A Chinese language risk actor is as soon as once more exploiting Ivanti distant entry units at massive.
In case you had a nickel for each high-profile vulnerability affecting Ivanti home equipment final yr, you’d have lots of nickels. There was the essential authentication bypass in its Digital Site visitors Supervisor (vTM), the SQL injection bug in its Endpoint Supervisor, a trio affecting its Cloud Companies Equipment (CSA), essential points with its Standalone Sentry and Neurons for IT Service Administration (ITSM), plus dozens extra.
It began final January, when two severe vulnerabilities had been found in Ivanti’s Join Safe (ICS) and Coverage Safe gateways. By the point of disclosure, the vulnerabilities had been already being exploited by the Chinese language-nexus risk actor UNC5337, believed to be an entity of UNC5221.
Now, one yr and one secure-by-design pledge later, UNC5337 has returned to hang-out Ivanti over again. The group has been exploiting a new essential vulnerability in ICS, which additionally impacts Coverage Safe and Neurons for Zero Belief Entry (ZTA) gateways. Ivanti has additional warned of a second, barely much less extreme bug that hasn’t been noticed in exploits but.
“Simply because we’re seeing these typically does not essentially imply that they are straightforward to drag off — it is a extremely refined group that’s doing this,” Arctic Wolf CISO Adam Marrè factors out, in protection of the downtrodden IT vendor. “Engineering shouldn’t be straightforward, and safe engineering is much more tough. So although you might be following the rules of secure-by-design, that does not imply that somebody is not going to have the ability to come alongside and both with new applied sciences, or new strategies, and sufficient time and sources, hack in.”
2 Extra Safety Bugs in Ivanti Units
As but unexploited (so far as researchers can inform) is CVE-2025-0283, a buffer overflow alternative in ICS variations previous to 22.7R2.5, Coverage Safe earlier than 22.7R1.2, and Neurons for ZTA gateways earlier than 22.7R2.3. The “excessive” severity 7.0 out of 10-rated situation within the Frequent Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) may allow an attacker to escalate their privileges on a focused gadget, however requires them to be authenticated first.
CVE-2025-0282 — rated a “essential” 9.0 in CVSS — doesn’t include that very same caveat, permitting for code execution as root with no authentication required. Ivanti disclosed few particulars concerning the precise reason behind the problem, however researchers from watchTowr had been in a position to efficiently reverse engineer an exploit after evaluating ICS’s patched and unpatched variations.
In response to Mandiant, UNC5337 started exploiting CVE-2025-0282 in mid-December, deploying the identical “Spawn” household of malware it has utilized in exploits of earlier ICS bugs. These instruments embrace:
-
The SpawnAnt installer, which drops its malware colleagues and persists by way of system upgrades
-
SpawnMole, which facilitates back-and-forth communications with attacker infrastructure
-
SpawnSnail, a passive safe shell (SSH) backdoor
-
SpawnSloth, which tampers with logs to hide proof of malicious exercise
“The risk actor’s malware households show vital information of the Ivanti Join Safe equipment,” says Mandiant senior marketing consultant Matt Lin. The truth is, apart from UNC5337 and its spawn, researchers additionally noticed two extra unrelated however equally bespoke malware deployed to contaminated units. One — DryHook, a Python script — is designed to steal consumer credentials off focused units.
The opposite, PhaseJam, is a bash shell script that allows distant and arbitrary command execution. Most inventive, although, is its skill to keep up persistence by way of sleight of hand. If an administrator makes an attempt to improve their gadget — a course of that might unseat PhaseJam — the malware will as an alternative present them a faux progress bar that simulates every of the 13 steps one would possibly count on in a reputable replace. In the meantime, within the background, it prevents the reputable replace from operating, thereby guaranteeing that it lives one other day.
DryHook and PhaseJam may need been the work of UNC5337, Mandiant famous, or one other risk actor altogether.
Time to Replace
Information from The ShadowServer Basis means that north of two,000 ICS situations might be susceptible on the time of writing, with the best focus within the US, France, and Spain.
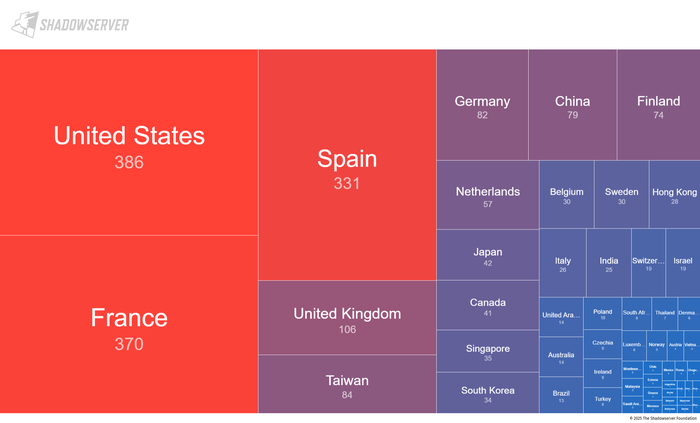
Supply: The Shadowserver Basis
Ivanti and the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Safety Company (CISA) have revealed directions for mitigating CVE-2025-0282, emphasizing that community defenders ought to run Ivanti’s built-in Integrity Checker Device (ICT) to hunt out infections, and implement patches instantly.
“We’ve launched a patch addressing vulnerabilities associated to Ivanti Join Safe,” an Ivanti spokesperson tells Darkish Studying. “There was restricted exploitation of one of many vulnerabilities and we’re actively working with affected clients. Ivanti’s ICT has been efficient in figuring out compromise associated to this vulnerability. Risk actor exploitation was recognized by the ICT on the identical day it occurred, enabling Ivanti to reply promptly and quickly develop a repair. We strongly advise clients to carefully monitor their inner and exterior ICT as a part of a sturdy and layered strategy to cybersecurity to make sure the integrity and safety of the whole community infrastructure.”
It might be value noting that in contrast to ICS, Coverage Safe and ZTA gateways will not be receiving their patches till Jan. 21. In its safety advisory, Ivanti acknowledged that ZTA gateways “can’t be exploited when in manufacturing,” and that Coverage Safe is designed to not be Web-facing, decreasing the danger of exploitation by way of CVE-2025-0282 or comparable vulnerabilities.
“It is vital that directors listed here are doing the proper issues,” Marrè says, noting, “That will lead to some downtime, which might be disruptive for organizations, which might result in them placing it off, or not fixing it as completely and in addition to they need to.”
Lin provides, “We’ve noticed organizations which have traditionally acted promptly in response to those threats didn’t expertise the identical damaging impacts when in comparison with organizations that did not do the identical.” He additionally acknowledges, “All of the swirl that takes place within the background as soon as one in all these patches is introduced.
“Safety groups throughout orgs need to scramble to not simply patch, but additionally perceive whether or not they’re susceptible, and in that case, do they solely must patch, or have they already been breached? And if they’ve been breached, that begins one other incident response, which creates huge workflows throughout firms around the globe. It’s vital to not lose sight of the toil and exhaustion that defenders undergo when assessing these situations and never be hyper essential of their preliminary response occasions.”

