After all, all of us bear in mind the Theranos debacle and the cautionary story of Elizabeth Holmes. If nothing else, it taught us that there isn’t a silver bullet for non-invasive diabetes diagnostics. The lesson was discovered: nobody is keen to supply false hope once more. This consciousness has solely intensified the race amongst researchers and Large Tech to ship actual, viable options on this vital discipline.
And the stakes could not be greater. In accordance with the World Well being Group, the variety of individuals dwelling with diabetes has skyrocketed—from 200 million in 1990 to 830 million in 2022. This means that the prevalence of diabetes has practically tripled over the previous three many years, with a rise of roughly 2.8 instances.
So, once I discovered {that a} crew from the College of Tokyo had developed a cutting-edge, non-invasive well being monitoring system, I couldn’t assist however get excited. Their system employs high-speed cameras and superior AI algorithms to detect early indicators of hypertension and diabetes. Just lately detailed within the American Coronary heart Affiliation’s Circulation journal, this progressive method bridges the accessibility hole by providing an answer that requires no wearables or bodily contact. It’s a leap ahead in well being monitoring and a glimpse into the way forward for really easy care.
The Want for Accessible Well being Monitoring Options
When you’ve learn my wearable critiques right here at nextpit, you already know I’m a powerful advocate for wearable expertise and the developments in smartphone-based well being apps. The potential for self-health monitoring is simple, providing people unprecedented management over their well-being. Nonetheless, the adoption of those applied sciences stays largely restricted to health-conscious people—and solely to those that can afford them.
For the broader inhabitants, notably these much less inclined towards proactive well being administration, these gadgets are removed from changing into mainstream. That’s exactly the problem the College of Tokyo’s current research goals to deal with. By introducing a non-contact, AI-powered system, the researchers hope to democratize illness detection, making superior well being monitoring accessible to everybody.
How It Works: Simplifying the Science
The researchers designed a classy well being monitoring system that doesn’t require bodily contact or wearable gadgets. Right here’s the gist of the way it works: a high-speed digital camera is about up about half a meter away from the particular person and captures detailed pictures of their face and arms. These pictures are then processed by synthetic intelligence (AI), which seeks particular patterns in blood movement underneath the pores and skin.
Hypertension Detection
For detecting hypertension, the system analyzes how blood strikes by the physique utilizing information like pulse wave transmission time (principally, how shortly blood flows). By combining these insights with fashionable well being requirements for hypertension, the AI reached a powerful 94% accuracy in figuring out hypertension. Even with fast scans—simply 30 seconds and even 5 seconds—the accuracy stayed excessive, at 86% and 81% respectively.
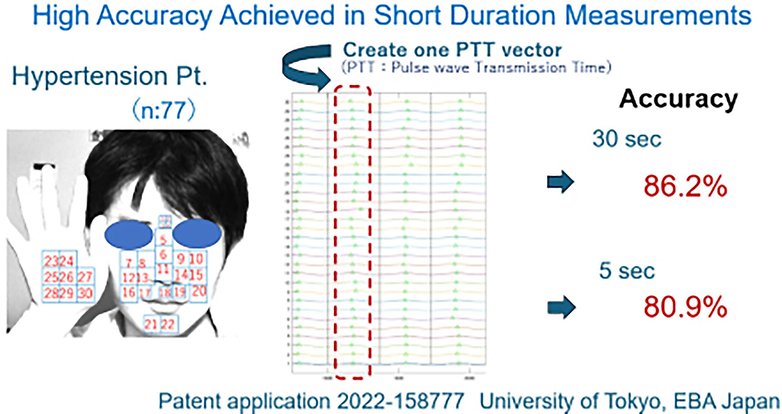
Diabetes Detection
Relating to diabetes, the system appears for indicators within the blood movement linked to greater blood sugar ranges, utilizing information just like conventional HbA1c assessments. Whereas not as exact because the hypertension readings, the AI nonetheless carried out nicely, figuring out diabetes with 75% accuracy—providing a glimpse into how non-invasive instruments might someday complement conventional assessments.
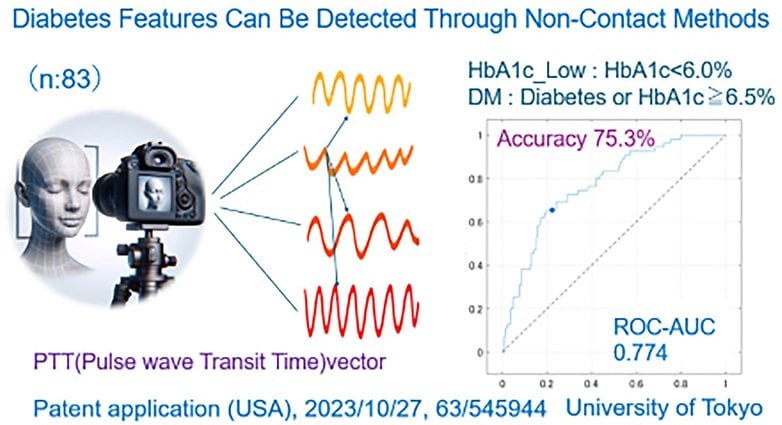
This method might be a game-changer for accessible, tech-driven well being care, ditching the necessity for wearables or time-consuming physician visits. For anybody obsessive about the intersection of well being and expertise, it’s a daring leap ahead, bringing AI-powered well being monitoring nearer to on a regular basis life.
The Potential Influence on International Well being
For individuals like me, this expertise seems like a game-changer within the quest for accessible, non-invasive diagnostics. By eliminating the necessity for bodily contact or wearable gadgets, this technique opens the door to smartphone-based well being monitoring—probably providing steady, unobtrusive monitoring for people in danger.
The significance of early detection for circumstances like hypertension and diabetes can’t be overstated. Catching these points early is essential to stopping extreme problems like strokes, coronary heart assaults, or organ harm.
What’s notably thrilling is the system’s ease of use and its non-contact design, which might make it way more approachable for individuals who usually keep away from common well being screenings. This can be a large win for inclusivity, reaching those that may in any other case slip by the cracks of conventional well being care programs.

Residing in Germany for a couple of years has given me a brand new perspective, however as somebody from Brazil, I can’t assist however take into consideration how transformative this expertise might be for underserved communities—like indigenous populations within the Amazon Rainforest. These communities typically lack entry to well being care however do have smartphones—which current a distinctive alternative to bridge gaps.
Whereas this innovation has the potential to learn individuals globally, its impression on those that are solely excluded from the well being system might be really life-changing.
Unanswered Questions and the Street Forward
Whereas the research outcomes are promising, there are nonetheless necessary unanswered questions in regards to the expertise’s broader applicability and real-world effectiveness. Based mostly on my interview with the research writer Dr. Ryoko Uchida, right here’s what we all know—and what stays to be addressed:
Demographics: A Lacking Puzzle Piece
One vital hole is knowing how nicely the system performs throughout completely different demographics. In accordance with Dr. Uchida, the research concerned 215 adults, primarily Japanese and “different” Asians, with a mean age of 64 years, and 36% of contributors had been feminine. Of those, 62 had hypertension, 88 had regular readings, and 65 fell in between. For diabetes, 44 contributors both had a previous analysis or an HbA1c stage of 6.5% or greater.
Nonetheless, the crew has but to investigate variations in accuracy throughout age teams, genders, or ethnicities. This can be a key space for future analysis to make sure the expertise works successfully for a extra numerous inhabitants.
Pattern Measurement: Promising however Preliminary
The research’s pattern dimension of 215 contributors offered promising outcomes, with no important variations in accuracy when evaluating preliminary information from 60 contributors to the complete set. Nonetheless, as Dr. Uchida identified, the efficiency of the system at scale—throughout probably thousands and thousands of customers—is unknown. She emphasised the necessity for large-scale medical research to additional validate the system’s reliability and effectiveness.
Actual-World Implementation: Past the Lab
The system was examined in a managed hospital setting, which naturally raises questions on the way it will carry out in real-world environments with various circumstances, reminiscent of completely different lighting, motion, and backgrounds. Dr. Uchida acknowledged these limitations, stating that enhancements to the algorithm are already underway.
For instance, the system’s present capability to attain excessive accuracy with simply 5 seconds of information suggests room for additional optimization—probably decreasing the required time to 2 or three seconds. Moreover, changes to account for variable lighting circumstances throughout information pre-processing are in improvement. These updates shall be vital for guaranteeing the system can adapt to much less managed environments, with additional real-world testing deliberate to evaluate its robustness.
Last Ideas
The College of Tokyo’s non-contact well being monitoring system is a daring leap ahead in preventive drugs. By leveraging AI and high-speed imaging, it transforms early detection for circumstances like hypertension and diabetes—no wearables, no difficult setups, simply seamless, user-friendly tech. This might redefine how we take into consideration well being care, bringing proactive monitoring to everybody, not simply the gadget-savvy.
Smartphone cameras, in the meantime, have quietly developed into highly effective well being instruments. As soon as restricted to taking images, they now ship refined options able to monitoring every thing from coronary heart charges to respiratory patterns. This transformation alerts the smartphone’s rising function as a well being companion.
Google’s Pixel cameras are a fantastic instance. With Google Match, these telephones use AI to measure coronary heart and respiratory charges utilizing solely the digital camera. It’s well being monitoring made ridiculously straightforward—no additional gadgets, no friction, simply on the spot insights from the gadget you’re already utilizing day by day.
Different apps have jumped on board too, turning your telephone’s digital camera and flash right into a makeshift well being tracker. By analyzing delicate adjustments in pores and skin shade brought on by blood movement, these apps can monitor your pulse and supply a real-time glimpse into your well being.
Whereas this tech nonetheless falls underneath the wellness class and hasn’t earned FDA recognition, it’s a testomony to the untapped potential of current smartphone {hardware}. With the fitting software program, even the gadgets we already carry can ship highly effective well being insights which are only a faucet away.
Because the College of Tokyo’s system evolves, pairing this non-contact AI expertise with the capabilities of right now’s smartphone cameras might change the sport solely. Well being administration might turn out to be as routine—and as easy—as checking your notifications. For anybody invested in tech’s function in fashionable well being care, it’s an thrilling step ahead.

