You would possibly assume that connecting anonymously to a public Wi-Fi community doesn’t reveal a lot about you. You could be utilizing a VPN (digital non-public community) to guard all the pieces you do. Even when you aren’t, the overwhelming majority of internet sites and e mail servers (and just about all these run by firms) use client-to-server encryption. However what when you may very well be tracked anyway?
Apple has an answer for this because it does for a lot of monitoring techniques. The corporate’s trick lies in how Wi-Fi (and ethernet) adapters determine themselves over an area community.
How MAC addresses work
Each community adapter has a singular, factory-assigned deal with baked in or programmed in at its manufacture. It’s known as a Media (or Medium) Entry Management deal with; the abbreviation is MAC, confusingly sufficient, but it surely has nothing to do with Macintoshes. The place an IP (Web Protocol) deal with defines your machine’s location on the web, a MAC deal with defines it in your native space community (LAN). The MAC is partly how gadgets on a LAN all talk with each other, whether or not over Wi-Fi or ethernet.
Apple acknowledged that any fastened identifier may very well be used to trace somebody if the ID may very well be tied to information shared past an area community. Once you hook up with a wi-fi hotspot, your Wi-Fi MAC deal with will get transmitted as a result of it’s an inherent a part of that connection. If that MAC deal with doesn’t change over time, the backend of a hotspot portal or a enterprise location’s point-of-sale system may construct up a profile of you (or your machine) utilizing a wide range of clues that features any Bluetooth broadcasts, logging right into a portal to achieve free entry, utilizing a reduction card whereas paying, and emitting different broadcast identifiers.
They might promote this data to third-party data brokers who may monitor you extensively throughout areas that additionally share and promote data and goal you with advertisements even when all of your internet, e mail, and file-transfer connections have been safe, as is the case in most eventualities in the present day. Worse, it’s clear that legislation enforcement and authorities companies routinely buy entry to location data with out use of subpoenas or authorized mechanisms {that a} supplier otherwise you would learn of and will struggle.
Whereas a MAC deal with is manufacturing facility assigned, it may be modified. As an illustration, you’ll have had the expertise of connecting to a Wi-Fi gateway to configure it and seeing an choice buried in superior settings to change the MAC deal with. (This will typically be useful whenever you’re changing a router, and your ISP’s broadband modem or adapter is registered to that older machine’s MAC deal with.)
The power for a MAC to vary and the potential for a MAC to be tracked is why Apple launched a Non-public Wi-Fi deal with as a characteristic in iOS 14, iPadOS 14, and watchOS 7. It later added it to macOS. The characteristic is enabled by default for all Wi-Fi connections on all platforms. Apple made this characteristic extra granular—providing methods to tune it additional—in iOS 18, iPadOS 18, macOS 15 Sequoia, and watchOS 11.
Apple makes use of the time period “Non-public Wi-Fi deal with” to check with the MAC deal with for a Wi-Fi adapter. It’s equivalent to a MAC deal with, however the firm doesn’t provide non-public MAC addresses for Ethernet connections.
Change your non-public deal with settings
You may view the settings just for particular person networks as a result of Apple lets you’ve completely different settings for every community to which you join.
- On an iPhone or iPad, go to Settings > Wi-Fi and faucet the linked community title. You may as well change Non-public Wi-Fi choices by tapping the i (information) icon subsequent to a close-by community, or tapping Edit on the high of Wi-Fi settings and tapping the i icon.
- On a Mac, go to System Settings > Wi-Fi and click on Particulars subsequent to the linked community. You may as well faucet the … (Extra) button subsequent to a community proven as close by to make modifications to the Non-public Wi-Fi deal with settings. (You may’t change saved MAC settings in macOS.)
- On a Watch, go to Settings > Wi-Fi, faucet the title of the community, and the Non-public Handle setting seems.
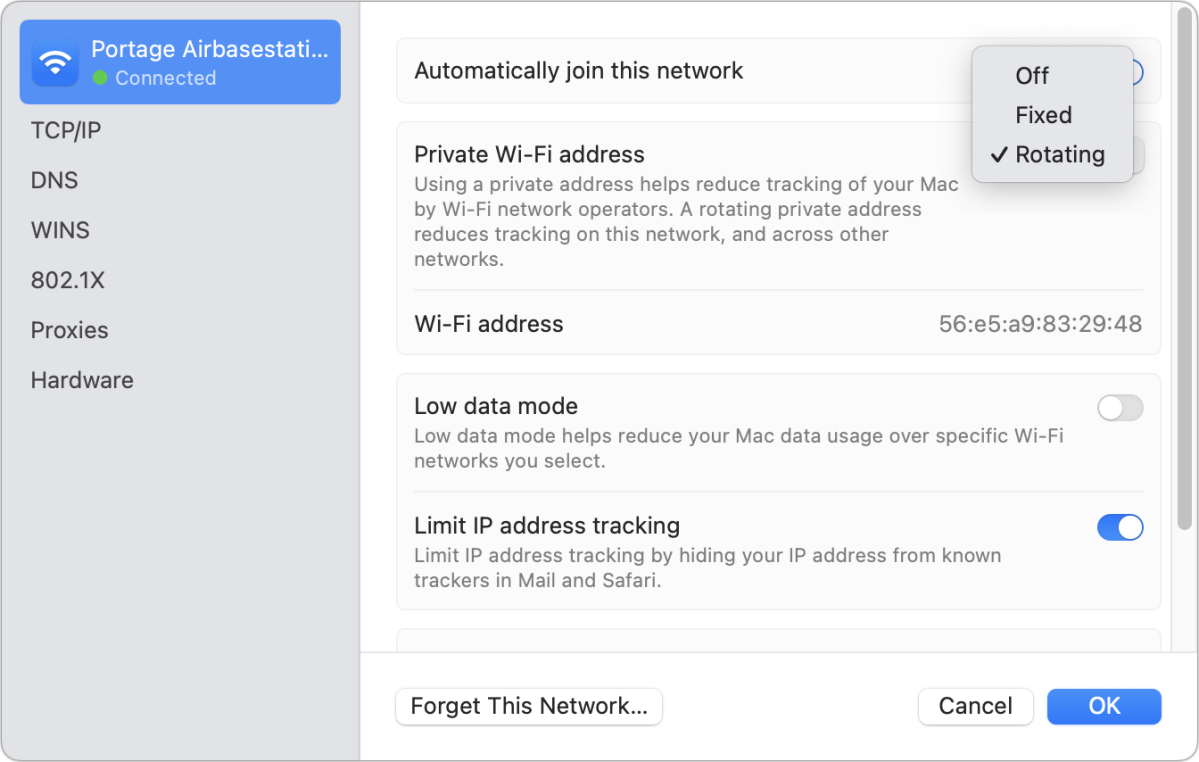
The Non-public Wi-Fi deal with setting enables you to management how a lot long-term data you leak about your machine to close by networks.
Foundry
The newest releases of working techniques added a menu that provides Off, Fastened, and Rotating decisions.
By default whenever you hook up with an open community (one with no encryption) or one utilizing outdated encryption strategies (WEP or the unique WAP taste), your working system routinely units the choice to Rotating. On this case, your machine invents a MAC deal with for each community you be a part of and makes use of that deal with for 2 weeks. The deal with additionally modifications when you select Overlook This Community after which join once more after 24 hours, or when you use the machine’s settings to reset your community settings (Settings > Common > Switch or Reset iPhone/iPad > Reset > Reset Community Settings).
You would possibly ask: what if Apple generates a MAC deal with already in use? The variety of potential addresses is huge—over 280 trillion prospects—and in contrast to a world IP deal with, it solely must be distinctive on the native community.
In the event you hook up with a community with WPA2 or later encryption, your machine makes use of Fastened by default. You may additionally select this on a private or workplace native community even when Apple’s default isn’t set to Fastened to be able to guarantee your deal with stays constant.
In the event you choose Off, you’re warned about monitoring and have to verify earlier than Non-public Wi-Fi deal with is disabled.
You would possibly change from Rotating to Off or Fastened when you assume you’re experiencing issues with a hotspot community that retains shedding your login. I’ve seen this with airplane Wi-Fi and haven’t recognized whether or not it’s a difficulty with the airplane’s authentication system or non-public MAC addressing.
This Mac 911 article is in response to a query submitted by a Macworld reader.
Ask Mac 911
We’ve compiled a listing of the questions we get requested most continuously, together with solutions and hyperlinks to columns: learn our tremendous FAQ to see in case your query is roofed. If not, we’re all the time on the lookout for new issues to unravel! E mail yours to mac911@macworld.com, together with display captures as applicable and whether or not you need your full title used. Not each query might be answered, we don’t reply to e mail, and we can’t present direct troubleshooting recommendation.
