false positives, we estimate organizations can save round seven and one-half person-years in figuring out and repairing safety alerts.
On this put up, I give an summary of how Redemption makes use of ACR know-how, the sorts of errors Redemption can repair, how the software works, and what’s subsequent for its growth.
Redemption: An Overview
Automated Code Restore
The SEI has longstanding analysis pursuits in ACR and its purposes. You possibly can consider ACR for static alerts like a programmer’s spell checker: the ACR identifies errors and affords a doable restore. The developer can then select whether or not or to not implement the suggestion.
In our use of ACR in Redemption, now we have adopted three fundamental growth rules. First, in distinction to ACR, Redemption doesn’t detect alerts of its personal; it merely parses the alerts from different SA instruments. Second, even when an alert is a false constructive, repairing the alert mustn’t break the code, akin to inflicting this system to crash or fail a sound take a look at case. Third, Redemption is idempotent. That’s, the software doesn’t modify code it has already repaired. We comply with these rules to make sure that Redemption produces sound fixes and doesn’t break good code.
Static Evaluation Instruments and Error Classes
Redemption isn’t a SA software; that you must have a separate SA program in your workflow to make use of Redemption. Presently, Redemption works with three SA instruments, clang-tidy, Cppcheck, and rosecheckers, although we’d like so as to add further instruments as we develop Redemption additional.
As we started to work on Redemption, we wanted to slim down the alert classes we wished to concentrate on first, since SA alerts are so quite a few. We ran SA testing on the open supply initiatives Git and Zeek to find out which errors appeared essentially the most distinguished. Our testing generated greater than 110,000 SA alerts for the 2 initiatives, giving us a broad pattern to investigate. We selected three widespread alert classes to begin, and we intend to broaden to further classes sooner or later. These classes embrace:
Code weaknesses that fall into these classes are safety vulnerabilities and will trigger this system to crash or behave unexpectedly. Of the 110,000 alerts, roughly 15,000 had been in these three classes. Our preliminary objective is to restore 80 p.c of alerts in these classes.
Steady Integration Workflows
A high precedence for our DoD collaborators is integrating Redemption into their steady integration (CI) pipelines. A CI server routinely and ceaselessly builds, checks, and merges software program, instantly reporting construct failures and take a look at regressions. This course of makes it simpler for groups to catch errors shortly and prevents main merge conflicts. CI workflows sometimes embrace testing, together with SA checks.
To combine Redemption right into a CI pipeline, we added the software as a plugin to an occasion of Gitlab. Redemption reads the output of an SA software, produces doable fixes, and creates a pull request, also called a merge request (MR). The developer can then select to merge the request and implement the recommendations, modify the MR, or reject the proposed fixes.
By bringing Redemption right into a CI pipeline, groups can combine the software with SA software program they’re already utilizing and create safer, cleaner code.
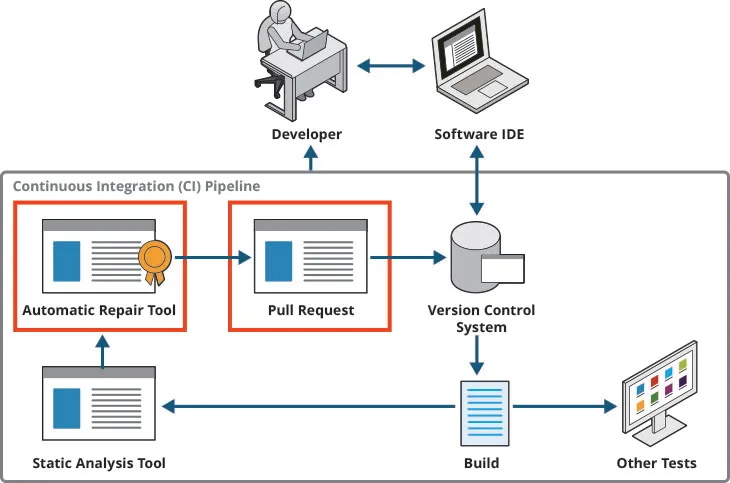
Determine 1: An automated restore software in a CI pipeline
Testing Redemption
Earlier than making Redemption accessible to our collaborators and the broader public, we wanted to ensure the software was viable and behaving as anticipated. We examined it all through the event course of, together with the next:
- regression testing—checks that every enchancment to the software doesn’t break beforehand working take a look at instances
- stumble-through testing—verifies that the restore software doesn’t crash or dangle. The software was examined on all alerts in all codebases, and the take a look at failed if the software crashed, hung, or threw exceptions.
- pattern alert testing—ensures repairs are passable, verified by builders. Since we generated greater than 15,000 alerts, we had to decide on random samples of alerts to test repairs.
- integration testing—checks that the repairs didn’t change the code habits, akin to inflicting the code to crash or fail a sound take a look at case
- efficiency testing—ensures repairs don’t considerably impede time or reminiscence efficiency
- recurrence testing—verifies that repaired alerts aren’t re-reported or re-repaired
This testing ensured that the software carried out reliably and safely for our collaborators and broader person base. Now that we’re assured that Redemption can meet these requirements, we’ve begun to work with our collaborators to combine it into their software program growth workflows.
Redemption in Motion
To see Redemption in motion, you possibly can view or fork the code accessible in our GitHub repository. (Observe that, along with an SA software, Redemption requires Docker because the code runs inside a container.)
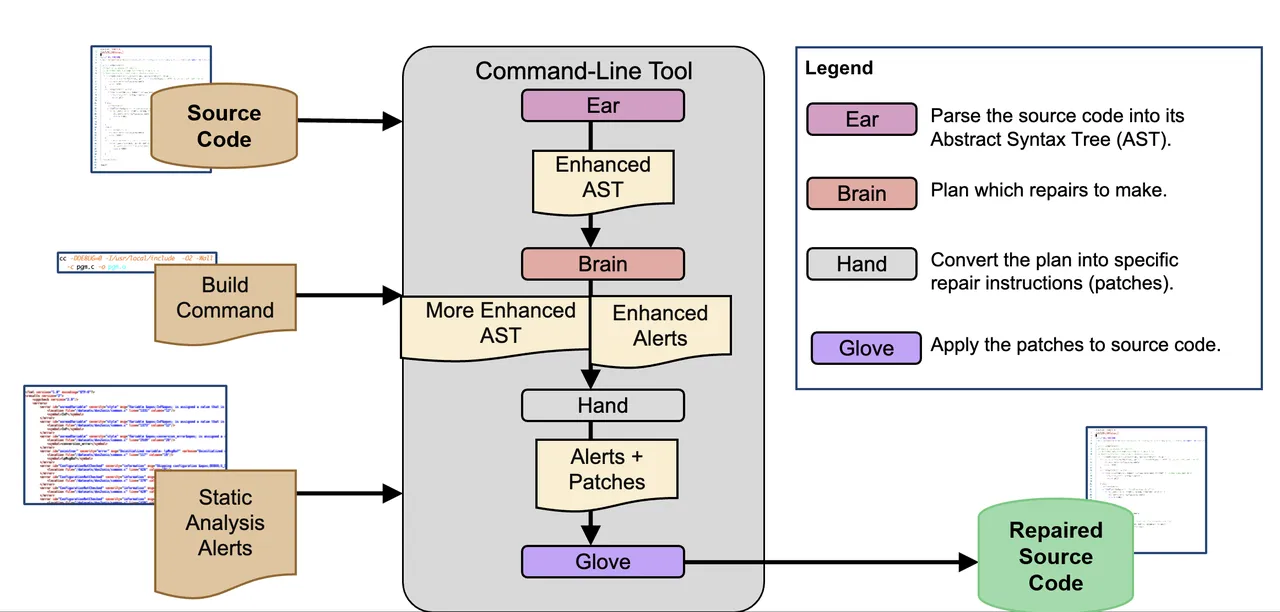
Determine 2: A diagram of Redemption’s workflow
At a excessive degree, Redemption works by following these steps:
- An SA software checks the code for any potential errors. A file is generated containing the SA alerts.
- The file is transformed to a JSON format that Redemption can learn.
- Redemption’s “Ear” module parses the code into an Summary Syntax Tree (AST).
- Redemption’s “Mind” module identifies which repairs to make.
- Redemption’s “Hand” module turns these restore plans into patches.
The picture under reveals the distinction between the preliminary output from an SA software in crimson and the repairs from Redemption in inexperienced. On this case, Redemption has added checks for a null pointer to restore potential null pointer dereference errors. Redemption has additionally initialized some uninitialized variables. From right here, a developer can select to use or reject these patches.
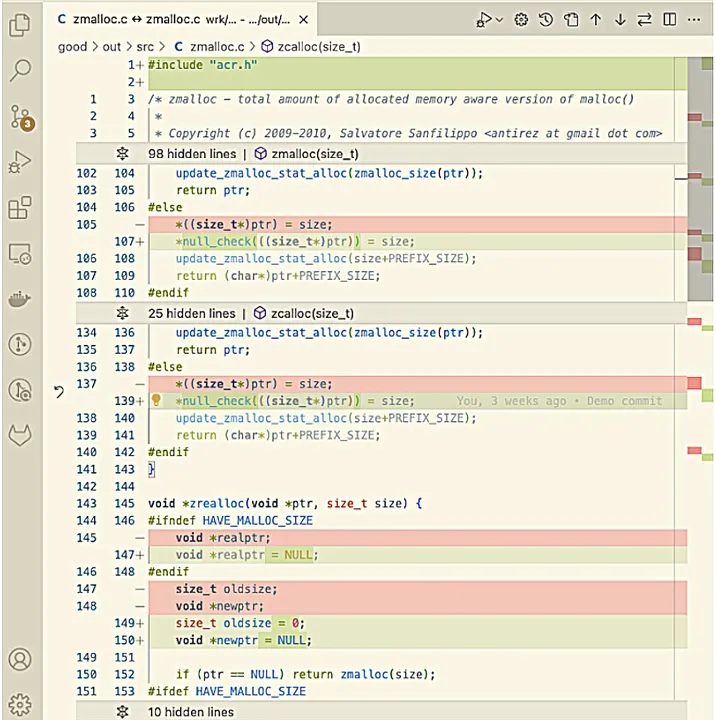
Determine 3: Repaired code after operating Redemption
Increasing Redemption to Extra CI Pipelines
What’s subsequent for Redemption? As we transfer into the following phases, now we have recognized a number of areas for additional growth. As I famous above, we want to add assist for added SA instruments, and we plan to extend the variety of restore classes from three to 10, together with repairs of integer overflows and ignored operate return values. As we broaden the restore classes, we will additionally restore extra varieties of defects, like indentation errors.
We additionally see potential to assist further instruments in CI workflows. For instance, future growth might embrace assist for extra IDEs. Redemption presently works with Gitlab, however further CI pipelines could possibly be included. Should you’d like to assist with any of this work, we welcome code repairs and different contributions to the Redemption codebase on GitHub.

