Preparation and characterization of BC and BM nanoparticles
In line with our earlier research [32, 33], we constructed BC and BM nanoparticles through nanoprecipitation in an aqueous setting within the presence of BSA. Properly-dispersed BC and BM nanoparticles with uniform morphology had been obtained (Fig. 2A). The particle sizes of the BC and BM nanoparticles had been 8.4 ± 2.1 and 9.0 ± 3.4 nm, respectively, whereas the zeta potentials had been ~ − 11 mV and ~ − 5 mV, respectively (Fig. 2B, C). The XRD patterns of BC and BM point out the presence of CuS and MnO2, though the presence of BSA decreased the variety of crystalline peaks (Fig. 2D). Then, we evaluated the catalytic efficiency of BCM in ROS era and scavenging in vitro. Metallic ions have been confirmed to exhibit catalytic exercise much like that of some enzymes within the Fenton response. Because of the universality of the imbalanced redox setting in strong tumors and the overproduction of H2O2 in tumors, we evaluated the flexibility of BC and BM nanoparticles to catalyze the manufacturing of ROS within the presence of H2O2. BC nanoparticles and BM nanoparticles exhibited completely different performances in catalyzing the manufacturing of ROS. No enhanced electron spin resonance (ESR) sign was detected within the presence of BM nanoparticles within the DMPO/H2O2 answer, whereas the addition of BC nanoparticles enhanced the ESR sign of each. OH and ·O2. This discovering indicated that BC nanoparticles promote the era of ROS, whereas BM nanoparticles don’t (Fig. 2E, F). The ESR assay outcomes are in line with the ROS era spectrometry leads to an aqueous setting within the presence of MB (Fig. 3G). In distinction, within the case of ROS scavenging, the ESR sign of .OH considerably decreased after the addition of a low focus of BM nanoparticles, whereas the sign depth was much like that of the clean pattern. Though the addition of BC nanoparticles additionally decreased the ESR sign of .OH, the amplitude was a lot smaller than that of the BM nanoparticles (Fig. 3H). This discovering demonstrated that BM nanoparticles facilitate the scavenging of ROS reasonably than promote the era of ROS. BC and BM nanoparticles with completely different catalytic performances had been efficiently ready. Created in BioRender. Peng, J.(2024) https://BioRender.com/f14i369.
Building and characterization of BC and BM nanoparticles. A TEM photos of BC and BM nanoparticles. B The particle sizes calculated from the TEM photos. C The zeta potentials of the nanoparticles. D XRD patterns of BC and BM. E ESR spectra of.OH after the introduction of BC and BM, respectively, in a ·OH era mannequin assay. F ESR spectra of ·O2 after the introduction of BC or BM. G UV–seen spectra of MB options after the introduction of BC, BM or a mix of BC/BM on the identical concentrations. H ESR spectra of ·OH after the introduction of BC and BM, respectively, in a ·OH deletion mannequin assay
A, B DCFH-DA-positive MC38 cells handled with BC and BM, respectively. C JC-1 fluorescence photos of MC38 cells after remedy with BC or BM. D The mechanism by which JC-1 fluorescence modifications. E, F DCFH-DA-positive RAW264.7 cells handled with BC and BM, respectively. G JC-1 fluorescence photos of RAW264.7 cells after remedy with BC or BM. H DCM photos of RAW264.7 cells after remedy with BC or BM. I Move cytometry outcomes of BMDMs handled with completely different mixtures of BC/BM at completely different Cu/Mn ratios. J The proportions of F4/80+CD86+ cells in I. Ok Gene expression within the cell samples collected in I
Mobile actions of BC and BM nanoparticles in tumor cells and macrophages
Moreover, the flexibility of BC and BM nanoparticles to induce ROS era was additionally evaluated in vitro within the MC38 cell line and RAW264.7 macrophage line. The ROS sign was higher within the group cocultured with BC nanoparticles than within the BM nanoparticle-treated group, and the ROS era within the BM nanoparticle-treated group was additionally considerably higher than that within the management group (Fig. 3A, B). This discovering demonstrated that not solely is the potential of BC nanoparticles to stimulate ROS era maintained on the mobile stage but additionally that BM nanoparticles can stimulate the era of ROS. By measuring the mitochondrial membrane potential induced by JC-1, we additional confirmed that each BC and BM nanoparticles decreased the mitochondrial membrane potential (elevated inexperienced fluorescence depth and decreased the purple/inexperienced fluorescence ratio) (Fig. 3C), indicating the induction of ROS manufacturing from mitochondria (Fig. 3D).
Then, we additional carried out related assays in vitro within the RAW264.7 macrophage line. With rising BC nanoparticle concentrations, a rise in ROS era was noticed (Fig. 3E). In distinction, with the introduction of BM nanoparticles, the ROS era of macrophages decreased at low concentrations of BM nanoparticles. Because the focus of BM nanoparticles elevated, ROS era elevated barely in contrast with that within the management group (Fig. 3E, F). Additional analysis of JC-1 staining within the RAW264.7 cell line revealed that the depth of JC-1 monomers in BC-treated RAW264.7 cells elevated, indicating the induction of ROS manufacturing from mitochondria, much like the leads to tumor cells. Nonetheless, a rise within the depth of JC-1 aggregates in BM-treated RAW264.7 cells was noticed (Fig. 3G), which demonstrated that the BM nanoparticles didn’t promote ROS manufacturing from mitochondria and tended to strengthen mitochondrial integrity. Furthermore, a number of pseudopod morphologies had been noticed within the BM-treated RAW264.7 cells, which indicated that the BM promoted RAW264.7 cell differentiation to the M1 phenotype, whereas the group handled with BC nanoparticles exhibited a morphology in line with the M2 phenotype, and the variety of pseudopods within the group handled with BM is considerably greater than that handled with BC nanoparticles (Fig. 3H and Supplementary Fig. 1). Though ROS are the principle promoters concerned within the growth of inflammatory signaling, completely different downstream signaling pathways management the course of inflammatory signaling. The outcomes point out that the BM-treated RAW264.7 cells differentiated into proinflammatory cells through a signaling pathway completely different from that within the BC-treated group.
BC/BM mixtures with completely different ratios activate completely different inflammatory signaling pathways
We additional evaluated the impact of the mix of BC/BM nanoparticles at completely different ratios on the differentiation of macrophages [bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMDMs)]. The F4/80+CD86+ phenotype indicated the proinflammatory subtype. As the quantity of BM elevated (whereas the dose of BC elevated), the proportion of F4/80+CD86+ BMDMs elevated and reached a plateau, whereas the proportion of F4/80+CD86+ BMDMs peaked as the quantity of BC elevated (whereas the dose of BM decreased) (Fig. 3I, J). By additional measuring the expression of genes associated to irritation in BMDMs after completely different remedies, we discovered that the expression ranges of CXCL10 and IFNb, that are indicators of the sort I interferon response, had been considerably elevated within the group handled with BC/BM mixed with Cu/Mn = 4:1. Furthermore, the expression ranges of IL-6 and TNF, that are indicators of NK-kB-induced irritation, had been surprisingly decreased on this group (Fig. 3Ok). This means that the mix of BC/BM nanoparticles can regulate the differentiation of macrophages by optimizing the ratios of BC and BM.
Building and characterization of BCM hybrid nanoparticles and diAMP-loaded BCM (diAMP-BCM) nanoparticles
Primarily based on the above outcomes, we additional synthesized BCM nanoparticles through a two-step process: first, BSA-CuS (BC) nanoparticles had been constructed, after which MnO2 was precipitated from the BC nanoparticles (Fig. 4A). BCM nanoparticles with a mean diameter of 25.3 ± 5.7 nm (noticed by TEM, ~ 50 nm was measured by DLS) had been obtained (Fig. 4B, C). The zeta potential of BCM was ~ − 7 mV. The XPS and XRD outcomes additional supported the profitable linkage of CuxS and MnO2 within the nanoparticles (Supplementary Figs. 2–4). In contrast with BC and BM nanoparticles, BCM nanoparticles exhibit a core–shell morphology (low contraction within the core area and excessive contraction within the outer area) (Fig. 4B, enlargement). In line with the ICP-AAS measurements, the contents of Cu and Mn within the BCM nanoparticles had been 4.2 ± 0.4 µg/mg and 18.1 ± 3.2 µg/mg, respectively, with a Cu/Mn ratio of roughly 4.3:1. The UV–seen spectrum of the MB answer within the presence of H2O2 decreased dramatically after the addition of BCM nanoparticles, indicating the era of ROS (Fig. 4D). Then, we evaluated the catalytic efficiency of BCM in vitro. Enhanced electron spin resonance (ESR) alerts for each ·OH and ·O2 had been detected within the DMPO/H2O2 answer with the addition of BCM nanoparticles (Fig. 4E, F).
A Preparation of BCM nanoparticles. B TEM photos of BCM nanoparticles. C The particle measurement distribution of the BCM nanoparticles. D UV–seen spectra of MB options after the introduction of BCM. E ESR spectra of O2 after the introduction of BCM. F ESR spectra of.OH after the introduction of BCM at completely different concentrations. G, H The era of ROS in MC38 cells after the introduction of BCM nanoparticles. I Fluorescence photos of MC38 cells handled with BCM and stained with JC-1. J DCM picture of BMDMs after remedy with BCM. Ok Preparation of diAMP-BCM and L TEM picture of diAMP-BCM. M The expression of inflammation-related genes in BMDMs after coculture with diAMP or diAMP-BCM. N Heatmap of gene expression in BMDMs after coculture with completely different samples, as measured by transcriptome sequencing, and the principle pathways analyzed by KEGG are additionally listed. O Heatmap of the expression of the principle genes associated to irritation, together with protumor and antitumor genes. P, Q Enrichment of genes associated to the NF-kB pathway after completely different remedies. R Illustration of the impact of EGFR on the activation of sort I interferon. S The expression of inflammation-related genes in BMDMs after coculture with diAMP-BCM mixed with the EGFR inhibitor sorafenib. T, U The in vivo inhibition of CT26 CRC by diAMP-BCM with or with out the introduction of sorafenib, respectively
In mobile assays, the introduction of BCM nanoparticles promoted the era of ROS in MC38 cells and triggered the dissociation of JC-1 aggregates and the discharge of JC-1 monomers (Fig. 4G–I). As well as, the coculturing of BCM nanoparticles and RAW264.7 cells promoted macrophage differentiation to an M1-like phenotype (Fig. 4J). The outcomes demonstrated that the obtained BCM nanoparticles maintained the properties of the BC and BM nanoparticles.
DiAMP-BCM preferentially reinforces antitumor inflammatory signaling through the STING/IRF7/CXCL10 pathway
As BM nanoparticles exhibit completely different results on tumor cells and macrophages and since Mn ion launch from BM nanoparticles has the potential to stimulate STING, which may set off the era of a sort I interferon response, we additional adsorbed the STING agonist cyclic diadenosine monophosphate (diAMP) into BCM nanoparticles and obtained diAMP-BCM nanohybrids with a morphology and particle distribution much like these of BCM nanoparticles in addition to a loading capability of 0.6 ± 0.1% (µg diAMP/µg BSA) (Fig. 4Ok, L). By measuring the hydrodynamic diameters of diAMP-BCM, we discovered that the diAMP-BCM maintained ~ 80 nm within the serum (Supplementary Fig. 5). The hydrodynamic diameters are bigger than that calculated within the TEM photos, which is the outcomes of the thick hydration layer fashioned from BSA, it additionally the explanation that the particles within the TEM photos disperse evenly. Coculturing BMDMs with diAMP-BCM considerably elevated the expression of the principle inflammatory genes of BMDMs, comparable to CXCL10 and IFNB1, whereas the expression of TNFa and IL6 remained unchanged (Fig. 4M). This means that the loading of diAMP additionally promotes the activation of the sort I interferon response and doesn’t activate the expression of protumor genes.
Then, we carried out transcriptome sequencing to judge the impact of diAMP-BCM on the RNA panorama of BMDMs extracted from mice. Totally different landscapes had been noticed within the heatmap exhibiting the gene expression patterns of the BMDMs handled with diAMP-BCM in contrast with these of the opposite teams handled with LPS/IFN, diAMP, and BCM (Fig. 4N). Subsequently, protumor-related inflammatory genes and antitumor-related inflammatory genes had been extracted from the RNA sequencing outcomes, and the outcomes indicated a lower within the expression of IL6, TNF, and so on., whereas the expression of CXCL10 and IRF7 elevated within the BMDMs handled with diAMP-BCM (Fig. 4O). KEGG evaluation additionally indicated that diAMP-BCM remedy primarily regulated genes associated to the NF-kB signaling pathway in a way reverse to that of LPS/IFN (Fig. 4P, Q). These findings demonstrated that diAMP-BCM suppressed the activation of NF-kB signaling.
The preferential activation of the sort I interferon response mediated by diAMP-BCM in BMDMs was not directly supported by the inhibition of EGFR dampening the expression of genes associated to sort I interferon activation (Fig. 4R, S) [34]. After the introduction of sorafenib, an EGFR inhibitor, the elevated expression of CXCL10 and IFNB1 decreased to the management stage. EGFR mediates the translocation of STING to late endosomes, which is a crucial course of that promotes the activation of the sort I interferon response. When EGFR was inhibited, the expression of CXCL10 and IFNB1 in diAMP-BCM-treated BMDMs didn’t improve, indicating that the activation of the sort I interferon response by diAMP-BCM relies primarily on the translocation of STING to late endosomes. The underlying mechanism nonetheless wants additional investigation.
Moreover, by establishing CT26 CRC fashions in BALB/c mice, we evaluated the potential of diAMP-BCM to inhibit CT26 CRC development in vivo. Tumor regression was noticed within the group handled with diAMP-BCM, and three in 5 of the tumor-bearing mice had been eradicated (Fig. 4T). Notably, the tumors within the group handled with BCM grew sooner than these within the management group. When tumor-bearing mice had been handled with diAMP-BCM (i.t.) mixed with sorafenib (i.p.), tumor regression mediated by diAMP-BCM was inhibited (Fig. 4U).
diAMP-BCM additionally preferentially activated antitumor inflammatory signaling in BMDCs and T cells
As diAMP is a STING agonist, STING activation is a prevailing signaling pathway in DCs that promotes DC maturation and generates a sort I interferon response. Whereas evaluating with LPS, the parts of mature DCs after handled by free diAMP are nearly equal to the management group, which is far decrease than the group handled by LPS (Supplementary Fig. 6). It signifies that the free diAMP has little impact onto the stimulation of DCs maturing. Research have demonstrated that Mn has the potential to stimulate the cGAS-STING pathway, which additional induces DC maturation and TAM polarization. We first evaluated the results of the ionic types of Mn and Cu on the maturation of DCs stimulated by a STING agonist. No apparent enhancement of DC maturation was detected by circulate cytometry. Extra importantly, even within the presence of diAMP, no enhanced DC maturation was noticed as the quantity of metallic ions elevated. This discovering indicated that the extracellular ionic types of Mn and Cu can not effectively stimulate the activation of STING (Fig. 5A, B). Due to this fact, a supply system was launched not just for ions but additionally for STING agonists. In contrast with the ionic types of Mn/Cu alone, the BCM nanoparticles not solely promoted the maturation of DCs but additionally enhanced the potential of diAMP to stimulate DC maturation (Fig. 5B). Extra curiously, as both the Cu content material or the diAMP content material elevated, the proportion of mature DCs elevated (Fig. 5B, C). Though a rise in Mn content material favors additional stimulation of DC maturation, the hostile impact of Mn ions impedes the appliance of those nanoparticles in vivo. After stimulation, the morphology of the BMDM-derived DCs expanded, and promoted pseudopod formation was noticed with the introduction of diAMP (Fig. 5D).
A The extraction and in vitro tradition of BMDCs and BMDMs. B, C Move cytometry outcomes of BMDM-derived DCs after completely different remedies. D Fluorescence photos of BMDM-derived DCs after completely different remedies. Con.1, Con.2, and Con.3 characterize completely different concentrations of Mn and Cu. E Quantitative evaluation of CD80+CD86+ DCs measured in E. F DiAMP-BCM promotes the manufacturing of proinflammatory cytokines by APCs. G diAMP-BCM promotes the activation of T cells. H Remoted splenic CD3+ T cells. I qPCR outcomes exhibiting Ifnb1, Puma and Noxa expression in T cells after remedy with diAMP-BCM
Furthermore, we additional evaluated cytokine ranges, that are the results of DC maturation after STING activation, within the supernatant of BMDM-derived DCs after coculturing with completely different formulations. The concentrations of IL-12p70, TNF, IFN-gamma and IL-6 had been dramatically elevated within the BM-treated BMDCs, whereas diAMP-BCM-treated DCs exhibited decreases in IL-6 and TNF and will increase in IL-12p70 and IFN-gamma (Fig. 5E). Furthermore, the IL-10 stage was additionally apparently upregulated within the supernatant of the cells handled with diAMP-BCM in a dose-dependent method (Fig. 5E). The upregulation of IL-10 is the results of destructive suggestions, whereas irritation and maturation are induced in cells, and a few stories additionally point out that IL-10 favors the enhancement of antitumor immunity. These outcomes additional point out that diAMP-BCMs exhibit the potential to induce the maturation and polarization of APCs, particularly DCs and macrophages, to generate proinflammatory cytokines (Fig. 5F).
Moreover, we remoted CD3+ T cells from splenumentally extracted cells by destructive choice through a mouse CD3+ T-cell isolation equipment. Then, the cells had been stimulated with aCD3/aCD28 for a number of days (Fig. 5G, H). Then, the stimulated CD3+ T cells had been cocultured with completely different BCM formulations. Gene ranges associated to postactivation of STING had been measured by RT-qPCR. The upregulation of Ifnb1, Puma, and Noxa was clearly noticed within the cells handled with diAMP-BCM (Fig. 5I). These findings point out that diAMP-BCM additionally effectively stimulates the activation of CD3+ T cells through the STING pathway.
DiAMP-BCM facilitates the recruitment and differentiation of monocytes by inducing the apoptosis/pyroptosis of CRC cells
Though diAMP-BCM has exhibited nice potential in regulating the conduct of APCs, recruitment of APCs to the tumor website favors the long-lasting regulation of antitumor immunity. Most cancers cell apoptosis, notably pyroptosis, promotes the recruitment of monocytes to tumors, and the recruited monocytes might be differentiated to a proinflammatory phenotype by diAMP-BCM to inflame the TiME. Thus, we first carried out mobile cytometry assays and CCK8 assays to judge the cytotoxicity of diAMP-BCM and its potential to induce tumor cell apoptosis/pyroptosis. The CT26 and MC38 CRC cell traces had been used. Because the diAMP-BCM focus elevated, a dramatic lower in most cancers cell survival was noticed, and the IC50 of diAMP-BCM for CT26 cells was ~ 1.25 µg diAMP (Fig. 6A). No apparent apoptosis was noticed within the group handled with diAMP alone, and the apoptosis of the CT26 cells handled with diAMP-BCM was much like that of the cells handled with BCM (Fig. 6B). Nonetheless, the mobile morphology after diAMP-BCM remedy indicated that pyroptosis additionally occurred (Fig. 6C). The proportion of surviving cells at this focus of diAMP-BCM was roughly 0%, which can also be inconsistent with the share of apoptotic cells (solely ~ 14%). This means that the majority most cancers cell dying could also be the results of pyroptosis.
diAMP-BCM promotes the recruitment and differentiation of monocytes. A Survival of CT26 cells handled with diAMP-BCM. B Apoptosis and C optical photos of CT26 cells after remedy with diAMP-BCM. D, E The apoptosis of various BCM-treated MC38 most cancers cell traces was measured by circulate cytometry. F The survival of MC38 cells handled with diAMP-BCM (measured by a CCK-8 assay). G, H In vivo development inhibition of MC38 most cancers cells by diAMP-BCM. I Illustration of the analysis of monocyte recruitment by diAMP-BCM. J, Ok Populations of intratumour monocytes in MC38 CRC and CT26 CRC mice after completely different remedies, respectively. L, M The proportions of F4/80+CD86+ bone marrow-derived cells (BMDCs) after completely different remedies had been measured by circulate cytometry. Mn: 0.3 µg/mL, Cu: 1.2 µg/mL, diAMP: 1 µg/mL. BMDCs had been extracted from the bone marrow of mice and stimulated with M-CSF. N diAMP-BCM regulates versatile cell conduct to boost tumor inhibition
Within the case of MC38 CRC cells, by apoptosis assay analysis, we discovered that prime percentages of early apoptosis and late apoptosis had been each noticed in MC38 cells handled with BCM, and the odds additional elevated within the presence of diAMP, through which the share of whole apoptotic cells reached ~ 60%, which was a lot higher than that within the BCM-treated group (Fig. 6D). The potential of diAMP-BCM to induce tumor apoptosis was dose dependent (Fig. 6E and Supplementary Fig. 7). As a consequence, diAMP-BCM effectively inhibited the expansion and proliferation of tumor cells in vitro. The apoptosis outcomes had been in line with these of the CCK-8 assays carried out within the MC38 cell line (Fig. 6F). The potential anticancer impact of diAMP-BCM was additional supported by the inhibition of MC38 development in vivo. After intratumoral injection, the tumors handled with diAMP-BCM regressed inside 12 days, and 4 in 5 of the tumor-bearing mice had been eradicated (Fig. 6G, H). Notably, the tumors handled with BCM nanoparticles alone all tended to progress, with considerably bigger common tumor volumes than these within the management group (which signifies that hyperprogression occurred) (Fig. 6G, H).
The apoptosis or pyroptosis of most cancers cells might promote the recruitment of monocytes, which might be differentiated into macrophages or DCs. After one intratumoral injection, the dose of diAMP was decreased to five µg per mouse (Fig. 6I). On day 3, monocytes, in addition to DCs, had been clearly recruited to the diAMP-BCM-treated tumors. These findings point out that diAMP-BCM promotes the recruitment of monocytes (Fig. 6J, Ok). The recruitment of monocytes was primarily ascribed to the apoptosis of tumor cells brought on by Cu and STING through the Fenton response and STING pathway activation. As beforehand reported, the recruited monocytes can differentiate into TAMs within the immunosuppressive TME, and the differentiated TAMs additional worsen the immunosuppressive TiME, thus selling the exhaustion of T cells. By extracting and deriving monocytes from the bone marrow, BMDMs had been differentiated straight by diAMP-BCM in vitro. The outcomes indicated that proinflammatory phenotypes had been induced within the extracted BMDMs through the options of M1 macrophages (Fig. 6L, M). These findings demonstrated that diAMP-BCM itself can promote the differentiation of monocytes to proinflammatory phenotypes with antitumor results in vivo (Fig. 6N).
DiAMP-BCM reshaped the TiME panorama to “sizzling” tumors throughout aPD-1 ICB remedy for CRC
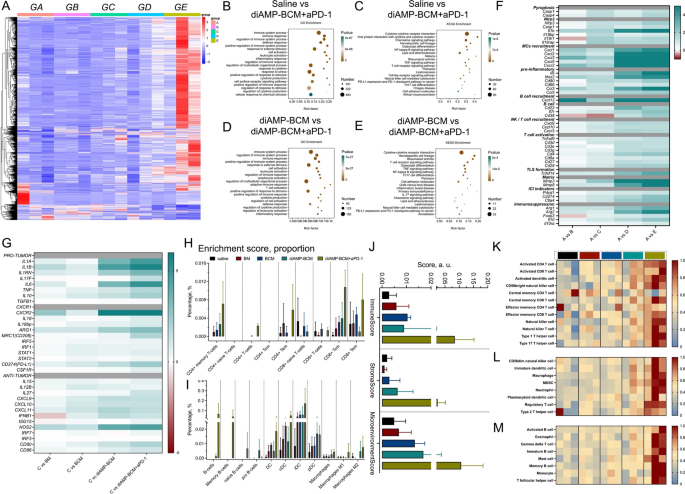
It has been demonstrated that the principle therapeutic results of aPD-1 remedy in vivo are primarily associated to T-cell exhaustion and the recruitment of latest peripheral T cells from circulation or from tumor-draining lymphatic nodes (TDLNs) [6]. The lower in tumor-resident CD4+ T cells and CD8+ T cells and the following recruitment of T cells might favor the enhancement of aPD-1 remedy and reworking of the tumor immune microenvironment. Right here, we investigated the impact of diAMP-BCM on the TiME and the potential of diAMP-BCM mixed with aPD-1 to rebuild the lymphocytic microenvironment through transcriptome sequencing of mouse tumors after completely different remedies. Considerably completely different transcriptional landscapes had been noticed within the diAMP-BCM- and diAMP-BCM+aPD-1-treated teams in contrast with the opposite teams (saline-, BM-, and BCM-treated teams), notably within the diAMP-BCM+aPD-1-treated teams (Fig. 7A). Greater than 1200 genes had been upregulated within the tumors of mice handled with diAMP-BCM+aPD-1, which was a lot higher than the variety of upregulated genes within the tumors of mice handled with diAMP-BCM (Supplementary Fig. 8). This discovering indicated that the introduction of aPD-1 additional reshaped the TiME. By Gene Ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) enrichment analyses (Fig. 7B–E), we discovered that the mix of diAMP-BCM and aPD-1 promoted the stimulation of immune responses, because the DEGs had been primarily related to immune responses, and genes associated to “PD-L1 expression and the PD-1 checkpoint pathway in most cancers” had been additionally discovered to be upregulated.
The underlying mechanism deduced from the transcriptome sequencing of entire MC38 tumors after completely different remedies. A Heatmap of the transcriptome sequencing outcomes of entire tumors after completely different remedies. (GA: management, GB: BM, GC: BCM, GD: diAMP-BCM, GE: diAMP-BCM+aPD-1, G = group). B–E GO enrichment evaluation (B, C) and KEGG enrichment evaluation (D, E) of the transcriptional panorama of tumors handled with diAMP-BCM (B, D) and diAMP-aPD-1 (C, E). F Gene expression representing completely different mobile behaviors of tumors after completely different remedies. G Heatmap of the expression of the principle genes associated to irritation, together with protumor and antitumor genes. H–J xCELL evaluation revealing immune infiltration of tumors after completely different remedies. Ok–M ssGSEA revealed variations within the TiME of the tumors after completely different remedies
Moreover, genes associated to pyroptosis, mast cell (MC) recruitment, irritation, B-cell recruitment, NK cell/T-cell recruitment, T-cell activation, and tertiary lymphoid construction (TLS) formation had been considerably upregulated within the diAMP-BCM+aPD-1-treated group, whereas solely genes associated to MC recruitment, irritation, and TLS formation had been upregulated within the diAMP-BCM-treated group. Genes associated to immune checkpoint indicators and immunosuppression had been additionally upregulated within the diAMP-BCM+aPD-1-treated group, indicating suggestions regulation of the immune system. (Fig. 7F). Moreover, in contrast to the outcomes obtained for BMDMs in vitro, the expression of IL6 and TNF in tumor tissues was nonetheless considerably elevated after diAMP-BCM remedy, notably throughout aPD-1 ICB remedy. These findings point out that different cell varieties past APCs overexpress protumor inflammatory genes, e.g., IL6 and TNF. In line with the cytotoxicity outcomes of diAMP-BCM to most cancers cells, pyroptosis might happen when most cancers cells are handled with diAMP-BCM. Pyroptosis of most cancers cells may promote the expression of pro-tumor inflammatory cytokines, together with IL6, TNF, and IL1, that are all overexpressed in tumor tissues handled with diAMP-BCM with or with out aPD-1 remedy (Fig. 7F, G).
Utilizing xCELL and immuneCC analyses, we discovered that the proportions of CD8+ T cells and CD8+ effector reminiscence T (Tem) cells had been considerably decreased within the group of mice handled with diAMP-BCM alone. With the introduction of aPD-1, the proportions of CD8+ T cells and CD8+ Tem cells in addition to the proportion of CD8+ central reminiscence (Tcm) cells elevated (Fig. 7H). These modifications had been accompanied by a synchronous improve within the variety of B cells and APCs, together with DCs and macrophages (Fig. 7I). The immune rating, stroma rating and microenvironment rating additionally indicated that the introduction of aPD-1 modified the TiME (Fig. 7J). Comparable outcomes had been obtained by single-sample gene set enrichment evaluation (ssGSEA), which revealed a marked improve within the proportion of effector T cells and their associated immunocytes (Fig. 7Ok–M).
The diAMP-BCM enhances the efficacy of CRC ICB (aPD-1) immunotherapy in vivo
To guage the potential of diAMP-BCM mixed with aPD-1 to transform the TiME and improve the efficacy of immunotherapy, we additional assessed the impact of diAMP nanoparticles (diAMP-BM, diAMP-BC, and diAMP-BCM with completely different Cu/Mn ratios) on ICB CRC immunotherapy. In the course of the administration of aPD-1, the expansion of MC38 cells was inhibited in vivo. Nonetheless, with out steady administration of aPD-1, the expansion of MC38 cells was much like that of the management group (Supplementary Fig. 9). With the introduction of diAMP-BCM, tumor development was clearly inhibited, and regression was noticed in among the tumors. On the identical dose of both Mn or Cu, the tumor development inhibition within the teams handled with diAMP-BM or diAMP-BC was considerably inferior to that within the diAMP-BCM-treated group, though reasonable tumor development inhibition was achieved by these remedies. As well as, the outcomes indicated that the Cu/Mn ratio critically impacts the therapeutic consequence of ICB. Because the Cu/Mn ratio elevated from 0.25/1 to 1:1, the typical quantity and tumor weight elevated, though there have been no vital variations between these two teams. Because the Cu/Mn ratio additional elevated (Fig. 8A–C). This discovering demonstrated that Cu/Mn-based remedy enhanced the therapeutic efficacy of ICB when mixed with a STING agonist and that the therapeutic efficacy might be regulated by the Cu/Mn ratios inside the nanoparticles.
Tumor development inhibition of diAMP-BCMs together with aPD-1 in vivo and results on the TiME. A The tumor space of MC38 tumors implanted in C57/B6J mice after completely different remedies. B {Photograph} of the tumors ex vivo on the endpoint of the remedies. C The tumor weights ex vivo on the endpoint of the remedies. D Immunofluorescence photos of the tumors after completely different remedies through which the immunocytes and APCs had been labeled
Then, we additional evaluated the results of various remedies on the TiME, notably on macrophages and immunocytes, by immunofluorescence staining of tumor sections (Fig. 8D). Each the teams handled with diAMP-BM+aPD-1 and diAMP-BCM+aPD-1 (Cu/Mn = 4:1) exhibited an elevated proportion of F4/80+CD86+ macrophages, that are thought of proinflammatory, or M1 macrophages. Furthermore, these two teams additionally exhibited a lower within the proportion of F4/80+CD206+ macrophages. This discovering indicated that the TiME reworked to a proinflammatory state in response to those two remedies. Notably, the group handled with diAMP-BC+aPD-1 exhibited an elevated proportion of F4/80+CD206+ macrophages. Extra importantly, the proportion of CD3+CD8+ T cells was a lot higher than that within the different group, and this T-cell phenotype was uncommon within the diAMP-BCM+aPD-1 (Cu/Mn = 4:1)-treated group. Nonetheless, the diAMP-BCM+aPD-1 (Cu/Mn = 4:1)-treated group had a considerably higher variety of CD3+ cells surrounding the tumor (Fig. 6D). This discovering indicated that diAMP-BCM+aPD-1 (Cu/Mn = 4:1) decreases the proportion of CD3+CD8+ T cells however promotes the recruitment or cloning of CD3+ cells within the preliminary interval after remedy.
diAMP-BCM mixed with ICIs facilitates distal tumor administration and alleviates distal T-cell exhaustion
This research demonstrated that diAMP-BCM promoted the rebuilding of the tumor lymphocytic microenvironment and elevated the efficacy of immunotherapy, which indicated the potential of this technique for inhibiting the expansion of distal tumors. CRC usually happens in a number of areas. It’s mandatory to determine a CRC therapeutic technique to inhibit distal tumors. Due to this fact, we established an MC38 tumor mannequin on each flanks of C57BL/6J mice concurrently; solely the tumors on the best facet had been intratumorally injected with diAMP-BCM, and all the mice besides the management mice had been subsequently intraperitoneally injected with aPD-1 (Fig. 9A). The volumes of the tumors on either side had been recorded. Essentially the most environment friendly tumor development inhibition was noticed within the group handled with diAMP-BCM+aPD-1, which inhibited the expansion of not solely the handled right-sided tumors but additionally the handled distal left-sided tumors (Fig. 9B–D). Tumor development was barely inhibited within the group handled with diAMP+aPD-1, however the tumor development on this group was far sooner than that within the diAMP-BCM+aPD-1-treated group. This discovering revealed that BCM has a synergistic impact with ICB immunotherapy. Then, we evaluated the impact of mixture remedy on the TiME of tumors on the handled facet and the distal nontreated facet. An apparent improve within the proportion of F4/80+CD11c+ cells was noticed within the group handled with diAMP-BCM+aPD-1 in each the handled tumors and distal tumors (Fig. 9E, H). Comparable outcomes concerning the proportions of CD3+CD8+ T cells had been obtained (Fig. 9F, I). Extra importantly, by additional staining for the exhausted T-cell markers PD-1 and TIM-3, we discovered that the proportion of CD3+CD8+PD-1+TIM3+ T cells in distal tumors dramatically decreased within the group handled with diAMP-BCM+aPD-1, whereas the proportion of CD3+CD8+PD-1+TIM3+ T cells on the handled facet didn’t considerably differ (Fig. 9G, J). The outcomes of multiplex immunohistochemistry (mIHC) staining of tumor slices of distal tumors additional revealed a lower in exhausted T cells with enhanced enrichment of CD3+CD8+ T cells and CD3+CD8+TCF1+ T cells (Fig. 9Ok, L). Additional investigation of the tumor tissues obtained 3 days after the ultimate intratumor injection revealed enhanced monocyte enrichment within the group handled with diAMP-BCM+aPD-1 (Supplementary Fig. 10), with a rise in CD3+CD8+ T cells, indicating the enlargement of effector T cells; furthermore, in each the handled tumors and the distal tumors, a lower within the proportion of CD3+CD8+PD-1+TIM3+ T cells was additionally noticed on this group (Supplementary Fig. 11 and Supplementary Fig. 12). We additionally discovered that the proportion of CD3+CD8+PD-1+TIM3+ T cells within the spleens of the mice handled with diAMP-BCM+aPD-1 was decrease than that within the different teams (Supplementary Fig. 13). Within the preliminary interval, diAMP-BCM+aPD-1 not solely promoted the enlargement of effector T cells but additionally alleviated T-cell exhaustion in each main tumors and distal tumors.
Impact of diAMP-BCM mixed with aPD-1 on the expansion inhibition of distal tumors and the underlying immune response. A Schematic illustration of tumor development inhibition in distal tumor fashions. B–D Tumor quantity variation after completely different remedies (B, D) and ex vivo photos of the tumors. E The proportions of F4/80+CD11c+ macrophages within the handled and distal tumors after completely different remedies. F Populations of CD3+CD4+ and CD3+CD8+ T cells within the handled and distal tumors after completely different remedies. G The odds of exhausted T cells within the tumor tissues had been measured by circulate cytometry. H–J Statistical evaluation of the odds of F4/80+CD11c+ T cells, CD3+CD8+ T cells, and CD3+CD8+PD-1+TIM3+ T cells in handled tumors and distal tumors. Ok mIHC fluorescence picture of tumor slices from distal tumors after remedy with diAMP-BCM+aPD-1. L The proportions of various lymphocytes calculated from the mIHC photos