All analysis complies with the related moral laws. For experiments on zebrafish, all protocols used have been accepted by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Ethic Committee (PRBB–IACUEC) and carried out in line with nationwide and European laws. C. elegans is a nematode and, thus, exempt from moral approval and laws.
Principle and simulation of the bead displacement in a viscoelastic medium in a time-varying trapping potential
The impact of getting two alternating optical traps on the precise measurement of the response operate χt(ω), and, due to this fact, G modulus G(ω), is launched on this part and detailed within the Supplementary Data. Two strategies are launched. First, we use a numerical methodology within the time area, aiming on the trajectory of the trapped probe, to emulate the violation of the continuity situation between the pressure F(t) = F1(t) + F2(t) and place xp = F2/okay measurements (Fig. 1). Second, by truncating the dynamic, oscillatory trapping potential on the first harmonic, we receive an analytical expression within the frequency area that we additional use to compensate the time-sharing impact, that’s, to retrieve χ(ω) from χt(ω).
Research of deviation by way of FDEs
Beneath an AOD-modulated time-sharing regime, the laser spot step by step vanishes from lure 1 and seems into lure 2 because the acoustic wave enters the laser beam cross-section on the AOD crystal (Supplementary Data). In our setup, this happens inside a transition time of τ = 10 µs. After that, the laser spot stays at lure 2 for 30 µs and the transition is, due to this fact, reversed again into lure 1. In the meantime, a voltage knowledge level is sampled with a delay of 33 µs with respect to the rising fringe of the acoustic wave. As a result of traps 1 and a pair of fall throughout the linear regime of the trapped particle, forces performing onto it are equal to that from a single lure present process the next trapezoidal trajectory (Supplementary Data):
$${x}_{l,n}(t)=left{start{array}{ll}start{array}{ll}{x}_{2,n}-frac{t}{tau }left({x}_{2,n}-{x}_{1,n}proper) & 0le t < 10,upmu {rm{s}} {x}_{1,n} & 10,upmu {rm{s}}le t < 40,upmu {rm{s}} {x}_{1,n}-frac{t}{tau }left({x}_{1,n}-{x}_{2,n}proper) & 40,upmu {rm{s}}le t < 50,upmu {rm{s}} {x}_{2,n} & 50,upmu {rm{s}}le t < 80,upmu {rm{s}}finish{array} & n=0,,1,,2ldots finish{array}proper.,$$
(2)
the place x2,n = 0, ∀n and x1,n are discrete values of x1(t) = 2x0sin(ωt) sampled at ft = 12.5 kHz. Right here the amplitude of oscillation in x1(t) is expressed as A = 2x0 for mathematical comfort. To seize the power-law rheological behaviour of most samples in biology, we use the fractional time-derivative operator ({D}_{{rm{t}}}^{alpha }), which describes the stress–pressure relationship of a springpot as (sigma (t)=C_{alpha} {D}_{{rm{t}}}^{,alpha }epsilon (t)) (ref. 19). We numerically solved equations (3)–(5) to acquire the trajectory of the probe bead within the laboratory body x(t) for various supplies and at completely different driving frequencies ωj. Due to this fact, the instantaneous pressure is obtained as F(t) = okay(xl(t) – x(t)), from which the interleaved BFP interferometry voltage indicators V1(t1,i) and V2(t2,i) are sampled at time factors t1,i and t2,i, respectively. Lastly, the quick Fourier remodel of the 2 indicators is taken and the response operate (hat{chi}_t(omega_j)) and G modulus (hat{G}_t(omega_j)) are obtained utilizing equations (1a) and (1b). A Python code (v. 3.9.7) is offered to hold out the FDE simulations (Supplementary Data, https://gitlab.icfo.internet/rheo/Tweezers/timsom). The comparability between the bodily response operate (hat{chi}(omega_j)) and the one accounting for the time-sharing deviation (hat{chi}_t(omega_j)) is proven in Fig. 1g for 3 completely different power-law supplies. The corresponding G moduli (each bodily and time-sharing deviated) are proven in Prolonged Information Fig. 1.
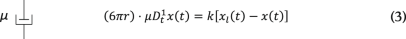
(3)
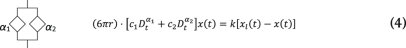
(4)
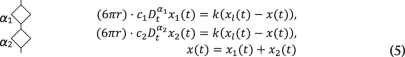
(5)
FHA
To right the noticed deviations within the FDE and the experiment, we analytically solved the equations of movement of the bead (hat{x}(omega’)) within the area of frequencies ω′:
$$hat{x}left({omega }^{{prime} }proper)=hat{chi }left({omega }^{{prime} }proper)kleft[{hat{x}}_{l}left({omega }^{{prime} }right)-hat{x}left({omega }^{{prime} }right)right],$$
(6)
which turns into
$$hat{x}left({omega }^{{prime} }proper)={hat{chi }}_{{rm{a}}}left({omega }^{{prime} }proper)okay{hat{x}}_{l}left({omega }^{{prime} }proper),$$
(7)
Right here (hat{chi}_a(omega’)) is the the response operate of the lively–passive system (Supplementary Equation (3)). (hat{x}_l(omega’)) is the Fourier remodel of the FHA of the lure trajectory, which—within the time area t—reads as
$${x}_{{rm{l}}}(t)=frac{{x}_{1}}{2}exp ({rm{i}}omega t)left[1+sin left({omega }_{{rm{t}}}cdot tright)right],$$
(8)
the place the complicated oscillation exp(iωt) is used, as a substitute of an actual one equivalent to sin(ωt) or cos(ωt), with the only goal of simplifying the notation within the frequency area. After Fourier remodel, the lure trajectory reads
$${hat{x}}_{{rm{l}}}left({omega }^{{prime} }proper)=frac{{x}_{1}}{2}left[delta left({omega }^{{prime} }-omega right)+frac{delta left({omega }^{{prime} }-{omega }_{+}right)-delta left({omega }^{{prime} }+{omega }_{-}right)}{2{rm{i}}}right],$$
(9)
the place ω± = ωt ± ω and δ(ω′) is the Dirac distribution.
To acquire the linear response operate χt(ω) from the FHA approximation, the identical steps recognized for the FDE simulation should be adopted, however this time utilizing an analytical strategy. The main points of the calculations are given in Supplementary Part 1.8. The obtained expression of (hat{chi}_t(omega)) is a operate of the response operate of the fabric (hat{chi}), time-sharing frequency ωt and lure stiffness okay. It reads as
$${hat{chi }}_{{rm{t}}}(omega )=gleft(hat{chi },{omega }_{{rm{t}}},kright)(omega )=frac{hat{chi }(omega )-{hat{chi }}_{1}(omega )+kleft[;hat{chi }(omega ){hat{chi }}_{1}(omega )-{hat{chi }}_{+}(omega ){hat{chi }}_{-}^{* }(omega )right]}{1+2k{hat{chi }}_{1}(omega )+{okay}^{2}{hat{chi }}_{+}(omega ){hat{chi }}_{-}^{* }(omega )},$$
(10)
the place
$${hat{chi }}_{1}(omega )=frac{1}{2}left[{hat{chi }}_{+}left(omega right)+{hat{chi }}_{-}^{,* }left(omega right)right],$$
(11a)
$${hat{chi }}_{+}(omega )=hat{chi }left({omega }_{{rm{t}}}+omega proper),$$
(11b)
$${hat{chi }}_{-}^{* }(omega )={hat{chi }}^{* }left({omega }_{{rm{t}}}-omega proper)=hat{chi }left(-{omega }_{{rm{t}}}+omega proper).$$
(11c)
The asterisk ‘*’ denotes the complicated conjugate operation.
The goodness of the FHA approximation was then checked by evaluating the outcomes predicted utilizing equation (10) with these predicted utilizing the FDE strategy. To take action, we utilized the FHA correction to the deviated knowledge simulated by FDE (Fig. 1g).
Optical micromanipulation and fluorescence microscopy
Optical tweezers
Our optical micromanipulation and microscopy platform is constructed round an inverted microscope (Nikon Ti2) with a spinning-disc module (Andor DragonFly 505)23. The optical tweezer unit (SENSOCELL, Impetux Optics) is coupled to the rear epifluorescence port of the Ti2 microscope. The 1,064 nm (most output energy, 5 W) trapping laser is modulated by a pair of AODs (for x– and y-axes management) optically conjugated to the doorway pupil of a water-immersion goal (Nikon Plan Apo, ×60, numerical aperture = 1.2), which, in flip, focuses the trapping beam onto the focal airplane, thereby producing the optical traps. The AODs are addressed at a frequency of 25 kHz, for which every lure is addressed at 12.5 kHz within the dual-trap time-sharing configuration and therefore the utmost oscillatory frequency for lively microrheology outcomes is 6.25 kHz (Nyquist frequency).
Drive and place detection with time-sharing optical tweezers
Optical pressure measurements have been carried out with a BFP interferometry system (SENSOCELL, Impetux Optics), optimized for gentle momentum detection59. The ahead scattered gentle is captured utilizing a high-numerical-aperture condensor and conveyed to a position-sensitive detector for which volt-to-piconewton conversion issue α is calibrated by the producer. Probe positions—relative to the lure—have been derived after measurements of the trapping stiffness okay (pN µm–1) by quick scanning the lure throughout the probe. Variations within the preliminary gentle momentum and lure energy over the sector of view are compensated by the driving software program of the optical traps (LightAce v. 1.6.2.0 SDK for buying optical tweezer pressure spectroscopy and for lively microrheology, Impetux Optics). An in depth protocol for the startup and use of this optical tweezer platform might be discovered elsewhere23.
Energetic microrheology
Our lively microrheology measurements consist of 4 steps.
-
Centering the laser on the trapping probe utilizing the ‘Particle Scan’ routine of the LightAce software program: that is solely wanted for strong samples. Conveniently, for primarily liquid samples (water or protein droplets), the bead is pulled into the trapping potential with none centring routine.
-
Selection of G0 (Supplementary Textual content 7.1)
-
Measure the lure stiffness: to do that, the laser is scanned throughout the trapping probe. A linear match to the linear regime, inside −200 nm ≤ 0 ≥ 200 nm, was utilized. The slope of the road immediately supplies okay by a hyperlink between pressure (F, as measured by momentum modifications on the position-sensitive detector22) and lure place xl such that okay = F/xl.
-
Apply a sequence of oscillations with particular parameters of frequency, amplitude and measurement period. The frequencies and amplitudes utilized in each measurement are laid out in Supplementary Tables 3–5
-
Retrieval of χ(ω) and G(ω) values from (hat{chi}_t(omega_j)) by the FHA methodology (RheoAnalysis, Impetux Optics).
Microrheology in calibrated supplies
Glycerol options
Completely different concentrations of glycerol (from 0% (= MilliQ water) to 95%) combined with a fluorescent bead resolution (1 µm microspheres, Thermo Fisher, F8816) have been used. Parameters for the rheology routine are offered in Supplementary Desk 3. The viscosity ηTimSOM for the glycerol mixtures was obtained from the slope of the loss modulus G″(ω) = ηTimSOMω (Fig. 2a and Prolonged Information Fig. 2a(iii)). Stokes-drag pressure measurements have been carried out by shifting the identical bead with rising velocities, vlure (Prolonged Information Fig. 2a). The fixed plateau pressure throughout the bead motion, Fdrag, was associated to the rate. The viscosity ηdrag was decided by becoming Fdrag(vlure) = (6πηdrag Rvlure) to the pressure–velocity plots, the place R is the radius of the trapped microsphere (Prolonged Information Fig. 2a(iii)). To keep away from modifications in viscosity as a result of laser absorption, trapping energy was left under P = 65 mW (ref. 60). To keep away from hydrodynamic interplay with the chamber surfaces, the trapping airplane was stored at a relative peak of z = 20 µm (ref. 61).
PAA gels
PAA gels have been polymerized from a modification of the recipe utilized in ref. 62. Actual portions for acquiring particular gel stiffness are tabulated in Supplementary Desk 4 and the protocol to supply the gel is detailed in Supplementary Textual content 6. Earlier than the microrheology measurement, the probe/lure centring routine, adopted by the lure stiffness measurements, was carried out. The fractional Kelvin–Voigt mannequin was match to the obtained rheological spectrum (Fig. 2c) to extract the related parameters and in contrast with present literature63.
Creep compliance measurements
Creep compliance measurements have been carried out on 2% PAA gel utilizing force-clamp utility of the LightAce software program (LightAce v. 1.6.2.0 SDK, Impetux, Spain). We used a lure stiffness of 890 pN µm–1 and 220 pN µm–1 for stiff and comfortable gels, respectively. A relentless pressure of F0 = 40 pN was utilized, which results in a typical viscoelastic compliance curve x(t) (Prolonged Information Fig. 2b). A customized MATLAB code was carried out to calculate the frequency-dependent shear modulus from measurements of J(t) within the time area25. The place of the trapped probe was calculated as xbead = xlure − F/okay. The low-frequency plateau modulus was calculated from the frequency-dependent storage G modulus after becoming to a fractional Kelvin–Voigt mannequin (Fig. 2c(ii)).
PDMS
PDMS prepolymer was combined with a curing agent at 100:1 and combined completely with d = 1 µm microspheres (F8816, Thermo Fisher). The answer was degassed in a vacuum pump to eradicate bubbles launched throughout mixing. The combination was instantly used for rheology to keep away from the long-term curation of silicone. Earlier than rheology measurements, the probe/lure centring routine was carried out utilizing the LightAce software program. Additional particulars can be found in Supplementary Textual content 6.
Zebrafish experiments
Microsphere injection and cell preparation
Zebrafish embryos have been injected with 1 nl of microspheres (F8816, Thermo Fisher; diameter, d = 1 µm) at 1:5 of the inventory resolution on the one-cell zygote stage to make sure correct distribution of microspheres23. Microspheres have been coinjected with mRNAs (Supplementary Textual content 6). At 4 h post-fertilization, embryos have been dechorionated with a pair of forceps and their cells have been manually dissociated and left to get well till used64. To visualise the nucleus, the dissociated cells have been incubated for six min in DNA Hoechst at a closing focus of 1 µg ml–1 following the protocol in one other work23. A layer of double Scotch tape (roughly 20 × 20 mm2 extensive) was used as a spacer between the decrease and higher surfaces. A 1 × 1 cm2 gap was made and the layer was adhered onto the underside dish (GWST-5040, WillCo). After incubation with concanavalin A to advertise cell adhesion (t = 30 min, 100 µl, 0.5 mg ml–1; C5275 Sigma), cells have been allowed to settle onto the underside dish floor65 and the cavity was coated on the high with a 22 × 22 cm2 cowl glass (Ted Pella).
Energetic microrheology measurements in zebrafish progenitor stem cells
To carry out lively microrheology measurements inside a cell, first, a cell with one or two microspheres within the cytoplasm is chosen. Then, a working optical airplane is recognized taking a look at nucleus fluorescence, the place the nucleus has its greatest cross-section. Subsequently, the microsphere is trapped and positioned within the chosen airplane between the plasma and nuclear membrane, avoiding adhesions to both one. After placement, the lively microrheology is initialized (Supplementary Desk 5 lists the parameters).
After the measurement of the cytoplasm is accomplished, the bead is positioned to keep up a correspondence with the nuclear envelope. That is completed by slowly shifting the microsphere in direction of the nucleus and observing the pressure sign as a result of bead displacement (Supplementary Video 3). A pressure peak is seen as soon as the bead touches the nucleus. Then, the microrheology routine was carried out perpendicular to the nuclear envelope floor. All lively microrheology measurements are carried out utilizing a lure energy of 60–100 mW on the pattern airplane and have been discovered to not affect the pattern behaviour (Supplementary Textual content 5.1).
Microsphere insertion into the nucleus
The method of inserting the microsphere contained in the cell nucleus consists of making use of a relentless pressure utilizing the optical pressure suggestions system defined above (pressure setpoint, F = 100−200 pN, Prolonged Information Fig. 7). On this means, the microsphere is pushed into the nucleus. First, the bead is positioned involved with the nucleus on the optical airplane by which its fluorescent cross-section is the most important. Then, the clamp is ready from 100 pN to 150 pN and it’s activated till the bead is inserted, or till the microsphere doesn’t indent extra or will get misplaced. The primary 5 s of the bead trajectory, and earlier than insertion, have been used to calculate the creep compliance of the nucleus. Lastly, after the bead was inserted within the nucleus, a rheology routine was carried out contained in the nucleus. The oscillations of this measurement have been completed perpendicular to the insertion course.
Evaluation of creep compliance knowledge
Microsphere displacement beneath clamping pressure was analysed as a creep compliance routine fitted with a Jeffrey’s mannequin utilizing a customized Python script (v. 3.10). All of the experimental routines have been analysed, together with these the place insertion was unsuccessful. For profitable insertion trials, solely the preliminary part—throughout which the bead indents however doesn’t penetrate the nucleus—was thought of. For these routines, the normalized place was fitted utilizing66
$$frac{x,(t)}{{f}_{{{rm{FC}}}}}=frac{1}{kappa }left(1-{{rm{e}}}^{-frac{kappa }{{gamma }_{1}}t}proper)+frac{t}{{gamma }_{2}},$$
(12)
the place x(t) is the displacement of the microsphere, which is split by clamping pressure fFC. This normalization compensates for variations within the forces used for bead insertion in several cells. The fittings enable the extraction of restoring stiffness κ and viscoelastic drags γ1 and γ2.
Experiments in C. elegans
C. elegans upkeep
Strains have been maintained and manipulated beneath customary situations67. Nematode strains have been grown at 20 °C on nematode progress medium plates with OP50 micro organism and synchronized utilizing the usual alkaline hypochlorite remedy methodology68. Solely age-matched, synchronized grownup hermaphrodites (day 1 or day 8) have been used on this research. N2 wild-type pressure was used as a management, except in any other case acknowledged.
Lipid droplet isolation
C. elegans lipid droplet isolation was carried out following the protocol beforehand described47 with minor modifications. Briefly, for pattern preparation, MSB1136 animals have been grown on peptone-enriched plates seeded with NA22 micro organism and synchronized utilizing the usual alkaline hypochlorite remedy methodology68. Then, 2 × 104 synchronized larva-1-stage nematodes have been plated and grown at 20 °C till both day 1 or day 8 maturity for pattern assortment. For lipid droplets, day 8 assortment, animals have been washed with M9 and separated from laid eggs by gravity (to keep away from era mixing) earlier than transferring them to new plates. On the day of the experiment, plates have been washed off, and animals have been collected utilizing phosphate-buffered saline. After washing the pattern thrice with buffer A47, the pellet was resuspended in the identical buffer supplemented with a protease inhibitor (Sigma-Aldrich, P8340). After this, the pattern was manipulated both on ice or at 4 °C. Nematode homogenization and cell disruption have been carried out through the use of an ultrasonic tub (VWR, USC300TH) 4 occasions, 1 min every time, with 30 s intervals. Lipid droplets have been collected in buffer B47 from the post-nuclear fraction by ultracentrifugation adopted by three washing steps. Remoted lipid droplets have been used throughout the similar day for lively microrheology routine in PAA gels (see the part above).
Refractive-index-matching assay
The refractive index of freshly remoted lipid droplets was measured as described48,69 utilizing the commercially obtainable iodixanol resolution (OptiPrep, D1556, Sigma-Aldrich). Lipid droplet resolution was gently combined at completely different iodixanol concentrations till reaching the matching refractive focus (48%) and 0.5% membrane dye BioTracker NIR750 (Sigma-Aldrich, SCT113). For the optical lure scanning and imaging of the lipid droplets, the pattern was mounted in an optical trapping chamber after which sealed with a #1.5 cowl glass, as beforehand described23.
Lipid droplet characterization by TimSOM in vitro
To organize PAA gels of various stiffness values containing each lipid droplets and microspheres, freshly remoted lipid droplet resolution was gently combined with the reagents famous in Supplementary Desk 4. The water was substituted by the identical quantity of lipid droplet resolution for every class of PAA gel. The combo was transferred into the optical trapping cavity after which sealed with a #1.5 cowl glass, as beforehand described23. To extract each lipid droplet measurement and stiffness values, the measurements have been carried out alternatively utilizing lipid droplets and microspheres following the process detailed above.
In vivo TimSOM on C. elegans intestinal epithelial cells throughout ageing
All strains have been seeded on nematode progress medium plates on the identical day and allowed to develop till day 1 (three days post-seeding) and day 8 (ten days post-seeding) maturity. The animals evaluated on day 8 have been transferred to new plates on daily basis throughout the egg-laying interval to keep away from mixing generations. As a result of each LW697 and BN20 introduced one-day developmental delay in contrast with wild kind and BN19, lively microrheology measurements on day 1 and day 8 maturity for these strains have been carried out 4 days and 11 days post-seeding, respectively. On the day of the experiment, nematodes have been mounted on 2% agar pads, immobilized with 10 µM levamisole hydrochloride resolution (Sigma-Aldrich, 31742) after which coated with a 25 × 25 mm2 cowl glass (Ted Pella, #1.5) sealed with fingernail polish. Energetic microrheology was carried out, as described above, for zebrafish progenitor stem cells on C. elegans intestinal cells utilizing endogenous lipid droplets inside 1 h after immobilization to keep away from injury to the animals.
Information evaluation
Evaluation of the info measured utilizing lively microrheology is carried out in RheoAnalysis (Impetux Optics). On this program, the complicated shear modulus is retrieved by performing the required compensations (Supplementary Textual content 1.12). Moreover, fittings from the primary two third-order fashions might be utilized to the dataset by choosing the respective preliminary situations. The evaluation of different calibration experiments such because the Strokes-drag pressure measurements, creep compliance measurements and simulations was completed on personalised MATLAB (v. 2020b) and Python (v. 3.10) scripts.
Statistics and reproducibility
Statistical modelling and speculation testing have been carried out in MATLAB (v. 2020b) and R (v. 4.2.2). No statistical strategies have been used to predetermine the pattern sizes, however our pattern sizes are just like these reported in earlier publications. Information distributions have been assumed to be regular, except clearly not, however this was not formally examined. All of the paired measurements have been examined with a paired, two-sided t-test. All datasets have been acquired in a randomized style, and once they weren’t (for instance, frequency sweep within the rheology routine), the info weren’t biased by the historical past. Information weren’t collected blind to the genotype, however the knowledge introduced in Fig. 5 have been analysed blind to the experimental situation. Damaging knowledge factors within the rheological spectrum have been excluded from the becoming procedures.
Reporting abstract
Additional info on analysis design is offered within the Nature Portfolio Reporting Abstract linked to this text.

