Property lists are basically XML recordsdata with a .plist extension. Here is how you can edit them utilizing the command line within the macOS Terminal app.
XML is an open knowledge format which gained recognition within the mid-1990’s when the web first turned commercialized. It is a text-based format which makes use of key/worth pairs to retailer knowledge. Keys present knowledge labels, and values retailer the info associated to every key.
Knowledge sorts in XML embody Booleans (true/false), numbers, dates, strings (textual content), arrays, dictionaries, and plain knowledge. A dictionary is only a bundled desk of values additionally with its personal set of keys – one for every knowledge merchandise.
By combining and embedding these knowledge sorts in an XML file, you possibly can retailer quite a lot of nested knowledge for absolutely anything. Whereas XML is often saved as plain textual content, it has additionally grow to be one normal for data knowledge interchange throughout the web – though at this time it has been outmoded largely by JSON (Javascript Object Notation), which is considerably comparable.
XML on Apple platforms
When the primary model of Mac OS X shipped in 2000, Apple made it clear it was adopting XML as a file format for a lot of the Mac working system. Apple makes use of a local file format known as Property Lists (.plist) which is apparent XML with some customized Apple XML header data on the high of every file.
You will have seen .plist recordsdata in your macOS Preferences folders in /Library/Preferences, or ~/Library/Preferences. These are easy XML recordsdata containing lists of XML knowledge which might be learn by apps or macOS itself to retailer preferences.
For instance, the macOS Finder’s settings file lives within the Preferences folder and is known as com.apple.Finder.plist. Most .plist settings recordsdata use this type of reverse DNS notation: the second element within the file identify identifies the corporate that makes the software program, then the app’s identify, then the .plist extension.
You may open a .plist file in Apple’s TextEdit app to learn it as uncooked textual content, or you possibly can open it in Apple’s developer IDE, Xcode – or in most every other plain-text editor app.
Xcode has a particular formatting characteristic that shows a .plist file as a desk editor with every kind of information in a row containing the kind of knowledge, and its key. By clicking a popup menu subsequent to every merchandise within the desk you possibly can change its kind to any identified formatted sort.
.plist knowledge of generic, unknown, or opaque sorts are handled as an information blob – or within the case of Apple platform programming an information kind of Knowledge (in Swift), or NSData in Goal-C.
Apps additionally bundle .plist recordsdata inside on macOS, iOS, iPadOS, and watchOS to each describe apps and to retailer content material. The Information.plist file, for instance describes every app and its capabilities to the working system.
There are system APIs in Apple’s working methods to rework and serialize XML and .plists to and from different knowledge codecs.
Modifying property lists
As talked about, you possibly can edit .plist recordsdata instantly by opening them in both a plain textual content editor, or in Xcode.
In the event you open a .plist file in TextEdit for instance, you will see unformatted XML with tags. To alter a .plist file’s knowledge in a textual content editor you will want to know XML tags and the way they work. XML tags are similar to HTML tags.
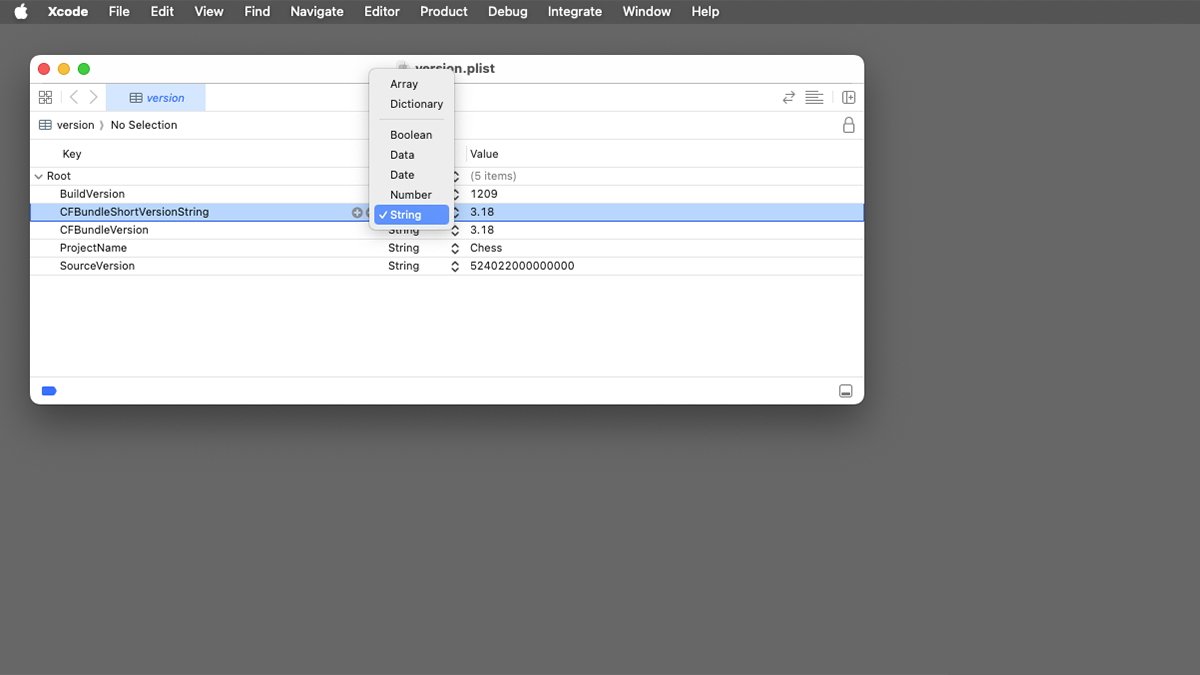
In Xcode you possibly can merely open a .plist file, or add it to an Xcode venture window after which single-click it within the Venture Navigator on the left. This shows the .plist’s contents within the pane on the suitable:
The above window reveals the model.plist file for Apple’s Chess app: every row is one knowledge merchandise, keys for every merchandise are listed within the left column, every knowledge kind is proven within the middle column, and every key’s worth within the column on the suitable.
To alter a .plist file’s knowledge in Xcode both single-click on one row’s knowledge or key and kind in new data, or click on the small popup menu within the middle column within the row to vary its kind. Within the popup menu solely identified, allowable .plist knowledge sorts are listed.
As soon as you’ve got made all of the adjustments you need, merely File->Save the .plist file (or press Command-S in your keyboard).
One big benefit to XML is you possibly can edit the recordsdata on any platform, save them, then copy them between computer systems with out having to transform them. Software program localization is usually performed this manner – with strings of textual content saved in .strings recordsdata for translation between languages. Strings recordsdata additionally comprise normal XML utilizing key/worth pairs.
InfoPlist.strings recordsdata bundled inside apps comprise localized variations of strings discovered within the descriptive data for figuring out an app. That is the textual content that seems, for instance if you do a File->Get Information on an app within the Finder.
Extra not too long ago a model.plist file bundled inside every app might comprise the app’s versioning data saved in XML format utilizing Apple keys equivalent to CFBundleVersion and CFBundleShortVersionString .
Apple has a piece within the developer documentation discussing data property lists.
The “CF” prefix in Apple .plist keys represents Core Basis – a C-based API used to govern base knowledge sorts and .plists on Apple platforms.
Strings recordsdata in Apple platform growth
In Apple growth, strings are sometimes saved in a .strings file or a strings desk for localization. Builders can outsource their strings recordsdata for localization to translation corporations so they do not have do the interpretation.
In the event you look inside an app’s bundle (folder) you may even see a number of .strings recordsdata saved in language folders, with every folder ending in “.lproj” and with an ISO-standard two-character prefix for the nation identify. By duplicating and altering the contents of every model of strings recordsdata, builders can add new languages to app interfaces with out having to know the languages.
macOS and iOS are sensible sufficient to load the proper localized strings file or desk for the present language in use on an Apple system.
By utilizing separate strings and .plist recordsdata, the consumer interface of an app might be modified at runtime or later – with out having to compile the textual content into the app’s binary code. This is named Dynamic Loading.
Because of this you are capable of change the system language in Settings on an Apple system and have the identical app replace its UI textual content for the brand new language chosen. In older working methods distributors needed to ship separate language-specific variations of an app for every nation or language.
Dynamic Loading additionally reduces an app’s reminiscence footprint at runtime since strings aren’t loaded into reminiscence till they’re really used.
Modifying property lists in Terminal
macOS features a (UNIX) Terminal (shell) app which lets you challenge instructions on the command line to carry out actions. Some of the highly effective makes use of of Terminal is batch processing and writing scripts to automate processes.
Many Terminal instructions embody an -r (recursive) flag to inform the command to proceed processing all recordsdata it finds in a given folder irrespective of how deeply nested these recordsdata could also be.
You should use Terminal to each manually and robotically course of .plist and .strings recordsdata for sooner modifying.
This will save time, for instance in case you have a batch of recordsdata for a number of languages and wish to change all their values with new localized textual content from language tables or another inputs. Otherwise you may wish to change all keys for a sure merchandise in a batch of recordsdata without delay with out having to edit every file manually.
We can’t get into shell scripting automation on this article however there are various good books and on-line tutorials for writing shell scripts for batch processing.
Modifying a property checklist in Terminal manually
To edit a .plist file in Terminal, use the built-in defaults command. defaults means that you can each edit and consider .plist recordsdata, in addition to set system settings for identified working system .plist recordsdata utilizing names.
For full utilization of the defaults instructions, in Terminal kind:
man defaults and press Return in your keyboard.
To exit the person system in Terminal press Management-Z.
The principle choice to defaults to vary a worth in an present .plist file is the write possibility adopted by the brand new knowledge to be written.
As the person web page mentions, the brand new knowledge have to be in a selected format (often one other .plist or dictionary) and should comprise the keys and values to be written. The format of this knowledge must be precise or else the command might fail or the file’s knowledge may grow to be corrupted.
For instance the person web page demonstrates altering an array in a .plist which has a reputation of “Default Colour” to a brand new worth of (255,0,0). To do that you’d use the command:
defaults write com.companyname.appname "Default Colour" '(255, 0, 0)'
The place “appname” is the identify of the app for firm “companyname”.
You may as well overwrite present values in a .plist with one other .plist. For instance:
defaults write com.companyname.appname '{ "Default Colour" = (255, 0, 0); "Default Font" = Helvetica; }';
On this instance the brand new .plist knowledge is enclosed in curly braces, and incorporates two key/worth pairs: “Default Colour” and “Default Font”.
Watch out when writing to present settings recordsdata as a result of in case you corrupt the info in a .plist file utilized by macOS, your Mac might cease working appropriately.
There are additionally delete choices for defaults, however remember delete is much more harmful than the write possibility. A few of the delete choices destroy knowledge – and may even delete all knowledge in a website with a single command.
You may print an inventory of all domains in your Mac by utilizing the domains possibility:
Modifying a property checklist file outdoors a settings area
To edit any arbitrary .plist file positioned at any writable location within the filesystem, use the filepath possibility. This lets you edit a .plist in the identical approach you probably did above for settings recordsdata, however for any .plist file at any given path. filepath additionally works with the learn command.
defaults learn ~/Library/Containers/com.apple.TextEdit/Knowledge/Library/Preferences/com.apple.TextEdit.plist
reads the TextEdit app settings file positioned within the consumer’s Library folder.
However the filepath possibility works for any .plist file – not only for settings recordsdata or recordsdata belonging to apps.
By writing and mixing defaults instructions into an automatic script file, you possibly can see how straightforward it will be to batch course of .plist recordsdata with out an excessive amount of effort.
The truth is, a lot third-party Apple Software program is constructed this manner: often a construct engineer writes automation scripts to retrieve a codebase from a server, batch course of localized .plist and strings recordsdata, then run builds on all software program parts. Builds are often then post-processed utilizing one other set of scripting recordsdata to assemble the ultimate software program for launch.
The defaults command additionally has choices for including or changing particular kinds of knowledge to a .plist file.
The defaults system has been round in macOS, Mac OS X, and iOS for many years and actually was one of many unique applied sciences utilized in NeXTStep – the precursor to most of Apple’s working methods at this time.
When you grasp the defaults system you will end up utilizing it quite a bit to examine and alter macOS settings and to edit .plist recordsdata. Simply be certain you are comfy and assured doing so earlier than you utilize it.
Apple has a brief part within the Terminal Consumer Information which describes how you can use the defaults system to edit .plist recordsdata and settings.
In the event you use a Home windows laptop, take a look at the actually cool XML modifying instruments made by Altova.