YADB (But One other Database Benchmark)
The world has a plethora of database benchmarks, beginning with the Wisconsin Benchmark which is my favourite. Firstly, that benchmark was from Dr David Dewitt, who taught me Database Internals once I was a graduate pupil at College of Wisconsin. Secondly, it’s in all probability the earliest convention paper (circa 1983) that I ever learn. And thirdly, the outcomes of this paper displeased Larry Ellison a lot that he inserted a clause in newer Oracle releases to forestall researchers from benchmarking the Oracle database.
The Wisconsin paper clearly describes how a benchmark measures very particular options of databases, so it follows that as database capabilities evolve, new benchmarks are wanted. In case you have a database that has new conduct not present in present databases, then it’s clear that you simply want a brand new benchmark to measure this new conduct of the database.
At this time, we’re introducing a brand new benchmark, RockBench, that does simply this. RockBench is designed to measure a very powerful traits of a real-time database.
What Is a Actual-Time Database?
An actual-time database is one that may maintain a excessive write price of latest incoming information, whereas on the identical time permitting functions to make queries based mostly on the freshest of information. It’s totally different from a transactional database the place essentially the most vital attribute is the flexibility to carry out transactions, which is why TPC-C is essentially the most cited benchmark for transactional databases.
In typical database ACID parlance, a real-time database offers Atomicity and Sturdiness of updates similar to most different databases. It helps an eventual Consistency mannequin, the place updates present up in question outcomes as shortly as doable. This time lag is known as information latency. An actual-time database is one that’s designed to reduce information latency.
Totally different functions want totally different information latencies, and the flexibility to measure information latency permits customers to decide on one real-time database configuration over one other based mostly on the wants of their software. RockBench is the one benchmark at current that measures the info latency of a database at various write charges.
Knowledge latency is totally different from question latency, which is what is usually used to benchmark transactional databases. We posit that one of many distinguishing components that differentiates one real-time database from one other is information latency. We designed a benchmark known as RockBench that may measure the info latency of a real-time database.
Why Is This Benchmark Related within the Actual World?
Actual-time analytics use circumstances. There are various decision-making programs that leverage massive volumes of streaming information to make fast selections. When a truck arrives at a loading dock, a fleet administration system would want to provide a loading listing for the truck by inspecting supply deadlines, delay-charge estimates, climate forecasts and modeling of different vans which can be arriving within the close to future. One of these decision-making system would use a real-time database. Equally, a product group would take a look at product clickstreams and consumer suggestions in actual time to find out which characteristic flags to set within the product. The quantity of incoming click on logs could be very excessive and the time to assemble insights from this information is low. That is one other use case for a real-time database. Such use circumstances have gotten the norm lately, which is why measuring the info latency of a real-time database is helpful. It permits customers to select the correct database for his or her wants based mostly on how shortly they need to extract insights from their information streams.
Excessive write charges. Essentially the most crucial measurement for a real-time database is the write price it could actually maintain whereas supporting queries on the identical time. The write price may very well be bursty or periodic, relying on the time of the day or the day of the week. This conduct is sort of a streaming logging system that may soak up massive volumes of writes. Nonetheless, one distinction between a real-time database and a streaming logging system is that the database offers a question API that may carry out random queries on the occasion stream. With writing and querying of information, there may be all the time an inherent tradeoff between excessive write charges and the visibility of information in queries, and that is exactly what RockBench measures.
Semi-structured information. Most of real-life decision-making information is in semi-structured type, e.g. JSON, XML or CSV. New fields get added to the schema and older fields are dropped. The identical subject can have multi-typed values. Some fields have deeply nested objects. Earlier than the appearance of real-time databases, a consumer would sometimes use a knowledge pipeline to wash and homogenize all of the fields, flatten nested fields, denormalize nested objects after which write it out it to a information warehouse like Redshift or Snowflake. The information warehouse is then used to assemble insights from their information. These information pipelines add to information latency. Alternatively, a real-time database eliminates the necessity for a few of these information pipelines and concurrently affords decrease information latency. This benchmark makes use of information in JSON format to simulate extra of these kinds of real-life situations.
Overview of RockBench
RockBench contains a Knowledge Generator and a Knowledge Latency Evaluator. The Knowledge Generator simulates a real-life occasion workload, the place each generated occasion is in JSON format and schemas can change regularly. The Knowledge Generator produces occasions at numerous write charges and writes them to the database. The Knowledge Latency Evaluator queries the database periodically and outputs a metric that measures the info latency at that prompt. A consumer can fluctuate the write price and measure the noticed information latency of the system.
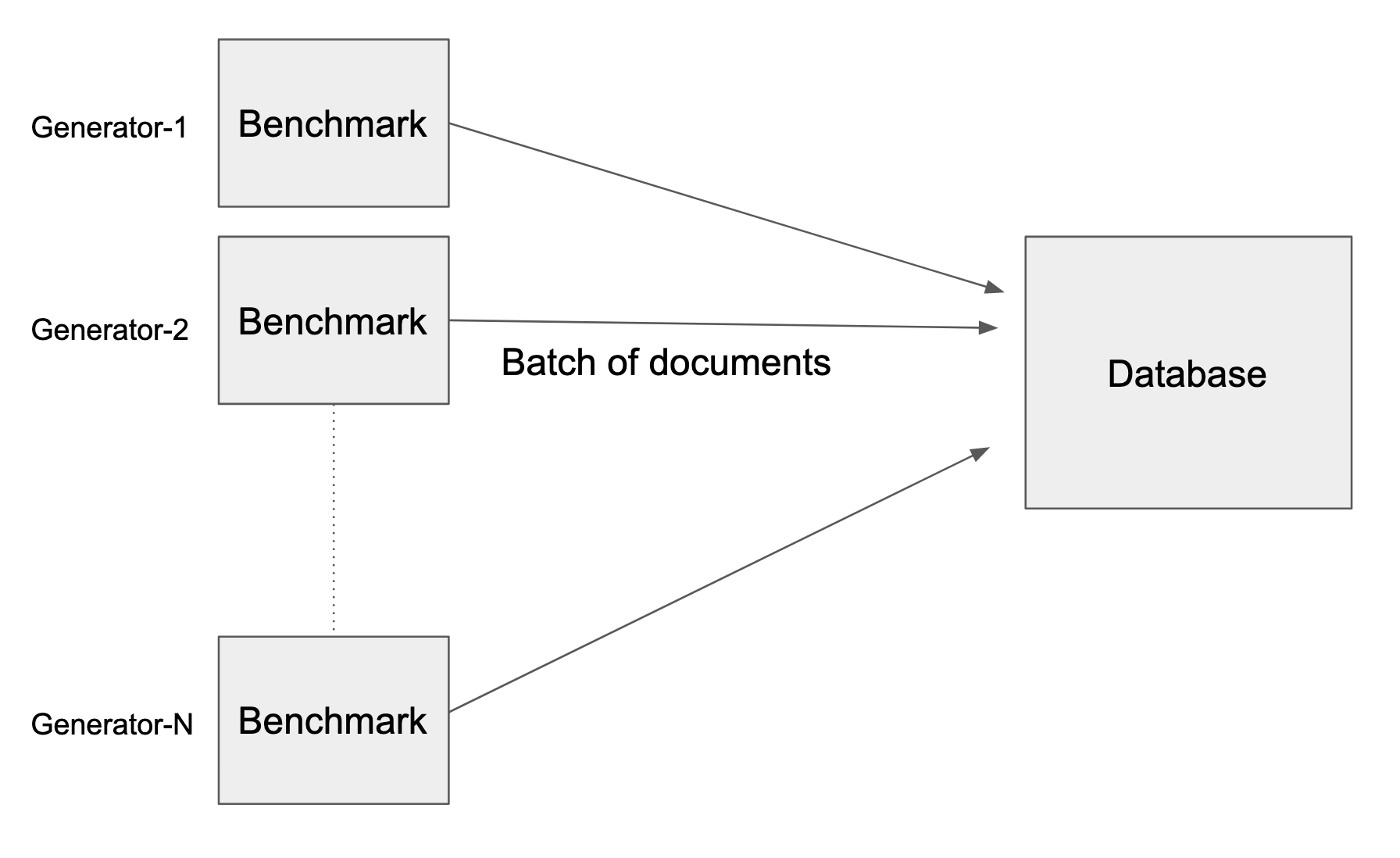
A number of situations of the benchmark hook up with the database underneath take a look at
The Evaluating Knowledge Latency for Actual-Time Databases white paper offers an in depth description of the benchmark. The dimensions of an occasion is chosen to be round 1K bytes, which is what we discovered to be the candy spot for a lot of real-life programs. Every occasion has nested objects and arrays inside it. We checked out lots of publicly obtainable occasions streams like Twitter occasions, inventory market occasions and on-line gaming occasions to select these traits of the info that this benchmark makes use of.
Outcomes of Working RockBench on Rockset
Earlier than we analyze the outcomes of the benchmark, let’s refresh our reminiscence of Rockset’s Aggregator Leaf Tailer (ALT) structure. The ALT structure permits Rockset to scale ingest compute and question compute individually. This benchmark measures the velocity of indexing in Rockset’s Converged Index™, which maintains an inverted index, a columnar retailer and a file retailer on all fields, and effectively permits queries on new information to be obtainable virtually immediately and to carry out extremely quick. Queries are quick as a result of it could actually leverage any of those pre-built indices. The information latency that we file in our benchmarking is a measure of how briskly Rockset can index streaming information. Full outcomes could be discovered right here.
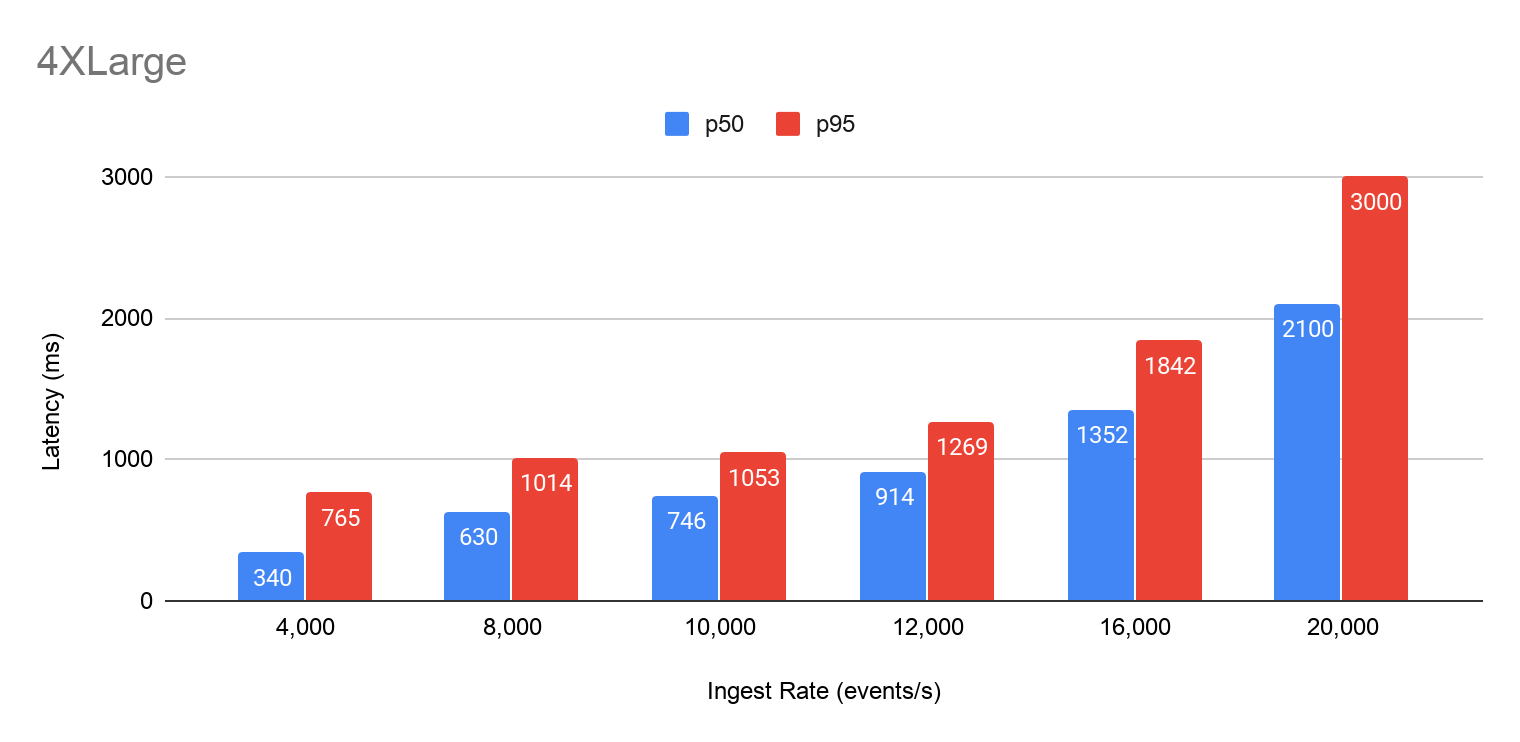
Rockset p50 and p95 information latency utilizing a 4XLarge Digital Occasion at a batch measurement of fifty
The primary commentary is {that a} Rockset 4XLarge Digital Occasion can help a billion occasions flowing in day by day (approx. 12K occasions/sec) whereas protecting the info latency to underneath 1 second. This write price is adequate to help quite a lot of use circumstances, starting from fleet administration operations to dealing with occasions generated from sensors.
The second commentary is that if it’s important to help the next write price, it is so simple as upgrading to the following increased Rockset Digital Occasion. Rockset is scalable, and relying on the quantity of assets you dedicate, you may cut back your information latency or help increased write charges. Extrapolating from these benchmark outcomes: a web-based gaming system that produces 40K occasions/sec and requires a knowledge latency of 1 second could also be glad with a Rockset 16XLarge Digital Occasion. Additionally, migrating from one Rockset Digital Occasion to a different doesn’t trigger any downtime, which makes it straightforward for customers emigrate from one occasion to a different.
The third commentary is that in case you are operating on a hard and fast Rockset Digital Occasion and your write price will increase, the benchmark outcomes present that there’s a gradual and linear enhance within the information latency till CPU assets are saturated. In all these circumstances, the compute useful resource on the leaf is the bottleneck, as a result of this compute is the useful resource that makes lately written information queryable instantly. Rockset delegates compaction CPU to distant compactors, however some minimal CPU continues to be wanted on the leaves to repeat recordsdata to and from cloud storage.
Rockset makes use of a specialised bulk-load mechanism to index stationary information and that may load information at terabytes/hour, however this benchmark is to not measure that performance. This benchmark is purposely used to measure the info latency of high-velocity information when new information is arriving at a quick price and must be instantly queried.
Futures
In its present type, the workload generator points writes at a specified fixed price, however one of many enhancements that customers have requested is to make this benchmark simulate a bursty write price. One other enchancment is so as to add an overwrite characteristic that overwrites some paperwork that already exists within the database. Yet one more requested characteristic is to fluctuate the schema of a number of the generated paperwork in order that some fields are sparse.
RockBench is designed to be extensible, and we hope that builders within the database group would contribute code to make this benchmark run on different real-time databases as effectively.
I’m thrilled to see the outcomes of RockBench on Rockset. It demonstrates the worth of real-time databases, like Rockset, in enabling real-time analytics by supporting streaming ingest of 1000’s of occasions per second whereas protecting information latencies within the low seconds. My hope is that RockBench will present builders a vital instrument for measuring information latency and deciding on the suitable real-time database configuration for his or her software necessities.
Sources:

