This information dives into constructing a customized conversational agent with LangChain, a strong framework that integrates Massive Language Fashions (LLMs) with a variety of instruments and APIs. Designed for versatility, the agent can deal with duties like producing random numbers, sharing philosophical insights, and dynamically fetching and extracting content material from webpages. By combining pre-built instruments with customized options, we create an agent able to delivering real-time, informative, and context-aware responses.
Studying Aims
- Achieve data of the LangChain framework and its integration with Massive Language Fashions and exterior instruments.
- Study to create and implement customized instruments for specialised duties inside a conversational agent.
- Purchase expertise in fetching and processing stay information from the online for correct responses.
- Develop a conversational agent that maintains context for coherent and related interactions.
This text was printed as part of the Information Science Blogathon.
Why Combine LangChain, OpenAI, and DuckDuckGo?
Integrating LangChain with OpenAI and DuckDuckGo empowers us to construct superior conversational AI functions that may carry out each structured and unstructured searches. OpenAI’s language fashions allow pure language understanding, whereas DuckDuckGo offers a dependable, privacy-respecting search API. Collectively, they permit our AI to not solely generate coherent and contextual responses but in addition fetch real-time info, enhancing its versatility and relevance. This setup is right for creating clever, responsive chatbots or digital assistants that may deal with a variety of consumer inquiries, making it a strong toolkit for builders in conversational AI.
Putting in Important Packages
First, you’ll want to put in the required Python packages, together with langchain and openai, and the DuckDuckGo search device. You possibly can simply do that utilizing pip:
!pip -q set up langchain==0.3.4 openai
pip set up langchain
!pip -q set up duckduckgo-search
As soon as put in, affirm the set up of LangChain to make sure that it’s arrange appropriately:
!pip present langchain
Configuring API Entry
To make the perfect use of OpenAI’s fashions, you’ll have to arrange an API key. For this, you should use the os library to load your API keys into the atmosphere variables:
import os
os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = "your_openai_key_here"
Be sure that to exchange “your_openai_key_here” along with your precise OpenAI API key. This key will likely be required for interacting with the GPT-3.5-turbo mannequin.
Connecting OpenAI Fashions to LangChain
We’ll now arrange a connection to OpenAI’s mannequin utilizing LangChain. This mannequin offers the flexibleness to deal with a variety of language duties, from fundamental conversations to extra superior queries:
from langchain import OpenAI
from langchain.chat_models import ChatOpenAI
from langchain.chains.dialog.reminiscence import ConversationBufferWindowMemory
# Arrange the turbo LLM
turbo_llm = ChatOpenAI(
temperature=0,
model_name="gpt-4o"
)
On this case, we’ve configured the GPT-4o mannequin with a low temperature (temperature=0) to make sure constant responses.
To make your agent extra versatile, you’ll need to combine instruments that allow it to entry exterior information. On this case, we’ll combine the DuckDuckGo search device, which permits the agent to carry out internet searches:
from langchain.instruments import DuckDuckGoSearchTool
from langchain.brokers import Software
from langchain.instruments import BaseTool
search = DuckDuckGoSearchTool()
# Defining a single device
instruments = [
Tool(
name = "search",
func=search.run,
description="useful for when you need to answer questions about current events. You should ask targeted questions"
)
]The DuckDuckGoSearchTool is about up right here as a Software object, with its description indicating that it’s ultimate for answering questions associated to present occasions.
Creating Customized Functionalities
Along with the usual instruments offered by LangChain, you may as well create customized instruments to boost your agent’s talents. Beneath, we exhibit how you can create a few easy but illustrative instruments: one which returns the which means of life, and one other that generates random numbers.
Customized Software: That means of Life
The primary device is a straightforward operate that gives a solution to the age-old query, “What’s the which means of life?”. On this case, it returns a humorous response with a slight twist:
def meaning_of_life(enter=""):
return 'The which means of life is 42 if rounded however is definitely 42.17658'
life_tool = Software(
identify="That means of Life",
func= meaning_of_life,
description="Helpful for when it's essential to reply questions concerning the which means of life. enter needs to be MOL "
)
This device might be built-in into your agent to supply some enjoyable or philosophical insights throughout a dialog.
Customized Software: Random Quantity Generator
The second device generates a random integer between 0 and 5. This could possibly be helpful in conditions the place randomness or decision-making is required:
import random
def random_num(enter=""):
return random.randint(0,5)
random_tool = Software(
identify="Random quantity",
func= random_num,
description="Helpful for when it's essential to get a random quantity. enter needs to be 'random'"
)
By integrating this device into your LangChain agent, it turns into able to producing random numbers when wanted, including a contact of unpredictability or enjoyable to the interactions.
Making a conversational agent with customized instruments opens up countless potentialities for tailoring interactions to particular wants. By integrating distinctive functionalities, we are able to construct a dynamic, responsive assistant that goes past customary responses, delivering customized and contextually related info.
Initializing the Agent
We begin by importing the initialize_agent operate from LangChain and defining the instruments we’ve created earlier—DuckDuckGo search, random quantity generator, and the “That means of Life” device:
from langchain.brokers import initialize_agent
instruments = [search, random_tool, life_tool]
Including Reminiscence to the Agent
To allow the agent to recollect current elements of the dialog, we incorporate reminiscence. The ConversationBufferWindowMemory function permits the agent to maintain a rolling reminiscence of the previous few messages (set to three on this case):
from langchain.chains.dialog.reminiscence import ConversationBufferWindowMemory
reminiscence = ConversationBufferWindowMemory(
memory_key='chat_history',
ok=3,
return_messages=True
)
This reminiscence will enable the agent to take care of context over quick conversations, which is particularly helpful for a extra pure dialogue move.
Constructing the Conversational Agent
We initialize the agent utilizing initialize_agent. The important thing parameters embrace the next:
- agent: Specifies the kind of agent. On this case, we’re utilizing the conversational ReAct-style agent (chat-conversational-react-description).
- instruments: The instruments we’ve outlined are handed right here.
- llm: The OpenAI GPT-3.5-turbo mannequin.
- verbose: Set to True in order that we are able to see detailed output of the agent’s conduct.
- reminiscence: The reminiscence object that permits the agent to recall dialog historical past.
- max_iterations: These are set to cease the agent after a most of three iterations or when it generates a sound reply.
conversational_agent = initialize_agent(
agent="chat-conversational-react-description",
instruments=instruments,
llm=turbo_llm,
verbose=True,
max_iterations=3,
early_stopping_method='generate',
reminiscence=reminiscence
)
Testing the Agent
Now you can work together with the agent utilizing pure language queries. Listed here are some examples of questions you’ll be able to ask the agent:
Ask for the present time in a metropolis
conversational_agent("What time is it in London?")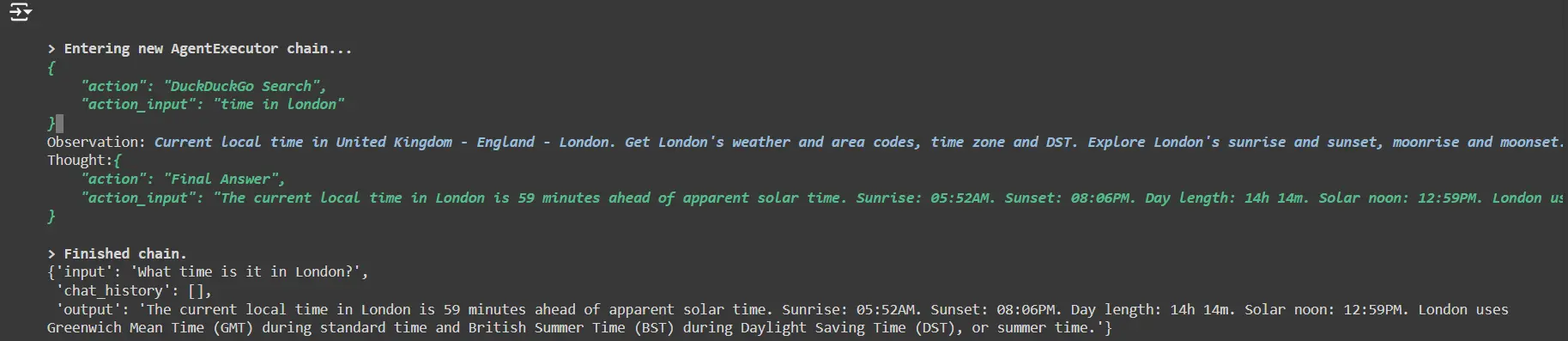
- The agent will use the DuckDuckGo search device to search out the present time in London.
Request a random quantity:
conversational_agent("Are you able to give me a random quantity?")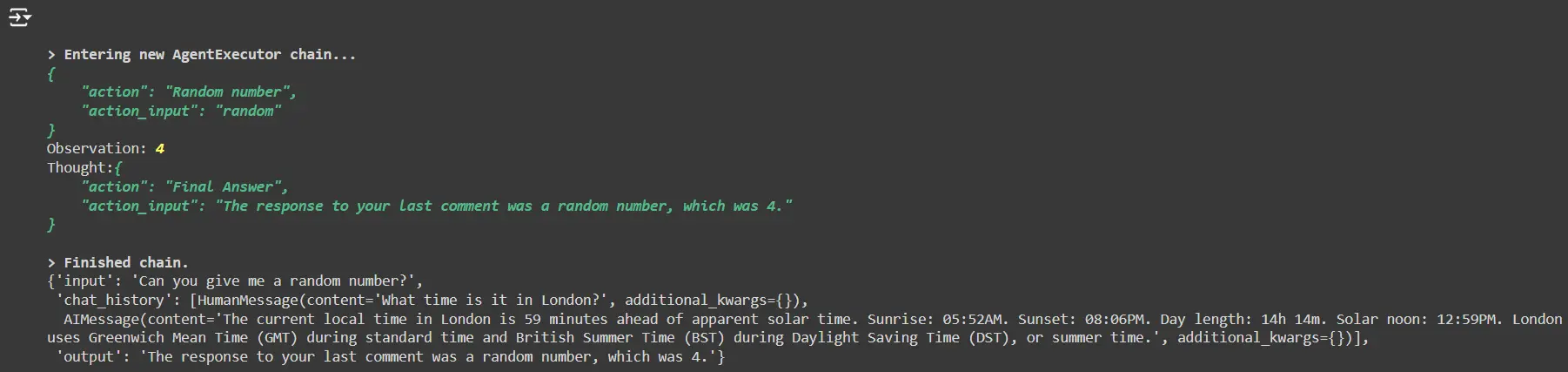
- The agent will generate a random quantity utilizing the customized random_tool.
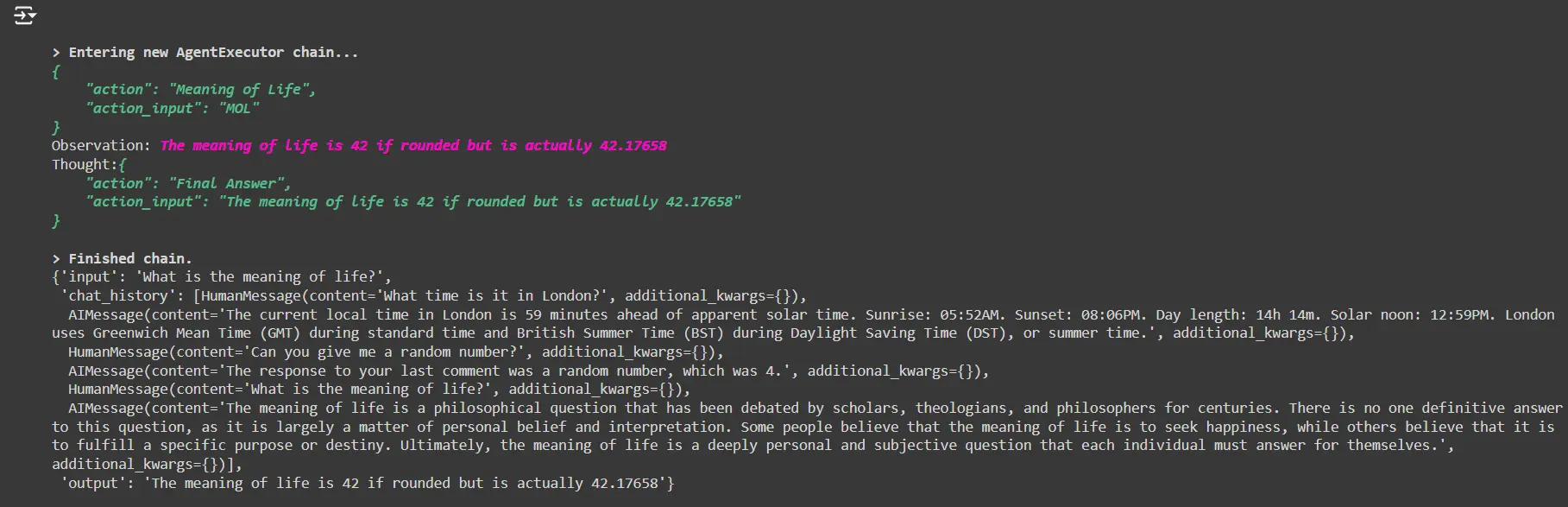
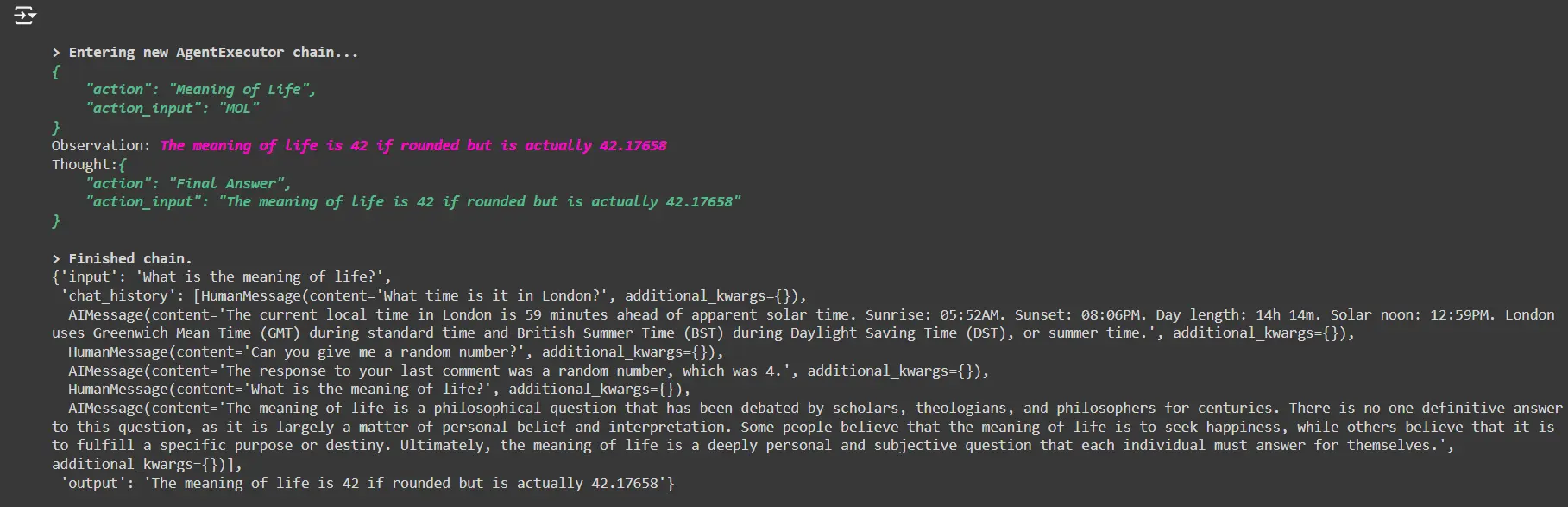
Ask for the which means of life
conversational_agent("What's the which means of life?")The agent will reply this query by using the customized life_tool.
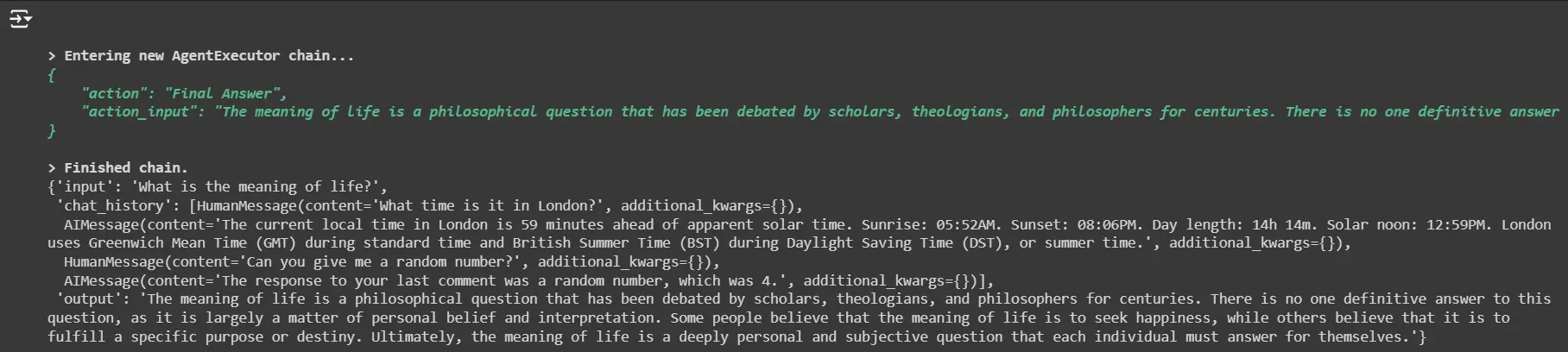
Customizing the System Immediate
To information the agent’s conduct extra successfully, we are able to modify the system immediate it follows. By default, the agent offers common help throughout quite a lot of matters. Nonetheless, we are able to tailor this by explicitly telling it to make use of instruments for particular duties, reminiscent of answering questions on random numbers or the which means of life.
Right here’s how we modify the system immediate:
# system immediate
conversational_agent.agent.llm_chain.immediate.messages[0].immediate.template

fixed_prompt=""'Assistant is a big language mannequin educated by OpenAI.
Assistant is designed to have the ability to help with a variety of duties, from answering
easy inquiries to offering in-depth explanations and discussions on a variety of
matters. As a language mannequin, Assistant is ready to generate human-like textual content primarily based on the enter it receives, permitting it to interact in natural-sounding conversations and supply responses which might be coherent and related to the subject at hand.
Assistant does not know something about random numbers or something associated to the which means
of life and may use a device for questions on these matters.
Assistant is consistently studying and bettering, and its capabilities are continuously
evolving. It is ready to course of and perceive massive quantities of textual content, and may use
this data to offer correct and informative responses to a variety of
questions. Moreover, Assistant is ready to generate its personal textual content primarily based on the
enter it receives, permitting it to interact in discussions and supply explanations and
descriptions on a variety of matters.
Total, Assistant is a strong system that may assist with a variety of duties and
present helpful insights and data on a variety of matters. Whether or not you want
assist with a particular query or simply need to have a dialog a few explicit
matter, Assistant is right here to help.'''We then apply the modified immediate to the agent:
conversational_agent.agent.llm_chain.immediate.messages[0].immediate.template = fixed_promptNow, when the agent is requested about random numbers or the which means of life, it’ll make sure you seek the advice of the suitable device as a substitute of making an attempt to generate a solution by itself.
Testing with the New Immediate
Let’s take a look at the agent once more with the up to date immediate:
conversational_agent("What's the which means of life?")This time, the agent ought to name the life_tool to reply the query as a substitute of producing a response from its personal data.
On this part, we’ll create a customized device that may strip HTML tags from a webpage and return the plain textual content content material. This may be significantly helpful for duties like summarizing articles, extracting particular info, or just changing HTML content material right into a readable format.
Constructing the Internet Scraper Software
We’ll use the requests library to fetch the webpage and BeautifulSoup from the bs4 bundle to parse and clear the HTML content material. The operate beneath retrieves a webpage, removes all HTML tags, and returns the primary 4000 characters of the stripped textual content:
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import requests
def stripped_webpage(webpage):
# Fetch the content material of the webpage
response = requests.get(webpage)
html_content = response.textual content
# Operate to strip HTML tags from the content material
def strip_html_tags(html_content):
soup = BeautifulSoup(html_content, "html.parser")
stripped_text = soup.get_text()
return stripped_text
# Strip the HTML tags
stripped_content = strip_html_tags(html_content)
# Restrict the content material to 4000 characters to keep away from lengthy outputs
if len(stripped_content) > 4000:
stripped_content = stripped_content[:4000]
return stripped_content
# Testing the operate with a pattern webpage
stripped_webpage('https://www.google.com')

How It Works
- Fetching the webpage: The operate makes use of the requests library to get the uncooked HTML content material from a given URL.
- Stripping HTML tags: Utilizing BeautifulSoup, we parse the HTML content material and extract solely the textual content, eradicating all HTML tags.
- Character restrict: To keep away from overly lengthy outputs, the textual content is restricted to the primary 4000 characters. This retains the content material concise and manageable, particularly to be used in a conversational agent.
Testing the Software
You possibly can take a look at this device by passing any URL to the stripped_webpage operate. For instance, when used with https://www.google.com, it’ll return a text-only model of Google’s homepage (restricted to the primary 4000 characters).
Integrating into LangChain as a Software
Now you can wrap this operate inside a LangChain Software and combine it into your agent for dynamic internet scraping:
from langchain.brokers import Software
# Create the device for internet scraping
web_scraper_tool = Software(
identify="Internet Scraper",
func=stripped_webpage,
description="Fetches a webpage, strips HTML tags, and returns the plain textual content content material (restricted to 4000 characters)."
)
Now, this internet scraper device might be a part of the agent’s toolbox and used to fetch and strip content material from any webpage in actual time, including additional utility to the conversational agent you’ve constructed.
On this part, we’re constructing a customized WebPageTool class that may enable our conversational agent to fetch and strip HTML tags from a webpage, returning the textual content content material. This device is beneficial for extracting info from web sites dynamically, including a brand new layer of performance to the agent.
Defining the WebPageTool Class
We begin by defining the WebPageTool class, which inherits from BaseTool. This class has two strategies: _run for synchronous execution (the default for this device) and _arun which raises an error since asynchronous operations will not be supported right here.
from langchain.instruments import BaseTool
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import requests
class WebPageTool(BaseTool):
identify = "Get Webpage"
description = "Helpful for when it's essential to get the content material from a particular webpage"
# Synchronous run methodology to fetch webpage content material
def _run(self, webpage: str):
# Fetch webpage content material
response = requests.get(webpage)
html_content = response.textual content
# Strip HTML tags from the content material
def strip_html_tags(html_content):
soup = BeautifulSoup(html_content, "html.parser")
stripped_text = soup.get_text()
return stripped_text
# Get the plain textual content and restrict it to 4000 characters
stripped_content = strip_html_tags(html_content)
if len(stripped_content) > 4000:
stripped_content = stripped_content[:4000]
return stripped_content
# Async run methodology (not applied)
def _arun(self, webpage: str):
increase NotImplementedError("This device doesn't help async")
# Instantiate the device
page_getter = WebPageTool()
How the WebPageTool Works
- Fetching Webpage Content material: The _run methodology makes use of requests.get to fetch the webpage’s uncooked HTML content material.
- Stripping HTML Tags: Utilizing BeautifulSoup, the HTML tags are eliminated, leaving solely the plain textual content content material.
- Limiting Output Measurement: The content material is truncated to 4000 characters to keep away from extreme output, making the agent’s response concise and manageable.
Reinitializing the Conversational Agent
Subsequent, we have to combine the brand new WebPageTool into our conversational agent. This entails including the device to the agent’s toolbox and updating the system immediate to instruct the agent to make use of this device for fetching webpage content material.
Updating the System Immediate
We modify the system immediate to explicitly instruct the assistant to all the time test webpages when requested for content material from a particular URL:
fixed_prompt=""'Assistant is a big language mannequin educated by OpenAI.
Assistant is designed to have the ability to help with a variety of duties, from answering
easy inquiries to offering in-depth explanations and discussions on a variety of
matters. As a language mannequin, Assistant is ready to generate human-like textual content primarily based on the
enter it receives, permitting it to interact in natural-sounding conversations and supply
responses which might be coherent and related to the subject at hand.
Assistant does not know something about random numbers or something associated to the which means
of life and may use a device for questions on these matters.
Assistant additionally does not know details about content material on webpages and may all the time
test if requested.
Total, Assistant is a strong system that may assist with a variety of duties and
present helpful insights and data on a variety of matters. Whether or not you want
assist with a particular query or simply need to have a dialog a few explicit
matter, Assistant is right here to help.'''
This immediate clearly instructs the assistant to depend on instruments for sure matters, reminiscent of random numbers, the which means of life, and webpage content material.
Reinitializing the Agent with the New Software
Now we are able to reinitialize the conversational agent with the brand new WebPageTool included:
from langchain.brokers import initialize_agent
instruments = [search, random_tool, life_tool, page_getter]
# Reuse the reminiscence from earlier
conversational_agent = initialize_agent(
agent="chat-conversational-react-description",
instruments=instruments,
llm=turbo_llm,
verbose=True,
max_iterations=3,
early_stopping_method='generate',
reminiscence=reminiscence
)
# Apply the up to date immediate
conversational_agent.agent.llm_chain.immediate.messages[0].immediate.template = fixed_prompt
conversational_agent.agent.llm_chain.immediate.messages[0]

Testing the WebPageTool
We are able to now take a look at the agent by asking it to fetch content material from a particular webpage. For instance:
conversational_agent.run("Is there an article about Clubhouse on https://techcrunch.com/? right now")
The agent will:
- Use the WebPageTool to scrape TechCrunch’s homepage.
- Search by the primary 4000 characters of content material to test if there are any mentions of “Clubhouse.”
- Present a response primarily based on whether or not it finds an article associated to Clubhouse in that scraped content material.
Prime Tales on CBS Information : Working:
conversational_agent.run("What are the titles of the highest tales on www.cbsnews.com/?")
The agent will:
- Fetch and course of the textual content content material from CBS Information’ homepage.
- Extract potential headings or story titles by analyzing textual content patterns or sections that appear like titles.
- Reply with the highest tales or a abstract of what it discovered within the webpage content material.
Conclusion
Now we have efficiently developed a flexible conversational agent utilizing LangChain that may seamlessly combine quite a lot of instruments and APIs. By harnessing the capabilities of Massive Language Fashions alongside customized functionalities—reminiscent of random quantity technology, philosophical insights, and dynamic internet scraping—this agent demonstrates its capability to handle a variety of consumer queries. The modular design permits for straightforward enlargement and adaptation, making certain that the agent can evolve as new instruments and options are added. This mission not solely showcases the ability of mixing AI with real-time information but in addition units the stage for future enhancements, making the agent a useful useful resource for interactive and informative conversations.
Key Takeaways
- Constructing a conversational agent with LangChain permits for a modular strategy, making it simple to combine varied instruments and increase performance.
- The combination of internet scraping and search instruments permits the agent to offer up-to-date info and reply to present occasions successfully.
- The power to create customized instruments empowers builders to tailor the agent’s capabilities to particular use instances and consumer wants.
- Using reminiscence options ensures that the agent can preserve context throughout conversations, resulting in extra significant and coherent interactions with customers.
The media proven on this article isn’t owned by Analytics Vidhya and is used on the Creator’s discretion.
Incessantly Requested Questions
A. LangChain is a framework designed for constructing functions that combine Massive Language Fashions (LLMs) with varied exterior instruments and APIs, enabling builders to create clever brokers able to performing advanced duties.
A. The conversational agent can reply common data questions, generate random numbers, present insights concerning the which means of life, and dynamically fetch and extract content material from specified webpages.
A. The agent makes use of instruments just like the DuckDuckGo Search and a customized internet scraping device to retrieve up-to-date info from the online, permitting it to offer correct and well timed responses to consumer queries about present occasions.
A. The mission primarily makes use of Python, together with libraries reminiscent of LangChain for constructing the agent, OpenAI for accessing the language fashions, requests for making HTTP requests, and BeautifulSoup for parsing HTML content material.
A. You possibly can increase the agent’s capabilities by including extra instruments or APIs that serve particular features, modifying present instruments for higher efficiency, or integrating new information sources to complement the responses.
The media proven on this article isn’t owned by Analytics Vidhya and is used on the Creator’s discretion.

